Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eye: The Organ of Sight. The Eye Has A Number of Components. These Components Include But
Uploaded by
Christian Antonio Sumalbag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThe cornea is the clear front window of the eye that transmits and focuses light into the eye. The iris is the colored part of the eye regulating the amount of light that enters. The lens is the transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina. The retina is the nerve layer that lines the back of the eye, senses light and creates impulses that travel through the optic nerve to the brain.
Original Description:
Original Title
Eye.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe cornea is the clear front window of the eye that transmits and focuses light into the eye. The iris is the colored part of the eye regulating the amount of light that enters. The lens is the transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina. The retina is the nerve layer that lines the back of the eye, senses light and creates impulses that travel through the optic nerve to the brain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageEye: The Organ of Sight. The Eye Has A Number of Components. These Components Include But
Uploaded by
Christian Antonio SumalbagThe cornea is the clear front window of the eye that transmits and focuses light into the eye. The iris is the colored part of the eye regulating the amount of light that enters. The lens is the transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina. The retina is the nerve layer that lines the back of the eye, senses light and creates impulses that travel through the optic nerve to the brain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
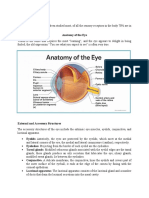
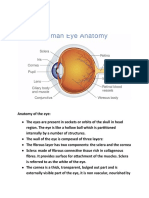
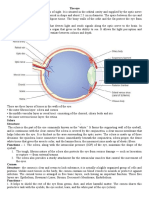
Eye: The organ of sight. The eye has a number of components.
These components include but
are not limited to the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, macula, optic nerve, choroid and vitreous.
The cornea is the clear front window of the eye that
transmits and focuses light into the eye.
The iris is the colored part of the eye that helps
regulate the amount of light that enters the eye.
The pupil is the dark aperture in the iris that
determines how much light is let into the eye.
The lens is the transparent structure inside the eye that
focuses light rays onto the retina.
The retina is the nerve layer that lines the back of the
eye, senses light and creates impulses that travel
through the optic nerve to the brain.
The macula is a small area in the retina that contains special light-sensitive cells and allows us to
see fine details clearly.
The optic nerve is the nerve that connects the eye to the brain and carries the impulses formed by
the retina to the visual cortex of the brain.
The choroid is a thin vascular layer between the sclera and the retina that supplies blood to the
retina and conducts arteries and nerves to other structures in the eye.
The vitreous humor is a clear, jelly-like substance that fills the middle of the eye.
The word "eye" come from the Teutonic "auge."
You might also like
- EYE Eye Anatomy Facts: RetinaDocument6 pagesEYE Eye Anatomy Facts: RetinaEdgar Betancourt VeraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Visual DisordersDocument21 pagesVisual DisordersJobelle Acena100% (1)
- Cross Section Drawing of The Eye - (Side View) With Major Parts LabeledDocument7 pagesCross Section Drawing of The Eye - (Side View) With Major Parts LabeledCamille ReneeNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The EyesDocument5 pagesStructure and Function of The EyesPreeti ShuklaNo ratings yet
- FearlessDocument10 pagesFearlessAko ToNo ratings yet
- 1-Anatomy of The EyeDocument2 pages1-Anatomy of The EyeRadhwanNo ratings yet
- Parts of The EyeDocument2 pagesParts of The EyeNicah Rose AstilleroNo ratings yet
- Special Senses EYEDocument4 pagesSpecial Senses EYEDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- The EyesDocument4 pagesThe EyesAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Human Eye 13Document1 pageHuman Eye 13Dorcas CuevasNo ratings yet
- Human Eye 1Document13 pagesHuman Eye 1GUNJAN SHARMANo ratings yet
- Presentation1 (2) 4Document10 pagesPresentation1 (2) 4Shokunbi TolaniNo ratings yet
- F2 Science C1-EyeStructureWSDocument3 pagesF2 Science C1-EyeStructureWSCerdik CekapNo ratings yet
