Professional Documents
Culture Documents
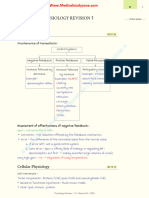
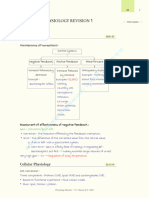
Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation
Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation
Uploaded by
hgfree41392Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation
Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation
Uploaded by
hgfree41392Copyright:
Available Formats
Mechanisms of Hormonal
Regulation
Chapter 20
Hormones
General characteristics
Specific rates and rhythms of secretion
Diurnal, pulsatile and cyclic, and patterns depending
on circulating substances
Operate within feedback systems
Affect only cells with appropriate receptors
The liver inactivates hormones, rendering the
hormones more water soluble for renal excretion
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
The Endocrine System
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
Regulation of Hormone Release
Hormones are released:
In response to an alteration in the cellular
environment
To maintain a regulated level of certain substances
or other hormones
Hormones are regulated by chemical,
hormonal, or neural factors
Negative feedback
Positive feedback
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
Feedback
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
Hormone Transport
Hormones are released into the circulatory
system by endocrine glands
Water-soluble hormones circulate in free,
unbound forms
Lipid soluble hormones are primarily circulating
bound to a carrier
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
Cellular Mechanism of Hormone
Action
Target cell
Up-regulation
Down-regulation
Hormone effects
Direct effects
Permissive effects
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
Cellular Mechanism of Hormone
Action
Hormone receptors
Water-soluble hormones
Located in or on the plasma membrane or in the
intracellular compartment of the target cell
High molecular weight
Cannot diffuse across the plasma membrane
Lipid-soluble hormones
Easily diffuse across the plasma membrane and
bind to cytosolic or nuclear receptors
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
Cellular Mechanism of Hormone
Action
Water-soluble hormones
First messenger
Signal transduction
Second-messenger molecules
Calcium
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
Cellular Mechanism of Hormone
Action
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
10
Cellular Mechanism of Hormone
Action
Lipid-soluble hormones
Steroid hormones
Diffuse across the plasma membrane
Androgens, estrogens, progestins, glucocorticoids,
mineralocorticoids, and thyroid hormones
Bind to cytoplasmic or nuclear receptors
Activate
RNA polymerase
DNA transcription and translation
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
11
Lipid-Soluble Hormones
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
12
Structure and Function of the
Endocrine Glands
Hypothalamic-pituitary axis
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
13
The Pituitary Gland
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
14
Posterior Pituitary Hormones
Synthesized with their binding proteins in the
supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the
hypothalamus
Secreted by the posterior pituitary
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Controls plasma osmolality
Oxytocin
Uterine contractions and milk ejection in lactating
women
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
15
Posterior Pituitary Hormones
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
16
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone
Growth hormone
Prolactin
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
Luteinizing hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone
-lipotropin
-endorphins
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
17
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
18
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
Thyroid gland
Two lobes lateral to the trachea
Isthmus
Follicles (follicle cells surrounding colloid)
Parafollicular cells (C cells)
Secrete calcitonin
Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone and thyroid
stimulating hormone
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
19
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
Thyroid hormones
90% T4 and 10% T3
Bound to thyroxine-binding globulin, thyroxinebinding prealbumin, or albumin
Affect growth and maturation of tissues, cell
metabolism, heat production, and oxygen
consumption
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
20
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
21
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
Parathyroid glands
Small glands located behind the upper and lower
poles of the thyroid gland
Produce parathyroid hormone
Regulator of serum calcium
Antagonist of calcitonin
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
22
Parathyroid Glands
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
23
Parathyroid Glands
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
24
Endocrine Pancreas
The pancreas is both an endocrine and an
exocrine gland
Houses the islets of Langerhans
Secretion of glucagon and insulin
Cells
Alphaglucagon
Betainsulin
Deltasomatostatin and gastrin
F cellspancreatic polypeptide
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
