Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study of Appendicitis
Case Study of Appendicitis
Uploaded by
Oamaga NajlaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study of Appendicitis
Case Study of Appendicitis
Uploaded by
Oamaga NajlaCopyright:
Available Formats
I.
Patient Profile
Name: Bernardo Matobato
Age: 26 years old
Gender: male
Occupation: construction worker
Educational Attainment: grade 4
Civil Status: single
Nationality: filipino
Address: brgy. Dapdap Alang-alang Leyte
Religion: catholic
C/C: abdominal pain
Date Admitted: july 22, 2010 @ 9:00pm
Admitting Diagnosis: ruptured appendicitis
Attending Physician: Dr. Baez
Source of Information: patient and mother
Reliability: 90%
II. Present Illness:
14 hours prior to admission, the patient experienced mild pain on his right lower quadrant abdomen
while eating in the morning, followed by a severe pain. The client tried to eliminate the pain using herbal oil
but were not eradicated.
Persistence of the noticed pain, prompted his mother to bring him to EVRMC, hence this admission.
III. Past Health History:
The patient did not receive any vaccination as claimed by the mother, has experienced acute
respiratory infection such as cough, cold and mild fever and took biogesic (250mg) every 4 hours for fever and
some herbal plants (decoction of lagundi) for cough relief. Pain in the right lower abdomen 1
st
felt when the
client was 25 years old but were ignored no history of hospitalization.
IV. Family History:
The mother claimed that her mother is asthma positive, and noted hypertension history on the
paternal side.
V. Birth History:
The patient is 3
rd
on eight siblings of Mr. and Mrs. Matobato. Born via normal vaginal delivery on their
house.
VI.Psychosocial history:
The patient sorrounding is good and there were no lakes, swamp or river nearby. They used a deep
well for drinking and taking a bath. He smokes 5 sticks of cigar. Per day, and play basketball in freetime.
PATTERNS OF FUNCTIONING CLINICAL INSPECTION OTHER SOURCES
1. RESPIRATORY
- (+) Hx of Asthma
- Consumed 5 sticks of
cigar/day
- Started smoking since
17 y.o
2. CIRCULATORY
- (+)Hx of HPN
3. FOODS AND FLUIDS INTAKE
- Usual food taken: leafy
vegetables, fish, rice,
root crops
- (-)food allergies
- (-)food preferences &
dislikes
- Drink 4 glasses of water
each day
- Drink 10 glasses of tuba
occasionally
4. ELIMINATION
- Void more than 5x/day
- Defecate 1x/day or
sometimes 1 time every
2 days
- Fun of retaining stools if
at work
5. REGULATORY MECHANISM
- (+) mild fever during
childhood
6. HYGIENE
- Take a bath 1-2x/day
- Seldom use shampoo
- Change cloth everyday
- No allergies to soap &
shampoo
- Combs hair
7. EXERCISE & LOCOMOTION
- Take the daily activities
as exercise
- RR = 26cpm
- No accessory
muscle used
- No respiratory aids
used
- No cough and cold
- BP = 110/70 mmHg
- PR = 53 bpm
- No presence of
discoloured or
swollen parts
- Good capillary refill
- Good skin turgor
- Dry lips
- With an IVF of D5LR
@ 30gtts/min
- No NGT
- Not constipated
- Presence of
indwelling catheter
- (-) nausea
- T = 36.6
- Afebrile
- (-) chills
- Untidy to look at
- (-)skin lesions
- Hair is equally
distributed
- (+)Halitosis
- Poor dental care
- Presence of plaque
- Impaired mobility
due to pain
Hematology:
WBC: 18.30x10^9/L
Neutrophil: .90
Lymphocyte: .10
Hematocrit: .46
URINALYSIS
Color : Dark yellow
Transparency: Turbid
