Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arundhati Roy: Arundhati Roy (Born 24 November 1961) Is An Indian Novelist, Essayist and Activist Who
Uploaded by
sarayooOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arundhati Roy: Arundhati Roy (Born 24 November 1961) Is An Indian Novelist, Essayist and Activist Who
Uploaded by
sarayooCopyright:
Available Formats
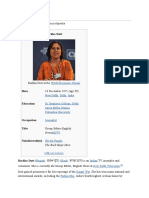
Arundhati Roy
Arundhati Roy (born 24 November 1961) is an Indian novelist, essayist and activist who
focuses on issues related to social justice and economic inequality. She won the Booker Prize in
1997 for her novel, The God of Small Things, and has also written two screenplays and several
collections of essays. Her writings on various social, environmental and political issues have
been a subject of major controversy in India.
For her work as an activist she received the Cultural Freedom Prize awarded by the Lannan
Foundation in 2002
Early life and background
Arundhati Roy was born in Shillong, Meghalaya,
[1]
India, to a Keralite Syrian Christian mother,
the women's rights activist Mary Roy, and a Bengali father, Ranjit Roy, a tea planter by
profession.
She spent her childhood in Aymanam in Kerala, and went to school at Corpus Christi, Kottayam,
followed by the Lawrence School, Lovedale, in Nilgiris, Tamil Nadu. She then studied
architecture at the School of Planning and Architecture, New Delhi, where she met her first
husband, architect Gerard da Cunha.
Roy met her second husband, filmmaker Pradip Krishen, in 1984, and played a village girl in his
award-winning movie Massey Sahib. Until made financially stable by the success of her novel
The God of Small Things, she worked various jobs, including running aerobics classes at five-
star hotels in New Delhi. Roy is a cousin of prominent media personality Prannoy Roy, the head
of the leading Indian TV media group NDTV,.
[2]
She lives in New Delhi.
Advocacy and controversy
Since The God of Small Things Roy has devoted herself mainly to nonfiction and politics,
publishing two more collections of essays, as well as working for social causes. She is a
spokesperson of the anti-globalization/alter-globalization movement and a vehement critic of
neo-imperialism and of the global policies of the United States. She also criticizes India's nuclear
weapons policies and the approach to industrialization and rapid development as currently being
practiced in India, including the Narmada Dam project and the power company Enron's activities
in India.
You might also like
- Arundhati Roy: Made By: Martin Pavlov, XIIDocument9 pagesArundhati Roy: Made By: Martin Pavlov, XIIMartin PavlovNo ratings yet
- Arundhati RoyDocument33 pagesArundhati RoyDaisy DaisyNo ratings yet
- Arundhati Ry PDFDocument13 pagesArundhati Ry PDFnarasimha rajuNo ratings yet
- Anshul Yadav 11th BDocument76 pagesAnshul Yadav 11th BanshulNo ratings yet
- Arundhati RoyDocument19 pagesArundhati Roydeepika_naikNo ratings yet
- Empoweredwomenarundhatiroy 150224070731 Conversion Gate01Document10 pagesEmpoweredwomenarundhatiroy 150224070731 Conversion Gate01Kartik SawantNo ratings yet
- Arundhati Roy.Document2 pagesArundhati Roy.Khawar ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Some Bright Spots: The God of Small ThingsDocument3 pagesSome Bright Spots: The God of Small ThingsDaniel MorrisNo ratings yet
- MD Daniyal Ansari - Prof Saroj Mahananda - MA English SEM 3 - NFP 2Document4 pagesMD Daniyal Ansari - Prof Saroj Mahananda - MA English SEM 3 - NFP 2Daniyal AnsariNo ratings yet
- The God of Small Things author Arundhati Roy biographyDocument4 pagesThe God of Small Things author Arundhati Roy biographygangsurajNo ratings yet
- Raja Ram Mohan Roy UPSC NotesDocument2 pagesRaja Ram Mohan Roy UPSC Notesmanishagrawal003No ratings yet
