Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biologia 12: An Outbreak of Legionnaires
Uploaded by
Ana Jordão0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesimunologia
Original Title
BIO 12 - Legionela
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentimunologia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesBiologia 12: An Outbreak of Legionnaires
Uploaded by
Ana Jordãoimunologia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
BIOLOGIA 12
An outbreak of Legionnaires
Nuno Correia 2014
Nuno Correia 2014
Nuno Correia 2014
Legionella pneumophila is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes legionellosis or Legionnaires' disease. L.
pneumophila is a facultative intracellular bacterium that can invade and replicate inside amoebae in the
environment. In humans, L. pneumophila invades and replicates in macrophages.
Upon phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages, L. pneumophila delivers a large number of bacterial proteins,
or e...ffectors, into the host-cell cytosol through the Type IVB secretion system known as Dot/Icm to inject
effector proteins into the host. Some of those effectors help L. pneumophila redirect proteins and
membrane material of the infected cell to its Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV), thereby establishing a
protective compartment to shield themselves from being destroyed by host lysosomes. In this protected
compartment, the bacteria multiply. Formation and maintenance of the vacuole are crucial for pathogensis.
Once the nutrients of the host macrophage are depleted, the newly replicated bacteria move into their
transmissive phase, lyse the host macrophage and restart the process of infection. In the transmissive form,
they become motile and thick-walled allowing them to survive in the face of environmental fluctuations.
Today, there is a report of "An outbreak of Legionnaires' disease" that "has killed at least four people just
outside the Portuguese capital Lisbon and left dozens hospitalized, with the source of the outbreak yet to be
found.
Nuno Correia 2014
You might also like
- Biologia 12: An Outbreak of LegionnairesDocument5 pagesBiologia 12: An Outbreak of LegionnairesAna JordãoNo ratings yet
- Biology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseFrom EverandBiology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseNo ratings yet
- 2 - Lower Respiratory InfectionsDocument106 pages2 - Lower Respiratory InfectionsAda JoraimiNo ratings yet
- Candida albicans biofilm formation and antifungal resistanceDocument9 pagesCandida albicans biofilm formation and antifungal resistanceaaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3Niña MoradaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument4 pagesPulmonary TuberculosisAyumi StarNo ratings yet
- VHF Final ScriptDocument23 pagesVHF Final Scriptodhiambo samwelNo ratings yet
- Salmonella Enterica Serovars Typhimurium and Typhi As Model OrganismsDocument14 pagesSalmonella Enterica Serovars Typhimurium and Typhi As Model OrganismsShaznay Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Chapter ConceptsDocument0 pagesMicrobiology: Chapter ConceptsSilaxNo ratings yet
- Immune Responses To Intracellular Bacteria: Stefan H.E. Kaufmann, Helen L. Collins, Ulrich E. SchaibleDocument21 pagesImmune Responses To Intracellular Bacteria: Stefan H.E. Kaufmann, Helen L. Collins, Ulrich E. SchaibleEmmanuela Stefany SugiartoNo ratings yet
- Ijeb 47 (6) 412-423Document12 pagesIjeb 47 (6) 412-423Daniela MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 34Document6 pagesLesson 34Abdelraouf ElmanamaNo ratings yet
- How Can Immunology Contribute To The Control of Tuberculosis?Document11 pagesHow Can Immunology Contribute To The Control of Tuberculosis?Parijat BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- BACTERIOPHAGEDocument7 pagesBACTERIOPHAGEShagufta ZamanNo ratings yet
- PATHOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS OF TUBERCULOSISDocument46 pagesPATHOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS OF TUBERCULOSISJaya Semara PutraNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis TB Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesTuberculosis TB Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramkatrin anne f. carpenaNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument2 pagesTuberculosisAmnaNo ratings yet
- Modern Biology ReviewerDocument3 pagesModern Biology Reviewer22-02442No ratings yet
- MIcro Chapter 4Document39 pagesMIcro Chapter 4Resulto, Reylyn T.No ratings yet
- Acid Fast Bacteria: M. Tuberculosis, M. LepraeDocument22 pagesAcid Fast Bacteria: M. Tuberculosis, M. LepraeelaNo ratings yet
- Viral Properties and ReplicationDocument43 pagesViral Properties and ReplicationSarah PavuNo ratings yet
- Viral ReplicationDocument26 pagesViral ReplicationJhann100% (1)
- Taxonomic Classification and Pathology of Legionella pneumophilaDocument5 pagesTaxonomic Classification and Pathology of Legionella pneumophilaOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers Causes Symptoms TreatmentDocument58 pagesViral Hemorrhagic Fevers Causes Symptoms Treatmentodhiambo samwelNo ratings yet
- Granulomatous InflammationDocument96 pagesGranulomatous InflammationIvonne Trujillo TorbiscoNo ratings yet
