Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Salmonela Thyposa: Disease Etiology Unique S&S Brief Patophysiology Diagnostic Treatment / Plan Others
Salmonela Thyposa: Disease Etiology Unique S&S Brief Patophysiology Diagnostic Treatment / Plan Others
Uploaded by
Nicole PramonoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Salmonela Thyposa: Disease Etiology Unique S&S Brief Patophysiology Diagnostic Treatment / Plan Others
Salmonela Thyposa: Disease Etiology Unique S&S Brief Patophysiology Diagnostic Treatment / Plan Others
Uploaded by
Nicole PramonoCopyright:
Available Formats
Vaccinated Diseases - Nathania S.
/07120100071
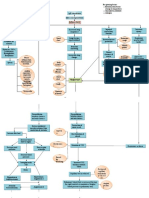
Disease
Etiology
Unique S&S
Brief Patophysiology
Diagnostic
Treatment / Plan
- survive in the acidic environment
of gaster
- pass to the wall and contact with
phagocytic cells in Peyers Patch
(M cells)
- ruffled enterocyte cell membrane
& cytoskeletal adhesion
- bacteria endocytosed
- B exit the basilar aspect in the cell
and free in lamina propra
- phagocyted in Peyers Patch
- Hematogenous & lymphatic
dissemination -> LIVER &
SPLEEN & BONE MARROW
- blood culture
using GALL
culture (GOLD)
- Widal test
1st : chloramphenicol,
ceftriaxone
2nd : ampicillin and/or
ciprofloxacin (adult)
TIMING :
w1 : blood
w2 : urine, feces
w3 : feces,
auscultation
(perforation?)
Penicillin allergic : TMP/
SMX (child),
chloramphenicol (adult)
- VIRULANCE FACTOR :
1. Bacteria : invasion, proliferation
in the local tissue
2. Toxin : necrosis
- can affect tonsil, pharynx, nasal
cavity, pharingeal & tonsilar,
laryngeal, cutaneous, genital
Clinical
- antitoxin (IM or IV)
- antibiotic : PenG (IM)
- oxygen & tracheostomy if
indicated
- supportive therapy
Others
TYPHOID VACCINE
TYPHOID
FEVER
Salmonela
thyposa
- Gr. (-)
- diarrhea continued by
constipation
- continous fever,
exacerbated at night
- roseola (rare among
Indonesians)
- delirium
- paroxysmal
bradycardia
DPT (IM)
- DTwP - whole cell
- DTaP - acellular components
DIPHTERIAE
Corrynebacter - pseudomembrane
ium diphteriae - bullneck appearance
Gr. (+)
Pelayanan
Kesehatan
Anak di
Rumah
Sakit.pdf Kemenkes
Vaccinated Diseases - Nathania S. /07120100071
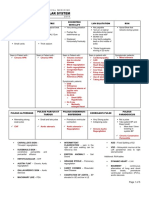
Disease
TETANUS
Etiology
Unique S&S
Clostridium
tetani
Gr. (+)
- trismus (lock jaw)
- risus sardonicus
- ophistotonus
(melengkung)
Port dentry : WOUND, ingested
TOXIN :
- tetanospasmin : blocks
transmission of inhibiting neurons
- tetanolisin : necrotizing cells
- rigidity and spasm
- irritability
- unable to be breastfed
born from non-immunized mother or
unsterilized equipment during labor
(esp. when the cutting of umbilical
cord)
Plan a good ANC to prevent
and good and sterile
delivery process
- whooping cough
- 100 days of cough
- tussis quinta
- bacteria : attached in respiratory
Clinical
cillia, inflammation cause inhibition
of sputum clearance and
pulmonary secretion
- toxin
- Antibiotic : erythromycin
(oral)
- Oxygen
- Airway management
- DO NOT GIVE antitussive,
sedative, mucolytic and
antihistamine
Tetanus
neonatorum
PERTUSSIS
Bordetella
persussis
Gr. (-)
Brief Patophysiology
Diagnostic
Clinical
STAGES :
- catarrahal (2w) - CONTAGIOUS
- paroxysmal / spasmodic
- centravalence
Treatment / Plan
- antibiotic Penicillin OR
Tetracyclin (CI : child)
- antitetanus serum
- diazepam
- wound healing protocol
MMR - IM
MUMPS
(Gondongan)
Mumps virus
- painful swelling on the
salivary glands,
unilateral
MoT : droplet & saliva
The virus invade and replicate
within the cell in salivary gland
Clinical
self limiting disease
Others
Vaccinated Diseases - Nathania S. /07120100071
Disease
MEASLES
(Campak) /
Rubeolla /
Morbili
Etiology
Morbili virus
Unique S&S
Brief Patophysiology
Diagnostic
Treatment / Plan
3C :
- coryza
- conjunctivitis
- copliks spot (the truth
is ...KOPLIKs spot)
MoT : respiratory droplet & direct
contact
- adhesion & invasion of respiratory
epithelium
Clinical
- vitamin A : to protect
mucosa & re-epithelization
Respiratory transmission of the
virus, replication in the
nasopharynx and regional lymph
nodes, transplacental
Clinical
self limiting disease
From head to toe spread
- macula -> papula ->
desquamation
RUBELLA
(Campak
Jerman)
Rubella virus
Congenital
Rubella
- exanthem rash
(maculopapular)
- lymphadenopathy
- abrupt onset
TRIAD :
- microcephaly
- PDA
- catarract
can be prevented!
- blueberry muffin lesion
- ichteric
- IUGR
VARICELLA
Varicella (Cacar Varicella
air)
zoster virus
- vesicopustular
- centrifugal spread
Little known about this disease.
Clinical
acyclovir on high risk
patients (AIDS, pregnant
woman, >12 yo)
Others
Vaccinated Diseases - Nathania S. /07120100071
Disease
Etiology
Unique S&S
Brief Patophysiology
Diagnostic
Treatment / Plan
Others
POLIO
Poliomyelitis
TORCH
Polio virus
type : asymptomatic,
MoT : oral-oral or fecal-oral
without any disease,
- replicated in the pharynx and
abortive p., non-paralytic lower GI tract.
p., paralytic p.
- spread to the regional lymph node
- affecting the cornu anterior
- biphasic paralytic and
medula spinalis, vermis medularis
sudden onset
cerebelum, midbrain, thalamus,
- assymetrical paralysis
hypothalamus, paladium, motoric
or paresis
cerebrum cortex
- bladder paralysis or
- in the medulla, causing paralysis
atoni of GI tract
- spacicity, stiff neck
(kaku kuduk),
hypothonus and
sensory abnormality
- stool
examination for
polio virus
(WHO)
- CSF
examination
- serologic
neutralizing antibody (1
week after infection)
slide dr.
dina!
Vaccinated Diseases - Nathania S. /07120100071
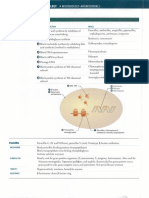
Disease
Etiology
Unique S&S
Toxoplasma
Toxoplasma
gondii
MATERNAL
- asymptomatic
- lymphadenopathy
- visual changes
BABY
- chorioentinitis
- hydocephalus or
microcephaly
- cerebral calcification
Brief Patophysiology
Diagnostic
Treatment / Plan
definitive host : your beloved cat
- tachyzoit : IgA response
- spread from GI tract to multiple
organs (lymphatic, striated
muscle, myocardium, retina,
placenta and CNS
- destruction of tachyzoid
manifested in MOF (necrotizing
encephalitis, pneumonia and
myocarditis)
- bradyzoit : clinical manifestation
PCR DNA, USG
Serology :
- IgG (1-2 w) peak
at 1-2 month
(positive for
lifetime)
- IgM : 10 days
after infection
**routine prevention is not
recommended except in
HIV
MATERNAL :
- spiramycin
FETUS :
- pyrimethamine
- sulfonamide
- folinic acid (prevent NTD)
Rubella
Already described
CMV
Cytomegalovi
rus
unknown prematurity
and fetal death
- asymptomatic to
infectious
mononucleosis
MoT : nasopharynx droplet, urine,
saliva, semen, cervix, vertical and
breast milk
Clinical
- symptomatic management
- ganciclovir (cat : C)
Herpes
HSV
- painful vesicles
Mot : intrauterine, peripartum, post
natal
Clinical
Management of delivery :
- no lesion : vaginal
- lesion : sectio caesarea
Trimester 1 : abortus
Trimester 2 : prematutiry
Others
Read by yourself
affecting nervous system to the
axon
Antivirus :
- acyclovir, valcyclovir,
famcyclovir
Others
Vaccinated Diseases - Nathania S. /07120100071
Disease
Etiology
Unique S&S
Brief Patophysiology
Diagnostic
Prodromal :
- pruritus and
paresthesia in the biten
site
- paralytic
- myoedema (mounding
part)
virus from wild dog -> muscle ->
replicating and go to the peripheral
nervous terminal.
Clinical, post
mortem biopsy :
NEGRI BODIES.
centripetal spread to the CNS, then
to ANS, skeletal muscle,
myocardium, adrenal gland, kidney,
eye and pancreas.
EEG : slow wave
with paroxysmal
spike
Treatment / Plan
RABIES
Vaccines :
- Nerve tissue vaccine (NTV)
- Non-nerve tissue vaccine
Rabies
Rabies virus
Acute neurology st. :
- furious (hyperactive,
disoriented,
hallucinating), agitated,
etc. intermitten every
1-5 mins
- paralytic
- hydrophobia
- aerophobia
- photophobia
ANTHRAX (IM)
Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed (AVA)
virus existed in salivary gland,
lacrimal gland and resp. system;
breast milk and urine.
complication : raised ICP, diabetes
insipidus, SIADH.
- neutralizing antibody
(vaccine)
Others
Vaccinated Diseases - Nathania S. /07120100071
Disease
Anthrax /
Woolsorters
disease /
Siberian ulcer /
charbon /
ragsorters
disease
Etiology
Bacillus
anthraxis
Gr. (+) with
spore
Unique S&S
Brief Patophysiology
- Cutaneous : papule
lession and itchy, black
carbuncle appearance,
kalor, rubor, non-pitting
edema, local
lymphadenopathy
- Inhalation : phase 1 not specific, phase 2 high fever, hypoxia,
stridor, cyanosis. NOT
PNEUMONIA
- Ingestion : diffused
abdominal pain,
hematemesis and
melena, messenteric
lymphadenitis, ascites,
perforated intestine.
VIRULANCE FACTOR :
PA (protective antigen), EF (edema
factor), LF (lethal factor)
cutaneous :
port dentry : wound
secreting exotoxin and
antiphagocytic material capsule,
lymphatogenous, lymphadenitis
inhaled :
spore in the alveoli, phagocyted by
macrophage, spread to the
mediastinal lymph node,
germination causing hemorrhagic
and lymphadenitic in mediastinum
ingested : pharynx swelling,
tracheal obstruction, cervical
lymphadenopathy, necrosis and
hemorrhage of intestinal mucosa,
ascites and sepsis
TRAVELLERS DIARRHEA
Diagnostic
Clinical
Treatment / Plan
- Pennicilin G.
Alternative :
tetracyclin,
chloramphenicol,
erythromycin
Others
Vaccinated Diseases - Nathania S. /07120100071
Disease
Etiology
E. Coli - ETEC
E. coli
(enterotoxi
genic)
Unique S&S
diarrhea ... and other
non specific symptoms
Gr. (-)
Giardiasis
Read on your gastro book!
Shigella
Read on your gastro book!
Brief Patophysiology
Diagnostic
- fimbrial adhesins of the bacteria
bind enterocyte cells in small
intestine
- toxins :
LT - similar to cholera toxin
ST - causes cGMP accumulation
and stimulate to secrete fluid and
electrolytes into the intestinal
lumen
Stool examination
for polio virus
(WHO)
CSF examination
serologic
Treatment / Plan
prevention : safe food &
drink!
Antibiotic : amoxicillin
(beware of the resistance)
Others
You might also like
- Tumor Immunology: I. Common Tumor MarkersDocument2 pagesTumor Immunology: I. Common Tumor MarkersDivineGloryMalbuyoNo ratings yet
- Diseases Link To Chromosomal Abnormalities: Chromoso Me Abnormality DiseaseDocument7 pagesDiseases Link To Chromosomal Abnormalities: Chromoso Me Abnormality Diseasenreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Genital Ulcer Differential Diagnosis of Genital UlcersDocument3 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Genital Ulcer Differential Diagnosis of Genital UlcersNurhayati HasanahNo ratings yet
- Hi Stop Hath Ology 2Document22 pagesHi Stop Hath Ology 2vivek govardhanamNo ratings yet
- Gyneacology Revision by All TeamDocument14 pagesGyneacology Revision by All TeamSara EhabNo ratings yet
- 1 Ge Stimulations Mast Cell Degeneration Asthma AttackDocument4 pages1 Ge Stimulations Mast Cell Degeneration Asthma Attacknebbie06No ratings yet
- Low BP - Decreased Cardiac Output - Improved Renal Blood FlowDocument2 pagesLow BP - Decreased Cardiac Output - Improved Renal Blood Flowtantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Staph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusDocument5 pagesStaph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusTom PedersonNo ratings yet
- Abdo Exam TableDocument2 pagesAbdo Exam Tableapi-195986134No ratings yet
- Clinical Medicine CVS Tabulated 2019Document5 pagesClinical Medicine CVS Tabulated 2019Justin TayabanNo ratings yet
- Cardio Block 3Document62 pagesCardio Block 3Maya LaPradeNo ratings yet
- Neisseria Meningitidis Strep Pneumoniae E. ColiDocument3 pagesNeisseria Meningitidis Strep Pneumoniae E. ColiÐr SalmaNo ratings yet
- Disease Causative Agent Diagnosis Classification/ S&S TreatmentDocument4 pagesDisease Causative Agent Diagnosis Classification/ S&S Treatmentfreya_28No ratings yet
- Gene Related DiseaseDocument3 pagesGene Related Diseasevivek govardhanamNo ratings yet
- Present at 4-12 Months, Development Arrest From Pre-B To BDocument2 pagesPresent at 4-12 Months, Development Arrest From Pre-B To BWaoNo ratings yet
- Antimycobacterial Drugs PDFDocument3 pagesAntimycobacterial Drugs PDFCas BuNo ratings yet
- First Aid PharmacoDocument61 pagesFirst Aid PharmacogirNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Arteritis ChartDocument3 pagesCardiology Arteritis ChartM PatelNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary System: Renal FailureDocument6 pagesGenitourinary System: Renal FailureEn ConejosNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis: Disorder Vessels Pathology Presentation Test TX OtherDocument3 pagesVasculitis: Disorder Vessels Pathology Presentation Test TX OthermcwnotesNo ratings yet
- FCPS Part1 Q BANK Physiology Flash Cards Very Important For Part 1Document49 pagesFCPS Part1 Q BANK Physiology Flash Cards Very Important For Part 1Sehar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Handouts Integumentary Sys Sp11 B201Document7 pagesHandouts Integumentary Sys Sp11 B201Kelly TrainorNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Quick TablesDocument276 pagesInternal Medicine Quick Tablesjoey plouffeNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Pharm GuideDocument41 pagesUltimate Pharm GuideeanguyenNo ratings yet
- Heartsound MurmurDocument2 pagesHeartsound MurmurDya AndryanNo ratings yet
- Table of Genetic DisordersDocument9 pagesTable of Genetic DisordersjeslymailNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionDocument1 pagePathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Neuro Written III TablesDocument5 pagesNeuro Written III TablesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- The Better You Get at Something, The More Enjoyable It Can BecomeDocument6 pagesThe Better You Get at Something, The More Enjoyable It Can BecomeAshNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloproliferative Acute Lymphoproliferative Chronic Myeloproliferative Chronic Lymphoproliferative Plasma Cell NeoplasmDocument1 pageAcute Myeloproliferative Acute Lymphoproliferative Chronic Myeloproliferative Chronic Lymphoproliferative Plasma Cell NeoplasmAudreySlitNo ratings yet
- Board Review Blood SupplyDocument6 pagesBoard Review Blood Supplynewguy927No ratings yet
- 'Aliah's Cardiovascular SystemDocument45 pages'Aliah's Cardiovascular SystemLuqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- NephroticDocument8 pagesNephroticsangheetaNo ratings yet
- Navle Master ListDocument60 pagesNavle Master Listhari krishnaa athotaNo ratings yet
- Step1 Review TopicsDocument32 pagesStep1 Review TopicsAsif AbidiNo ratings yet
- Characterstic Drug ToxicitiesDocument3 pagesCharacterstic Drug ToxicitiesJorge PalazzoloNo ratings yet
- NSAID's "Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs": Mmbakhaitan@uqu - Edu.saDocument19 pagesNSAID's "Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs": Mmbakhaitan@uqu - Edu.saAhmed HossamNo ratings yet
- CURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment: Nephrology & Hypertension, 2009 Chapter 46. Cystic Diseases of TH e KidneyDocument1 pageCURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment: Nephrology & Hypertension, 2009 Chapter 46. Cystic Diseases of TH e KidneyFate ChanNo ratings yet
- Kidney NewDocument4 pagesKidney NewParth BhayanaNo ratings yet
- Marrow Study PlannerDocument2 pagesMarrow Study Plannerpooja singh50% (2)
- MC Tumor MC Ca MC 1° Ca BrainDocument12 pagesMC Tumor MC Ca MC 1° Ca BrainRyan TurnerNo ratings yet
- Infection of Skin Muscles, Bone FinalDocument90 pagesInfection of Skin Muscles, Bone FinalNoelani-Mei Ascio100% (1)
- Microbiology Summary DocumentDocument7 pagesMicrobiology Summary DocumentKNo ratings yet
- I 2x Get Laid On FridaysDocument3 pagesI 2x Get Laid On FridaysRoma Fe MabanagNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis MindnodeDocument1 pageVasculitis MindnodeToño VargasNo ratings yet
- Parvo BacteriaDocument2 pagesParvo BacteriaErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDNo ratings yet
- ID Bug chart-DKDocument92 pagesID Bug chart-DKNeil M D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGYDocument36 pagesHEMATOLOGYMA. ANDREA NICOLE BITOINNo ratings yet
- Poliomyelitis Haemophilus Influenzae Type B VariecellaDocument4 pagesPoliomyelitis Haemophilus Influenzae Type B VariecellaJeanna Chong100% (1)
- Staph, Strep Bacillus Clostridium Neisseria Pleiomorphic Enterobact-EriceaeDocument2 pagesStaph, Strep Bacillus Clostridium Neisseria Pleiomorphic Enterobact-Ericeaelola100% (1)
- Antivirals, Rubella, Peecorna VIRUSDocument3 pagesAntivirals, Rubella, Peecorna VIRUSErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Central Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesExamination of The Central Nervous Systemkenners100% (13)
- Elbow AnatomyDocument2 pagesElbow Anatomyapi-195986134No ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument2 pagesLeukemiaAyeshaArifNo ratings yet
- Drugs For BacteriaDocument4 pagesDrugs For BacteriaShabd SANo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Chart For MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesAntibiotics Chart For MicrobiologyTrevorNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument1 pageRespiratory Tract InfectionsShannon RamsumairNo ratings yet
- Pathogens That Involve The Respiratory TractDocument28 pagesPathogens That Involve The Respiratory TractLeeShauran100% (2)
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument41 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingPagarigan VianNo ratings yet
- MicrobesDocument12 pagesMicrobesDiMa MarshNo ratings yet
- Phrases Clauses and SentencesDocument15 pagesPhrases Clauses and SentencesAnanto Arya FahresyNo ratings yet
- English Assignment 2Document7 pagesEnglish Assignment 2Zeuss MohamedNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Effects of Thai Medicinal Plants On Human Lymphocyte Activity PDFDocument8 pagesIn Vitro Effects of Thai Medicinal Plants On Human Lymphocyte Activity PDFmadelineNo ratings yet
- Motivation Theories Description and CriticismDocument14 pagesMotivation Theories Description and CriticismAhmed Elgazzar89% (18)
- DILO C-1054-01 - Concept For The Reuse of SF6Document9 pagesDILO C-1054-01 - Concept For The Reuse of SF6Técnica Fase, S.A.No ratings yet
- PerDev Finals ReviewerDocument10 pagesPerDev Finals ReviewerPedro HampaslupaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Principles of AnalysisDocument13 pagesLecture 6 - Principles of AnalysisSUKH SIDHUNo ratings yet
- MBS 3000 Pressure TransmitterDocument4 pagesMBS 3000 Pressure Transmitterganesamoorthy1987No ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocument11 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Product and Company Identificationsriatul2006No ratings yet
- Zentel 400mg PIDocument4 pagesZentel 400mg PIVikas Thakur100% (1)
- Chapter 2 FluidDocument29 pagesChapter 2 FluidLeonard TanNo ratings yet
- Walk Up Complaint - Pacific Embryo LitigationDocument14 pagesWalk Up Complaint - Pacific Embryo LitigationBrianNo ratings yet
- The Metallurgy and Processing Science of Metal Additive Manufacturing PDFDocument47 pagesThe Metallurgy and Processing Science of Metal Additive Manufacturing PDFGautam RanganNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Dissertation ExamplesDocument5 pagesMidwifery Dissertation ExamplesWriteMyPaperCheapSiouxFalls100% (1)
- HP Bleed Valve FaultDocument9 pagesHP Bleed Valve FaultSuman BajracharyaNo ratings yet
- Field Welding of Casing To WellheadsDocument2 pagesField Welding of Casing To Wellheadsabrar100% (2)
- ReviewerDocument14 pagesReviewerSK SchreaveNo ratings yet
- Specific Gravity of Soil SolidsDocument7 pagesSpecific Gravity of Soil SolidsChristian CabacunganNo ratings yet
- Occidental Mindoro-sec-Agri Fishery ArtsDocument4 pagesOccidental Mindoro-sec-Agri Fishery ArtsPRC BoardNo ratings yet
- Kravitz Et Al (2010)Document5 pagesKravitz Et Al (2010)hsayNo ratings yet
- 10 2020 Lose For Life Kickstart GuideDocument28 pages10 2020 Lose For Life Kickstart GuideLorraine CardonaNo ratings yet
- Reading Derby AccomplishmentDocument28 pagesReading Derby Accomplishmenthoney beeNo ratings yet
- MBT-Term Test 1Document45 pagesMBT-Term Test 1lkokodkodNo ratings yet
- Gly. CarbonateDocument5 pagesGly. Carbonate13201940No ratings yet
- LSBM - Fellows 27th Dec 2022 2 PDFDocument2 pagesLSBM - Fellows 27th Dec 2022 2 PDFMullai Kodi KNo ratings yet
- 100 General Knowledge Question of Different PapersDocument26 pages100 General Knowledge Question of Different PapersAli HusnainNo ratings yet
- Preservatin of Spare and EquipmentsDocument38 pagesPreservatin of Spare and EquipmentsSamNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa InggrisDocument8 pagesSoal Bahasa InggrisMuna ShufiyaNo ratings yet
- Watch Jay ShettyDocument2 pagesWatch Jay ShettyRica Angelyn AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Vikram Tea Case StudyDocument2 pagesVikram Tea Case StudyAlberto Del RioNo ratings yet