Specific gravity: 1.025
PH: 6.0
Glucose: negative
Albumin: trace
WBC: 2-3/hpf
Bacteria: moderate
Mucus threads: many
Costs: coarse granular: 0-1/lpf
Uric acid: moderate
8. REST & SLEEP
- Retire @ 9pm, rises @
5am
- Side lying position
- Uses 2 pillow
9. COMMUNICATION &
SPECIAL SENSES
- Right handed
- No visual/auditory
disturbances
- Speaks waray
- (-)ear, eye gadgets
10. SENSORY
- (-) Hx of convulsions, Hx
of epilepsy
11. PAIN & DISCOMFORT
- Pain experienced in the
RLQ of the abdomen &
used herbal oil &
kerosene for relief
12. RECREATION/DIVERSION
- Playing basketball for
fun
13. RELIGIOUS LIFE
- Roman Catholic
14. COPING MECHANISM
- Self keeping of problem
15. SOCIAL OCCUPATION
- Heavy type of work
- Interrupted sleep
due to pain
- Eyelashes are
equally
Distributed
- Whitish sclera
- Pinkish conjunctiva
- (-) convulsions nor
epilepsy
- Pain scale of 8
- Impaired mobility
due to pain
- Throw jokes while
interview process
- No medals worn
- Friendly
LABORATORY RESULTS
Hematology:
Components Normal values Results Interpretation Clinical Significance
1. WBC
2. Neutrophils
3. Lymphocyte
4. Hematocrit
4.5 11x10
9
/L
0.45 0.73
0.2 0.4
Males: 42 52 %
Females: 35 47 %
18.30 x 10
9
/L
0.90
0.10
46 %
Increased
Increased
Decreased
Normal
Presence of inflammation
Acute infection, trauma or
surgery
Aplastic anemia, SLE,
immunodeficiency including
AIDS
Balance proportion of blood
volume that is occupied by
RBC
Urinalysis:
Components Normal Results Interpretation Clinical Significance
1. Color
2. Transparency
3. Specific gravity
4. PH
5. Glucose
6. Albumin
7. WBC
8. Bacteria
9. Casts
10. Uric Acid
Pale yellow to amber
Clear to slightly hazy
1.015-1.025
4.5-8.0
Negative
Negative
Negative or rare
Negative
Occasionally hyaline casts
1.58-4.43 mmol/24 h
Dark Yellow
Turbid
1.025
6.0
Negative
Negative
2-3/hpf
Moderate
Coarse granular: 0-1/hpf
3.13 mmol/24 h
Not normal
Not normal
Normal
Normal
Normal
Normal
Not normal
Not normal, bacteremia
Not normal
Normal
Not enough water intake,
presence of bilirubin
Cystisis, presence of bacteria
Properly diluted urine
Not risk for calcification, and
infection
Absence of DM
Proper filtration of glumerolus
Cystisis, nephritis,
Urinary tract infection
Presence of renal infection or
disease
Absence of calculi
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
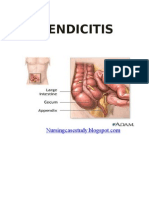
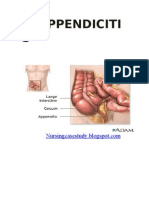
Vermiform appendix
In human anatomy, the appendix (or vermiform appendix; also cecal (or caecal)
appendix; also vermix) is a blind-ended tube connected to the cecum (or caecum),
from which it develops embryologically. The cecum is a pouchlike structure of the
colon. The appendix is near the junction of the small intestine and the large intestine.
The appendix averages 10 cm in length, but can range from 2 to 20 cm. The
diameter of the appendix is usually between 7 and 8 mm. The appendix is located in
the lower right quadrant of the abdomen, or more specifically, the right iliac fossa the
position within the abdomen corresponds to a point on the surface known as
McBurney's point. While the base of the appendix is at a fairly constant location, 2 cm
below the ileocaecal valve, the location of the tip of the appendix can vary from being
retrocaecal to being in the pelvis to being extraperitoneal. In rare individuals with situs
inversus, the appendix may be located in the lower left side.
