Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KANBAN
Uploaded by
shantanujana1988Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KANBAN
Uploaded by
shantanujana1988Copyright:
Available Formats
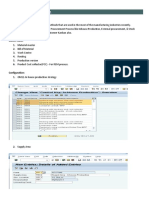
Describe the overall process of KANBAN step by step.
Currently, SAP KANBAN functionality is used only for procuring raw materials
from outside vendors and transferring stock between plants.
Interplant transfers (STO's) use internally generated schedule lines for
replenishment. Vendor kanban uses Summarized JIT Calls to communicate JIT
requirements to suppliers.
Interplant Kanban is transparent to supplying plant. No additional work is required
from the supplying plant.
Advantages:
1. Keeps raw material inventory in check
2. Prevents overshipping
3. Incorrect inventory balances, BOMs, etc. do not affect shipping
4. Supplier schedules stay in sync with actual production
Disadvantages:
1. Requires more discipline from the supplier and the shop floor. Example:
controls in processing of scrap; maintenance and tracking of
Kanbancards;adherence to ship windows.
2. More master data to maintain.
3. May hide procedural or data problems.
T-codes for Kanbans
Control cycle is a pre-requisite for KANBAN. You can create it with t code PK01
The major steps in KANBAN are:
1. Maintain supply area, PK05
2. Create control cycle, PK01
3. Kanban correction, PK31
4. Quantity signal input, PK22
5. Kanban board, PK13N
You might also like
- KANBAN: Streamlining Workflow for Effortless Efficiency (2023 Guide for Beginners)From EverandKANBAN: Streamlining Workflow for Effortless Efficiency (2023 Guide for Beginners)No ratings yet
- Kanban InstructionsDocument17 pagesKanban InstructionsDũng TNNo ratings yet
- The Kanban SystemDocument5 pagesThe Kanban SystemAnil SinghNo ratings yet
- Repetitive manufacturing with KanbanDocument3 pagesRepetitive manufacturing with KanbanFarooq JamalNo ratings yet
- Apparel Quality Lean Tools VSMDocument34 pagesApparel Quality Lean Tools VSMSaloni YadavNo ratings yet
- CAPP Systems ExplainedDocument23 pagesCAPP Systems ExplainedAnvit TiwariNo ratings yet
- KANBAN Process Steps - Inhouse ProductionDocument20 pagesKANBAN Process Steps - Inhouse ProductionSagar GoliwarNo ratings yet
- Just-In-Time and Kanban: Push or Pull?Document43 pagesJust-In-Time and Kanban: Push or Pull?cristianpetriceanNo ratings yet
- Kanban: A Lean Manufacturing Scheduling SystemDocument25 pagesKanban: A Lean Manufacturing Scheduling SystemJabir AghadiNo ratings yet
- Kanban System IntroductionDocument23 pagesKanban System Introductionzohairimtiaz86% (7)
- Kanban System Proposed for Stirling Engine Manufacturing CellDocument21 pagesKanban System Proposed for Stirling Engine Manufacturing CellBayu SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Cif Post ProcessingDocument10 pagesCif Post ProcessingdiptirakaNo ratings yet
- Sap PPDocument19 pagesSap PPJegathu Singh100% (2)
- Kanban SystemDocument23 pagesKanban SystemSachin MaheshwarNo ratings yet
- Kanban AssignmentDocument12 pagesKanban AssignmentআশরাফুলইসলামNo ratings yet
- Kanban System ExplainedDocument23 pagesKanban System ExplainedSlamet Dwi HaryantoNo ratings yet
- Kanban System ExplainedDocument23 pagesKanban System ExplainedSlamet Dwi HaryantoNo ratings yet
- Jit-Just in TimeDocument90 pagesJit-Just in Timearvind ronNo ratings yet
- Kanban: Abdullah Aftab M Ahmed IslamDocument7 pagesKanban: Abdullah Aftab M Ahmed IslamEngr Abdullah Aftab HaansNo ratings yet
- KANBAN PROCESS IN SAP for TOYOTADocument20 pagesKANBAN PROCESS IN SAP for TOYOTAShweta SinhaNo ratings yet