- TB & MalariaDocument9 pagesTB & MalariaSpurgeNo ratings yet
- Viral Properties, Cultivation and IdentificationDocument54 pagesViral Properties, Cultivation and IdentificationGregory McBasketballNo ratings yet
- MB 703 Clinical Microbiology MB CCTP-9 Clinical Microbiology Core Compulsory Theory PaperDocument148 pagesMB 703 Clinical Microbiology MB CCTP-9 Clinical Microbiology Core Compulsory Theory PaperAbhi ShetyeNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Department FK UmsuDocument53 pagesMicrobiology Department FK UmsufarhanNo ratings yet
- Biofilms and DiseaseDocument39 pagesBiofilms and Diseaseapi-19762689No ratings yet
- The NeisseriaDocument16 pagesThe Neisseriashahbaz100% (1)
- Mycobacterium: Acid Fast BacilliDocument36 pagesMycobacterium: Acid Fast BacilliSrawy SrawyNo ratings yet
- VirusDocument4 pagesVirusEnzo AblangNo ratings yet
- Virus Replication: John Goulding, Imperial College London, UKDocument1 pageVirus Replication: John Goulding, Imperial College London, UKnawal asmadiNo ratings yet
- VIRUSES, Viroids and PrionsDocument66 pagesVIRUSES, Viroids and PrionsGabz GabbyNo ratings yet
- Bacteriophage: Viruses That Infect BacteriaDocument4 pagesBacteriophage: Viruses That Infect BacteriaHannah OfracioNo ratings yet
- DXX 075Document9 pagesDXX 075mclimacoNo ratings yet
- Bacteriophage Definition Parts and FunctionDocument4 pagesBacteriophage Definition Parts and FunctionGian AndrewNo ratings yet
- Essay: Institute of Biology and Biomedicine Education Program General Medicine (English)Document7 pagesEssay: Institute of Biology and Biomedicine Education Program General Medicine (English)sabrina elkhirNo ratings yet
- Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument17 pagesMycobacterium TuberculosisKate Anya Buhat-DiesmaNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial MicrobiologyDocument60 pagesMaxillofacial MicrobiologyAbel AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Moraxella: Prepared By: Prem G.M Class Roll No. 30 Exam Roll No.: 227 (5 Sem)Document9 pagesMoraxella: Prepared By: Prem G.M Class Roll No. 30 Exam Roll No.: 227 (5 Sem)RabinNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Biotechnology. VirophagesDocument17 pagesInnovations in Biotechnology. VirophagesDariy ChrisanfNo ratings yet
- Filarial NematodesDocument15 pagesFilarial NematodesOpi SaNg MadRidistasNo ratings yet
- Evasion InmuneDocument8 pagesEvasion Inmunenydiacastillom2268No ratings yet
- 5 Virology Pathogenesis SNUDocument44 pages5 Virology Pathogenesis SNUanas cabdisalaam NuurNo ratings yet
- Host Immune Response To Chlamydia InfectionDocument17 pagesHost Immune Response To Chlamydia Infectionapi-266835840No ratings yet
- Enteritis Viral JubbDocument17 pagesEnteritis Viral JubbSandraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Viruses 2Document32 pagesIntroduction To Viruses 2mega kharisma kusumawarniNo ratings yet
- 7-Micro 2016Document19 pages7-Micro 2016Hakim SimonNo ratings yet
- Cytolog Viruses (Stud)Document5 pagesCytolog Viruses (Stud)OnSolomonNo ratings yet
- European Foulbrood of Honey Bees: 1. Identification of The AgentDocument5 pagesEuropean Foulbrood of Honey Bees: 1. Identification of The AgentPınar BarkanNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelDocument11 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelSaeed AbdulhadiNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelDocument11 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelsalmaNo ratings yet
- Diversity of MICROBIAL WORLDDocument47 pagesDiversity of MICROBIAL WORLDAdya Arradikha100% (1)
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 pagesPa Tho PhysiologyhsiriaNo ratings yet
- My Co BacteriaDocument30 pagesMy Co BacteriaDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: Mark S. Bailey, MRCP, Diana N.J. Lockwood, BSC, MD, FRCPDocument9 pagesCutaneous Leishmaniasis: Mark S. Bailey, MRCP, Diana N.J. Lockwood, BSC, MD, FRCPeva yustianaNo ratings yet
- 15 Infectious Diseases LectureDocument29 pages15 Infectious Diseases LectureAadi VashishthaNo ratings yet
- Adult and Child Crossback Apron Patterns 2017Document26 pagesAdult and Child Crossback Apron Patterns 2017Ana JordãoNo ratings yet
- Nanda RH154636668PTDocument1 pageNanda RH154636668PTAna JordãoNo ratings yet
- Ar Quip Lagoda MadeiraDocument62 pagesAr Quip Lagoda MadeiraAna JordãoNo ratings yet
- A Special Focus On Non-Coding RNAs in Epigenetic RegulationDocument2 pagesA Special Focus On Non-Coding RNAs in Epigenetic RegulationAna JordãoNo ratings yet
- Epigenetics and CancerDocument22 pagesEpigenetics and CancerAna JordãoNo ratings yet
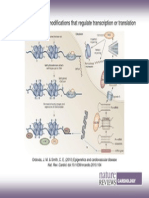
- Figure 2 Epigenetic Modifications That Regulate Transcription or TranslationDocument1 pageFigure 2 Epigenetic Modifications That Regulate Transcription or TranslationAna JordãoNo ratings yet
- Ewa 30jan2012Document0 pagesEwa 30jan2012Ana JordãoNo ratings yet
- Wham Bam Thank You Lamb Neckwarmer: MaterialsDocument1 pageWham Bam Thank You Lamb Neckwarmer: MaterialsAna JordãoNo ratings yet
- Epigenetics and CancerDocument22 pagesEpigenetics and CancerAna JordãoNo ratings yet
- Wham Bam Thank You Lamb Neckwarmer: MaterialsDocument1 pageWham Bam Thank You Lamb Neckwarmer: MaterialsAna JordãoNo ratings yet