Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PPP Homework 3
Uploaded by
Mahmud ZubarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PPP Homework 3
Uploaded by
Mahmud ZubarCopyright:
Available Formats
Nama : I Made wiratha Nungrat
NIM : 13209057
Homework 3
Problem 3.5 A Large manufacturer of household consumer goods is considering integrating an
aggregate planning model into its manufacturing strategy. Two of the company vice presidents
disagree strongly as to the value of the approach. What arguments might each of the vice presidents
use to support his or her point of view?
Answer:
- First possible argument is Aggregate planning always assumed that forecast demand in the
future is perfect. This mean that it depends strongly on availability of forecast demand
which is has possibility of error of sometime in the future. Forecast demand itself actually
wrong because demand in the future is impossible to measure exactly, which is turns out to
be some margin of error.
- Second possible argument is implementation of aggregate planning need extra careful
calculation otherwise the firm can lose a lot of money and has several problem which are
could bring some devastating effect to the firm or company such as Smoothing cost: The
cost of changing production and workforce. Changing the workforce mean that the firm
needs to fire or hire labor frequently to meet the demand and production plan. Firing and
hiring labor is not easy that it look because it need extra cost for interviewing and train new
labor and cost for laid off labor.
Problem 3.9 Small farm in the Salinas Valley grows apricots. The manager estimates that sales over
the next five years will be as follows:
Figure 1. Table of forecasts
Given :
- Current workers = 3
- Current Inventory (end of December) = 20.000 packages
- Each worker is paid $ 25.000/30.000 package/year
- Inventory Cost = 4 cent/package/year
- Cost of Hiring = $ 500
- Cost of Firing = $ 1.000
Year Forecasts demand
1 300000
2 120000
3 200000
4 110000
5 135000
a. Assuming shortage are not allowed, determine the minimum constant workforce that he will
need over the next five years.
Answer:
Note :
Year 1 demand forecast is 300.000, but the end of current year inventory is 20.000 packages.
The minimum constant workforce that he needed for next five years is 7 workers.
b. Evaluate The cost of plan found in part a
Answer:
Because the worker at the end of current year is 3, he needed only 4 more workers.
Total cost:
- Cost of Hiring = 4 x 500
= $ 2.000
-
= $ 11.800
- Total Cost = 11.800 + 2.000
= $ 13.800
If we use Zero Inventory Method,
Year Forecasts demand Net Cumulative demand Cum. # of unit produced per worker Ratio C/D Rounding
1 300000 300000 30000 10 10
2 120000 420000 60000 7 7
3 200000 620000 90000 6,888888889 7
4 110000 730000 120000 6,083333333 7
5 135000 865000 150000 5,766666667 7
Year # of unit produced per Worker Yearly Production Cumulative Production Cumulative Net Demand Ending Inventory
1 30000 210000 210000 300000 -90000
2 30000 210000 420000 400000 20000
3 30000 210000 630000 600000 30000
4 30000 210000 840000 710000 130000
5 30000 210000 1050000 845000 205000
295000
Year Forecasts demand Cumulative Net Dmand # of workers required Rounding
1 280000 280000 9,333333333 10
2 120000 400000 4 4
3 200000 600000 6,666666667 7
4 110000 710000 3,666666667 4
5 135000 845000 4,5 5
Total cost:
- Cost of Hiring = 11 x $ 500
= $ 5.500
- Cost of Firing = 9 x $ 1.000
= $ 9.000
- Cost of Inventory = 165.000 x $ 0,04
= $ 6.600
Total = 5.500 + 9.000 + 6.600 = $ 21.100
For this problem, Constant workforce plan give us a better solution.
Problem 3.11 An Implicit assumption made in Problem 9 was that dried apricots unsold at the end
of a year could be sold in subsequent years. Suppose that apricots unsold at the end of any year
must be discarded. Assume that a disposal cost of $ 0,20 per package.