25
Endocrine Pancreas
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
26
Endocrine Pancreas
Insulin
Synthesized from proinsulin
Secretion is promoted by increased blood glucose
levels
Facilitates the rate of glucose uptake into the cells
of the body
Anabolic hormone
Synthesis of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
27
Endocrine Pancreas
Glucagon
Secretion is promoted by decreased blood glucose
levels
Stimulates glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, and
lipolysis
Somatostatin
Possible involvement in regulating alpha and beta
cell secretions
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
28
Endocrine Pancreas
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
29
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal cortex
80% of an adrenal glands total weight
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciculata
Zona reticularis
Adrenal medulla
Innervated by the sympathetic and
parasympathetic nervous systems
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
30
Endocrine Pancreas
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
31
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal cortex
Stimulated by adrenocorticotropic hormone
(ACTH)
Glucocorticoid hormones
Direct effects on carbohydrate metabolism
Anti-inflammatory and growth-suppressing effects
Influence awareness and sleep habits
Most potent naturally occurring glucocorticoid is
cortisol
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
32
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal cortex
Mineralocorticoid hormones
Affect ion transport by epithelial cells
Increase the activity of the sodium pump of the epithelial
cells
Cause sodium retention and potassium and hydrogen loss
Most potent naturally occurring mineralocorticoid is
aldosterone
Regulated by the renin-angiotensin system
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
33
Aldosterone
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
34
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal cortex
Adrenal estrogens and androgens
Estrogen secretion by the adrenal cortex is minimal
The adrenal cortex secretes weak androgens
Androgens are converted by peripheral tissues to stronger
androgens such as testosterone
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
35
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal medulla
Chromaffin cells (pheochromocytes)
Chromaffin cells secrete the catecholamines
epinephrine (majority) and norepinephrine
Release of catecholamines has been characterized
as a fight or flight response
Catecholamines promote hyperglycemia
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
36
Catecholamines
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
37
Neuroendocrine Response to Stress
The endocrine system reacts with the nervous
system to respond to stressors
The stress response also involves the immune
system
Influenced by corticotropin-releasing
hormone from the hypothalamus
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
38
Tests of Endocrine Function
Radioimmunoassay
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
(ELISA)
Bioassay
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
39
Aging and the Endocrine System
Thyroid gland
Glandular atrophy, fibrosis, nodularity, and
increased inflammatory infiltrates
Parathyroid glands
Related to alterations in calcium balance
Inadequate intake, malabsorption, or renal changes
Adrenal glands
Decreased clearance of cortisol
Mosby items and derived items 2006 by Mosby, Inc.
40
You might also like
- The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesThe Endocrine SystemОксана КрасильниковаNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones (Part 1)Document31 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones (Part 1)arun231187100% (1)
- The-Cell-Cycle-Worksheet With AnswersDocument3 pagesThe-Cell-Cycle-Worksheet With AnswersHiezel Dapat100% (1)
- SCIENCE 10 Genetics Worksheets With Answers 1Document4 pagesSCIENCE 10 Genetics Worksheets With Answers 1Anngela Arevalo Barcenas100% (1)
- Oral ContraceptivesDocument25 pagesOral ContraceptivesAdhitya Yudha MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument133 pagesEndocrine SystemAudrey KenfacNo ratings yet
- Bio1 11 - 12 Q1 0101 PF FDDocument41 pagesBio1 11 - 12 Q1 0101 PF FDRobbie Jule De Los SantosNo ratings yet
- Chemosensory Transduction: The Detection of Odors, Tastes, and Other ChemostimuliFrom EverandChemosensory Transduction: The Detection of Odors, Tastes, and Other ChemostimuliFrank ZufallNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HormonesDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Hormonesنورالهدى حسام عليNo ratings yet
- Serotonin: The Mediator that Spans EvolutionFrom EverandSerotonin: The Mediator that Spans EvolutionPaul M. PilowskyNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 5th Edition Mahon Test BankDocument25 pagesTextbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 5th Edition Mahon Test BankRhondaFisherjity100% (46)
- Power Point Week #11Document87 pagesPower Point Week #11Raelene MarceauNo ratings yet