- F2 Science - EyeStructureWSDocument3 pagesF2 Science - EyeStructureWSCerdik CekapNo ratings yet
- D Out About Different Parts of The EyeDocument2 pagesD Out About Different Parts of The EyeAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Special Senses EYEDocument27 pagesSpecial Senses EYENadiabloshii NadiabloshiiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Eyesen_subhasis_58No ratings yet
- Creating 3D Eyes: One: The Anatomy of The Human EyeDocument2 pagesCreating 3D Eyes: One: The Anatomy of The Human Eyekora_c995No ratings yet
- Eyes AnatomyDocument2 pagesEyes AnatomyAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Your Eye AnatomyDocument4 pagesYour Eye AnatomyAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Eye How The Eye and Brain Work Together PDFDocument4 pagesFact Sheet Eye How The Eye and Brain Work Together PDFWy TeayNo ratings yet
- Hassan Nawaz - 202321192010Document15 pagesHassan Nawaz - 202321192010hassanNo ratings yet
- Working of Human EyeDocument13 pagesWorking of Human EyeVikashKeshavNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument1 pageThe Human EyeKasim KarimNo ratings yet
- Windows To The World - Unveiling The Wonders of The Human EyeDocument2 pagesWindows To The World - Unveiling The Wonders of The Human EyeYienNo ratings yet
- Basic Eye Anatomy: CorneaDocument6 pagesBasic Eye Anatomy: CorneaGayatri Gaur100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Left EyeDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The Left EyeJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Göz AnatomiDocument4 pagesGöz AnatomiArdaNo ratings yet
- What Makes Up An EyeDocument3 pagesWhat Makes Up An EyenandhantammisettyNo ratings yet
- Special Senses: VisionDocument22 pagesSpecial Senses: VisionLord arainNo ratings yet
- Eye AnatomyDocument2 pagesEye AnatomyVince DaymielNo ratings yet
- Human Senses: Monique MavronicolasDocument10 pagesHuman Senses: Monique MavronicolasMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Technical College of Health ShekhanDocument9 pagesTechnical College of Health ShekhanSaadNo ratings yet
- Eye NotesDocument21 pagesEye NotesViswaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On GlaucomaDocument26 pagesSeminar On GlaucomaPriya ANo ratings yet
- Eyes Explained: Actions For This PageDocument3 pagesEyes Explained: Actions For This PageAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EyeDocument17 pagesPhysiology of EyeHanna ShibuNo ratings yet
- 181 Anatomy Eyes and EarsDocument23 pages181 Anatomy Eyes and EarsAnita YadavNo ratings yet
- Bionic Eye EB KNS 2019Document58 pagesBionic Eye EB KNS 2019Lalitaditya DivakarlaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EyeDocument1 pageAnatomy of EyedehinnetagimasNo ratings yet
- Handout (Sample)Document22 pagesHandout (Sample)judssalangsangNo ratings yet
- 181 Anatomy Eyes and EarsDocument23 pages181 Anatomy Eyes and Earsmuhammad chughtaiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Eye: Prepared By: Spervised byDocument33 pagesAnatomy of The Eye: Prepared By: Spervised byahmed500600No ratings yet
- Class 10 Module On Eye IDocument5 pagesClass 10 Module On Eye IDarkAngelNo ratings yet
- Our Sense of Sight and LightDocument6 pagesOur Sense of Sight and LightCikgu EzanNo ratings yet
- Coordination: NotesDocument6 pagesCoordination: Notesyuki soraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: The EyeDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: The EyeMarvin Manuel RamosNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument6 pagesThe EyeDebiprasad GhoshNo ratings yet
- Info Sheet 4 - 1Document8 pagesInfo Sheet 4 - 1Francis ObmergaNo ratings yet
- Maryam PresentationDocument9 pagesMaryam PresentationUsman MuneerNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Structure of Human EyeDocument8 pagesSense Organs: Structure of Human EyeRanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Sense OrgansDocument18 pagesChapter 11 Sense OrgansMichael Oconnor100% (2)
- Pig EyeDocument6 pagesPig Eyeaims_sluNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument21 pagesSpecial SensesJhemDelfinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EyeDocument4 pagesAnatomy of EyeBellarmine JanellaNo ratings yet
- L5 - 2 - Special SensesDocument87 pagesL5 - 2 - Special Sensesbotchwaylilian17No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Eye WorksheetDocument1 pageAnatomy of The Eye WorksheetIrfan ArifNo ratings yet
- EYE Notes IgcseDocument3 pagesEYE Notes IgcseTay HermyNo ratings yet