- Raja Ram Mohan Roy Indian Social Reformer NCERT NotesDocument2 pagesRaja Ram Mohan Roy Indian Social Reformer NCERT Notesprabal pratap singh rajputNo ratings yet
- Pratiksha Sarda WPC BiographyDocument6 pagesPratiksha Sarda WPC BiographyPratiksha SardaNo ratings yet
- 1514188768raja (1Document15 pages1514188768raja (1Yuseer AmanNo ratings yet
- Indian Novelists and Their ContributionsDocument6 pagesIndian Novelists and Their ContributionsSumeet SainiNo ratings yet
- Indian PersonalitiesDocument16 pagesIndian Personalitiessarin15juneNo ratings yet
- National: Allah Rakha Rahman Baba AmteDocument16 pagesNational: Allah Rakha Rahman Baba AmteShibin JohnNo ratings yet
- Barkha Dutt: World Economic ForumDocument4 pagesBarkha Dutt: World Economic ForumK.l. NagendraNo ratings yet
- Legendary Photographers From IndiaDocument8 pagesLegendary Photographers From IndiaPallavi MukkamalaNo ratings yet
- Book Review - Listening To GrasshoppersDocument2 pagesBook Review - Listening To GrasshoppersImran Ahmed100% (1)
- Meghnad Saha: Renowned Indian astrophysicist and mathematicianDocument11 pagesMeghnad Saha: Renowned Indian astrophysicist and mathematiciansiuuuuuuuNo ratings yet
- Sarojini Naidu: Poet and Freedom FighterDocument12 pagesSarojini Naidu: Poet and Freedom FighterYuvika GuptaNo ratings yet
- RajneeshDocument42 pagesRajneeshStephan WozniakNo ratings yet
- Khushwant SinghDocument11 pagesKhushwant SinghGautam KashyapNo ratings yet
- Guru Ghasidas Viswavidyalaya A Project On "M.N ROY"Document16 pagesGuru Ghasidas Viswavidyalaya A Project On "M.N ROY"priyankaNo ratings yet
- Postmodern Gandhi and Other Essays: Gandhi in the World and at HomeFrom EverandPostmodern Gandhi and Other Essays: Gandhi in the World and at HomeNo ratings yet
- Rajneesh - WikipediaDocument28 pagesRajneesh - WikipediaNilesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Swami Vivekananda: Shāmi BibekānondoDocument7 pagesSwami Vivekananda: Shāmi BibekānondoshivaNo ratings yet
- Review by Jon P. Dorschner: The Doctor and The Saint Is An Analytical Essay of The Conflict Between Gandhi and Dr. B. RDocument3 pagesReview by Jon P. Dorschner: The Doctor and The Saint Is An Analytical Essay of The Conflict Between Gandhi and Dr. B. Rpandu mandalaNo ratings yet
- Khushwant Singh Biography: Quick FactsDocument5 pagesKhushwant Singh Biography: Quick FactsGobinda debnathNo ratings yet
- IJCRT1135264Document4 pagesIJCRT1135264devanshpannu27No ratings yet
- Amitav Ghosh (Born July 11, 1956: The God of Small ThingsDocument4 pagesAmitav Ghosh (Born July 11, 1956: The God of Small ThingsDeepak MakkadNo ratings yet
- Mahabharata in Polyester: The Making of the World's Richest Brothers and Their FeudFrom EverandMahabharata in Polyester: The Making of the World's Richest Brothers and Their FeudRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- NachniDocument15 pagesNachniBlot JournalNo ratings yet
- Contribution of Eminent JournalistsDocument4 pagesContribution of Eminent JournalistsAnjali GuptaNo ratings yet
- Kiran Bedi BiographyDocument1 pageKiran Bedi BiographyWhatsapp99No ratings yet
- Relevance of Dayanand in ModernDocument2 pagesRelevance of Dayanand in ModernVikas PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Swami Dayanand SaraswatiDocument7 pagesSwami Dayanand SaraswatiMevika Merchant100% (1)
- Gandhi & The LeftDocument14 pagesGandhi & The LeftMegha khannaNo ratings yet
- Her Contributions: Vinita Jhamtani Pa-52 (1032192204)Document12 pagesHer Contributions: Vinita Jhamtani Pa-52 (1032192204)vinita jhamtaniNo ratings yet
