Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Agents of Erosion
Uploaded by
api-2685331450 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesOriginal Title
agents of erosion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesAgents of Erosion
Uploaded by
api-268533145Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
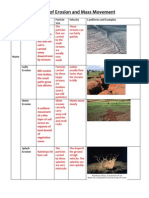
Agents of Erosion and Mass Movement
Erosion Agent What Happens? Particle Size Velocity Landforms and
Examples
Water
Rill
Erosion
Soil is removed
by water running
through little
streams.
Medium sized to
small
Faster On slopes-
Badlands National
Park
Gully
Erosion
Occurs when
surface water is
trapped in a
stream and
begins to erode
channels in the
ground.
Medium sized Medium paced Anywhere near a
flowing body of
water for
landforms.
Examples are
common in farming
areas.
Sheet
Erosion
Removes soil in
thin layers via
rain and
overland flow.
Decent sized
particle
Quick due to slope Normally on sloped
land. Hills.
Splash
Erosion
When raindrops
first hit the bare
soil and move it.
Small particles
(not packed
together)
Pretty quick, dont
move far.
Any landforms, as
long as there is bare
soil. Examples are
just when it rains
on open freshly
planted soil.
Wave
(Shoreline)
Erosion
Loss of sand
from the beach
or sand dunes
that may be
temporary or
permanent.
Small Decent pased Location is on the
coastline obviously.
Storms are an
example as they
cause a lot of
shoreline erosion.
Glacial
When glaciers
move they take
out large
portions of
Earths
landscape along
with them.
Very large
(Huge rocks and
boulders)
Slow Leave behind
valleys with
waterfalls and or
lakes. These are
common in New
England, and other
parts of the
Northern United
States.
Wind
The wind simply
picks up the
particles and
moves them
elsewhere.
Smaller particles Decent
pace/medium
Areas with limited
precipitation and
high temperatures.
Also landforms
with little
vegetation. An
example is Death
Agents of Erosion and Mass Movement
Valley.
Anthropogenic
Human activity
moves sediment
whether it be
intentional or
unintentional.
Can vary from
small to large
Depends on
activity... can be
fast or slow
Can occur on any
landforms.
Examples are from
drilling, digging,
planting a garden,
or even tracking
dirt on your shoes.
You might also like
- Agents ErosionDocument1 pageAgents Erosionapi-265487375No ratings yet
- ErosionDocument15 pagesErosionSreedhar Reddy SajjalaNo ratings yet
- How Rocks and Soil Move Downslope Due To The Direct Action of GravityDocument3 pagesHow Rocks and Soil Move Downslope Due To The Direct Action of GravityMarkinzo FNo ratings yet
- Types of ErosionDocument2 pagesTypes of Erosiondiahema100% (1)
- Exogenic ProcessDocument6 pagesExogenic ProcessCharis Ann Limotan MataNo ratings yet
- Agents of ErosionDocument2 pagesAgents of Erosionapi-264885511No ratings yet
- Erosion and TransportationDocument17 pagesErosion and TransportationbibsNo ratings yet
- ErosionDocument3 pagesErosionLouis ChavezNo ratings yet
- 8 - Weathering & Erosion (B 2)Document31 pages8 - Weathering & Erosion (B 2)Saad AbbasiNo ratings yet
- GEODocument3 pagesGEObrynie watson ssekajjigoNo ratings yet
- Weathering and Soil Erosion G5Document39 pagesWeathering and Soil Erosion G5Neil DeclaroNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - Group 1Document19 pagesEarth Science - Group 1HerwienNo ratings yet
- The Agents of Erosion: 1. Erosion & Deposition 2. Water 3. Wind 4. IceDocument26 pagesThe Agents of Erosion: 1. Erosion & Deposition 2. Water 3. Wind 4. IceThegame1991usususNo ratings yet
- Kid’s Guide to Types of Landforms - Children's Science & NatureFrom EverandKid’s Guide to Types of Landforms - Children's Science & NatureNo ratings yet
- LESSON 7 - Exogenic ProcessesDocument40 pagesLESSON 7 - Exogenic ProcessesJhudiel Dela ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Weathering & ErosionDocument3 pagesGrade 4 Weathering & ErosionAshoka NarayananNo ratings yet
- Q4-DRRR-lesson-1 (1)Document25 pagesQ4-DRRR-lesson-1 (1)Ella C. AragoNo ratings yet
- DRRR WordDocument38 pagesDRRR WordLeauvie MendesNo ratings yet
- Mass Wasting: Processes and HazardsDocument55 pagesMass Wasting: Processes and HazardsTricia Mae QuezadaNo ratings yet
- DRRR PDFDocument39 pagesDRRR PDFLeauvie MendesNo ratings yet
- Analyze The Causes of Geological HazardDocument13 pagesAnalyze The Causes of Geological HazardDaniel Arradaza100% (1)
- What Is ErosionDocument5 pagesWhat Is ErosionJoya Sugue AlforqueNo ratings yet
- External Forces Shaping The EarthDocument11 pagesExternal Forces Shaping The EarthJesse RamroopNo ratings yet
- Weathering of Rocks Describes The Process of Weakening and Breaking Down of Rocks and MineralsDocument18 pagesWeathering of Rocks Describes The Process of Weakening and Breaking Down of Rocks and MineralsJean Nalla AndusNo ratings yet
- Weathering, Soil Formation, and Erosion ch7-8Document48 pagesWeathering, Soil Formation, and Erosion ch7-8Nikee Rolin Gomez CastroNo ratings yet
- Risks of Landslides and SinkholesDocument7 pagesRisks of Landslides and SinkholesRalph Louis RosarioNo ratings yet
- Erosion & Mass Wasting ProcessesDocument11 pagesErosion & Mass Wasting ProcessesCristina YusonNo ratings yet