Answer:
If we still using Constant Workforce Plan, the result is still same and fails to predict the cost
a. Minimum constant workforce
Answer :
We still need 7 Workers
b. Total Cost
Total cost is becoming 13.800 + 77.000 = $ 90.800
Year # Workers # Hired # Fired # of units per worker #unit produced Cum. production Cum. demand Ending Inventory
1 10 7 30000 300000 300000 280000 20000
2 4 6 30000 120000 420000 400000 20000
3 7 3 30000 210000 630000 600000 30000
4 4 3 30000 120000 750000 710000 40000
5 5 1 30000 150000 900000 845000 55000
11 9 165000
Year # of unit produced per Worker Yearly Production Cumulative Production Cumulative Net Demand Ending Inventory
1 30000 210000 210000 300000 -90000
2 30000 210000 420000 400000 20000
3 30000 210000 630000 600000 30000
4 30000 210000 840000 710000 130000
5 30000 210000 1050000 845000 205000
295000
Problem 3.14 Table of demand forecasting for a semiconductor company
Answer :
- Current workers = 675
- Current Inventory (end of December) = $ 120.000
- Nexxt Inventory = $ 100.000
- K = $ 60.000/year = $ 240 day/worker
- Inventory Cost = 25% annual interest rate charge
- Cost of Hiring = $ 200
- Cost of Firing = $ 400
a. Minimum constant workforce is 673 workers
This is the cheapest scenario for next year production portofolio which is need 673
workers
b. Total cost of plan
- Cost of firing = 675-673 = 2 workers
= 2 x 400 = $ 800
Month Production Days Predicted Demand($ 10.000)
January 22 340
February 16 380
March 21 220
April 19 100
May 23 490
June 20 625
July 24 375
August 12 310
September 19 175
October 22 145
November 20 120
December 16 165
Month # of dollars per worker Monthly Production Cum. Production Cum. Net Demand Ending Inventory
January 5280 3553440 3553440 3280000 273440
February 3840 2584320 6137760 7080000 -942240
March 5040 3391920 9529680 9280000 249680
April 4560 3068880 12598560 10280000 2318560
May 5520 3714960 16313520 15180000 1133520
June 4800 3230400 19543920 21430000 -1886080
July 5760 3876480 23420400 25180000 -1759600
August 2880 1938240 25358640 28280000 -2921360
September 4560 3068880 28427520 30030000 -1602480
October 5280 3553440 31980960 31480000 500960
November 4800 3230400 35211360 32680000 2531360
December 3840 2584320 37795680 35330000 2465680
361440
- Cost of Inventory = 361.440 + 100.000
= 461.440 X 25% (annual interest charge) = 115.360
Total Cost = 115.360 + 800 = $ 116.160
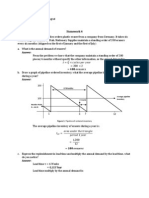
Problem 3.16 Graph the cumulative net demand
Answer:
0
5000000
10000000
15000000
20000000
25000000
30000000
35000000
40000000
C
u
m
u
l
a
t
i
v
e
n
u
m
b
e
r
o
f
u
n
i
t
(
d
o
l
l
a
r
s
)
Cum. Net Demand
You might also like
- Nahmias Chapter 3 SolutionsDocument9 pagesNahmias Chapter 3 SolutionsDiego Andres Vasquez100% (1)
- PPP - Homework 4Document7 pagesPPP - Homework 4Wiratha Nungrat67% (3)
- Aggregate Plan and MRP - ExcerciseDocument8 pagesAggregate Plan and MRP - ExcerciseAlessandro NájeraaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Horace Cheung100% (1)
- Chap 10 WEDocument5 pagesChap 10 WENPNo ratings yet
- Assign. 2 F-07Document3 pagesAssign. 2 F-07api-263151280% (1)
- Solution Chapter5Document8 pagesSolution Chapter5Aykut Yıldız0% (1)
- Chapter 03 SolvedDocument24 pagesChapter 03 SolvedMN NabiNo ratings yet
- Solution Chapter8Document8 pagesSolution Chapter8Bunga Safhira Wirata50% (2)
- Excercises Section 3,4Document12 pagesExcercises Section 3,4Eber Mancipe100% (1)
- Solution Chapter6Document4 pagesSolution Chapter6Bunga Safhira WirataNo ratings yet
- Decision TreeDocument8 pagesDecision TreePham TinNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: F (Q) Co Cu+CoDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource Was: F (Q) Co Cu+Comarvin mayaNo ratings yet
- 574716238Document9 pages574716238aaltivegreenNo ratings yet
- Nahmias Solutions Chapter 2Document5 pagesNahmias Solutions Chapter 2RafiaZaman50% (2)
- HW 5 SolDocument5 pagesHW 5 SolSrikar VaradarajNo ratings yet
- Lean Application at LantechDocument2 pagesLean Application at Lantechehadjulaeha100% (1)
- Chapter4 Ans NahmiasDocument10 pagesChapter4 Ans NahmiasCansu KapanşahinNo ratings yet
- Testbank SolutionsDocument58 pagesTestbank SolutionsHaider KamranNo ratings yet
- SCM ch01Document49 pagesSCM ch01summiasaleemNo ratings yet
