Professional Documents
Culture Documents
02 Venturi Meter
02 Venturi Meter
Uploaded by
shinee_jayasila2080Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
02 Venturi Meter
02 Venturi Meter
Uploaded by
shinee_jayasila2080Copyright:
Available Formats
VENTURIMETER
INTRODUCTION:
The Ventura meter used in this experiment consists of successive converging, uniform and
diverging sections equipped with pressure taps at selected locations.
A Ventura meter is a device for determining the flow-rate of a fluid down a pipe. One measures
the pressure difference between the venture inlet and neck, and from this the flow-rate can be
determined.
OBJECTIVE:
To stud the variation of !
od
and discharge with respect the head b plotting the following graphs
Qa Vs h
Qa Vs h
Taking h and h on x-axis and Qa on -axis
THEORY:
Venturimeter is a device used for measuring the rate of flow of a fluid through a pipe. The basic
principle on which a venturimeter works is that b reducing the cross sectional area of the flow
of passage, a pressure difference is created and the measurement of the pressure difference
enables the determination of the discharge through a pipe.
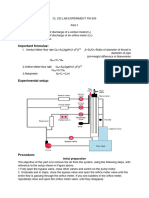
The Venturimeter consists of three main parts as shown in fig ".
1. !onvergent cone
2. A !lindrical throat
3. #ivergent cone
The inlet section of the venturimeter is of the same diameter as that of the pipe, which is
followed b a convergent cone. The convergent cone is a short pipe, which tapers from the
original si$e of the pipe to that of the throat of the venturimeter. The throat of the venturimeter is
a short parallel-sided tube having uniform cross sectional area smaller than that of the pipe. The
divergent cone of the venturimeter is a graduall diverging pipe with its cross sectional area
increasing from that of the throat to the original si$e of the pipe. At the inlet section and at the
throat, %i.e., section " and &' pressure taps are provided to measure the pressure difference. (
appling the (ernoulli equation to the inlet section and at the throat, %i.e., section " and &' an
expression for the discharge is obtained.
)ater is allowed to flow through the meter at different rates ranging from $ero to the maximum
and the corresponding pressure differences shown in the manometer are noted. The actual
discharge A is determined using the measuring tank and the stop watch.
Actual discharge %A' *
Where
a Area of measuring tank in cm
2
h Height differences in pyrometer in cm
t Time to collect water for a height difference of h cm measured in !econds
Theoretical discharge is gi"en #y
)here
A
1
The area at inlet side in cm
2
A
2
The area at throat in cm
2
H
w
Head difference in the manometer con"erted to cm of water
g Acceleration due to gra"ity $%.&1 m'sec()
*oefficient of discharge is gi"en #y
OBSERVATIONS AND CALCULATIONS:
+lan area of the tank A ,
Sl. no
Time for
10cm rise
of !"er
le#el $s%
&c"'!l
(isc)!r*e &
cm
+
,s
Differen"i!l
)e!( in cm. of
merc'r-
Differen"i!l
)e!( in cm. of
!"er.
T)eore"ic!l
(isc)!r*e
.
")/
cm
+
,s.
Coefficien" of
(isc)!r*e C
o(
)
1
)
0
)
1
1 )
0
H
'*
"
1
"
0
"
m
1
0
+
2
3
M&NU&4:
+tart the experiment b pressing the start button with keeping default values of inlet die of
venturimeter and throat die and rise of water level , and discharge ,then pass the experiment
after few ccles and note the observations.
O5ser#!"ions1:
"' Allow the water to flow from the inlet or gate valve through the pipe to the convergent cone,
then the level of the prometer rises up to some height.
&' Then the measure the pressure head in the prometer.
O5ser#!"ion0:
"' Then allow the water to flow from the convergent to throat and from the throat to the
divergent cone.
&' ,en level in the prometer rises up to some height. -ising depends upon the rate of flow of
water.
O5ser#!"ion+:
"' Then allow the water to flow in to the collecting through the outlet and after filling some
amount of water in the collecting tank ,the water level in the collecting is increased and the
measure the time taken to collect the water for ever ".cms rise.
