Professional Documents
Culture Documents
60 Years of Transistor22
60 Years of Transistor22
Uploaded by
wayneCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
60 Years of Transistor22
60 Years of Transistor22
Uploaded by
wayneCopyright:
Available Formats
60 YEARS OF THE TRANSISTOR: 1947 2007
1947 When it comes to
helping jumpstart innovation
and technology, no invention is
more important than the
transistor created 60 years ago
at Bell Labs.
The Revolution Begins
Invented 60 years ago, the transistor is a key
building block of todays digital world.
Perhaps the most important invention of the
20th century, transistors are found in many
devices and are the building blocks of
computer chips. Intel, the largest manufacturer of computer chips, continues to innovate
to help PCs and laptops become smaller,
faster, sleeker and more energy-efficient.
Many new applications and inventions
powered by transistors have impacted all of
our lives over the past 60 years.
1976 An operator in an early
bunnysuit shows how a 4-inch
wafer is prepared for a positive
acid spin.
1960 Sony introduces the first
portable, transistorized TV, the
TV8-301. It has a modest 5-inch
screen and uses 23 silicon and
germanium transistors.
1981 The Intel 8088
microprocessor was selected to
power the IBM PC.
1965 Moores Law, which states that the
number of transistors on a chip doubles about
every two years, is born when Intels Gordon
Moore made a prediction about the
semiconductor business that still holds true
today.
1953 The first commercial device
to make use of the transistor is put
on the market the Sonotone 1010
hearing aid.
1983 Mobile communication
changes forever when
Motorola introduces the first
commercial mobile phone
the DynaTAC 800X powered
by transistors and costing a
mere $3,995.
1972 Intels first microprocessor,
powered the Busicom calculator
and paved the way for the
personal computer.
2000 Silicon Valley based company develops
TiVo - a device that records TV programs on an
internal hard drive.
1947
1971 Busicom introduces the
first single-chip, pocket-size
calculator, the LE-120A "HANDY,"
which uses a MOSTEK MK6010
integrated circuit.
1950
2003 Intel Centrino mobile
technology brought high performance,
enhanced battery life, and integrated
WLAN capability to thinner, lighter PCs.
1982 Intel launches their new high
performance, 16-bit 80286
microprocessor featuring 134,000
transistors.
1960
Intel continues to deliver on the promise
of Moores Law with the introduction
of powerful multi-core technologies,
transforming the way we live, work and
play once again.
2007 45nm Intel debuts the Penryn chip the biggest
change to transistors (all 820 million of them in our
quad-core processors) in 40 years based on the companys
45 nanometer transistor technology. More than 2,000
45nm transistors fit across the width of a human hair.
1993 With the creation of the World
Wide Web in 1990, the need for transistor
speed becomes greater than ever.
1975 The Altair 8800
microcomputer, based on the Intel
8080 microprocessor, was the first
successful home or personal
computer.
The Revolution Continues
2006 The dual core Intel Itanium 2
processor launches with the worlds most
intricate product design to date, utilizing
more than 1.72 billion transistors.
1981 IBM introduces the first
personal computer with an Intel
8088 processor serving as the
brains behind the computer.
1971 Intel launches its first
microprocessor, the 4004, containing
just over 2,000 transistors.
1954 The first transistor radio, the Regency
TR-1, goes on the market for just $49.99. The
radio contains just four transistors.
2005 Dual-core technology
was introduced.
2000 The 42-million transistor debuts. If
automobile speed increased similarly over
that same period, you could drive from New
York City to San Francisco in 13 seconds.
1982 Within six years of its release, an
estimated 15 million 286-based
personal computers were installed
around the world.
1993 The World Wide Web
debuts and Intel responds with
its Pentium processor, boasting
speeds of 66 and 60 MHz 3.1
million transistors.
1970
1980
1990
2007 In the second half of 2007, Intel began
production of the next generation Intel Core2 and
Xeon processor families based on 45-nanometer
(nm) Hi-k metal gate silicon technology.
