Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Force Area Gauge Pressure: Pressure Pressure (Symbol: P or P) Is The
Uploaded by
karthickumaragOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Force Area Gauge Pressure: Pressure Pressure (Symbol: P or P) Is The
Uploaded by
karthickumaragCopyright:
Available Formats
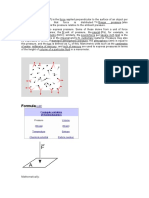
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: p or P) is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area
over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled gage pressure)[a][not in citation given] is the
pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.
Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a
unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre;
similarly, the pound-force per square inch (psi) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and
US customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure;
the atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure and the torr is defined as 1760 of this. Manometric units
such as the centimetre of water, millimetre of mercury and inch of mercury are used to express
pressures in terms of the height of column of a particular fluid in a manometer.
You might also like
- 3 Unit PressureDocument51 pages3 Unit PressureRalph Ian GodoyNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument228 pagesPressureDhirajMadanNo ratings yet
- Pressure FundamentalsDocument30 pagesPressure Fundamentalsartup3l0nNo ratings yet
- Pressure: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesPressure: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadarla999No ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document21 pagesChapter 3hailemebrahtuNo ratings yet
- O'level Physics PressureDocument11 pagesO'level Physics PressureToretto100% (1)
- PressureDocument1 pagePressuresathviknayakNo ratings yet
- Formula: Pressure (Symbol: P or P) Is The Force Applied Perpendicular To The Surface of An Object PerDocument3 pagesFormula: Pressure (Symbol: P or P) Is The Force Applied Perpendicular To The Surface of An Object PerHSENo ratings yet
- Chapter1 InstrumentTerminologyDocument4 pagesChapter1 InstrumentTerminologydfsdfsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 InstrumntdfsDocument4 pagesChapter2 InstrumntdfsdfsdfsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 InstrumentTerminologyDocument4 pagesChapter1 InstrumentTerminologydfsdfsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 InstrumentTerminologyDocument4 pagesChapter2 InstrumentTerminologydfsdfsdNo ratings yet
- Pressure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesPressure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaLeo Kyaw MinNo ratings yet
- Basics of Pressure MeasurementDocument4 pagesBasics of Pressure MeasurementPatoriku KunNo ratings yet
- ME LabDocument32 pagesME LabiamjemahNo ratings yet
- Formula: Pressure (Symbol: P or P) Is TheDocument1 pageFormula: Pressure (Symbol: P or P) Is TheBlack ThunderNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measurement: Fundamentals of Pressure and ForceDocument17 pagesPressure Measurement: Fundamentals of Pressure and Forcedinesh_akabariNo ratings yet
- SIALANA Pressure of GasDocument14 pagesSIALANA Pressure of GasTito V. Bautista Jr.No ratings yet
- What Is PressureDocument2 pagesWhat Is Pressurewalidderbel1981No ratings yet
- Units of PressureDocument3 pagesUnits of PressureEric PierceNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Force Area Perpendicular Gauge PressureDocument6 pagesPressure: Force Area Perpendicular Gauge PressureSyed Rameez MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Process Variables-PressureDocument9 pagesProcess Variables-PressureFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measurements.: TheoryDocument3 pagesPressure Measurements.: Theorymbahbim2No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids-Ce31-2Document43 pagesMechanics of Fluids-Ce31-2Justin SolisNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure: Atmospheric Pressure, Also Known As Barometric Pressure (After TheDocument1 pageAtmospheric Pressure: Atmospheric Pressure, Also Known As Barometric Pressure (After TheDexterNo ratings yet
- Pressure: This Article Is About Pressure in The Physical Sciences. For Other Uses, SeeDocument7 pagesPressure: This Article Is About Pressure in The Physical Sciences. For Other Uses, SeekopokopoNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesAtmospheric Pressure: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRobert RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Fluid Pressure and Pressure GaugesDocument47 pagesFluid Pressure and Pressure GaugesSin Za DolaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Pressure and Fluid StaticsDocument35 pagesFluid Mechanics: Pressure and Fluid StaticsYusf ari jerjisNo ratings yet