&' -epeat the experiment b changing the discharge, inlet die and throat and rise of water level.
RESU4T: Coefficien" of (isc)!r*e of #en"'rime"re Co( 6
M&INTEN&NCE:
1. After completing the e-periment close the inlet "al"e and open all the gate
"al"es and needle "al"es to "ent any air trapped inside and then close them.
2. .rain the water from measuring tank after completing the e-periment.
.UI7:
1) Venturimeter is used to measure average velocit
a) true
#) false
2) Angle of contraction is more than angle of diversion
a) true
#) false
3) The inlet length of the Venturimeter/s greater than outlet pipe
a) true
#) false
/) Actual discharge is obtained b %A'* a x h0t
a) true
#) 1alse
0) !oefficient of discharge is calculated b *d *QaQt
a' True
b' 1alse
RE8ERENCE:
1) 1234# 56!,A74!+ - -8 (A7+A2
2) 69:6-4567T+ O7 1234# 56!,A74!+ - +A-A(;4T +47<,
3) )484:6#4A
/) The constructor- http=00theconstructor.org0
You might also like
- Clinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenDocument8 pagesClinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenPreeti Joan Buxani100% (1)
- VenturimeterDocument45 pagesVenturimetersulakshna kiranNo ratings yet
- Notch and WeirsDocument33 pagesNotch and WeirsAbdur RashidNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis in Adults: Overview of Complications, General Management, and Prognosis - UpToDateDocument21 pagesCirrhosis in Adults: Overview of Complications, General Management, and Prognosis - UpToDateDan ChicinasNo ratings yet
- FLUID MECHANICS Lab ManualDocument65 pagesFLUID MECHANICS Lab ManualPaulNo ratings yet
- 1878 Cabul - The Ameer His Country and His People by Robinson S PDFDocument100 pages1878 Cabul - The Ameer His Country and His People by Robinson S PDFBilal AfridiNo ratings yet
- Experiment To Study Flow Through A VenturimeterDocument26 pagesExperiment To Study Flow Through A VenturimeterRoshan Ram57% (7)
- Orifice MeterDocument15 pagesOrifice Metermurad67% (3)
- Hydraulic CoefficientsDocument6 pagesHydraulic CoefficientsGerrold RamosNo ratings yet
- STD 9 TH Maths English Bridge CourseDocument104 pagesSTD 9 TH Maths English Bridge CourseshaguptaNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Venturi MeterDocument9 pagesCalibration of Venturi Meterseminarproject40% (5)
- Almuete v. PeopleDocument2 pagesAlmuete v. PeopleCharmila SiplonNo ratings yet
- Calibration of VenturimeterDocument5 pagesCalibration of VenturimeterRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Calibration of VenturimeterDocument5 pagesCalibration of VenturimeteramarparimiNo ratings yet
- Venturi MeterDocument8 pagesVenturi MeterSwati SachanNo ratings yet
- VENTURIMETERDocument4 pagesVENTURIMETERKailash RajuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Lab ReportDocument17 pagesChemical Lab Reportoprudra2000No ratings yet
- 3 OrificesDocument7 pages3 OrificesPraful N KNo ratings yet
- Venturimeter, Orificemeter & Rotameter Calibration Set-Up: Experiment No. 4Document9 pagesVenturimeter, Orificemeter & Rotameter Calibration Set-Up: Experiment No. 4Somya MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Venturimeter Exp. 250412Document4 pagesVenturimeter Exp. 250412abhishekpatil21No ratings yet
- Experiment No 3 HM LabDocument5 pagesExperiment No 3 HM Labprajwalwanjari5524No ratings yet
- 5 VenturiDocument3 pages5 VenturiMickey S LNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice Meterf20221047No ratings yet
- Im316 Flow MeasurementDocument67 pagesIm316 Flow MeasurementSelvarajNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument23 pagesLab ReportAmy Farhana100% (1)
- Fluid Lab ManualDocument27 pagesFluid Lab ManualvenkiteshksNo ratings yet
- ReviewDocument31 pagesReviewkarlobrondialNo ratings yet