- Overview On Kanban Methodology and Its ImplementationDocument4 pagesOverview On Kanban Methodology and Its Implementationlaukik_rautNo ratings yet
- SCM - GATP System Monitoring Support Processes DocumentDocument16 pagesSCM - GATP System Monitoring Support Processes DocumentSnehal PatilNo ratings yet
- KANBANDocument4 pagesKANBANMarija IlievskaNo ratings yet
- Kanban Scheduling SystemsDocument8 pagesKanban Scheduling SystemsharsurajNo ratings yet
- E-Kanban and Its Practical Use: Ing. Olga MAŘÍKOVÁDocument10 pagesE-Kanban and Its Practical Use: Ing. Olga MAŘÍKOVÁAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- MRP PDFDocument45 pagesMRP PDFSamNo ratings yet
- BAAN Audit ProgramDocument19 pagesBAAN Audit ProgramcotwancoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Just-in-Time (Lean) Purchasing: Group 6: Holanda, Olleras and SabantoDocument10 pagesChapter 6: Just-in-Time (Lean) Purchasing: Group 6: Holanda, Olleras and SabantoMarie Antoinette HolandaNo ratings yet
- Overview On Kanban Methodology and Its Implementation: July 2015Document5 pagesOverview On Kanban Methodology and Its Implementation: July 2015prajwal upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Lean Facility ManagementDocument5 pagesLean Facility ManagementfhfhfhNo ratings yet
- Line Rejection Guide for SAPDocument5 pagesLine Rejection Guide for SAPDebasish BeheraNo ratings yet
- 01113-Lea NDocument26 pages01113-Lea NSasiKumar PetchiappanNo ratings yet
- Overview On Kan Ban Sdsdmethodology and Its ImplementationDocument5 pagesOverview On Kan Ban Sdsdmethodology and Its ImplementationyirgaNo ratings yet
- ManufacturingDocument26 pagesManufacturingSasiKumar PetchiappanNo ratings yet
- KANBANDocument3 pagesKANBANBrenda GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Lean ManufacturingDocument18 pagesPresentation On Lean ManufacturingZErin Khan LoraNo ratings yet
- Top of Page: Load LevelingDocument4 pagesTop of Page: Load LevelingKraken TitanNo ratings yet
- Batch Activation - Real-Time Challenges and SolutionDocument11 pagesBatch Activation - Real-Time Challenges and Solutionsumpler100% (1)
- SAP For SCM OTIF Improvement ProjectDocument5 pagesSAP For SCM OTIF Improvement ProjectMANOJNo ratings yet
- JIT FinalDocument10 pagesJIT FinalMarie Antoinette HolandaNo ratings yet
- Just in Time Manufacturing: Introduction, Elements of JIT, Pull Versus Push Method, Kanban SystemDocument39 pagesJust in Time Manufacturing: Introduction, Elements of JIT, Pull Versus Push Method, Kanban SystemAjeshSomanPulladNo ratings yet
- Toyota Production System & Dual Kanban System: Irfan Kazi & Naresh SDocument25 pagesToyota Production System & Dual Kanban System: Irfan Kazi & Naresh SLabiz Saroni ZidaNo ratings yet
- Kanban, MRP, DRP, Warehouse, ASRSDocument10 pagesKanban, MRP, DRP, Warehouse, ASRSMilanNo ratings yet
- Kanban ProcessDocument45 pagesKanban ProcessAvinash DondapatyNo ratings yet
- LSCM - Case StudyDocument6 pagesLSCM - Case StudyMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Development of Kanban System at Local Manufacturing Company in Malaysia - Case StudyDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Kanban System at Local Manufacturing Company in Malaysia - Case StudyAarthy ChandranNo ratings yet
- A Research Paper 1 For Incon Bymanish Gupta - KanbanDocument9 pagesA Research Paper 1 For Incon Bymanish Gupta - KanbanMANISH GUPTANo ratings yet
- Shop Floor Control System GuideDocument6 pagesShop Floor Control System Guidearavind6No ratings yet
- Unit 8 Operational Efficiency and Business Process PerformanceDocument24 pagesUnit 8 Operational Efficiency and Business Process Performanceestihdaf استهدافNo ratings yet