Maintaining gut flora: major function
Although it was long accepted that the immune tissue, called gut associated lymphoid
tissue, surrounding the appendix and elsewhere in the gut carries out a number of
important functions
The digestive tract's immune system is often referred to as gut-associated lymphoid
tissue (GALT) and works to protect the body from invasion. GALT is an example of
mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue.
The mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) (also called mucosa-associated
lymphatic tissue) is the diffuse system of small concentrations of lymphoid tissue found
in various sites of the body such as the gastrointestinal tract, thyroid, breast, lung,
salivary glands, eye, and skin.
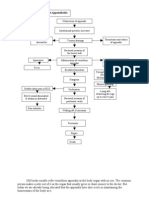
FOR the PATHOPYSIOLOGY just go to this site :
http://www.scribd.com/doc/46437230/Pathophysiology-of-Appendicitis
Nursing Diagnosis Scientific analysis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Limited movement related to
pain as manifested by:
Subjective:
Anay, hinay hinay la ke ma
ol-ol tak samad as
verbalized by the patient.
Objective:
Temp - 36.6
o
C
PR - 53 bpm
RR - 26 cpm
BP - 110/70mmhg
weakness
facial grimace
guarding behavior
incision on RLQ
Having an Appendectomy is
a procedure that has the
need to cause the tissue to
be traumatized, which leads
to the inflammatory process
characterized by pain,
redness, swelling and loss of
function of some part, it is
effective in the treatment of
appendicitis with perforation,
surgery leaves tissue
damage that causes the
release of chemical
mediators, and WBCs which
causes to form exudates then
this exudates causes the
nerve endings to be
compressed thus making
pain and this pain makes a
person to have limited
movement.
Reference:
Medical Surgical nursing by
Brunner and Suddarth 11
th
edition; Vol.2 pages 1240-
1242
After 8 hours of nursing
interventions, the patient will
be able to Regain / maintain
mobility at the higher
possible level, Demonstrate
techniques that enable
resumption of activities, and
Increase strength/ function
of affected and
compensatory body parts.
INDEPENDENT:
1. Instruct the client to
minimize activities
that will put pressure
on his abdomen.
2. Reposition
periodically and
slowly and
encourage deep
breathing exercises.
3. Encourage rest.
4. Move patient
slowly and
deliberately.
5. Administer
analgesics as
ordered
1. Activity that require
holding the breath and
bearing down can result
in pain to surgical site in
RLQ, bradycardia and
rebound tachycardia
with elevated BP.
2. Prevent / reduces
incidence of skin and
respiratory
complications.
3. Reduces myocardial
workload / oxygen
consumption, reducing
risk of complication.
4. Reduces muscle
tension or guarding,
which may help
minimize pain of
movement.
5. To maintain
acceptable level in
pain. Notify physician if
regimen is inadequate
to meet pain control
goal.
After 8 hours of nursing
interventions the patient
is able to Rest quietly Sit
in a high-fowlers position
from lying in bed, and
know the proper way in
seating from a supine
position. therefore:
GOAL MET
Nursing Diagnosis Scientific analysis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Impaired skin integrity
related to surgical incision
SUBJECTIVE:
katapus ko la ka operahe
as verbalize by the patient
OBJECTIVE:
- open wound
- visible surgical incision
- post-operative patient
Temp - 36.6
o
C
PR - 53 bpm
RR - 26 cpm
BP - 110/70mmhg
Surgical intervention involves
removal of appendix within 24
to 28 hours in which surgery
can be performed through a
small incision that causes a
disruption or damage to the
skin tissues. Which will leads
to impairment of the first
protective layer from
infections or foreign object.
Reference:
Medical surgical nursing by
brunner and suddarth, 11
th
edition volume 2 @ page:
1242
After 8 hours of nursing
intervention the patient
will Achieve timely
wound healing and be
free of infection,
demonstrate how to
keep wound dry and
promote healing.
