Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DR Drug Study
Uploaded by
Francis SargentoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DR Drug Study
Uploaded by
Francis SargentoCopyright:
Available Formats
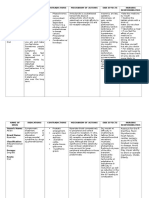
TOM FRANCIS D.
SARGENTO
BSN-IV
GROUP II
DRUG NAME
CLASSIFICAT
ION
MECHANISM
OF ACTION
INDICAITON
CONTRAINDICA
TION
ADVERSE
REACTION
Midazolam
Benzodiazepin
e (shortacting)
CNS
depressant
Exact
mechanism of
action not
understood;
acts mainly at
the limbic
system and
reticular
formation;
potentiates
the effects of
GABA, an
inhibitory
neurotransmitt
er; anxiolytic
and amnesia
effects occur
at doses below
those needed
to cause
sedation,
ataxia; has
little effect on
cortical
Midazolam is
indicated for
use in
pediatric
patients for
sedation,
anxiolysis
and amnesia
prior to
diagnostic,
therapeutic
or endoscopic
procedures or
before
induction of
anesthesia.
Contraindicat
ed with
hypersensitiv
ity to
benzodiazepi
nes;
psychoses,
acute
narrow-angle
glaucoma,
shock, coma,
acute
alcoholic
intoxication;
pregnancy;
neonates.
Use
cautiously in
elderly or
debilitated
patients;
with
impaired
liver or renal
Blurred vision;
changes in
blood
pressure,
breathing,
and
heartbeats;
coughing;
dizziness;
drowsiness;
dry mouth;
headache;
hiccups; low
blood
pressure
(children);
nausea; pain
during
injection;
pain, redness,
or tenderness
at the
injection site;
short-term
memory loss;
slurred
speech;
vomiting.
NURSING
RESPONSIBILI
TY
Do not
use small
veins for IV
injection.
Administ
er IM
injections
deep into
muscle.
Monitor
IV injection
site for
extravasati
on.
Arrange
to reduce
dosage of
midazolam
if patient is
also being
given
oploid
analgesics;
reduce
function.
function,
lactation.
Severe
allergic
reactions
(rash; hives;
difficulty
breathing;
tightness in
the chest;
swelling of the
mouth, face,
lips, or
tongue);
agitation;
chest pain;
combativenes
s; irregular
breathing
patterns;
pain, swelling,
or redness at
the injection
site; slow or
difficult
breathing;
unusual or
involuntary
muscle
movements or
muscle
tremor.
dosage by
at least
50% and
monitor
patient
closely.
Monitor
level of
consciousn
ess before,
during, and
for at least
2-6 hr after
administrati
on of
midazolam.
Carefully
monitor P,
BP, and
respirations
during
administrati
on.
You might also like
- Drug Study - DiazepamDocument1 pageDrug Study - Diazepammarengbib100% (1)
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMAnna Marie Ong ArseñaNo ratings yet
- MidazolamDocument1 pageMidazolamMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Diazepam Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDiazepam Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY3DIAZEDocument1 pageDRUGSTUDY3DIAZEEryn_Casaclang_6640No ratings yet
- HaloperidolDocument4 pagesHaloperidolKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol PDFDocument4 pagesHaloperidol PDFfatimahNo ratings yet
- Methylphenidate (Oral) Methylphenidate (Transdermal) : (Meth-Ill-Fen-I-Date)Document4 pagesMethylphenidate (Oral) Methylphenidate (Transdermal) : (Meth-Ill-Fen-I-Date)Seth LastNo ratings yet
- Requirement Drug Study PsycheDocument6 pagesRequirement Drug Study PsycheRegine Lorenzana Mey-AngNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyZyryll LaoanNo ratings yet
- Edited Psyche DrugsDocument49 pagesEdited Psyche Drugsa_lavina02No ratings yet
- AmobarbitalDocument2 pagesAmobarbitalidullrufaidahNo ratings yet
- Course ReqDocument3 pagesCourse ReqEricka Jordan AberinNo ratings yet
- TramadolDocument2 pagesTramadolAllen Vincent Cauton TulaganNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyJaessa Feliciano50% (2)
- TemazepamDocument1 pageTemazepamCris TanNo ratings yet
- Midazolam FinalDocument2 pagesMidazolam FinalAhmad AbqariNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyMeraflor BahonsuaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Form TJDocument4 pagesDrug Study Form TJJasmin Santiago CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Leaflet For Dd1 AssgmntDocument2 pagesLeaflet For Dd1 AssgmntayuNo ratings yet
- BENZODIAZEPINESDocument20 pagesBENZODIAZEPINESHamza DossaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Anti-Psychotic DrugsDocument10 pagesDrug Study - Anti-Psychotic DrugsSarah Carretero0% (1)
- Dekinet Tablets: Use in PregnancyDocument3 pagesDekinet Tablets: Use in Pregnancyddandan_2No ratings yet
- Vii. Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVii. Drug StudySarah BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Aksi DiazepamDocument4 pagesMekanisme Aksi DiazepamWijaya Kusuma MaheruNo ratings yet
- CLOZAPINEDocument5 pagesCLOZAPINEMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- NPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesDocument83 pagesNPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesValeria AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Lorazepam (Drug Monograph)Document1 pageLorazepam (Drug Monograph)Muhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Exam 6 Study GuideDocument27 pagesExam 6 Study GuideBrandi WeaverNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Mother TDocument14 pagesDrug Study Mother TEuzelle Jeena ArandaNo ratings yet
- LorazepamDocument3 pagesLorazepamgovind_soni_15No ratings yet
- DrugDocument4 pagesDrugApril Daye B. AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Forcadilla - Drug Study orDocument31 pagesForcadilla - Drug Study orKeir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- DiphenhydramineDocument9 pagesDiphenhydramineFhey Bernadette BeltranNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument19 pagesDrugsJosef Nicco Sebastian AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykristen_ramos_3No ratings yet
- Drug PresentationDocument32 pagesDrug PresentationManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - EpilepsyDocument48 pagesLecture 5 - EpilepsyANNABELLE PAULINE L. REAMBONANZANo ratings yet
- DormitolDocument1 pageDormitolRamboNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyrubie ann tillorNo ratings yet
- GENERIC NAME: Alprazolam DRUG CLASS: Benzodiazepine, AnxiolyticDocument1 pageGENERIC NAME: Alprazolam DRUG CLASS: Benzodiazepine, AnxiolyticSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Psychia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPsychia Drug StudyJustin 葉志明 Yap Delapaz100% (1)
- ClozapineDocument3 pagesClozapineLofranco Artiaga MerliahsofiahblairehNo ratings yet
- NozinanDocument18 pagesNozinanTom StNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyRubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic DrugsDocument23 pagesAntipsychotic DrugsASHLEY DAWN BUENAFENo ratings yet
- NAME OF DRUG NozinanDocument3 pagesNAME OF DRUG NozinanMill Jan CruzNo ratings yet
- Forcadilla Drug Study 2Document32 pagesForcadilla Drug Study 2Keir Mrls ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Manisha Thapa Leeza ShresthaDocument12 pagesPrepared By: Manisha Thapa Leeza ShresthaManjesh Mishra XettriNo ratings yet
- Management of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument20 pagesManagement of Parkinson's DiseasePia S.No ratings yet
- Benzodiazepines and Hypnotics: Key PointsDocument4 pagesBenzodiazepines and Hypnotics: Key Pointssaman mousaviNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Medication For Older AdultsDocument3 pagesCommonly Used Medication For Older AdultsRaze AlemaniaNo ratings yet
- CNS UnlockedDocument28 pagesCNS Unlockedabdoelsharkaw211No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPao HinojosaNo ratings yet
- CC Rubie Ann G. Tillor: IM: (Schizophrenia)Document11 pagesCC Rubie Ann G. Tillor: IM: (Schizophrenia)Rubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyKate Chavez100% (3)
- Metoclopromide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoclopromide Drug Studymarklesterdeguzman087No ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document8 pagesDrug Study 2rey_tengNo ratings yet
- Modafinil. A Legit Smart Pill That Improves Cognitive FunctionFrom EverandModafinil. A Legit Smart Pill That Improves Cognitive FunctionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Swor PpmciDocument4 pagesSwor PpmciFrancis SargentoNo ratings yet
- NCPPPPPPPPPPPPPP XDDocument17 pagesNCPPPPPPPPPPPPPP XDFrancis SargentoNo ratings yet
- Tom Francis D. Sargento Bsn-Iv Group 2Document1 pageTom Francis D. Sargento Bsn-Iv Group 2Francis SargentoNo ratings yet
- DR Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDR Drug StudyFrancis SargentoNo ratings yet
- Tom Francis D. SargentoDocument2 pagesTom Francis D. SargentoFrancis SargentoNo ratings yet