- SNP Interview PreparationDocument15 pagesSNP Interview PreparationJagannadh BirakayalaNo ratings yet
- Increasing Output Through Lean ToolsDocument6 pagesIncreasing Output Through Lean ToolsRabiba ZiaNo ratings yet
- Lean Manufacturing DocumentDocument6 pagesLean Manufacturing DocumentSaumya SaumyaNo ratings yet
- KANBANDocument2 pagesKANBANmimoNo ratings yet
- Kanban VS MRPDocument16 pagesKanban VS MRPAffizul Azuwar100% (3)
- Print KanbanDocument14 pagesPrint KanbanMaruti ShingadeNo ratings yet
- KANBAN PROCESSES PROCEDURESDocument6 pagesKANBAN PROCESSES PROCEDURESmintu12353No ratings yet
- Creating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowFrom EverandCreating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Practical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]From EverandPractical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Prod Order VarrianceDocument25 pagesProd Order Varrianceshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- Edited - Make-To-Order Production - Finished Goods Sales and Final Assembly (BJE) - Process DiagramsDocument2 pagesEdited - Make-To-Order Production - Finished Goods Sales and Final Assembly (BJE) - Process Diagramsshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- Valuated and Non-Valuated Sale Order Scenarios - Business Process FlowDocument3 pagesValuated and Non-Valuated Sale Order Scenarios - Business Process FlowvrkattulaNo ratings yet
- QM Quality Management Overview FunctionsDocument16 pagesQM Quality Management Overview Functionsrvk386No ratings yet
- Work Center LearningDocument22 pagesWork Center Learningshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- SAP CostingDocument35 pagesSAP Costingshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- PP ConfigDocument38 pagesPP Configshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- CO-PC ConfigurationDocument57 pagesCO-PC Configurationnsricardo100% (1)
- Beginner's Guide For PI SheetsDocument12 pagesBeginner's Guide For PI Sheetsshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- PS HandBook For NPI Group Planner 1Document41 pagesPS HandBook For NPI Group Planner 1shantanujana1988No ratings yet
- SAP PI for Beginners: A Guide to SAP Process IntegrationDocument15 pagesSAP PI for Beginners: A Guide to SAP Process Integrationshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- PS StepsDocument1 pagePS Stepsshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- 13 DWDocument49 pages13 DWshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- PS MM CPR User ManualDocument12 pagesPS MM CPR User Manualshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- GR WRT PODocument3 pagesGR WRT POshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- Indigenous Proc - SAP User ManualDocument48 pagesIndigenous Proc - SAP User Manualshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- PM Tables and FieldsDocument17 pagesPM Tables and Fieldsshantanujana1988No ratings yet
- PS Config Document 10.12.2007Document51 pagesPS Config Document 10.12.2007shantanujana1988No ratings yet
- Activating Source Inspection For Externally Procured PartsDocument16 pagesActivating Source Inspection For Externally Procured PartsAnonymous MeeBXp4fINo ratings yet
- Quiz On CVP AnalysisDocument9 pagesQuiz On CVP AnalysisRodolfo ManalacNo ratings yet
- D B B D: General NotesDocument1 pageD B B D: General NotessamiabdulwahabNo ratings yet
- Registration Form.Document10 pagesRegistration Form.Omkar YadavNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time SemesterDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time SemesterMariel San PedroNo ratings yet