DEPENDENT:
1) Observe wound,
note characteristics
of drainage.
2) Change dressing as
needed using
aseptic technique.
3) Encourage side lying
position (on the left-
side) or a semi-
fowlers position.
4) Encourage guarding
behavior.
DEPENDENT
5) Administer
antibiotics as
doctors order
1. Post-operative
hemorrhage is likely
to occur during first 2
days, whereas
infection may
develop anytime.
2. Reduce skin irritation
and potential
infection, also to
prevent soaking the
dressing by any
discharges.
3. May decrease
pressure to operated
site, thus relieving
abdominal distention.
4. Promote protection to
the incision site.
5. Hasten the healing of
the wound.
After 8 hours of nursing
interventions the patients
wound appears to be dry and
freed from drainage or
purulent substances therefore
goal was met.
Nursing Diagnosis Scientific analysis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Risk for infection related to
surgical incision at right lower
quadrant of the body.
Objective:
incised skin @ right
lower quadrant
RR 26 cpm
PR 53 bpm
Temp 36.6
o
C
Incision pain
The creation of surgical
incision during appendectomy
disrupts the skin integrity of
the skin and its protective
function. Exposure of deep
body tissues to the pathogens
in the environment places the
patient at risk for infection of
the surgical site, a potentially
threatening complication.
Factors related to the surgical
procedure include the method
of preoperative skin
preparation, surgical attire of
the team, method of sterile
draping, duration of surgery
and length of procedure.
After 8 hours of
nursing intervention,
the patient will be able
to Verbalize and
understand the
causative/risk factor for
the infection.
Demonstrate
techniques in
minimizing infection.
Remove all possible
factors that may
contribute to the
infection process.
Achieve timely wound
healing; be free of
purulent drainage or
erythema.
INDEPENDENT:
1. Monitor vital signs,
onset of fever with
chills, and pain.
2. Practice/ instruct good
hand washing and
aseptic wound care.
3. Inspect incision site.
Note characteristics of
drainage from wound.
4. Change wound
dressing as indicated,
using proper
technique for
changing/ disposing of
contaminated
materials.
5. Encourage intake of
fluid and food that is
rich in Vitamin C.
1. Fever and pain indicate
inflammatory
responses, which
contribute to infection.
2. Reduces the risk for
infection or cross
contamination of
bacteria.
3. Provides early detection
of infection process, and
presence of discharges
may help to identify
whether there is an
infection.
4. To reduce/ correct
existing risk factors.
5. Promotes healing and
prevents dehydration.
After 8 hours of nursing
education and interventions,
the patient was More
conscious about his
environment and the patient
seems to be hesitated and
confused or failed to
express some of the
information imparted by the
nursing students therefore:
GOAL WAS PARTIALLY
MET.