- LAB MANUAL. EXPERIMENT 2. Calibration of Venturi MeterDocument3 pagesLAB MANUAL. EXPERIMENT 2. Calibration of Venturi Meterjames PrincipeNo ratings yet
- MiniTilting Flume - CollectingtankDocument11 pagesMiniTilting Flume - CollectingtankSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Che 222 Tutorial 2Document15 pagesChe 222 Tutorial 2naverfallNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics ApplicationDocument88 pagesFluid Dynamics Applicationkyledarbymanalo1437No ratings yet
- Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument6 pagesCalibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterMUTHUKURU VENKATA GOWTHAM REDDYNo ratings yet
- No. Page No.: Name of The ExperimentDocument27 pagesNo. Page No.: Name of The Experimentnitte5768No ratings yet
- Closed Circuit Venturimeter AimDocument3 pagesClosed Circuit Venturimeter Aimsaggam indureddyNo ratings yet
- Calbr of v-O-CS New-SS TankDocument3 pagesCalbr of v-O-CS New-SS TankSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- 1 Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument5 pages1 Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterRaghavanNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Flow Tthrough Venturi MeterDocument4 pagesExperiment: Flow Tthrough Venturi MeterMuhammadZAmjadNo ratings yet
- Ce6412 04Document114 pagesCe6412 04karthickaryanNo ratings yet
- Orifice MeterDocument6 pagesOrifice MeterShiva YadavNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5.1-5.5 Coefficients To TubesDocument18 pagesMODULE 5.1-5.5 Coefficients To TubesFrancis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter .6 Fluid MearsurementDocument31 pagesChapter .6 Fluid MearsurementMohammed Saif ALshareefNo ratings yet
- Inbound 8780671914746455564Document4 pagesInbound 8780671914746455564yinminayeyma1No ratings yet
- JJ 308 Experiment 1Document4 pagesJJ 308 Experiment 1Edmond Emmanuel LeeNo ratings yet
- VenturiMeter PDFDocument5 pagesVenturiMeter PDFLalalalalalalaalalalNo ratings yet
- Estimation The Volume Flow Rate Using Venturi-Meter Apparatus (Fluid Exp 6)Document10 pagesEstimation The Volume Flow Rate Using Venturi-Meter Apparatus (Fluid Exp 6)hayder alaliNo ratings yet
- Notches - V and Rect.Document4 pagesNotches - V and Rect.Venkat KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Fallsem2021-22 Che1005 Ela Vl2021220101507 Reference Material I 11-Aug-2021 1.flow Through VenturimeterDocument4 pagesFallsem2021-22 Che1005 Ela Vl2021220101507 Reference Material I 11-Aug-2021 1.flow Through Venturimeterkeerthana satheeshNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 01: Demonstration of Various Parts of Hydraulic Bench Hydraulic BenchDocument30 pagesExperiment No. 01: Demonstration of Various Parts of Hydraulic Bench Hydraulic BenchZain wazirNo ratings yet
- Pipe FrictionDocument4 pagesPipe FrictionShubham ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Fluids Lab Experiment:07 Name: Estimation The Volume Flow Rate Using Venturi-Meter ApparatusDocument5 pagesFluids Lab Experiment:07 Name: Estimation The Volume Flow Rate Using Venturi-Meter ApparatusDarivan DuhokiNo ratings yet
- Venturi and OrificemeterDocument10 pagesVenturi and OrificemeterVikrant KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Flow MeasurementDocument3 pagesExperiment 2: Flow MeasurementVicky RajasekharanNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Coefficient of Discharge of Given Orifice MeterDocument62 pagesDetermination of The Coefficient of Discharge of Given Orifice MeterPandiya RajanNo ratings yet
- User Manual Closed Circuit Venturimeter Test Rig & Orifece Meter Test RigDocument7 pagesUser Manual Closed Circuit Venturimeter Test Rig & Orifece Meter Test Rigrohit kumarNo ratings yet