2000
2007
Moores Law
In 1965, Intel co-founder Gordon Moore predicted that
the number of transistors on a chip would double about
every two years. Since then, Moores Law has fueled a
technology revolution as Intel has exponentially increased
the number of transistors integrated into its processors
for greater performance and energy efficiency.
Note: Number of transistors is an approximate number.
Intel 4004 processor
Introduced 1971
Initial clock speed
Intel 8008 processor
Introduced 1972
Initial clock speed
Intel 8080 processor
Introduced 1974
Initial clock speed
Intel 8086 processor
Introduced 1978
Initial clock speed
108 KHz
2,300
10
500-800 KHz
3,500
10
2 MHz
4,500
6
5 MHz
29,000
3
The groundbreaking Intel 4004
processor was introduced with
the same computing power
as ENIAC.
The Intel 8008 processor was
twice as powerful as the Intel
4004 processor.
The Intel 8080 processor made
video games and home
computers possible.
The Intel 8086 processor was the
first 16 bit processor and delivered
about ten times the performance
of its predecessors.
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
Intel 8088 processor
Introduced 1979
Initial clock speed
5 MHz
29,000
3
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
A pivotal sale to IBM's new personal
computer division made the Intel
8088 processor the brains of IBM's
new hit product--the IBM PC.
Intel 286 processor
Introduced 1982
Initial clock speed
6 MHz
134,000
1.5
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
The Intel 286 was the first
Intel processor that could
run all the software written
for its predecessor.
Intel386 processor
Introduced 1985
Initial clock speed
16 MHz
275,000
1.5
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
The Intel386 processor could run multiple
software programs at once and featured
275,000 transistorsmore than 100 times
as many as the original Intel 4004.
Intel486 processor
Introduced 1989
Initial clock speed
Intel Pentium processor
Introduced 1993
Initial clock speed
25 MHz
1,200,000
1
66 MHz
3,100,000
0.8
The Intel486 introduced the integrated
floating point unit. This generation of
computers really allowed users to go from a
command level computer into point and
click computing.
The Intel Pentium processor, executing
112 million commands per second, allowed
computers to more easily incorporate "real
world" data such as speech, sound,
handwriting and photographic images.
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
Intel Pentium Pro processor
Introduced 1995
Initial clock speed
200 MHz
5,500,000
0.6
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
The Pentium Pro processor delivered
more performance than previous
generation processors through an
innovation called Dynamic Execution.
This made possible the advanced 3D
visualization and interactive capabilities.
Intel Pentium II processor
Intel Pentium II Xeon processor
Introduced 1997
Initial clock speed
300 MHz
7,500,000
0.25
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
The Intel Pentium II processors significant
performance improvement over previous
Intel-Architecture processors was based on the
seamless combination of the P6
microarchitecture and Intel MMX media
enhancement technology.
Intel Pentium III processor
Intel Pentium III Xeon processor
Introduced 1999
Initial clock speed
500 MHz
9,500,000
0.18
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
The Intel Pentium III processor executed
Internet Streaming SIMD Extensions,
extended the concept of processor
identification and utilized multiple
low-power states to conserve power
during idle times.
Intel Pentium 4 processor
Introduced 2000
Intel Xeon processor
Introduced 2001
Initial clock speed
1.5 GHz
42,000,000
0.18
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
The Intel Pentium 4 processor
ushers in the advent of the
nanotechnology age.
Intel Pentium M processor
Introduced - 2002
Initial Clock Speed
1.7 GHz
55,000,000
90nm
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
The Intel Pentium M processor, the Intel
855 chipset family, and the Intel
PRO/Wireless 2100 network connection are
the three components of Intel Centrino
processor technology. Intel Centrino
processor technology was designed
specifically for portable computing.
Intel Itanium 2 processor
Introduced 2002
Initial clock speed
1 GHz
220,000,000
0.13
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
The Intel Itanium 2 processor is the successor
of the first Itanium processor.