You might also like
- Cirrohsis Case StudyDocument12 pagesCirrohsis Case Studykaitlynne lambertNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For AppendectomyDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Appendectomyvanessajane0989% (45)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document7 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2jnrue_aerith96% (28)
- 01 Case Study On AppendicitisDocument23 pages01 Case Study On Appendicitisamit84% (19)
- A Case Study On CholelithiasisDocument51 pagesA Case Study On CholelithiasisLusaka Shrestha84% (37)
- CASE STUDY Intestinal ObstructionDocument68 pagesCASE STUDY Intestinal ObstructionMaria Paula Bungay91% (22)
- Pathophysiology of ALL (Diagram)Document3 pagesPathophysiology of ALL (Diagram)Joann100% (77)
- Acute Appendicitis Case StudyDocument98 pagesAcute Appendicitis Case StudyDawn Ilish Nicole Diez100% (3)
- Appendectomy/ Appendicitis Case StudyDocument15 pagesAppendectomy/ Appendicitis Case StudyApril94% (31)
- A Case Study On Acute AppendicitisDocument56 pagesA Case Study On Acute AppendicitisIvy Mae Evangelio Vios92% (13)
- Appendicitis (Case Study)Document40 pagesAppendicitis (Case Study)Cherr Noll SanchezNo ratings yet
- Case Study AppendicitisDocument58 pagesCase Study AppendicitisArianne Joy Balon100% (2)
- Case Study of Ruptured Appendicitis With Localize Peritonitis (Final)Document76 pagesCase Study of Ruptured Appendicitis With Localize Peritonitis (Final)DRJC82% (22)
- Nursing Care Plan For Appendicitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Appendicitis NCPderic77% (43)
- Case Study CholecystitisDocument27 pagesCase Study Cholecystitisyhanne98% (225)
- Case Study AppendectomyDocument39 pagesCase Study AppendectomyHomework Ping100% (1)
- Cholecystitis Case StudyDocument104 pagesCholecystitis Case StudyJoshua Agawin50% (2)
- Sketchy Pharm RuntimesDocument5 pagesSketchy Pharm RuntimesBerkay ArslanNo ratings yet
- Case Study On AppendicitisDocument15 pagesCase Study On AppendicitisKristelle BonitaNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocument21 pagesAppendicitis Case Studyshayne100% (13)
- Case Study - AppendectomyDocument34 pagesCase Study - Appendectomypuchay_chiepipaii100% (1)
- Appendicits Case Study LATEST CHANGESDocument25 pagesAppendicits Case Study LATEST CHANGESJesse James Advincula Edjec100% (13)
- AppendicitisDocument32 pagesAppendicitisEarlKristofferdeGuia100% (3)
- Case Presentation AppendicitisDocument79 pagesCase Presentation AppendicitisCristina Tagle Garcia100% (5)
- Case StudyDocument36 pagesCase StudydeathwishesNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocument13 pagesAppendicitis Case StudyMelanie Agaran Bautista100% (1)
- Case Study AppendectomyDocument40 pagesCase Study AppendectomyArmin Joseph Pepito0% (1)
- Acute AppendicitisDocument11 pagesAcute AppendicitisMary Jual Pe CaytapNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy CSDocument30 pagesAppendectomy CSMASIINo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis - CSDocument29 pagesAcute Appendicitis - CSMASIINo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument79 pagesAppendicitisMaria Paula Bungay100% (1)
- AppendectomyDocument40 pagesAppendectomyenny100% (12)
- Case Study For Peri-Appendiceal AbcessDocument79 pagesCase Study For Peri-Appendiceal Abcessmarife100% (5)
- Appendicitis JoyDocument15 pagesAppendicitis JoyJoy Rachel TabernillaNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy Case ReportDocument42 pagesAppendectomy Case ReportDane CunananNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy Case StudyDocument16 pagesAppendectomy Case StudyMahmoud Al Abed100% (1)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute AppendicitisDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Acute Appendicitisromeo rivera100% (4)
- AppendicitisDocument31 pagesAppendicitisginosanNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis NCSDocument25 pagesAppendicitis NCSZyrah Ziska ZafraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of AppendicitisDocument22 pagesNursing Management of AppendicitisIta Puspita Sari100% (1)
