Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Citation Needed
Citation Needed
Uploaded by
Corina Taraș-LunguOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Citation Needed
Citation Needed
Uploaded by
Corina Taraș-LunguCopyright:
Available Formats
The kilogram or kilogramme (SI unit symbol: kg; SI dimension symbol: M), is the base
unit of mass in theInternational System of Units (SI) (the Metric system) and is defined as being
equal to the mass of the International Prototype of the Kilogram (IPK).
[2]
The avoirdupois (or international) pound, used in both the Imperial system and U.S. customary
units, is defined as exactly 0.45359237 kg, making one kilogram approximately equal to 2.2046
avoirdupois pounds. Other traditional units of weight and mass around the world are also defined in
terms of the kilogram, making the IPK the primary standard for virtually all units of mass on Earth.
The gram was originally defined in 1795 as the mass of one cubic centimeter of water at the melting
point of water, making the kilogram equal to the mass of one liter of water.[3] The original prototype
kilogram, manufactured in 1799 and from which the IPK is derived, had a mass equal to the mass of
1.000025 liters of water at 4 C.[citation needed]
The kilogram is the only SI base unit with an SI prefix ("kilo", symbol "k") as part of its name. It is
also the only SI unit that is still directly defined by an artifact rather than a fundamental physical
property that can be reproduced in different laboratories. Four of the seven base units in the SI
system are defined relative to the kilogram so its stability is important.
The International Prototype Kilogram was commissioned by the General Conference on Weights and
Measures(CGPM) under the authority of the Metre Convention (1875), and is in the custody of
the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) who hold it on behalf of the CGPM. After
the International Prototype Kilogram had been found to vary in mass over time, the International
Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM) recommended in 2005 that the kilogram be redefined
in terms of a fundamental constant of nature. At its 2011 meeting, the CGPM agreed in principle that
the kilogram should be redefined in terms of the Planck constant. The decision was originally
deferred until 2014; in 2014 it was deferred again until the next meeting. [4]
The International Prototype Kilogram (IPK) is rarely used or handled. Copies of the IPK kept
by national metrology laboratories around the world were compared with the IPK in 1889, 1948, and
1989 to provide traceability of measurements of mass anywhere in the world back to the IPK.
You might also like
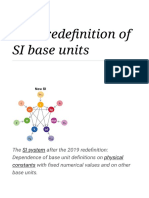
- 2019 Redefinition of SI Base UnitsDocument101 pages2019 Redefinition of SI Base UnitsGOPAL VERMANo ratings yet
- Recalibration of The U .S. National Prototype KilogramDocument21 pagesRecalibration of The U .S. National Prototype KilogramGesese GankaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 - Module 1.1Document28 pagesGeneral Physics 1 - Module 1.1joshua pagadoanNo ratings yet
- Physics MassDocument3 pagesPhysics MassRupendra Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Energy in Food and During Physical ActivityDocument25 pagesMeasurement of Energy in Food and During Physical Activitykrissh20No ratings yet
- Imperial UnitsDocument21 pagesImperial UnitsEmilJaredVirayPabustanNo ratings yet
- Maintaining and Disseminating The Kilogram Following Its RedefinitionDocument10 pagesMaintaining and Disseminating The Kilogram Following Its RedefinitionRaissaNo ratings yet
- The Planck Constant For The Definition and RealizationDocument9 pagesThe Planck Constant For The Definition and Realizationjuank3453No ratings yet
- Asset-V1 HKVU+COSAS+2021 Q4 R1+type@asset+block@si Unit-SeminarDocument41 pagesAsset-V1 HKVU+COSAS+2021 Q4 R1+type@asset+block@si Unit-SeminarppapyydsNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Equivalent One Size Does Not Fit AllDocument9 pagesMetabolic Equivalent One Size Does Not Fit AllVictor Hugo BarcelosNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1 Basic Principles, Concepts and Definitions (1 of 2)Document52 pagesThermodynamics 1 Basic Principles, Concepts and Definitions (1 of 2)Billy BeljeraNo ratings yet
- Energy MetabolismDocument15 pagesEnergy Metabolismshannon c. lewisNo ratings yet
- Nepal Standard Measurement and Weigh ActDocument20 pagesNepal Standard Measurement and Weigh ActGautamNo ratings yet
- 8 Introduction To Mass CalibrationDocument18 pages8 Introduction To Mass CalibrationHussein Hanoura100% (1)