- Knockoff WorldDocument3 pagesKnockoff WorldPrabhakar RaiNo ratings yet
- Reliable internet for all with green fiber opticsDocument2 pagesReliable internet for all with green fiber opticsNicaNo ratings yet
- Pcic VS Central CollegesDocument2 pagesPcic VS Central CollegesannlaurenweillNo ratings yet
- Taxation Quiz Week 9Document4 pagesTaxation Quiz Week 9Vee MaNo ratings yet
- Harvard Case 6: Tommy Hilfiger and Calvin Klein Post-Covid-19: What'S in Store?Document6 pagesHarvard Case 6: Tommy Hilfiger and Calvin Klein Post-Covid-19: What'S in Store?htet sanNo ratings yet
- 12go Booking 5475333Document5 pages12go Booking 5475333SherlockNo ratings yet
- BCM Business Administration Assignment - Strategic ManagementDocument3 pagesBCM Business Administration Assignment - Strategic ManagementAbdullah ShoaibNo ratings yet
- 2023 ALS Sustainability ReportDocument104 pages2023 ALS Sustainability ReportRichard NegronNo ratings yet
- WJ-Series WJ-Series: Turbine Meter Instructions Turbine Meter InstructionsDocument8 pagesWJ-Series WJ-Series: Turbine Meter Instructions Turbine Meter InstructionsIndra SUdirmanNo ratings yet
- Corporate CultureDocument2 pagesCorporate CultureMae MarinoNo ratings yet
- BSNL-: Bharat Sanchar Nigam LimitedDocument9 pagesBSNL-: Bharat Sanchar Nigam LimitedYogesh SinghNo ratings yet
- First Offer Adam GalinskyDocument3 pagesFirst Offer Adam GalinskyMark SchultzNo ratings yet
- Annual ReportDocument154 pagesAnnual Reportp15bipinbNo ratings yet
- Py 202303 Cgpay12023p03Document1 pagePy 202303 Cgpay12023p03Dark NationNo ratings yet
- Statement Summary: Run24.mx Sapi de CV Statement Date: Statement Period: Billing MethodDocument6 pagesStatement Summary: Run24.mx Sapi de CV Statement Date: Statement Period: Billing MethodnovelNo ratings yet
- Safuux Chain: LitepaperDocument20 pagesSafuux Chain: LitepaperKunwari WarikunNo ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIPDocument3 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIPMikaela FriasNo ratings yet
- IBM Active Governance Services Solution BriefDocument5 pagesIBM Active Governance Services Solution BriefAhmed elhouraniNo ratings yet
- Real Estate MortgageDocument2 pagesReal Estate MortgageRex Traya100% (1)
- sGAN INTERNSHIP REPORTDocument16 pagessGAN INTERNSHIP REPORTShubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Organization Culture and Open Innovation: A Quadruple Helix Open Innovation Model ApproachDocument8 pagesOrganization Culture and Open Innovation: A Quadruple Helix Open Innovation Model ApproachAyi Ayi WaeNo ratings yet
- A922905205_23792_22_2024_newK23LLCSE320SRStopic 4Document4 pagesA922905205_23792_22_2024_newK23LLCSE320SRStopic 45w2vr9k8c9No ratings yet
- 10 Proven Tips To Get Your First 1000 YouTube Subscribers NowDocument7 pages10 Proven Tips To Get Your First 1000 YouTube Subscribers NowJibran AzharNo ratings yet
- P - Issn: 2503-4413 E - Issn: 2654-5837, Hal 35 - 42: Jurnal Ekonomi Dan Bisnis, Vol. 11 No. 1 Juli 2022Document8 pagesP - Issn: 2503-4413 E - Issn: 2654-5837, Hal 35 - 42: Jurnal Ekonomi Dan Bisnis, Vol. 11 No. 1 Juli 2022Nova KartikaNo ratings yet
- Fahrul AsshiddiqiDocument124 pagesFahrul AsshiddiqiJKNNo ratings yet
- Floor Slab Chisling 3rd-5th CertfDocument1 pageFloor Slab Chisling 3rd-5th CertfwendmagegnNo ratings yet
























































![Practical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/235162742/149x198/2a816df8c8/1709920378?v=1)

















