- Complete Care Study, AppendicitisDocument50 pagesComplete Care Study, AppendicitisOjo Paul Adesina100% (1)
- Revised Case Report - HemorrhoidsDocument47 pagesRevised Case Report - Hemorrhoidschristina_love08100% (2)
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocument6 pagesAppendicitis Case StudyKimxi Chiu LimNo ratings yet
- Case Study CholecystitisDocument27 pagesCase Study Cholecystitismeed0290% (10)
- Chronic Gastritis Case StudyDocument17 pagesChronic Gastritis Case StudyKaren Evangelista50% (4)
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocument10 pagesAppendicitis Case StudyMarie JoannNo ratings yet
- NCP PresDocument40 pagesNCP Presjohn loyola0% (1)
- I Patient Assessment Data BaseDocument12 pagesI Patient Assessment Data BaseJanice_Fernand_1603No ratings yet
- CASE STUDY AbortionDocument32 pagesCASE STUDY AbortionSapna thakur94% (18)
- Case Presentation Febrile Neutropenia NizarDocument25 pagesCase Presentation Febrile Neutropenia NizarNizar IJNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastro Enteritis Case StudyDocument71 pagesAcute Gastro Enteritis Case Studygiadda100% (2)
- Case Study On GynaeDocument22 pagesCase Study On GynaeJay PaulNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument16 pagesBronchial AsthmaMOLINA, TANJA JAYNENo ratings yet
- Case Presentation AbortionDocument27 pagesCase Presentation AbortionSusmita SenNo ratings yet
- Oncology Health AssessmentDocument12 pagesOncology Health AssessmentHimani PatelNo ratings yet
- Case Study in Vesicovaginal FistulaDocument14 pagesCase Study in Vesicovaginal FistulaIvory100% (4)
- Case Conference Saturday Morning Shift, MAY 18, 2019Document39 pagesCase Conference Saturday Morning Shift, MAY 18, 2019Aisya FikritamaNo ratings yet
- Amenorrhea: Definition - This Is The Symptom of Absence of MenstruationDocument10 pagesAmenorrhea: Definition - This Is The Symptom of Absence of MenstruationSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- رنا عبدالله الصبيح كيس ستديDocument23 pagesرنا عبدالله الصبيح كيس ستديرنا عبداللهNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument64 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseRoselle Joy D. RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Pakanna-BSN2D Chunk 1 Rot 1Document8 pagesPakanna-BSN2D Chunk 1 Rot 1FATIMA SHANNON INDASAN. PAKANNANo ratings yet
- Case Study of Acute AppendicitisDocument28 pagesCase Study of Acute AppendicitisDominique RamosNo ratings yet
- JaboneteDocument7 pagesJabonetejohn loyolaNo ratings yet
- LEVEL of STRESS Research ProposalDocument30 pagesLEVEL of STRESS Research ProposalArvin Ian Penaflor100% (2)
- Perceived Stressors and Coping Mechanism Among Caregivers of Autistic Children in Tacloban City: Basis For RecommendationDocument56 pagesPerceived Stressors and Coping Mechanism Among Caregivers of Autistic Children in Tacloban City: Basis For RecommendationArvin Ian PenaflorNo ratings yet
- InhalantDocument8 pagesInhalantArvin Ian Penaflor100% (1)
- Inflammation FracturesDocument2 pagesInflammation FracturesArvin Ian PenaflorNo ratings yet
- The Key Nutrients: Role and FunctionsDocument5 pagesThe Key Nutrients: Role and FunctionsArvin Ian PenaflorNo ratings yet
- Case Study of PneumoniaDocument8 pagesCase Study of PneumoniaArvin Ian Penaflor100% (5)
- Application LetterDocument1 pageApplication LetterArvin Ian PenaflorNo ratings yet
- Research or ThesesDocument22 pagesResearch or ThesesArvin Ian PenaflorNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisEldon SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Onset Positions in Induction of Anesthesia Spinal Anesthesia Nitrous Oxide Respiratory Complications Respiratory ObstructionDocument7 pagesOnset Positions in Induction of Anesthesia Spinal Anesthesia Nitrous Oxide Respiratory Complications Respiratory ObstructionArvin Ian Penaflor50% (2)