- Food Energy - WikipediaDocument28 pagesFood Energy - WikipediaviraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 17 NutritionDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 17 Nutritionharry potingNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors With RationaleDocument22 pagesConversion Factors With RationaleUJJWALNo ratings yet
- What Are SI UnitsDocument2 pagesWhat Are SI UnitsGeorge RichardsNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Dr. Kamel Mohamed GuedriDocument28 pagesFluid Mechanics: Dr. Kamel Mohamed GuedriAd Man GeTigNo ratings yet
- SLB General TermsDocument3 pagesSLB General TermsAndreas DimasNo ratings yet
- How Much Do You WeightDocument3 pagesHow Much Do You WeightALEJANDRO HERNANDEZ GARCESNo ratings yet
- Energy & Climate Change - Lect-6 (28.09.2021)Document25 pagesEnergy & Climate Change - Lect-6 (28.09.2021)humza abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Effects of Starvation On Proximate Chemical Composition and Energy Utilization of Plaice, LDocument10 pagesEffects of Starvation On Proximate Chemical Composition and Energy Utilization of Plaice, Ldaniel cretuNo ratings yet
- Ch06Document24 pagesCh06Crysthian EcathosNo ratings yet
- Cori Cycle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesCori Cycle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAniket Mittal100% (1)
- Si 2Document9 pagesSi 2mobinsaiNo ratings yet
- Imperial Units: Imperial Units or The Imperial System Is ADocument9 pagesImperial Units: Imperial Units or The Imperial System Is ASebastian TobaciaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Carbohydrates IntroductionDocument17 pagesLecture 1-Carbohydrates IntroductionOwor OrikoNo ratings yet
- IUPACDocument1 pageIUPAClalamoveNo ratings yet
- THERMO 1 Ppt. (Corrected)Document196 pagesTHERMO 1 Ppt. (Corrected)John ValenzonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Measurements: 1.1 Units of MeasurementDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Measurements: 1.1 Units of MeasurementJosh EllesoNo ratings yet
- The Imperial Vs The Metric SystemDocument15 pagesThe Imperial Vs The Metric Systemapi-250910942No ratings yet
- Food EnergyDocument9 pagesFood EnergyAnonymous Ke7FphgNo ratings yet
- Pound (Mapoundss)Document10 pagesPound (Mapoundss)Karolina LozančićNo ratings yet
- Add A Heading 1Document60 pagesAdd A Heading 1athenatr1207No ratings yet
- J Is The Amount ofDocument2 pagesJ Is The Amount ofEera SyairaNo ratings yet
- Chap-1 of 11 RevisedDocument40 pagesChap-1 of 11 RevisedMukul MathurNo ratings yet
- 1953 - Blaxter - Heat Tissue CombustionDocument9 pages1953 - Blaxter - Heat Tissue CombustionAlbyziaNo ratings yet
- Celluar Resp 2009Document58 pagesCelluar Resp 2009Kurt IgotNo ratings yet
- Determination of Food Thermal PropertiesDocument11 pagesDetermination of Food Thermal PropertiesHafidz HasanNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum AquaticDocument10 pagesLaporan Praktikum AquaticAdeniaNo ratings yet
- Monitoring of Bioimpedance Data During Exercise in CyclistsDocument6 pagesMonitoring of Bioimpedance Data During Exercise in CyclistsgvozdenNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: TA. Igor SepulvedaDocument20 pagesFluid Mechanics: TA. Igor SepulvedaIgor SepNo ratings yet
- Pascal UniteDocument10 pagesPascal UnitePape Modou FallNo ratings yet
- Lec4 ME233Document15 pagesLec4 ME233lukeNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Animal RespirationDocument12 pagesAquatic Animal Respirationsalma sabilaNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Work, Power, and Energy Expenditure: Prepared By: Sonya Arshad B.SC Hons, M.SC, B.Ed, MphillDocument40 pagesMeasurement of Work, Power, and Energy Expenditure: Prepared By: Sonya Arshad B.SC Hons, M.SC, B.Ed, MphillUzairNo ratings yet
- Medical Physics: Energy, Work and Power of TheDocument10 pagesMedical Physics: Energy, Work and Power of TheMarci MunirNo ratings yet
- 2a Units Review - Notes PagesDocument27 pages2a Units Review - Notes PagessrikarmallampatiNo ratings yet
- Second ParteDocument3 pagesSecond ParteWALID BOUTNo ratings yet
- DensityDocument4 pagesDensityHary SasmayaNo ratings yet
- Energy Value of FoodsDocument72 pagesEnergy Value of FoodsKen Ryan DizonNo ratings yet
- NPL Poster-MassDocument1 pageNPL Poster-MassMauroNo ratings yet
- Advantage and Disadvantage of Using Different SI UnitsDocument3 pagesAdvantage and Disadvantage of Using Different SI UnitsQunya LimNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument13 pagesCarbon Cyclejarina jeydNo ratings yet
- MeasurementsDocument29 pagesMeasurementsteacher zaneNo ratings yet
- Metabolism and NutritionDocument69 pagesMetabolism and NutritionNur Nadrah Hasfinie HasanuddinNo ratings yet