The architecture is based on Explicitly Parallel
Instruction Computing (EPIC). It is theoretically
capable of performing roughly eight times
more work per clock cycle than other CISC and
RISC architectures.
Intel Pentium D processor
Introduced 2005
Initial clock speed
3.2 GHz
291,000,000
65nm
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
The Intel Pentium D processor features the
first desktop duel-core design with two
complete processor cores, that each run at
the same speed, in one physical package.
Intel Core 2 Duo processor
Intel Core2 Extreme processor
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor
Introduced 2006
Initial clock speed
2.93 GHz
291,000,000
65nm
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
Intel Core2 Duo processor optimizes
mobile microarchitecture of the Intel
Pentium M processor and enhanced it
with many microarchitecture innovations.
Intel Centrino Pro and Intel vPro
processor technology provide excellent
performance from the Dual-Core Intel
Core2 Duo processor.
Dual-Core Intel Itanium 2 processor 9000 series
Introduced 2006
Initial clock speed
1.66 GHz
1,720,000,000
90nm
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
Dual-Core Intel Itanium 2 processor 9000 series
outperforms the earlier, single-core version of the
Itanium 2 processors. With more than 1.7 billion
transistors and with two execution cores, these
processors double the performance of previous
Itanium processors while reducing average power
consumption.
Quad-Core Intel Xeon processor
Quad-Core Intel Core2 Extreme processor
Introduced 2006
Intel Core2 Quad processors
Introduced 2007
Initial clock speed
2.66 GHz
582,000,000
65nm
Number of transistors
Manufacturing technology
The unprecedented performance of the Intel
Core2 Quad processor is made possible by each
of the four complete execution cores delivering
the full power of Intel Core microarchitecture.
The Quad-Core Intel Xeon processor provides
50 percent greater performance than industryleading Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor in the
same power envelope. The quad-core-based
servers enable more applications to run with a
smaller footprint.
Quad-Core Intel Xeon processor (Penryn)
Dual-Core Intel Xeon processor (Penryn)
Quad-Core Intel Core2 Extreme processor (Penryn)
Introduced 2007
Initial clock speed
> 3 GHz
820,000,000
45nm
45nm
Number of transistors
Manufacturing Technology
Manufacturing technology
Intels next generation Intel Core2 processor
family, codenamed "Penryn", contains
industry-leading microarchitecture
enhancements. Further, new SSE4 instructions
for improved video, imaging, and 3D content
performance and new power management
features will extend Penryn processor family
leadership in performance and energy efficiency.
You might also like
- Neo-Narcissism: Ra Uru HuDocument23 pagesNeo-Narcissism: Ra Uru HuZoia Zarnescu100% (7)
- Similarities Between Islam and ChristianityDocument34 pagesSimilarities Between Islam and ChristianitySyahirah Kaja MohideenNo ratings yet
- Running the World's Markets: The Governance of Financial InfrastructureFrom EverandRunning the World's Markets: The Governance of Financial InfrastructureNo ratings yet
- Suresh IAS Academy NotesDocument176 pagesSuresh IAS Academy NotesMohamed Harun92% (12)
- (PDF) Vibrations and Waves Full Books: Book DetailsDocument1 page(PDF) Vibrations and Waves Full Books: Book DetailsKostuv SoniNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument59 pages3 PDFPushpam0% (1)
- Handbook of Thermodynamic Diagrams Volume 3 PDFDocument407 pagesHandbook of Thermodynamic Diagrams Volume 3 PDFcyclon2010No ratings yet
- Astm E72Document11 pagesAstm E72filigrana2012No ratings yet
- AW139 EASA Operational Evaluation Board Report Rev 4 - 15 - 10 - 2012 AWTAx PDFDocument30 pagesAW139 EASA Operational Evaluation Board Report Rev 4 - 15 - 10 - 2012 AWTAx PDF060533No ratings yet
- Research Paper On BambooDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Bamboo01shubhamupadhyayNo ratings yet
- William K. Jones - Insult To Injury - Libel, Slander, and Invasions of Privacy-University Press of Colorado (2003)Document402 pagesWilliam K. Jones - Insult To Injury - Libel, Slander, and Invasions of Privacy-University Press of Colorado (2003)Emilia AvisNo ratings yet
- Pushing The Point - ShiatsuDocument59 pagesPushing The Point - ShiatsuTheMothershipNo ratings yet
- Familiar Talks on Science—World-Building and Life. Earth, Air and Water.From EverandFamiliar Talks on Science—World-Building and Life. Earth, Air and Water.No ratings yet
- Memorization TechniquesDocument2 pagesMemorization TechniqueslacojuniorNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow Analysis To Investigate Youth PitchingDocument9 pagesEnergy Flow Analysis To Investigate Youth Pitchingsilvio da costa guerreiroNo ratings yet
- Brick Work Revised On 12.09.2018: Third Floor Plan (Lvl. +44'-6")Document1 pageBrick Work Revised On 12.09.2018: Third Floor Plan (Lvl. +44'-6")sai associatesNo ratings yet
- Oil InterceptorDocument3 pagesOil InterceptorOkudetum RaphealNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument1 pageNotesassis alihNo ratings yet
- The Schur Algorithm: Digtal Signal Processing (Et 4235)Document22 pagesThe Schur Algorithm: Digtal Signal Processing (Et 4235)KrishNo ratings yet
- Trial PlotDocument1 pageTrial PlotArmand Mikhail TempladoNo ratings yet
- First Alert Carbon Monoxide CO710 ManualDocument2 pagesFirst Alert Carbon Monoxide CO710 Manualstephenson1975No ratings yet
- G3306 Generator Set Electrical System: Control Panel (Emcpii+)Document2 pagesG3306 Generator Set Electrical System: Control Panel (Emcpii+)Mr.Thawatchai hansuwanNo ratings yet
- Cat Dcs Sis ControllerDocument2 pagesCat Dcs Sis ControllerЮрий Шариков100% (5)
- Sunpower Performance Series 1500 Volt - P17Document2 pagesSunpower Performance Series 1500 Volt - P17sudarsan kingNo ratings yet
- DR.M Rafat Ka Tassure IlmDocument5 pagesDR.M Rafat Ka Tassure IlmMuhammad GhitreefNo ratings yet
- AC Oct 2011Document92 pagesAC Oct 2011Bogdanovici Barbu100% (2)
- Bat DWG DD PR 01 WW 2201 r1 WWTP Piping LayoutDocument1 pageBat DWG DD PR 01 WW 2201 r1 WWTP Piping LayoutBfboys EdissonNo ratings yet
- Pages From PTS-21EN1004 - Final - Part 2 of 2 910-930Document21 pagesPages From PTS-21EN1004 - Final - Part 2 of 2 910-930Saim KhanNo ratings yet
- Tender: Foyer Level PlanDocument4 pagesTender: Foyer Level PlanMohammad HaddadNo ratings yet
- SunPower P19 Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesSunPower P19 Product Data SheetUrfan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Pop 44860 106 - Rev1Document2 pagesPop 44860 106 - Rev1Muhammad NURMANNo ratings yet
- Revisions: Research in MotionDocument2 pagesRevisions: Research in Motionzulkafli othmanNo ratings yet
- Sobha Hartland Greens - Phase 02: InvestmentsDocument1 pageSobha Hartland Greens - Phase 02: InvestmentsrajatNo ratings yet
- Cartas Iquique y Pozo Almonte, 1:100.000, Región de Tarapacá, ChileDocument2 pagesCartas Iquique y Pozo Almonte, 1:100.000, Región de Tarapacá, Chilekrs2ballNo ratings yet
- Camana: Cuadro de MetradosDocument1 pageCamana: Cuadro de MetradosJohann Nick Flores AparicioNo ratings yet
- Distribution Board Internal Wiring-ModelDocument1 pageDistribution Board Internal Wiring-ModelGarlapati TrinadhNo ratings yet
- Dif340560 Dif340560Document9 pagesDif340560 Dif340560colasNo ratings yet
- Prelude 3Document1 pagePrelude 3Ovidiu IlocNo ratings yet
- ThedarkDocument2 pagesThedarkmaritozzi80No ratings yet
- dr-100 Setting Out Plan Drainage Layout1504791865707Document1 pagedr-100 Setting Out Plan Drainage Layout1504791865707Eng. Moutaz ChabanNo ratings yet
- Binghati Powr Coordination DrawingDocument1 pageBinghati Powr Coordination Drawingzafrikhan875No ratings yet
- Thiết Kế Kỹ Thuật: Lt Distribution Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageThiết Kế Kỹ Thuật: Lt Distribution Schematic DiagramAn BuiNo ratings yet
- Prelude 1Document1 pagePrelude 1Ovidiu IlocNo ratings yet
- Catálogo Catalogue 2021/22: Single BooksDocument46 pagesCatálogo Catalogue 2021/22: Single BooksJaime Alexander Diaz HernandezNo ratings yet
- Ea-679629 001 0000Document1 pageEa-679629 001 0000engrabbas75No ratings yet
- FolkformbassDocument7 pagesFolkformbassGiorgio FioriniNo ratings yet
- Disdainus Maximus WebpageDocument1 pageDisdainus Maximus WebpageMichael WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Disdainus Maximus Webpage PDFDocument1 pageDisdainus Maximus Webpage PDFDyanasthasiaNo ratings yet
- Diptico FinalDocument2 pagesDiptico Finalfaperador9753No ratings yet
- DLF BHHK D B3 Z1 2001Document1 pageDLF BHHK D B3 Z1 2001praveenNo ratings yet
- MOM Fortis, Kalyan 10.08.2022Document1 pageMOM Fortis, Kalyan 10.08.2022Mohd MustaqNo ratings yet
- 7 Conditions of La Ilaha IllalahDocument6 pages7 Conditions of La Ilaha Illalah619254No ratings yet
- Ugly Beauty: Transcribed by Dave FinkDocument4 pagesUgly Beauty: Transcribed by Dave FinkMPNo ratings yet
- Japanese Zone Neemrana LayoutDocument1 pageJapanese Zone Neemrana Layoutajay singhNo ratings yet
- SuryasathakamDocument180 pagesSuryasathakamsvsNo ratings yet
- Heredity-Evolution Part 01 and 02Document2 pagesHeredity-Evolution Part 01 and 02bathri091No ratings yet
- Mate ComprobanteDocument375 pagesMate ComprobanteNatalia ArroyaveNo ratings yet
- Psion VH10 Vehicle-Mount ComputerDocument166 pagesPsion VH10 Vehicle-Mount ComputerFrancisco GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- P1 P2 P3 A1 A2: (SCALE - Vertical: Horizontal (10:1)Document1 pageP1 P2 P3 A1 A2: (SCALE - Vertical: Horizontal (10:1)Chetan SontakkeNo ratings yet
- 81 Grundfos Serija 100 UpupsDocument116 pages81 Grundfos Serija 100 UpupsTrajce TefovNo ratings yet
- Flow Sheet Post MC O2 Wash Press 1552018Document1 pageFlow Sheet Post MC O2 Wash Press 1552018SabariyantoNo ratings yet
- UNESCO - Activity 554 46Document2 pagesUNESCO - Activity 554 46Ramius HamdaniNo ratings yet
- C++ Faq - The Definitive C++ Book Guide and List - Stack OverflowDocument18 pagesC++ Faq - The Definitive C++ Book Guide and List - Stack OverflowalfredNo ratings yet
- Tarot Card Meanings (A Quick Reference Guide)Document19 pagesTarot Card Meanings (A Quick Reference Guide)alfred100% (2)
- LanguageDocument55 pagesLanguagealfredNo ratings yet
- Comparative Politics 1 POL1010Document27 pagesComparative Politics 1 POL1010alfredNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief and Anti-Cavitation Valves (Cartridge Type) For Mobile ApplicationsDocument12 pagesPressure Relief and Anti-Cavitation Valves (Cartridge Type) For Mobile ApplicationsOleg080No ratings yet
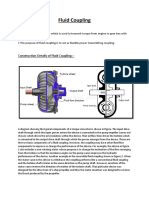
- Construction Details of Fluid CouplingDocument4 pagesConstruction Details of Fluid CouplingSagar Patil100% (1)
- Portafolio HPDocument2 pagesPortafolio HPgfdfgfdgNo ratings yet
- Impak HV Ind MotorDocument30 pagesImpak HV Ind MotorhashimNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Chemistry PT 2 Paper 2Document7 pagesGrade 9 Chemistry PT 2 Paper 2Naisha ParekhNo ratings yet
- Marvella RO User ManualDocument35 pagesMarvella RO User ManualPrashant MalveNo ratings yet
- READMEDocument2 pagesREADMEWongRongJingNo ratings yet
- Toll Free (800) 445-4155 - Fax (631) 348-7160Document100 pagesToll Free (800) 445-4155 - Fax (631) 348-7160Jorge Luis Galezo MuñozNo ratings yet
- Securing Personal Health Records in Cloud Using Attribute Based EncryptionDocument3 pagesSecuring Personal Health Records in Cloud Using Attribute Based EncryptionmrunneeNo ratings yet
- HTML TablesDocument7 pagesHTML Tablesmamcapiral25100% (1)
- CupolaDocument5 pagesCupolaRajan Goyal100% (2)
- (Vol VII), 2021 Rules For Small Vessels Up To 24 M, 2021Document261 pages(Vol VII), 2021 Rules For Small Vessels Up To 24 M, 2021Rahmat IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Force-L2 Operation Manual: Lithium-Ion Phosphate Energy Storage SystemDocument35 pagesForce-L2 Operation Manual: Lithium-Ion Phosphate Energy Storage SystemMarco Antonio Gutierrez DuranNo ratings yet
- UPS Fundamentals HandbookDocument48 pagesUPS Fundamentals Handbookmikelb5No ratings yet
- Compair Fluid Force 4000 IndonesiaDocument3 pagesCompair Fluid Force 4000 Indonesiaindolube75% (4)
- Installing and Configuring Provisioning ServicesDocument42 pagesInstalling and Configuring Provisioning ServiceschinnaphaniNo ratings yet
- Computational Aerodynamic Analysis of A Rear Spoiler On A Car in Two DimensionsDocument2 pagesComputational Aerodynamic Analysis of A Rear Spoiler On A Car in Two DimensionsDang Tien PhucNo ratings yet
- ICMIE 2015 ProgramDocument7 pagesICMIE 2015 ProgramCristian CarpNo ratings yet
- Functional Graded PlatesDocument19 pagesFunctional Graded PlatesaluruvamsiNo ratings yet
- ST-510 Manual ENDocument19 pagesST-510 Manual ENNazeer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Traffic Signa and Hazards Markers: Roadwork AheadDocument1 pageTraffic Signa and Hazards Markers: Roadwork AheadabigailNo ratings yet
- SPRING 2015 CDA 3101 Homework 3: Date-Assigned: Mar 27th, 2015 Due Dates: 11:55pm, April 7th, 2015Document5 pagesSPRING 2015 CDA 3101 Homework 3: Date-Assigned: Mar 27th, 2015 Due Dates: 11:55pm, April 7th, 2015ayylmao kekNo ratings yet
- Radiography Testing Level I and IIDocument16 pagesRadiography Testing Level I and IIJoshnewfoundNo ratings yet
- Finished Product Inspection ReportDocument1 pageFinished Product Inspection ReportJohn Carlos Moralidad CriticaNo ratings yet
- Rovetta PDFDocument53 pagesRovetta PDFJindaNo ratings yet