- Requirement in R.L.E. 10 - : CASE STUDY (Output) Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument1 pageRequirement in R.L.E. 10 - : CASE STUDY (Output) Community Acquired PneumoniaArvin Ian PenaflorNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisEldon SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisEldon SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisArvin Ian Penaflor100% (3)
- Case Study of UTI - Urinary Tract InfectionDocument9 pagesCase Study of UTI - Urinary Tract InfectionArvin Ian Penaflor75% (8)
- As FSDAFDSAFDocument2 pagesAs FSDAFDSAFTill PittNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel BlockersDocument4 pagesLocal Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel Blockersmed testNo ratings yet
- Pain in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: Experience, Expression, and AssessmentDocument6 pagesPain in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: Experience, Expression, and Assessmentflower21No ratings yet
- LESSON 3 ACIDOSIS and ALKALOSISDocument7 pagesLESSON 3 ACIDOSIS and ALKALOSISMaria VistalNo ratings yet
- Types of Crowns and BridgesDocument40 pagesTypes of Crowns and BridgesNoor HaiderNo ratings yet
- AstaReal MuscleDocument2 pagesAstaReal MuscleAmy HtunNo ratings yet
- Vanhoose 4102 FinalDocument14 pagesVanhoose 4102 Finalapi-510348262No ratings yet
- Final Manuscript GROUP2Document102 pagesFinal Manuscript GROUP222102279No ratings yet
- What Is A BacteriaDocument1 pageWhat Is A BacteriazunigahmNo ratings yet
- Uti - NCPDocument3 pagesUti - NCPRap De la Cruz100% (1)
- Download pdf An Introduction To Global Health Michael Seear ebook full chapterDocument34 pagesDownload pdf An Introduction To Global Health Michael Seear ebook full chapterwalter.richardson237100% (3)
- Barriers To Cancer Pain Management Among Nurses in Kenya - A  Focused EthnographyDocument7 pagesBarriers To Cancer Pain Management Among Nurses in Kenya - A  Focused EthnographyBIETRIS WARISYUNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin Induced Neurologic DamageDocument10 pagesBilirubin Induced Neurologic DamageAbd. Rahim MubarakNo ratings yet
- San Francisco Baseball Old Timers Association "From The Dugout" May 2020 EditionDocument7 pagesSan Francisco Baseball Old Timers Association "From The Dugout" May 2020 EditionKris K KimballNo ratings yet
- SINGI Solved Papers of ENTDocument430 pagesSINGI Solved Papers of ENTjbtcmdtjjvNo ratings yet
- Blepharitis and Eyelid HygieneDocument5 pagesBlepharitis and Eyelid Hygieneahykhh5No ratings yet
- Acl Rehab ProtocolDocument35 pagesAcl Rehab Protocolmatamea100% (3)
- GR 11 SLK Pe 1 Week 2 1ST Sem PDFDocument10 pagesGR 11 SLK Pe 1 Week 2 1ST Sem PDFwinslet villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Application and AssessmentDocument28 pagesApplication and AssessmentTrishia Mae Patalinghug100% (2)
- POP QUIZ Dịch báo cáoDocument15 pagesPOP QUIZ Dịch báo cáoNhư QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Ciad 696Document10 pagesCiad 696vsjsqz97nrNo ratings yet
- Non-Pharmacological Behaviour ManagementDocument13 pagesNon-Pharmacological Behaviour ManagementpokkeanggukNo ratings yet
- Excavation - FIRE FIGHTINGDocument8 pagesExcavation - FIRE FIGHTINGEm NiaxNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Fishmans Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Fishmans Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders PDFjeffrey.hemmings786100% (15)
- Ideas of The Passage "Reading"Document5 pagesIdeas of The Passage "Reading"Nurmala sariNo ratings yet
- Art Therapy and Neuroscience Blend: Working With Patients Who Have DementiaDocument8 pagesArt Therapy and Neuroscience Blend: Working With Patients Who Have DementiaLiliana Duarte PedrozaNo ratings yet
- September Issue 3 MCJ 36 Pages 2022Document36 pagesSeptember Issue 3 MCJ 36 Pages 2022Sathvika BNo ratings yet
- Manual CHARAK DDDRDocument80 pagesManual CHARAK DDDRsegurahNo ratings yet
- 07.02 Topnotch Pharmacology TableDocument64 pages07.02 Topnotch Pharmacology TableskzskzNo ratings yet