- Case Study:: Piper AlphaDocument2 pagesCase Study:: Piper AlphaHB KeshavaNo ratings yet
- Kip (Unit)Document2 pagesKip (Unit)ElvisyuriNo ratings yet
- Patriot RevivalDocument1 pagePatriot RevivalCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Speaking Bullshit To Power Populism and PDFDocument34 pagesSpeaking Bullshit To Power Populism and PDFCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Golful PersicDocument1 pageGolful PersicCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- TahitiDocument1 pageTahitiCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Celso Pereira de AlmeidaDocument1 pageCelso Pereira de AlmeidaCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Economic LiberalismDocument1 pageEconomic LiberalismCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- United States: Patriot (American Revolution) Patriot Movement Christian Patriot MovementDocument1 pageUnited States: Patriot (American Revolution) Patriot Movement Christian Patriot MovementCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- The Newton (Symbol: N) Is The (SI) of - It Is Named After in Recognition of His Work On, SpecificallyDocument1 pageThe Newton (Symbol: N) Is The (SI) of - It Is Named After in Recognition of His Work On, SpecificallyCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Carmen: (Ʒɔʁʒ Bizɛ) Romantic EraDocument1 pageCarmen: (Ʒɔʁʒ Bizɛ) Romantic EraCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- French Nationality LawDocument1 pageFrench Nationality LawCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Kentucky (: KƏN - EeDocument1 pageKentucky (: KƏN - EeCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- AzerbaijanDocument1 pageAzerbaijanCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Guadeloupe (: French PronunciationDocument1 pageGuadeloupe (: French PronunciationCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Serena Jameka WilliamsDocument1 pageSerena Jameka WilliamsCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- William Cuthbert FaulknerDocument1 pageWilliam Cuthbert FaulknerCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Astana (: US ListenDocument1 pageAstana (: US ListenCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Maria Yuryevna SharapovaDocument1 pageMaria Yuryevna SharapovaCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Bruges (: /bru Ʒ/ Dutch ( Brʏɣə) French (Bʁy Ʒ) Province West Flanders Flemish Region BelgiumDocument1 pageBruges (: /bru Ʒ/ Dutch ( Brʏɣə) French (Bʁy Ʒ) Province West Flanders Flemish Region BelgiumCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Spanish Quechua Lake Andes Bolivia Peru South America Lake Maracaibo BayDocument1 pageSpanish Quechua Lake Andes Bolivia Peru South America Lake Maracaibo BayCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Karim Mostafa BenzemaDocument1 pageKarim Mostafa BenzemaCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Genus Elapid Venomous Australasia Species SubspeciesDocument1 pageGenus Elapid Venomous Australasia Species SubspeciesCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Française), The Modern Country Is Sometimes Referred To As Guinea-Conakry in Order To Distinguish ItDocument1 pageFrançaise), The Modern Country Is Sometimes Referred To As Guinea-Conakry in Order To Distinguish ItCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Ludwig Van Beethoven (: Missa Solemnis FidelioDocument1 pageLudwig Van Beethoven (: Missa Solemnis FidelioCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- The Bahamas (/BƏ Hɑ MƏZ/ (Listen) ), Known Officially As The Commonwealth of The BahamasDocument1 pageThe Bahamas (/BƏ Hɑ MƏZ/ (Listen) ), Known Officially As The Commonwealth of The BahamasCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Island Venetian Lagoon Venice Archipelago Torcello: Burano Is AnDocument1 pageIsland Venetian Lagoon Venice Archipelago Torcello: Burano Is AnCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Co-Founders Named To Inc's 35 Under 35: Times' 2010 Tech and InnovationDocument3 pagesCo-Founders Named To Inc's 35 Under 35: Times' 2010 Tech and InnovationCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Puerto RicoDocument1 pagePuerto RicoCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Bermuda (: Clarification NeededDocument1 pageBermuda (: Clarification NeededCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- (V LF Aŋ Ama de S Mo Tsa T) Ɔ Ɡ Ʊ ʁ Classical Era Salzburg Keyboard ViolinDocument1 page(V LF Aŋ Ama de S Mo Tsa T) Ɔ Ɡ Ʊ ʁ Classical Era Salzburg Keyboard ViolinCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- Johannes Brahms (: GermanDocument1 pageJohannes Brahms (: GermanCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet