Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fetch Decode Execute2 PDF
Fetch Decode Execute2 PDF
Uploaded by
Sonofabch Maginer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
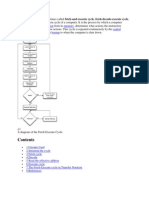
18 views2 pagesWhen a program runs, its executable binary file is copied into memory. The CPU then repeatedly fetches and executes instructions using a fetch-decode-execute cycle. During fetch, the program counter addresses memory to load an instruction into the instruction register. In decode, the instruction is analyzed to determine the operation. In execute, the specified operation such as an arithmetic, logic, or I/O function is performed. Key components involved are the CPU, memory, and bus that transfers instructions and data.
Original Description:
Original Title
Fetch-Decode-Execute2.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWhen a program runs, its executable binary file is copied into memory. The CPU then repeatedly fetches and executes instructions using a fetch-decode-execute cycle. During fetch, the program counter addresses memory to load an instruction into the instruction register. In decode, the instruction is analyzed to determine the operation. In execute, the specified operation such as an arithmetic, logic, or I/O function is performed. Key components involved are the CPU, memory, and bus that transfers instructions and data.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesFetch Decode Execute2 PDF
Fetch Decode Execute2 PDF
Uploaded by
Sonofabch MaginerWhen a program runs, its executable binary file is copied into memory. The CPU then repeatedly fetches and executes instructions using a fetch-decode-execute cycle. During fetch, the program counter addresses memory to load an instruction into the instruction register. In decode, the instruction is analyzed to determine the operation. In execute, the specified operation such as an arithmetic, logic, or I/O function is performed. Key components involved are the CPU, memory, and bus that transfers instructions and data.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
An executable binary file contains
The machine instructions to be executed
Data
When a program is run
The executable binary file is copied from the disk drive into memory
The CPU repeated fetches an instruction and executes it using the fetch-decode-
execute cycle
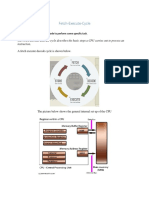
Components of the computer involved in execution
Memory: since the instructions and data are stored there
The bus: since the instructions and data must be transferred to the CPU
The CPU:
o The ALU manipulates both instructions and data
o The control logic decodes instructions and identifies what should happen
during execution
o The PC records where the next instruction is in memory
The PC is initially set to the starting address of the block of memory
o The Instruction Register (IR) holds the current instruction
o The Status Register (SR) records the results of the last instruction
The Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle
Fetch
o The PC is copied to the MAR
o A read signal is sent to memory
o The instruction is transferred from memory to the MBR
o The PC is incremented
o The MBR is copied to the IR
Several fetch steps may be required to get all the parts of an instruction
Decode
o Part or all of the instruction in the IR is extracted to determine what is to be
done
o Part of the instruction may contain
Data
A memory address to get data from
A memory address to put data
Execute
o The specified operation is performed
o Examples
Arithmetic operation
Logic operation
Read or write data from memory
Change PC to implement jumps
Send data to or from an I/O device
Terminate program (by causing an interrupt)
You might also like
- I O D S S D: Nput AND Utput Evices Econda RY Torage EvicesDocument5 pagesI O D S S D: Nput AND Utput Evices Econda RY Torage EvicesBhaskar NaiduNo ratings yet
- Fetch / Execute CycleDocument19 pagesFetch / Execute Cycleazhi100% (1)
- Chp3.2 controlUnitInstructionSetDocument4 pagesChp3.2 controlUnitInstructionSetheyfiez12No ratings yet
- Program Instruction Memory Central Processing Unit BootupDocument4 pagesProgram Instruction Memory Central Processing Unit BootupADSR100% (1)
- Title of The PresentationDocument14 pagesTitle of The PresentationBivekMazumderNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument16 pagesComputer OrganizationInnocent ChukwumaNo ratings yet
- Component of A Digital ComputerDocument15 pagesComponent of A Digital Computerreginaamondi133No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Organization (INCOMP)Document14 pagesIntroduction To Computer Organization (INCOMP)Amey KurdikarNo ratings yet
- Computer OrgnisationDocument138 pagesComputer OrgnisationmadhuNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument15 pagesCentral Processing Unithussain korirNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Top Level View of ComputerDocument6 pagesLecture Note - Top Level View of Computertesfu zewduNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document11 pagesAssignment 7ajit mhjNo ratings yet