- FM Lab ManualDocument9 pagesFM Lab ManualAbhimanyu Singh BhatiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualDocument25 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab Manualeklavya kumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document4 pagesExperiment 1prajwalwanjari5524No ratings yet
- Experiment No 7Document7 pagesExperiment No 7Faizan Ahmed67% (3)
- EXERCISEDocument6 pagesEXERCISEJerico Enriquez CacaoNo ratings yet
- CL 232 Lab Experiment FM-203Document3 pagesCL 232 Lab Experiment FM-203oprudra2000No ratings yet
- Hydraulics Lab ManualDocument21 pagesHydraulics Lab Manualসন্দীপ চন্দ্রNo ratings yet
- A Treatise on Meteorological Instruments: Explanatory of Their Scientific Principles, Method of Construction, and Practical UtilityFrom EverandA Treatise on Meteorological Instruments: Explanatory of Their Scientific Principles, Method of Construction, and Practical UtilityNo ratings yet
- Evid 4Document40 pagesEvid 4Jennilyn TugelidaNo ratings yet
- Itec 7430 Digital Tools Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesItec 7430 Digital Tools Lesson Planapi-664979295No ratings yet
- Swami VivekanandDocument2 pagesSwami VivekanandAnnabethNo ratings yet
- Scott Pack Restitution OrderDocument11 pagesScott Pack Restitution OrderMichael_Roberts2019No ratings yet
- Psychotherapy For Indonesians: Dahlia and MarthoenisDocument11 pagesPsychotherapy For Indonesians: Dahlia and MarthoenisAsri PutriNo ratings yet
- Milestone 4 Most Critical Module (MCM)Document1 pageMilestone 4 Most Critical Module (MCM)elvagojpNo ratings yet
- Crossing Over 1Document5 pagesCrossing Over 1Malik HamzaNo ratings yet
- C406-N 570-5060 F ManualDocument110 pagesC406-N 570-5060 F Manualanshit10% (1)
- Practice Test TOEFL CMEDIADocument24 pagesPractice Test TOEFL CMEDIAFebryanti SilabanNo ratings yet
- Heidegger and Jung On Wholeness As The T PDFDocument3 pagesHeidegger and Jung On Wholeness As The T PDFVolaNo ratings yet
- Integra SPPT Univerge sv8500 Configuration PDFDocument98 pagesIntegra SPPT Univerge sv8500 Configuration PDFWilliam BlackNo ratings yet
- DSP CEN352 ch4 DFTDocument59 pagesDSP CEN352 ch4 DFTTewodros100% (1)
- Mental HealthDocument7 pagesMental HealthCarla Moreno RuizNo ratings yet
- Paper 3: Question 1 1. Measuring and Using Numbers: Biology 3 - SPM Examination TechniquesDocument4 pagesPaper 3: Question 1 1. Measuring and Using Numbers: Biology 3 - SPM Examination TechniquesAisyahumaira_hidayah100% (1)
- BoholanerssDocument37 pagesBoholanerssAndres Rafael TomaganNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2: Ishikawa/Fish Bone/Cause & Effect DigaramDocument6 pagesAssignment No. 2: Ishikawa/Fish Bone/Cause & Effect DigaramPradeepLokhandeNo ratings yet
- 1.4.3 Assignment 1 Result of Finding Flow and Stock of Your Means ActivityDocument2 pages1.4.3 Assignment 1 Result of Finding Flow and Stock of Your Means ActivityHilario PongaronNo ratings yet
- Reverse OsmosisDocument2 pagesReverse Osmosistcd_usaNo ratings yet
- kirby-JA 1Document3 pageskirby-JA 1gio sususcoNo ratings yet
- Religion 9Document4 pagesReligion 9kimberlyNo ratings yet
- Mathavaraj 2015Document9 pagesMathavaraj 2015Mysonic NationNo ratings yet
- Material Apoyo 1 Ingles Dot WorksDocument10 pagesMaterial Apoyo 1 Ingles Dot WorksElvira Figueroa RomeroNo ratings yet
- Advance Structral Design Labortary Lab ManualDocument78 pagesAdvance Structral Design Labortary Lab ManualecostarNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - Quiz 2Document4 pagesStrategic Management - Quiz 2nm zuhdiNo ratings yet
- Abby ResumeDocument1 pageAbby Resumeapi-453887653No ratings yet