Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Local Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel Blockers
Uploaded by
med testOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Local Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel Blockers
Uploaded by
med testCopyright:
Available Formats
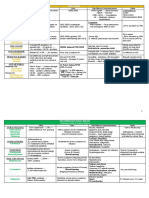
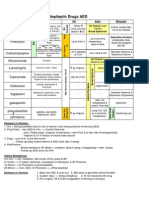
ANTI-ARRYTHMICS
Class I Class II Class III Class IV
Local anesthetics β-blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel Blockers
IA IB IC Propranolol Amiodarone (& Na+, , Ca2+) Verapamil
Quinidine Lidocaine Flecainide Acebutolol Dronedarone (same as above) Diltiazem
Procainamide Mexiletine Propafenone Esmolol (short acting) Sotalol (& ) Only cause vasodilation
Disopyramide Phenytoin Ibutilide (& Na+ window) (used in HTN, not here):
Tocainide Dofetilide (pure K+) Nifedipine, Bepridil
Block fast Na+ channels ↑QRS interval Gs→ cAMP→ Ca2+ in All ↑Refractory period (K+) in Ca2+ in phase 0 & 4 of
Do not affect SA or AV nodes phase 0 & 4 of fast & pacemaker potentials AV & SA Node
AV & SA Node
Moderate binding time Fast binding time Slow binding time Increases AV node Increases AV node
F e . de . Bl ck T ic bl ck refractory phase by refractory phase by
K+ efflux K+ efflux
Moderately prolonged No prolonged Very prolonged Prolongs phase 0 & 4 in
phase 0 phase 0 in normal phase 0 nodes
↑QT Only ↑QRS in ischemic ↑QT in atria ↑PR ↑QT ↑PR
(also blocks K+ efflux) tissue (blocks ↑Na+ (blocks K+ efflux) ↓HR ↓HR Amiodarone & Sotalol ↑HR (baroreceptor reflex
influx during plateau) ↑PR ↑PR & ↑QRS - Amiodarone b/c causes vasodilation)
(slows AV node) HR (nodal effects)
↑APD APD ~no to ↑APD ↑APD at AV node ↑APD No ∆APD
Rarely used ONLY v-tach/v-fib Wide spectrum Catecholamine Amiodarone everything, DOC SVT
Wide spectrum Best post-MI Atrial and ventricular sinus tachy. for v-tach/fib, can use in CHF, V-tach in atrial tach
Procainamide WPW tachycardias Slowing ventricular rate NO torsades (b/c Ca2+ channel Prevent DAD v-tach
during a-fib/flutter (SVT) blockade), (Ca overload)
*CAN use with heart failure
Quinidine also anti- Do not use in Prevent arrhythmia Dronedarone recurrent a-fib/a-
cholinergic (like atropine) asthmatics or COPD post-MI flutter
& α-antagonist Sotalol- wide, SV/V-tach
Do NOT USE with Ibutalide convert a-fib/a-tach in
asthmatics, COPD, first 3 weeks
diabetics Dofetilide maintain sinus
rhythm in a-fib
↑↑Torsades risk ~Torsades risk ↑Torsades risk Bronchospasm Amiodarone pulmonary Do NOT use with:
SLE-like syndrome with DO NOT use post- Hypotension with possible fibrosis, hepatotoxicity, Other AV blockers
procainamide MI or in CHF baroreflex tachycardia in thyroid, ↑LDL, photosensitivity (w/beta blocker esp)!!
Quinidine speeds up Can significantly HTN Dronedarone torsades, Hypotension
AV conduction, must prolong refractory Impotence kidney, CYP34A, ↑digoxin, Heart failure
give digitalis, B-blocker period in the AV CANNOT be used in heart
or Ca2+ channel block node Do not use in partial AV failure
1st blocks complete block All others torsades
Others:
Adenosine DOC in ER, slows AV node (↑PR), converts AV node/junctional rhythms
↑K+ efflux in AV/SA nodes= APD; hyperpolarization = HR
Ca2+ influx in AV node = ↑RP (Very rapid acting) ACLS: for PSVT & A-flutter tachy.