- Special Section - Temperature & Pressure - The Physics of Pressure - IsADocument3 pagesSpecial Section - Temperature & Pressure - The Physics of Pressure - IsAkumar_chemicalNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument53 pagesFluid MechanicsNIHAR NAIKNo ratings yet
- NI Tutorial 3639 enDocument4 pagesNI Tutorial 3639 enNishanthini SuppiahNo ratings yet
- EContent 3 2024 03 19 12 18 18 VARIOUSTYPESOFPRESSUREdocx 2024 03 19 12 06 34Document4 pagesEContent 3 2024 03 19 12 18 18 VARIOUSTYPESOFPRESSUREdocx 2024 03 19 12 06 34maanitghodasara.118845No ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between Gauge and Absolute Pressure?Document2 pagesWhat's The Difference Between Gauge and Absolute Pressure?reach_arindomNo ratings yet
- Pressure Hulls CanistersDocument13 pagesPressure Hulls CanistersbrufpotNo ratings yet
- ECE Module 5 6Document35 pagesECE Module 5 6June Paulo TejereroNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Josephine Bakewa A00224059Document9 pagesTutorial 3 Josephine Bakewa A00224059Josephine BakewaNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Introduction To Pressure - Psi and Pa - Online Pressure Units ConverterDocument3 pagesPressure: Introduction To Pressure - Psi and Pa - Online Pressure Units ConverterMauliNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Ibatan, Khyla Jhane Obias, Francheska Mae Reyes, Erben HannaDocument8 pagesPressure: Ibatan, Khyla Jhane Obias, Francheska Mae Reyes, Erben Hannateresita a. ibatanNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Pressure: Pressure) Is The Quantity Defined byDocument3 pagesDynamic Pressure: Pressure) Is The Quantity Defined bySeiyaleosinhoNo ratings yet
- G9 Physics - Monday Lesson NoteDocument2 pagesG9 Physics - Monday Lesson NotemicahxNo ratings yet
- PRESSUREDocument2 pagesPRESSUREZoteloNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument10 pagesPressureklaudioajdini9No ratings yet
- Pressure FundamentalsDocument29 pagesPressure FundamentalsJesus Osornio RamirezNo ratings yet
- Definition of Absolute PressureDocument1 pageDefinition of Absolute PressureNAVINDRAN KALAISELVAN (Student)No ratings yet
- Abhishek Thakur Xi-F 15 Physics Project File: Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument14 pagesAbhishek Thakur Xi-F 15 Physics Project File: Mechanical Properties of FluidsAbhishek ThakurNo ratings yet
- Pressure MeasurementDocument24 pagesPressure MeasurementOssy DewintaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Pressure Pressure (3.1)Document16 pagesDefinition of Pressure Pressure (3.1)Jr BagaporoNo ratings yet
- Abe 106 - 01Document6 pagesAbe 106 - 01emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Module 2 & 3Document180 pagesModule 2 & 3Piyush ShahaneNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measuring Devices: Experiment No: 01 Fluid MechanicsDocument12 pagesPressure Measuring Devices: Experiment No: 01 Fluid MechanicsGayantha Induwara RanasinghaNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Fluid StaticsDocument7 pagesPressure and Fluid StaticsNitishNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Pressure APIDocument74 pagesChemical Engineering Pressure APIAsadMalikNo ratings yet
- 2nd and 3rd WeeksDocument51 pages2nd and 3rd WeeksnaverfallNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 PIMDocument14 pagesChapter - 3 PIMmulatuNo ratings yet
- Defining Hydrostatics and Pressure: Figure 1. Pressure Distribution Around A Column of LiquidDocument10 pagesDefining Hydrostatics and Pressure: Figure 1. Pressure Distribution Around A Column of LiquidJohn GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Chap 02 MDF - EngDocument19 pagesChap 02 MDF - Engwardatrad2003No ratings yet
- Nama: Galih Achmad Prawiradiawan NIM: 20183020094 Kelas: D3 Teknologi Mesin B Tugas 3Document15 pagesNama: Galih Achmad Prawiradiawan NIM: 20183020094 Kelas: D3 Teknologi Mesin B Tugas 3Muhamad ZuhriNo ratings yet
- CyanohydrinDocument1 pageCyanohydrinkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Hypochlorous Acid, Chloric (I) Acid, Chloranol, HydroxidochlorineDocument1 pageHypochlorous Acid, Chloric (I) Acid, Chloranol, HydroxidochlorinekarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Antiparticle Proton Annihilated: AntiprotonDocument1 pageAntiparticle Proton Annihilated: AntiprotonkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- LKG Telugu Fa4Document1 pageLKG Telugu Fa4karthickumaragNo ratings yet