- C.R. Rajagopalachari - Indian Politician, Independence Activist & StatesmanDocument1 pageC.R. Rajagopalachari - Indian Politician, Independence Activist & Statesmankmsrini@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Outstanding People From India.: Members: Verónica C Danae J Rocío V Gabriel T Ayline R. Grade: 2ºFDocument13 pagesOutstanding People From India.: Members: Verónica C Danae J Rocío V Gabriel T Ayline R. Grade: 2ºFRocio Vásquez DíazNo ratings yet
- Sarojini Naidu121Document3 pagesSarojini Naidu121anshusainiNo ratings yet
- Political Landscapes and Social Crossroads: A Study of ‘The Ministry of Utmost Happiness’ by Arundhati RoyDocument15 pagesPolitical Landscapes and Social Crossroads: A Study of ‘The Ministry of Utmost Happiness’ by Arundhati RoyFaiz UllahNo ratings yet
- Remembering prominent Hindi poet and author Dharamvir BharatiDocument4 pagesRemembering prominent Hindi poet and author Dharamvir BharatipremNo ratings yet
- Profile of slain Indian journalist Gauri LankeshDocument10 pagesProfile of slain Indian journalist Gauri LankeshPrajwal NiceNo ratings yet
- Class 16 - Bengal Renaissance and Raja Rammuhan Roy - Nov 29 2022Document33 pagesClass 16 - Bengal Renaissance and Raja Rammuhan Roy - Nov 29 2022Afrin AnwarNo ratings yet
- Born Residence Citizenship Education Alma Mater Notable Work Partner(s) WebsiteDocument19 pagesBorn Residence Citizenship Education Alma Mater Notable Work Partner(s) WebsiteDr.H.M.Maralusiddaiah PatelNo ratings yet
- Raja Ram Mohan Roy's Religious and Social ReformsDocument6 pagesRaja Ram Mohan Roy's Religious and Social Reformspinku024No ratings yet
- Chanakya National Law University: Name-Sankalp Yash VardhanDocument21 pagesChanakya National Law University: Name-Sankalp Yash VardhanAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Encyclopaedia of Indian War of IndependenceDocument155 pagesEncyclopaedia of Indian War of IndependenceNaren Mukherjee100% (1)
- Chapter-III: Major Political Ideas of Acharya Narendra Deva: A Brief AppraisalDocument86 pagesChapter-III: Major Political Ideas of Acharya Narendra Deva: A Brief AppraisalBiddo Brahmin100% (1)
- Ram Mohan Roy Mahatma Jyotirao Phule Swami Vivekananda Swami Dayanand Saraswati InformationDocument1 pageRam Mohan Roy Mahatma Jyotirao Phule Swami Vivekananda Swami Dayanand Saraswati InformationJasvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Kiran Bedi Is The First Woman Officer To Join Indian Police OfficerDocument3 pagesKiran Bedi Is The First Woman Officer To Join Indian Police OfficerChinmaya NandanNo ratings yet
- Sarojini Naidu Biography: India's First Female Congress PresidentDocument7 pagesSarojini Naidu Biography: India's First Female Congress PresidentSocial SinghNo ratings yet
- Sarojini Naidu - Poet, Activist, First Woman Governor of UPDocument2 pagesSarojini Naidu - Poet, Activist, First Woman Governor of UPAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Competing Nationalisms in South Asia Essays for Asghar Ali Engineer CompressDocument309 pagesCompeting Nationalisms in South Asia Essays for Asghar Ali Engineer CompressMikael BilobovNo ratings yet
- Social ReformersDocument7 pagesSocial ReformersAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Political Science ProjectDocument9 pagesPolitical Science ProjectNim NagpurNo ratings yet
- Jayaprakash Narayan in Underground MovementDocument2 pagesJayaprakash Narayan in Underground MovementNitesh Kotian100% (4)
- 83-2014 Tide Watcher-Nca Ezhava-Hydrographic Survey Wing-Kkd KeyDocument1 page83-2014 Tide Watcher-Nca Ezhava-Hydrographic Survey Wing-Kkd KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- Final Answer Key 94/2014 Junior Assistant ExamDocument1 pageFinal Answer Key 94/2014 Junior Assistant ExamsarayooNo ratings yet
- 97-2014 Junior Instructor - Mechanic Industrial Electronics - Industrial Training KeyDocument1 page97-2014 Junior Instructor - Mechanic Industrial Electronics - Industrial Training KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- 4 15Document1 page4 15sarayooNo ratings yet