Lowers BP during Surgery (like ANP), CAD diagnosis, DOC for SVT conversion
Digoxin enhances vagal activity for a-fib/a-flutter
↑K+ efflux & Ca2+ influx HR, slows AV conduction (↑PR)
Atropine mAChR antagonist ↑HR, speeds AV conduction for vagal bradycardia
Magnesium for torsades & angina
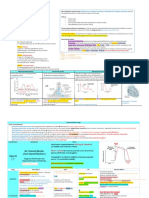
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES
MOA Additional Indications Contraindications Side Effects
Cardiac glycosides
s
Plasma volume TPR & preload 1 line HTN hypokalemic cardiac toxicity
↑RAAS use with ACE
Thiazides CO #1 in preventing CV Acid drugs renal tubule
Inh.
↑NE sensitivity vasodilation TPR complications of HTN excretion competition (penicillin,
NSAIDs)
Plasma volume TPR & preload
CO ↑RAAS use with ACE
Loops Edema
↑PGE2 venodilation preload Inh.
CO
Prior MI, CHF
1 on Heart HR, CO
Hyperlipidemia
Beta-blockers 1 on kidney renin TPR &
Atherosclerosis
preload
Cardiac remodeling
Fatigue, dry mouth,
CNS α-2 agonist SNS output → HR, CO, TPR & ↑diuresis Elderly CNS sefation/confusion
sexual dysfunction in men
Reflex tachycardia use
α1-antagonist Vasodilation TPR Extremely elevated BP
with -blocker
NEVER use Diltiazem &
To prevent effecting
Nifedipine & Bepridil only vasodilation Verapamil with other AV node Peripheral edema (All)
renal perfusion, GFR,
Ca2+ channel blockers Diltiazem & Verapamil - CO/HR/CF of suppressors ( -blockers, K+ AV node block (D&V)
salt, and water
heart & vasodilate channel blockers, adenosine, Cardiac depression (D&V)
excretion
cardiac glycosides)PINE
Direct Vasodilators
CHF Tachycardia (all)
Hydralazine Unknown mechanism
(Preference for arterial Hirsutism (Minoxidil)
Minoxidil Unknown mechanism
smooth muscle) Cyanide toxicity (Nitro.)
Nitroprusside Metabolized to ↑NO ↑cGMP
ACE Inhibitors (-pril)
Captopril, Cough (bradykinin) = 2/3
Enalapril Angioedema (bradykinin)
↑Bradykinin vasodilation (only ACEI)
Teratogenic
Lisinopril ATII effects= Diabetes
Ramipril Creatinine ↑ ( GFR)
Aldosterone & ADH Na/H2O & ↑K Renal failure
Pregnancy Teratogenic Hyperkalcemia
ARBs (-artan) CV hypertrophy Proteinuria
(Renal malformations) Hypotension
Isoartan, Systemic vasoconstriction ↑TPR CHF
SNS tone, naturesis
Valsartan Efferent arteriole constriction GFR Cardiac Remodeling
ARBs = aame ase ACEI
Azilsartan SNS outflow from CNS
except NO cough or
Irbesartan angioedema
Candesartan
Alikskiren Intracellular signaling Renin Isolated HTN
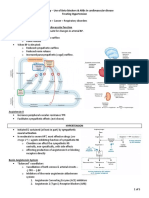
HEART FAILURE DRUGS
Class Drugs MOA Uses/Benefits Side Effects Other
In combo with Loops (synergy)
THIAZIDES Inhibits Na/Cl symporter in DCT **DOES NOT ↓mortality**
HTN
LOOPS
DIURETICS **DOES NOT ↓mortality**
Furosemide Inhibits NKCC symporter in TAL ↓↓Edema, Pulmonary congestion
↓Volume DO not use with NSAIDs
Bumetanide ↑PGE2 synthesis IV for decompensated HF
↓Preload (blunts efficacy by ↓PGs)
Torsemide
↓Edema
Limit K+ wasting
K+ SPARING
Aldosterone antagonist ↓/Reverse LV remodeling caused **↓CHF MORTALITY**
Spironolactone