- 11Document24 pages11karthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Mass Grams Mole Atoms Monatomic Chemical Element Standard Atomic WeightDocument1 pageMass Grams Mole Atoms Monatomic Chemical Element Standard Atomic WeightkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- 1912127028bio Molecules Study Notes PDFDocument20 pages1912127028bio Molecules Study Notes PDFkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Rodenticides: Rodenticides, Colloquially Rat Poison, Are Typically Non-SpecificDocument1 pageRodenticides: Rodenticides, Colloquially Rat Poison, Are Typically Non-SpecifickarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Assamese Town Area Committee Tinsukia District Assam India: Digboi Digboi (Document1 pageAssamese Town Area Committee Tinsukia District Assam India: Digboi Digboi (karthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Brønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory Species Reception of A Proton H Base Hydrogen Removal of A ProtonDocument1 pageBrønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory Species Reception of A Proton H Base Hydrogen Removal of A ProtonkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Fruit Drying Dehydrators MesopotamiaDocument1 pageFruit Drying Dehydrators MesopotamiakarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- MissileDocument1 pageMissilekarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Portable Building School ClassroomDocument1 pagePortable Building School ClassroomkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Anion Carbon: CarbanionDocument1 pageAnion Carbon: CarbanionkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- State Solid Liquid Standard Supercool Melting PointDocument1 pageState Solid Liquid Standard Supercool Melting PointkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Copper Mineral Type Locality Chessy-les-Mines Lyon France Carbonate Pliny The Elder Natural HistoryDocument1 pageCopper Mineral Type Locality Chessy-les-Mines Lyon France Carbonate Pliny The Elder Natural HistorykarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Spanning Tree ProtocolDocument1 pageSpanning Tree ProtocolkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Bengal South Asia Australia California Bungalow First World War North America United Kingdom Dormer Windows Portable ClassroomsDocument1 pageBengal South Asia Australia California Bungalow First World War North America United Kingdom Dormer Windows Portable ClassroomskarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Multicast Multicast, Where The Latter Makes It Possible For The Source To Efficiently Send To The Group in ADocument1 pageMulticast Multicast, Where The Latter Makes It Possible For The Source To Efficiently Send To The Group in AkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Electrode Conventional Current Mnemonic: CathodeDocument1 pageElectrode Conventional Current Mnemonic: CathodekarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- SolventDocument1 pageSolventkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Polypeptide Amino Acid Synthesized Signal Peptide TranslationDocument1 pagePolypeptide Amino Acid Synthesized Signal Peptide TranslationkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Cell Organisms Populations SpeciesDocument1 pageCell Organisms Populations SpecieskarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Chemical Element Atomic Number /ha DR RD ƏRƏM/ Ɪ Ɑ Ʒ Heavy D-Block Standard Conditions For Temperature and Pressure Bromine Caesium Gallium RubidiumDocument1 pageChemical Element Atomic Number /ha DR RD ƏRƏM/ Ɪ Ɑ Ʒ Heavy D-Block Standard Conditions For Temperature and Pressure Bromine Caesium Gallium RubidiumkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Physics Vaporize Vapor Pressure: VolatilityDocument1 pageChemistry Physics Vaporize Vapor Pressure: VolatilitykarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- CalorieDocument1 pageCaloriekarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Temperature Temperature Gradient Mercury-In-Glass ThermometerDocument1 pageTemperature Temperature Gradient Mercury-In-Glass ThermometerkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- T Lju L/ Ɒ Ɒ Water Paint Thinners Benzene CH Aromatic Hydrocarbon Feedstock SolventDocument1 pageT Lju L/ Ɒ Ɒ Water Paint Thinners Benzene CH Aromatic Hydrocarbon Feedstock SolventkarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- Organic Compound: Gaseous Liquid Solid Chemical Compounds Molecules Carbon Carbides Carbonates Oxides Cyanides InorganicDocument1 pageOrganic Compound: Gaseous Liquid Solid Chemical Compounds Molecules Carbon Carbides Carbonates Oxides Cyanides InorganickarthickumaragNo ratings yet
- CyanideDocument1 pageCyanidekarthickumaragNo ratings yet