- Ict L3Document71 pagesIct L3Asra KhalidNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Hardware The CPU ArchitectureDocument11 pages3.1 Hardware The CPU ArchitectureBatsirai NdiyengaNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Digital Circuit Arithmetic Bitwise Logical Integer Binary Numbers Central Processing UnitDocument1 pageDigital Electronics Digital Circuit Arithmetic Bitwise Logical Integer Binary Numbers Central Processing UnitPatuan TampuolonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Computer FunctionDocument34 pagesLesson 3 Computer FunctionJoseph DacanayNo ratings yet
- Basic Operational ConceptsDocument34 pagesBasic Operational ConceptsAngeL LightNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument12 pagesCentral Processing Unithussain korirNo ratings yet
- 03-Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection-Update-2022!09!21Document73 pages03-Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection-Update-2022!09!21Haikal GustiansyahNo ratings yet
- Computer Components FunctionsDocument26 pagesComputer Components Functionsmedzmedina2No ratings yet
- Instruction Cycle: Instruction Sub-Cycle Instruction Fetch and Execute CyclesDocument3 pagesInstruction Cycle: Instruction Sub-Cycle Instruction Fetch and Execute CyclesSANJAY NAYAKNo ratings yet
- Processor and Control UnitDocument71 pagesProcessor and Control Unitsarkar55ishikaNo ratings yet
- Organisasi Dan Arsitektur Komputer - 8Document18 pagesOrganisasi Dan Arsitektur Komputer - 8YuanserenadaNo ratings yet
- 9.4.4 Worksheet 10Document3 pages9.4.4 Worksheet 10bao065045No ratings yet
- Basic Structure of Computer ArchitectureDocument53 pagesBasic Structure of Computer Architecturenikhilmalagi0% (1)
- Fetch Execute Cycle PDFDocument4 pagesFetch Execute Cycle PDFAditya Ghose50% (2)
- Fetch Execute CycleDocument4 pagesFetch Execute Cycleلوبنا نسرينNo ratings yet
- Module 1 of Computer OrganizationDocument27 pagesModule 1 of Computer OrganizationNimmymolManuelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - CPU DesignDocument20 pagesLecture 5 - CPU Designnoberth nikombolweNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and Architecture: William StallingsDocument78 pagesComputer Organization and Architecture: William StallingsNITHIYA PAUL 1847244No ratings yet
- Ciclo de Búsqueda y Ejecución StallingDocument7 pagesCiclo de Búsqueda y Ejecución StallingMatias BeneitezNo ratings yet
- Ict NotesDocument4 pagesIct Noteschelsea nelsonNo ratings yet
- C4 - Central Processing UnitDocument22 pagesC4 - Central Processing UnitMuhamad Nurhafiz YusoffNo ratings yet
- What Is Instruction CycleDocument3 pagesWhat Is Instruction CycleSukhi Dhiman100% (1)
- Computer Org - L4Document36 pagesComputer Org - L4محمد العموديNo ratings yet
- CPU Structure and FunctionsDocument39 pagesCPU Structure and FunctionsNICE ONENo ratings yet
- BsjddsDocument31 pagesBsjddsJaswanth VemulaNo ratings yet
- Instruction CycleDocument32 pagesInstruction Cycleshudha.kr14187No ratings yet
- 1.4.2 The Fetch-Execute Cycle PDFDocument7 pages1.4.2 The Fetch-Execute Cycle PDFtalentNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 Edition System BusesDocument91 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 Edition System BusesassadNo ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument31 pagesComputer ScienceOkay NopeNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document9 pagesGroup 1chandani jainNo ratings yet
- What Is RegisterDocument2 pagesWhat Is RegisterHaris AkramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Third Week 2021Document45 pagesChapter 3 Third Week 2021sumeraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 The CPU and Register Org.Document11 pagesUnit 2 The CPU and Register Org.shashank2001tewariNo ratings yet
- Computer Arch. & Organization - I: The Basic Organization of ComputersDocument33 pagesComputer Arch. & Organization - I: The Basic Organization of Computerssaksham0506No ratings yet
- MAR Stand For Memory Address RegisterDocument2 pagesMAR Stand For Memory Address RegisterJenovic MapwasaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - Introduction To The Central Processing Unit (CPU)Document18 pagesLecture 13 - Introduction To The Central Processing Unit (CPU)flash driveNo ratings yet
- General Organisation of A Micro ProcessorDocument8 pagesGeneral Organisation of A Micro ProcessornelsrodrigNo ratings yet
- Component 2Document2 pagesComponent 2karmaNo ratings yet
- 18csc203j - Coa Unit 1Document25 pages18csc203j - Coa Unit 1Rishabh ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Computer ArchitectureDocument34 pagesChapter 6-Computer ArchitectureVongai MubaiwaNo ratings yet
- CSC 222: Computer Organization: & Assembly LanguageDocument22 pagesCSC 222: Computer Organization: & Assembly Languageذیشان چودھریNo ratings yet
- The ProcessorDocument19 pagesThe Processortarrant HighNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Department: Majlis Arts and Science College, PuramannurDocument24 pagesComputer Science Department: Majlis Arts and Science College, PuramannurSreejithNo ratings yet
- What Is The CPU?Document18 pagesWhat Is The CPU?Christine Mary EspirituNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - CSS PresentationDocument40 pagesGroup 1 - CSS PresentationlagurashannelleNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 EditionDocument59 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 EditionjumarNo ratings yet
- 3 RdunitcsoDocument38 pages3 RdunitcsoGourav DubeyNo ratings yet