- Fol I Culo GenesisDocument22 pagesFol I Culo GenesisDIANA LIZETTE ROJAS GARCIANo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology For Pharmacy Students-2023Document118 pagesEndocrine Physiology For Pharmacy Students-2023Alemnew YohannesNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument191 pagesThe Endocrine SystemRiska PriyaniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - HANDOUTSDocument20 pagesEndocrine System - HANDOUTSMeegs EstabilloNo ratings yet
- Endo SysDocument58 pagesEndo SysMono CerosNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGY Notes 2 PDFDocument131 pagesENDOCRINOLOGY Notes 2 PDFkomal pattabiNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Endocrine System Rev. Jan 22Document84 pages3.0 Endocrine System Rev. Jan 22[R2A] Khadijah AzlanNo ratings yet
- Harmonal Responses To ExerciseDocument78 pagesHarmonal Responses To Exerciseshazia_tabassumNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clinical Endocrinology: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Clinical Endocrinology: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanToukir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cells and OrganellesDocument52 pagesCells and OrganellesMohammed Mansour AbdullahNo ratings yet
- TG Ol XIlq Fe Yac TLxisDocument83 pagesTG Ol XIlq Fe Yac TLxisepic sound everNo ratings yet
- PHY LE 5 Finals ReviewerDocument26 pagesPHY LE 5 Finals Reviewerroxanne.viriNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument144 pagesEndocrinedaffodilrachagNo ratings yet
- Nguyễn Hoàng Kim Long - BTBCIU18124Document38 pagesNguyễn Hoàng Kim Long - BTBCIU18124Đặng Quỳnh NhưNo ratings yet
- MED 2056 Exam #1 Content 2018Document33 pagesMED 2056 Exam #1 Content 2018Marcelyn Chupoco CataligNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Sex Hormones: Molly Downing, PHD Clinical Instructor College of Pharmacy Downing.211@Osu - EduDocument25 pagesPharmacology of Sex Hormones: Molly Downing, PHD Clinical Instructor College of Pharmacy Downing.211@Osu - EduKaish DahiyaNo ratings yet
- 6 Regulación HormonalDocument31 pages6 Regulación HormonalAndy AcostaNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 6 Sistem EndokrinDocument61 pagesPertemuan 6 Sistem EndokrinKezia RachelNo ratings yet
- PHR 121 Anatomy & Physiology: Diploma in PharmacyDocument51 pagesPHR 121 Anatomy & Physiology: Diploma in PharmacyAzmi ArifinNo ratings yet
- Endo I 2005 PixDocument46 pagesEndo I 2005 Pixapi-3698357No ratings yet
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pages10 Endocrine SystemMardy Martin SorianoNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument223 pagesEndocrinologyMr mk RollinsNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE FinalDocument68 pagesENDOCRINE FinalJerick Sevilla SearesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument10 pagesEndocrine SystemJuan Andre' MarquinezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5-2Document27 pagesLecture 5-2Ushan KabirNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Pharmacology PDFDocument45 pagesEndocrine Pharmacology PDFNur TzNo ratings yet
- Endocine System Physiology 20-4-2020Document61 pagesEndocine System Physiology 20-4-2020Farah AljayyousiNo ratings yet
- 2 Regulation of Hormone Secretion and Hormone ReceptorsDocument56 pages2 Regulation of Hormone Secretion and Hormone Receptorsmedical.student.messiNo ratings yet
- 2017.06.03 8 BSAC 2017 SA RODRIGUES P. Pharmacology of Opiods 1Document46 pages2017.06.03 8 BSAC 2017 SA RODRIGUES P. Pharmacology of Opiods 1Meilia SuhermanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument61 pagesEndocrine Systemfanboiitsme20No ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology For AnesthesiaDocument135 pagesEndocrine Physiology For AnesthesiaBahredin AbdellaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Course OutllokDocument59 pagesEndocrinology Course OutllokJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pages10 Endocrine SystemGracia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesThe Endocrine SystemRODGIELYN MAE GEJONNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PDFDocument38 pagesEndocrine System PDFUlfat NiazyNo ratings yet
- Biokimia Kelompok 5 Revisi (Enzim, Hormon Dan Vitamin)Document50 pagesBiokimia Kelompok 5 Revisi (Enzim, Hormon Dan Vitamin)Uni NadhilaNo ratings yet
- Physiology Revision E6.5Document82 pagesPhysiology Revision E6.5Prakruti VaghaniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine BIOL 111Document30 pagesEndocrine BIOL 111Peter JungNo ratings yet
- Control of Hormone SecretionDocument77 pagesControl of Hormone Secretionjohanna deguzmanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System (Ch7)Document15 pagesEndocrine System (Ch7)moepiNo ratings yet
- TestesDocument15 pagesTestesTem GemechuNo ratings yet
- PD22 Hap1 L03Document33 pagesPD22 Hap1 L03Ka Yan LAUNo ratings yet
- E N D O C R I N E System: Hormonal Control of A. PituitaryDocument3 pagesE N D O C R I N E System: Hormonal Control of A. PituitaryMayet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Spermatogenesisvs OogenesisDocument96 pagesSpermatogenesisvs OogenesisZerica JohnNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument14 pagesEndocrine System NotesSteven100% (1)
- 6.6 Hormones, Homeostasis and Reproduction: Essential Idea: Hormones Are Used When Signals Need To Be Widely DistributedDocument37 pages6.6 Hormones, Homeostasis and Reproduction: Essential Idea: Hormones Are Used When Signals Need To Be Widely DistributedImeeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemJames CastroNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Biochemistry: Rodney BoyerDocument41 pagesConcepts in Biochemistry: Rodney Boyersalvi_darkNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument94 pagesEndocrineHira NawazNo ratings yet