- Coyle 9e CH 01Document20 pagesCoyle 9e CH 01HASHEMNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Selected Problems From Nahmias' Book EOQDocument6 pagesSolutions To Selected Problems From Nahmias' Book EOQDaniela Paz Retamal Cifuentes50% (2)
- SCM AssignmentDocument9 pagesSCM AssignmentAshutosh UkeNo ratings yet
- Solutions On Stoch Inventory CH 5. (Nahmias)Document9 pagesSolutions On Stoch Inventory CH 5. (Nahmias)Jarid Medina100% (4)
- Engineering Economics and Financial AccountingDocument5 pagesEngineering Economics and Financial AccountingAkvijayNo ratings yet
- Production Solution ManualDocument1 pageProduction Solution ManualMerve BilgiçNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain BasicsDocument1 pageSupply Chain BasicsDhanu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Models For Facility LocationDocument28 pagesMathematical Models For Facility LocationaddayesudasNo ratings yet
- PPP - Homework 2Document7 pagesPPP - Homework 2Wiratha Nungrat100% (2)
- TUTDocument2 pagesTUTNadia NatasyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Role of Logistics in Supply Chains: Learning ObjectivesDocument51 pagesChapter 2: Role of Logistics in Supply Chains: Learning ObjectivesHaider AliNo ratings yet
- Given An Actual Demand of 60 For A Period When Forecast of 70Document17 pagesGiven An Actual Demand of 60 For A Period When Forecast of 70arjunNo ratings yet
- PPP - Homework 5Document17 pagesPPP - Homework 5Wiratha Nungrat67% (9)
- Module 1 - Introduction and Management Decision Making - Homework SolutionsDocument4 pagesModule 1 - Introduction and Management Decision Making - Homework SolutionsAbelNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Logistics Management PromotionDocument23 pagesUnit IV Logistics Management PromotionDaniel AntonyNo ratings yet
- Ch11.Managing Economies of Scale in A Supply Chain - Cycle InventoryDocument65 pagesCh11.Managing Economies of Scale in A Supply Chain - Cycle InventoryFahim Mahmud100% (1)
- Krajewski Ism Ch13 SolutionDocument29 pagesKrajewski Ism Ch13 SolutionBryan Seow0% (1)
- Mid Term1 N SolutionDocument10 pagesMid Term1 N SolutionZain ImranNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Collaboration and Decision - Making in Sustainable Supply Chain Management - A Case Study Analysis On Skechers USA Inc.Document96 pagesThe Influence of Collaboration and Decision - Making in Sustainable Supply Chain Management - A Case Study Analysis On Skechers USA Inc.Angelica ChavesNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Planning: National Institute of Technology Calicut Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument10 pagesAggregate Planning: National Institute of Technology Calicut Department of Mechanical EngineeringEmily GrimaldoNo ratings yet
- Ise216 Mid-Term 2011 Answer2Document4 pagesIse216 Mid-Term 2011 Answer2David García Barrios100% (1)
- Bond ValuationDocument12 pagesBond ValuationvarunjajooNo ratings yet
- Home Work Chapter 1 To 12Document50 pagesHome Work Chapter 1 To 12Haha JohnNgNo ratings yet
- AssDocument2 pagesAssAndree ChicaizaNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Planning Practice ProblemsDocument1 pageAggregate Planning Practice ProblemsWalid Mohamed AnwarNo ratings yet
- 8 Managing of Economics of ScaleDocument38 pages8 Managing of Economics of ScaleDwita Permatasari100% (1)
- 6.HW Chap 13-1,11,13,15Document7 pages6.HW Chap 13-1,11,13,15Jyothi VenuNo ratings yet
- Inventory Models: Single Quantity: 1.purchase Model Without ShortagesDocument6 pagesInventory Models: Single Quantity: 1.purchase Model Without ShortagesmunotmanasNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Planning: Translating Demand Forecasts Production Capacity LevelsDocument27 pagesAggregate Planning: Translating Demand Forecasts Production Capacity LevelsDotecho Jzo EyNo ratings yet
- InventoryDocument6 pagesInventorysaaz77No ratings yet
- Logistics CostDocument26 pagesLogistics CostKhadija AlkebsiNo ratings yet
- 5 Evaluating A Single ProjectDocument32 pages5 Evaluating A Single ProjectImie CamachoNo ratings yet
- Chase Method of Aggregate PlanningDocument23 pagesChase Method of Aggregate Planningkaushalsingh20No ratings yet
- Logistics Principles and Applications 2nd Ed. McGraw-Hill Logistics Series by John LangfordDocument6 pagesLogistics Principles and Applications 2nd Ed. McGraw-Hill Logistics Series by John LangfordTauseef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture Engineering Economics FE Review ProblemsDocument23 pagesLecture Engineering Economics FE Review ProblemsLee Song HanNo ratings yet
- Operations Management ComprehensiveDocument9 pagesOperations Management ComprehensiveashishNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spreadsheets - FDP 2013Document24 pagesIntroduction To Spreadsheets - FDP 2013thayumanavarkannanNo ratings yet
- CA IPCC Costing Guideline Answers May 2015 PDFDocument20 pagesCA IPCC Costing Guideline Answers May 2015 PDFanupNo ratings yet
- Desain Kurikulum Electrical Engineering GeneralDocument1 pageDesain Kurikulum Electrical Engineering GeneralWiratha NungratNo ratings yet
- Laporan 3Document6 pagesLaporan 3Wiratha NungratNo ratings yet
- PPP - Homework 5Document17 pagesPPP - Homework 5Wiratha Nungrat67% (9)
- PPP - Homework 2Document7 pagesPPP - Homework 2Wiratha Nungrat100% (2)
- Tugas Manajemen Proyek Bab 9Document3 pagesTugas Manajemen Proyek Bab 9Wiratha Nungrat67% (3)
- Strategic Intervention Material in Earth Science Atmosphere PDFDocument13 pagesStrategic Intervention Material in Earth Science Atmosphere PDFRyan Negad100% (1)
- Django (Web Framework)Document6 pagesDjango (Web Framework)Asad AliNo ratings yet
- Is Technology Killing Thinking SkillsDocument2 pagesIs Technology Killing Thinking SkillsemaniaxNo ratings yet
- Fresh Foods Ordering ProcessDocument5 pagesFresh Foods Ordering ProcessSagarPatelNo ratings yet
- General Water Baths 1Document4 pagesGeneral Water Baths 1morton1472No ratings yet
- Ankit Sharma: EducationDocument2 pagesAnkit Sharma: EducationAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Martin ColeDocument21 pagesDr. Martin ColeBiswajit BalNo ratings yet
- Project On Electricity Billing SystemDocument17 pagesProject On Electricity Billing Systemjaishankar1240% (5)
- Documentary FILM REVIEWDocument2 pagesDocumentary FILM REVIEWCarlito DoringoNo ratings yet
- Contoh Tugas Fatigue-Fracture Mech 2017Document2 pagesContoh Tugas Fatigue-Fracture Mech 2017Raymond DanielleNo ratings yet
- B-Spline - Chapter 4 PDFDocument24 pagesB-Spline - Chapter 4 PDFMarius DiaconuNo ratings yet
- Array ProgramsDocument2 pagesArray ProgramsVipinNo ratings yet
- Angry Red PlanetsDocument23 pagesAngry Red PlanetsIbnu SyedNo ratings yet
- The Contributions of Adlerian TheoryDocument2 pagesThe Contributions of Adlerian TheoryHamza Abd Al-Muttalib100% (4)
- Strava PresentDocument46 pagesStrava PresentWiratama PratamaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management Training Kit v5.0Document59 pagesSupply Chain Management Training Kit v5.0Ajay ThakralNo ratings yet
- تربة بغدادDocument18 pagesتربة بغدادjust meNo ratings yet
- Tips - Geochemistry of Soil Radionuclides PDFDocument263 pagesTips - Geochemistry of Soil Radionuclides PDFRafael Armando ZaldañaNo ratings yet
- 04S ME304 MT1 SolutionsDocument5 pages04S ME304 MT1 SolutionsAnonymous LwNSginNo ratings yet
- Single Sex EducationDocument7 pagesSingle Sex EducationBreAnna SmithNo ratings yet
- Impact of Diversity Challenges On Organisational Cynicism - An Egyptian StudyDocument7 pagesImpact of Diversity Challenges On Organisational Cynicism - An Egyptian Studyleepsaiit@gmailcomNo ratings yet
- IELTS Essay Band 9 Sample Answers - IELTS PodcastDocument40 pagesIELTS Essay Band 9 Sample Answers - IELTS PodcastDivyesh Nihalani100% (1)
- Introduction From The Occidental Arts and Ecology Center CookbookDocument15 pagesIntroduction From The Occidental Arts and Ecology Center CookbookChelsea Green PublishingNo ratings yet
- Gartner Symposium Japan Brochure 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesGartner Symposium Japan Brochure 2019 PDFLiza De Los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Laporan Akhir - Perubahan Lahan Danau - 1996-2010Document16 pagesLaporan Akhir - Perubahan Lahan Danau - 1996-2010ilo halidNo ratings yet
- ApolloDocument12 pagesApolloRishabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydrology ReportDocument60 pagesHydrology ReportpanikarickyNo ratings yet
- Iii-Ii (I-Mid) Time TableDocument4 pagesIii-Ii (I-Mid) Time TableSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- 4 Jan 2022 Practical Instruction 4 Preparation of Chemical RegisterDocument2 pages4 Jan 2022 Practical Instruction 4 Preparation of Chemical Registershafiqah wongNo ratings yet
- Scale of Universe - SH TemplateDocument2 pagesScale of Universe - SH TemplateLauren PicheNo ratings yet