by aldosterone
ACE INHIBITORS Inhibit ACE → ↓ATII synthesis Cough
Captopril ↓Na/H2O reabsorption (↑bradykinin)
Enalapril ↓Aldosterone ↑K+
↓/Reverse LV remodeling caused
Lisinopril ↓SNS activity & NE sensitivity Hypotension **↓CHF MORTALITY**
by aldosterone & ATII
ARBs
ATII receptor antagonists ↓Side effects
Losartan
Same effects as ACE inhibitors (no ↑bradykinin)
Candesartan
VASODILATORS Nitroprusside Acute setting of CF (IV)
Thiocyanate toxicity
↓Preload (IV) ↓Preload (Veins) & Afterload (arteries)
Hypotension
↓Afterload Preference = Veins >
Chronic use Syncope
Coronaries > Arteries
Nitroglycerin Converted to ↑NO → ↑cGMP→ Sublingual = DOC for ongoing Orthostatic HTN
Tolerance = common
(topical, sublingual, IV) vasodilation angina attacks Reflex ↑HR st
No oral form - high 1 pass
Only ↓Preload Stealing effect
effect
(↑cardiac ischemia)
Isosorbide Dinitrite Only ↓Preload & Hydralazine + Isosorbide
(oral) ↑Renal blood flow **↓CHF MORTALITY**
(alt. to ACEI or ARBs esp. in
Hydralazine (oral) Sole arterial vasodilation Only ↓Afterload African Americans)
CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES + +
Inhibits Na /K ATPase → Narrow
**DOES NOT ↓mortality**
Digoxin + 2+
↑Na /Ca exchanger → Therapeutic Index
(Shorter T½ 1-2 hr, 2+
↑Intracellular Ca → ↑CO Anti-arrhythmic Hypokalemia →
Side Effect Antidotes =
Kidney excretion) (HF w/A-fib or A-flutter) ↑Side effects
↓Sensitivity of baroreflex → rd Lidocaine, ↑K+/K+ sparing
Digitoxin 3 line HF drug - after ACEI & Arrhythmias
↑Vagal activity → ↓AV diuretic, -blockers,
(Longer T½ 4 days, -blocker (DAD, V-tach/fib)
conduction → ↓HR Fab digitalis antibody
Liver metabolized) GI distress
1 AGONISTS Acute setting of CF (IV)
IONOTROPES Dopamine: D1> 1>>α1 agonist Tachycardia Often used together
Dopamine Dopamine: ↑Renal perfusion
↑CO Dobutamine: 1>> 2 Tolerance Not recommended long-term
Dobutamine Dobutamine: does not ↑HR
PDE INHIBITORS Inhibits PDE → Acute setting of severe CF (IV)
2+ Caffeine & Glucagon →
Inamrinone ↑cAMP → ↑Intracellular Ca ↓Preload, ↓Afterload & ↑CO
same effect
Milrinone ↑cGMP → vasodilation Short term antidote to -blockers
BLOCKERS 1 receptor antagonists → ONLY drug to ↑Ejection Fraction
Carvedilol ( 1/2>α1) ↓SNS effects on heart ↓Deleterious effects of Epi/NE
**↓CHF MORTALITY**
Metoprolol ( 1) ↓Renin → ↓Preload, ↓Afterload ↓/Reverse LV remodeling caused
Bisoprolol ( 1) ↑β-Arrestin pathway by Epi/NE, Aldo & ATII
2
LIPID LOWERING AGENTS
Drug MOA Lipid Profile Side Effects Interactions Other
Blocks enterohepatic cycling of Bitter/gritty taste Absorption of polar
Resins
bile acids LDL GI discomfort/constipation drugs = Warfarin,
Cholestyramine Most common lipid lowering
↑Bile acid synthesis by liver ↑HDL Fat soluble vit. Absorption digoxin, thyroxine,
Colestipol combination = statins + resin
↑VLDL synthesis by liver ↑TG (VLDL) Cholesterol gallstones statins (take at least 1 hr
Colesevelam
↑LDL receptors apart from taking resin)
Statins ↑Risk of myositis in Other beneficial effect (E.g.
Hepatotoxic
Lovastatin combination with Antioxidant,
Myopathy / Rhabdomyolysis
Simvastatin LDL fibrates, niacin, & antiinflammatory)
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors ↓Myelination
Pravastatin ↑HDL protease inhibitors Higher efficacy at night
cholesterol synthesis by liver ↑LDL receptors
Fluvastatin ↓TG (HAART) Short T½ with daily dose
Contraindicated in
Atorvastatin All metabolized by P450
pregnancy
Rosuvastatin except pravastatin
Flushed face (treat w/ASA)
Niacin ↓VLDL synthesis by liver LDL
Hyperglycemia (bad for ↑Statin myopathy Usually used in combo with
↓Adipose tissue lipolysis ↑↑HDL
(Vitamin B3) diabetes, acanthosis nigricans) fibrate, resin or statin
↓TG
Hyperuricemia (↑gout)
Displace warfarin from
Fibrates ↑LPL activity ↑FA uptake & LDL Nausea, skin rash, headache
albumin ( dose or give
Gemfibrozil oxidation in tissues & liver ↑HDL Cholesterol gallstones
drugs at diff. times)
Fenofibrate ↑TG clearance & VLDL synthesis ↓↓↓TG (VLDL) ↑LDL synthesis
↑Statin myopathy
↓LDL Metabolic = 400x as potent
Intestinal cholesterol absorption No major adverse effects
Ezetimibe ↑HDL and undergoes enterohepatic
inhibitor (diarrhea)
cycling to prolong action
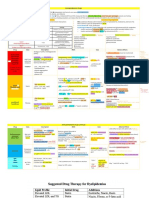
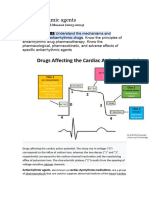
ANTI-ANGINALS
Nitrates -blockers Ca2+ channel blockers Na+ channel blocker
Nitroglycerin 1 Metoprolol, Atenolol Nifedipine, Amlodipine, Bepridil Ranolazine
Isosobide dinitrate 1/2 Propranolol, Nadolol Diltiazem, Verapamil
Effects Vessel Dilation: 1 block = Vasodilatory preference AP duration → contraction
Veins>coronaries>>arterioles CF/wall tension O2 demand Nifedipine/Amlodipine time → O2 damand
Venodilation Preload HR ↑Diastolic coronary flow Cardiac HR/CF preference
Coronary dilation Vasospasm 2 block = ↑TPR afterload, Diltiazem, Verapamil
Arteriole dilation Afterload ↑bronchospasm, insulin secretion (Also ectopic beats & cell damage
by intracellular Ca)
Uses Stable & unstable angina Stable & unstable angina Stable & unstable angina Chronic stable angina
P i me al a gi a -Especially post-MI -Especially with HTN NOT w/pre-existing ↑QT or
NOT with PDE inh. (Viagra) NOT PRIN METAL S P (DOC) esp. Nif. hepatic/renal impairment
Side effects Orthostatic hypotension, fainting, Hyperglycemia avoided in AV node blocks DO NOT use Constipation
headache (blood pooling in veins) diabetics (use selective 1) diltiazem. Verapamil with β-blocker Dizziness, headache, nausea
Reflex tachycardia → ↑angina Bronchospasms avoided in COPD Peripheral edema Edema
(use with -blocker) & asthmatics (use 1) Transient hypotension, Bradycardia Weakness
Flushing methemoglobinemia Impotence, bradycardia, Dizziness, flushing, headache
(Rare w/ isosorbide dinitrate) fatigue/lethargy
Other Tolerance develops rapidly Aspirin (169-325 mg) - At pain onset (unstable angina). daily (chronic stable) Do not use with diltiazem
st
Extensive 1 pass effect Dipyridamole adenosine uptake inhibitor vasodilation ( absorption) or CYP34A
Nicorandil - K+ cannel activation HR inhibitors (metabolized by it)
You might also like
- Aluminum OH Magnesium OH Calcium Carbonate: Pud & GerdDocument4 pagesAluminum OH Magnesium OH Calcium Carbonate: Pud & Gerdmed testNo ratings yet
- Aluminum OH Magnesium OH Calcium Carbonate: Pud & GerdDocument4 pagesAluminum OH Magnesium OH Calcium Carbonate: Pud & Gerdmed testNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DrugsDocument5 pagesCardiac Drugseric100% (17)
- Diabetes DrugsDocument1 pageDiabetes Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Common Cardiac MedicationsDocument1 pageCommon Cardiac MedicationsPaige HardekopfNo ratings yet
- Coagulation DrugsDocument1 pageCoagulation Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Coagulation DrugsDocument1 pageCoagulation Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DrugsDocument6 pagesEndocrine Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DrugsDocument6 pagesEndocrine Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocument18 pagesPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Respiratory DrugsDocument2 pagesRespiratory Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DrugsDocument2 pagesRespiratory Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- NSAIDS and SteroidsDocument2 pagesNSAIDS and Steroidsmed testNo ratings yet
- NSAIDS and SteroidsDocument2 pagesNSAIDS and Steroidsmed testNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Drug Reference SheetDocument12 pagesCritical Care Drug Reference SheetYanina CoxNo ratings yet
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocument3 pagesSphere: These Diarrheamed testNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Meds CompleteDocument3 pagesCardiac Meds CompleteDanielle100% (2)
- Opioids PDFDocument2 pagesOpioids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- ANS DrugsDocument2 pagesANS Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics ChartDocument10 pagesAntibiotics Chartadom09No ratings yet
- CardionotesDocument5 pagesCardionotesNichole Coletta100% (1)
- Common MedicationsDocument4 pagesCommon MedicationsFatima CarricoNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Anti-Coagulants PDFDocument3 pagesNinja - Anti-Coagulants PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFDocument6 pagesNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Ninja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFDocument3 pagesNinja - Antihyperlipidemics PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Ninja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFDocument4 pagesNinja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Managing Cardiac Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsDocument29 pagesManaging Cardiac Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsYlanni Coritana100% (1)
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Document1 pageBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testNo ratings yet
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Document1 pageBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testNo ratings yet
- GI Drugs PDFDocument6 pagesGI Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- 100 Most Important DrugsDocument13 pages100 Most Important Drugsngopya djiki67% (3)
- Poison/drug-Induced Tachycardia, 2/3 Heart Blocks: DigoxinDocument2 pagesPoison/drug-Induced Tachycardia, 2/3 Heart Blocks: DigoxinimperiouxxNo ratings yet
- Lab Values Chart GuideDocument5 pagesLab Values Chart GuideVanessaMUeller100% (3)
- Heart Failure: Signs, Causes, TreatmentsDocument1 pageHeart Failure: Signs, Causes, TreatmentsTrisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic TableDocument7 pagesAntibiotic TablenkuligowskiNo ratings yet
- 100 Essential Drugs1Document8 pages100 Essential Drugs1Sudip DevadasNo ratings yet
- Chan, Johnson - TreatmentGuidelines PDFDocument0 pagesChan, Johnson - TreatmentGuidelines PDFBogdan CarabasNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs Mechanisms Effects Uses Side Effects /TITLEDocument3 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs Mechanisms Effects Uses Side Effects /TITLEdoktorcoopNo ratings yet
- Patho A 1. 5 Hemodynamic Disorders (Bongat, 2015)Document12 pagesPatho A 1. 5 Hemodynamic Disorders (Bongat, 2015)Grant GarcesNo ratings yet
- Pharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106Document47 pagesPharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106sean liyanageNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Drug ChartDocument3 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Drug Chartlui.stephanie1751100% (1)
- Drug ChartDocument8 pagesDrug Chartstudentalwaysstudy100% (1)
- Hypertension: PharmacotherapyDocument23 pagesHypertension: Pharmacotherapytorr123No ratings yet
- Ninja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFDocument7 pagesNinja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Concise SEO-Optimized Title for Clotting DocumentDocument3 pagesConcise SEO-Optimized Title for Clotting DocumentRyan TurnerNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drug IntroductionDocument3 pagesCardiovascular Drug IntroductionSamah Khan100% (1)
- Pharmacology-ATI 150 Drug Cards PDFDocument4 pagesPharmacology-ATI 150 Drug Cards PDFhollyNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Nclex Notes Easy To Read PDFDocument97 pagesComprehensive Nclex Notes Easy To Read PDFKenia GeorgesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDocument5 pagesPharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDana20SNo ratings yet
- Test InformationDocument5 pagesTest InformationCatalina BorquezNo ratings yet
- 0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFDocument1 page0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Common Medications UsedDocument3 pagesCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Main DrugsDocument14 pagesPharmacology Main DrugsSabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Antianginal Drugs PDFDocument2 pagesNinja - Antianginal Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Heart Rhythms S SDocument3 pagesHeart Rhythms S SGloryJane100% (1)
- Ninja - Anemias PDFDocument1 pageNinja - Anemias PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Drug Names - Stems, Prefixes, Roots and Suffixes - NCLEX MasteryDocument5 pagesDrug Names - Stems, Prefixes, Roots and Suffixes - NCLEX MasteryMarcel YoungNo ratings yet
- Medications and assessmentsDocument225 pagesMedications and assessmentsJessica 'Baker' IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocument8 pagesApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuNo ratings yet
- Common infections and recommended antibioticsDocument3 pagesCommon infections and recommended antibioticsNicole BerryNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocument1 pageAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88No ratings yet
- Labs 1.19 ABG AnalysisDocument1 pageLabs 1.19 ABG AnalysisMonica GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Nitroglycerin Isosorbide Dinitrate: Class Class Use UseDocument17 pagesNitroglycerin Isosorbide Dinitrate: Class Class Use UseEdmond ChanNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrugsDocument4 pagesCardio DrugsAlex ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Antiarrythmic Agents: Antiarrythmic Drugs For HorsesDocument3 pagesAntiarrythmic Agents: Antiarrythmic Drugs For HorsesMageja TatendaNo ratings yet
- How To Deal Acute Pulmonary OedemDocument23 pagesHow To Deal Acute Pulmonary Oedemdhika2496No ratings yet
- Anti-Arrhythmic Drug Actions Use Side Effects DDI & Contraindications PharmacokineticsDocument1 pageAnti-Arrhythmic Drug Actions Use Side Effects DDI & Contraindications PharmacokineticsMohamed KhattabNo ratings yet
- Understanding Tachycardia and Bradycardia ClassificationsDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Tachycardia and Bradycardia ClassificationsZega AgustianNo ratings yet
- Pharma DR - Jawad Antiarrhythmic Agent Lec 4Document7 pagesPharma DR - Jawad Antiarrhythmic Agent Lec 4rkh647m7szNo ratings yet
- Neuro Clerkship - Dizziness & VertigoDocument7 pagesNeuro Clerkship - Dizziness & Vertigomed testNo ratings yet
- Neurology Clerkship DementiaDocument8 pagesNeurology Clerkship Dementiamed testNo ratings yet