- Topic3.1 Physiology Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument7 pagesTopic3.1 Physiology Introduction To EndocrinologyRen AlvNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Humoral RegulationDocument74 pagesLecture 9 - Humoral Regulationbadarbhai222No ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology For AnsthesiaDocument60 pagesEndocrine Physiology For AnsthesiaCHALIE MEQUNo ratings yet
- L1 Email Questions SolDocument4 pagesL1 Email Questions SolshahzuindNo ratings yet
- Ffects of Covid-19 Lockdown On Mental Health And: E Sleep Disturbances in ItalyDocument13 pagesFfects of Covid-19 Lockdown On Mental Health And: E Sleep Disturbances in ItalyshahzuindNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Computer Graphics CPCS 391 Session 2015/2016, Semester 1 Wednesday, 10 - 11.40 Thursday, 8.00-9.40Document2 pagesWeek 9 Computer Graphics CPCS 391 Session 2015/2016, Semester 1 Wednesday, 10 - 11.40 Thursday, 8.00-9.40shahzuindNo ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile CommunicationsDocument84 pagesGlobal System For Mobile CommunicationsshahzuindNo ratings yet
- Teerthanker Mahaveer University: Application FormDocument3 pagesTeerthanker Mahaveer University: Application FormshahzuindNo ratings yet
- Practice Osca Quiz 2015 - AnswerDocument7 pagesPractice Osca Quiz 2015 - Answerincognitus94No ratings yet
- Karolin Luger - Nucleosomes: Structure and FunctionDocument8 pagesKarolin Luger - Nucleosomes: Structure and FunctionDopameNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Physiology December 2023 DR Silva Ortiz - Parts 1-5Document183 pagesGastrointestinal Physiology December 2023 DR Silva Ortiz - Parts 1-5Jesus RiveraNo ratings yet
- 2022 in Silico Integration of Disease Resistance QTL, Genes and Markers With The Brassica Juncea Physical MapDocument20 pages2022 in Silico Integration of Disease Resistance QTL, Genes and Markers With The Brassica Juncea Physical Mapwsx kNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Nervous System: DR Sonnie P. Talavera 08162009 OlfuDocument162 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Nervous System: DR Sonnie P. Talavera 08162009 Olfuone_nd_onlyu0% (1)
- 19/jun/2021 06:14PM 32 Yrs/Male 19/jun/2021 12:08PM Dr. G.H. 01190178Document3 pages19/jun/2021 06:14PM 32 Yrs/Male 19/jun/2021 12:08PM Dr. G.H. 01190178Nitin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cell 5 E Model Lesson Plan FormDocument2 pagesCell 5 E Model Lesson Plan FormJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity PPT NGEC 9 MTDocument50 pagesBiodiversity PPT NGEC 9 MTLyndon P. PastranaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The HardyDocument11 pagesFactors Affecting The HardySK Imran RahmanNo ratings yet
- E Power of Movement Is Not Normally Associated WithDocument2 pagesE Power of Movement Is Not Normally Associated WithHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Self Domestication Hypothesis - Bonobo Case PDFDocument13 pagesSelf Domestication Hypothesis - Bonobo Case PDFZu MeyNo ratings yet
- Genetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition by Hartwell Goldberg Fischer ISBN Test BankDocument37 pagesGenetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition by Hartwell Goldberg Fischer ISBN Test Banklauren100% (24)
- A Handbook of Zoology: Book ReviewDocument2 pagesA Handbook of Zoology: Book ReviewDr A.K. VermaNo ratings yet
- Occupational Skin Cancer and Precancerous LesionsDocument9 pagesOccupational Skin Cancer and Precancerous LesionsAnonymous 7g5UghNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International GCSE January 2016 Biology Paper 1 (4SC0-1B)Document32 pagesEdexcel International GCSE January 2016 Biology Paper 1 (4SC0-1B)Jay SmithNo ratings yet
- Assignment of C3 PATHWAYDocument4 pagesAssignment of C3 PATHWAYWorld FootballNo ratings yet
- Python Fat Effect On Collagen Levels of Human Keloid TissueDocument3 pagesPython Fat Effect On Collagen Levels of Human Keloid TissueTuan Huynh0% (1)
- Human Reproduction MindmapDocument10 pagesHuman Reproduction MindmapSuyagya PundirNo ratings yet
- Biology of Depression: Edited by Julio Licinio and Ma-Li WongDocument38 pagesBiology of Depression: Edited by Julio Licinio and Ma-Li WongAnonymous 3Uy0HjXKNo ratings yet
- Essential Biology 05.1 Communities and EcosystemsDocument5 pagesEssential Biology 05.1 Communities and EcosystemsEbony Good100% (1)
- AP Biology Lab Review 1-4Document59 pagesAP Biology Lab Review 1-4swagsurferNo ratings yet
- Animals Science .Document24 pagesAnimals Science .Alkhair SangcopanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Cells Student NotesDocument4 pages1.1 Introduction To Cells Student NotesAheedNo ratings yet
- Summary of Dignitas PersonaeDocument6 pagesSummary of Dignitas PersonaeRizky Ananda PrimaNo ratings yet
- Etiology PPPDocument24 pagesEtiology PPPCresty Estalilla100% (1)
- Clinical and Physiological Perspectives of βGlucans in The Past, Present, and FutureDocument48 pagesClinical and Physiological Perspectives of βGlucans in The Past, Present, and FutureQualityMattersNo ratings yet