- Erosion Mass WastingDocument11 pagesErosion Mass WastingTina YusonNo ratings yet
- Name-Ananya Tiwari Class-9 Section-H Subject Teacher-Mrs - Stuti Mishra Topic-Weathering and DenudationDocument15 pagesName-Ananya Tiwari Class-9 Section-H Subject Teacher-Mrs - Stuti Mishra Topic-Weathering and DenudationNew UserNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: Weathering and Erosion AgentsDocument85 pagesEarth Science: Weathering and Erosion AgentsElijah Raphael YasaNo ratings yet
- Erosion: Physical ProcessesDocument5 pagesErosion: Physical ProcessesNisrinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 GEOLOGYDocument4 pagesLecture 6 GEOLOGYnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Land Sliding ReportDocument14 pagesLand Sliding ReportShahram BehniaNo ratings yet
- DRRR PPT 1Document34 pagesDRRR PPT 1Kim EstrebellaNo ratings yet
- Writing A Concept PaperDocument64 pagesWriting A Concept PaperJhedyl LambayanNo ratings yet
- Soil-Erosion and Mass WastingDocument14 pagesSoil-Erosion and Mass WastingJemielyn Camille FredelucesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document29 pagesLesson 4Ace De Jesus RascoNo ratings yet
- Soil Erosion - WikipediaDocument35 pagesSoil Erosion - WikipediaSmitha YohannanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 GeologyDocument5 pagesLecture 11 GeologynattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Mass Movements and Mass Movement ProcessesDocument6 pagesMass Movements and Mass Movement ProcessesFerry ZhumeNo ratings yet
- Landforms on Earth Explained in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesLandforms on Earth Explained in 40 CharactersnoemeNo ratings yet
- Els Week 6Document3 pagesEls Week 6Jessica BorromeoNo ratings yet
- CE114Document3 pagesCE114Benoit ゝNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Geological Processes of WindDocument11 pagesLecture 10 Geological Processes of WindEbi AckermanNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 Unstable LandDocument12 pagesChapter12 Unstable LandercilloNo ratings yet
- Second 2Document17 pagesSecond 2rakesh roshanNo ratings yet
- M1 Different Types of Geological Hazards - 083143Document13 pagesM1 Different Types of Geological Hazards - 083143Jamaica AdayNo ratings yet
- 3) Mass MovementDocument33 pages3) Mass MovementRaffee UsliNo ratings yet
- Soil Erosion PDFDocument20 pagesSoil Erosion PDFAja FightingNo ratings yet
- Mass Wasting orDocument4 pagesMass Wasting orSheryl Lou AngelesNo ratings yet
- Erosion ArticleDocument7 pagesErosion Articleapi-253899620No ratings yet
- Landslideandsoilerosion 160321131400Document32 pagesLandslideandsoilerosion 160321131400mardiradNo ratings yet
- Earth Science MASS WASTINGDocument2 pagesEarth Science MASS WASTINGvillasencio.shaneeNo ratings yet
- ES21Document2 pagesES21Catherine AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Presentation 085135Document22 pagesPresentation 085135SultanNo ratings yet
- Earth ChangesDocument9 pagesEarth Changesapi-249544695No ratings yet
- Exogenic Processeses 1Document7 pagesExogenic Processeses 1Teacher MelNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle 1.1.1 (C-D)Document5 pagesWater Cycle 1.1.1 (C-D)Royal ComedianNo ratings yet
- Different Types of WeatheringDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of WeatheringLyka MaeNo ratings yet
- Severe Weather WebquestDocument5 pagesSevere Weather Webquestapi-2685331450% (2)
- Webquest Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesWebquest Climate Changeapi-264150929No ratings yet
- Acid Rain Virtual Lab WorksheetDocument4 pagesAcid Rain Virtual Lab Worksheetapi-26475340350% (4)
- Climate NotesDocument2 pagesClimate Notesapi-264874516No ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument1 pageWhat Is Acid Rainapi-264150929No ratings yet
- Atmosphere Basics WebsquestDocument2 pagesAtmosphere Basics Websquestapi-2685331450% (1)
- AirmassandfrontsawebquestDocument4 pagesAirmassandfrontsawebquestapi-264090085No ratings yet
- Virtual Lab-Water QualityDocument5 pagesVirtual Lab-Water Qualityapi-268533145No ratings yet
- Freshwater Pollution Guided NotesDocument2 pagesFreshwater Pollution Guided Notesapi-330462935No ratings yet
- Food Production in Europe WebquestDocument2 pagesFood Production in Europe Webquestapi-268533145No ratings yet
- What-Is-A-Watershed-Webquest StudentworksheetDocument5 pagesWhat-Is-A-Watershed-Webquest Studentworksheetapi-268533145100% (1)
- Water Cycle Webquest 2Document6 pagesWater Cycle Webquest 2api-268533145No ratings yet
- MeatirxtrilogyquestionsDocument2 pagesMeatirxtrilogyquestionsapi-268533145No ratings yet
- Solid Waste Guided NotesDocument2 pagesSolid Waste Guided Notesapi-268533145No ratings yet
- Mining in My House 1Document1 pageMining in My House 1api-268533145No ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument2 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264150929No ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument2 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-264150929No ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Web Quest StudentDocument11 pagesPlate Tectonics Web Quest Studentapi-268533145100% (1)