- Neuro Clerkship - EpilepsyDocument11 pagesNeuro Clerkship - Epilepsymed testNo ratings yet
- Nurses Need to Know About Stroke CareDocument68 pagesNurses Need to Know About Stroke CareSuci Aning TNo ratings yet
- Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump Refresher CourseDocument17 pagesIntra-Aortic Balloon Pump Refresher Courseapi-301270014No ratings yet
- Systemic Effects of Local Anaesthesia in Hypertensive PatientsDocument6 pagesSystemic Effects of Local Anaesthesia in Hypertensive PatientsKarina HernandezNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Ischemia and Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument81 pagesMyocardial Ischemia and Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyroshamaharaniNo ratings yet
- Tony Cross CDU Low Risk ACS Proforma - V3.212 Review Due June 2014Document4 pagesTony Cross CDU Low Risk ACS Proforma - V3.212 Review Due June 2014ED@HEFTNo ratings yet
- Biology Worksheet Sheep Heart DissectionDocument3 pagesBiology Worksheet Sheep Heart DissectionFluphie Bunny0% (1)
- Z5 Mindray DatasheetDocument15 pagesZ5 Mindray DatasheetBertha DuránNo ratings yet
- Banti Syndrome PDFDocument8 pagesBanti Syndrome PDFWiyosa RusdiNo ratings yet
- CVS Qus. Banq 2023Document7 pagesCVS Qus. Banq 2023aniskoharNo ratings yet
- B CellDocument10 pagesB CellSonia Elizabeth SimonNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels, AnatomyDocument20 pagesBlood Vessels, AnatomyAbu BakarNo ratings yet
- Intro CVSDocument23 pagesIntro CVSumerjicNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle by Preetibala Sahu-1Document17 pagesCardiac Cycle by Preetibala Sahu-1aksahu01234No ratings yet
- Chap 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Mind Map Class 11 PDF - WatermarkDocument3 pagesChap 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Mind Map Class 11 PDF - Watermarkmominameen7No ratings yet
- Esc Guidelines For The Management of Heart Failure (Autosaved)Document80 pagesEsc Guidelines For The Management of Heart Failure (Autosaved)Ahmad AlKhataybehNo ratings yet
- Gangrene PowerpointDocument28 pagesGangrene PowerpointNadiyaSiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Troponin I Leve in STEMI and Clinical Correlation With LeftVentricular Dysfunction in Indian Population 2329 9517.1000116Document6 pagesCardiac Troponin I Leve in STEMI and Clinical Correlation With LeftVentricular Dysfunction in Indian Population 2329 9517.1000116panjiNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood PressureDocument4 pagesArterial Blood Pressure075 Keerthighaa SNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Criteria of Stroke: Monica - Monitoring Trends and Determinants of Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Criteria of Stroke: Monica - Monitoring Trends and Determinants of Cardiovascular DiseaseSamudra Hadi SantosaNo ratings yet
- McqsDocument5 pagesMcqsahsan gujjarNo ratings yet
- Pathology CVS #5 by Omar BaniErshaidDocument5 pagesPathology CVS #5 by Omar BaniErshaidبصيص اليقينNo ratings yet
- Unstable Angina PectorisDocument24 pagesUnstable Angina PectorisAkbar IskandarNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cath: Aortic Stenosis, CAD, Mitral RegurgitationDocument2 pagesCardiac Cath: Aortic Stenosis, CAD, Mitral RegurgitationIndranil Sinha100% (1)
- Fiitjee TRANSPORTATIONDocument8 pagesFiitjee TRANSPORTATIONAtharv AggarwalNo ratings yet
- ACC Anywhere Session ListingDocument9 pagesACC Anywhere Session ListingnideNo ratings yet
- DVT Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument19 pagesDVT Deep Vein ThrombosisDoctor MusicNo ratings yet
- Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous ConnectionDocument30 pagesTotal Anomalous Pulmonary Venous ConnectionGomathi ShankarNo ratings yet