- 91-2014 Lift Operator Various and Assistant Time Keeper KeyDocument1 page91-2014 Lift Operator Various and Assistant Time Keeper KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- 90-2014 Vocational Teacher Reception Book Keeping and Communication Kvhse KeyDocument1 page90-2014 Vocational Teacher Reception Book Keeping and Communication Kvhse KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- 65-2014 Recording Assistant - Kerala State Film Development Corporation LTD KeyDocument1 page65-2014 Recording Assistant - Kerala State Film Development Corporation LTD KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- Common Cause v. Union of IndiaDocument13 pagesCommon Cause v. Union of IndiaBar & BenchNo ratings yet
- 92-2014 Public Relation Officer - Co-Operative Sector in Kerala and Kerala State Co-Opertive Bank KeyDocument1 page92-2014 Public Relation Officer - Co-Operative Sector in Kerala and Kerala State Co-Opertive Bank KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- 81-2014 Vocational Instructor - Catering and Restaurant Management - Kvhse KeyDocument1 page81-2014 Vocational Instructor - Catering and Restaurant Management - Kvhse KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- 59-2014 Lecturer in Philosophy - Kerala Collegiate Education KeyDocument1 page59-2014 Lecturer in Philosophy - Kerala Collegiate Education KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- 82-2014 Hospitality Assistant Nca Pta Ekm KeyDocument1 page82-2014 Hospitality Assistant Nca Pta Ekm KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- 54-2014 Lecturer in Islamic History KeyDocument1 page54-2014 Lecturer in Islamic History KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- Final Answer Key 61/2014 Laboratory Technician Gr. II ExamDocument1 pageFinal Answer Key 61/2014 Laboratory Technician Gr. II ExamsarayooNo ratings yet
- 55-2014 Lecturer in Economics KeyDocument1 page55-2014 Lecturer in Economics KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- 45-2014 Architectural Head Draftsman - Kerala State Housing Board KeyDocument1 page45-2014 Architectural Head Draftsman - Kerala State Housing Board KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- PHD in Law Course CurriculumDocument4 pagesPHD in Law Course CurriculumsarayooNo ratings yet
- 56-2014 Lecturer in Zoology KeyDocument1 page56-2014 Lecturer in Zoology KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- Right of DisabledDocument28 pagesRight of DisabledsarayooNo ratings yet
- 50-2014 Lecturer in English KeyDocument2 pages50-2014 Lecturer in English KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- 48-2014 Lecturer in Hindi KeyDocument1 page48-2014 Lecturer in Hindi KeysarayooNo ratings yet
- What Is BiodiversityDocument1 pageWhat Is BiodiversitysarayooNo ratings yet
- Judges Transfer CaseDocument3 pagesJudges Transfer CasesarayooNo ratings yet
- Bio DiversityDocument6 pagesBio DiversitysarayooNo ratings yet
- The Rural Development in India Is One of The Most Important Factors For The Growth of The Indian EconomyDocument2 pagesThe Rural Development in India Is One of The Most Important Factors For The Growth of The Indian EconomysarayooNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For StudentsDocument16 pagesSyllabus For StudentssarayooNo ratings yet
- 50-2014 Lecturer in English QDocument12 pages50-2014 Lecturer in English QsarayooNo ratings yet
- TransportDocument7 pagesTransportsarayooNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency Is One of The Most CommonDocument4 pagesVitamin B12 Deficiency Is One of The Most CommonsarayooNo ratings yet
- The Ozone LayerDocument3 pagesThe Ozone LayersarayooNo ratings yet