Professional Documents
Culture Documents
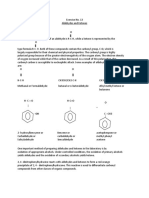
Tests For Organic Substances
Tests For Organic Substances
Uploaded by
KarenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tests For Organic Substances
Tests For Organic Substances
Uploaded by
KarenCopyright:
Available Formats
Tests for organic substances
Use the Simple test for organic substances found on the EdExcel Practical Chemistry 2008 CD-ROM on the school
intranet to complete the table below.
http://intranet/cdroms/chemistryedexcel2008/simple_tests_for_organic.htm
Substance
Test
Result if positive
Explanation of
result
White fumes seem which
turn damp blue litmus
red
HCl gas released
OH groups
Add PCl5
Primary and
secondary alcohols
Add acidified potassium
dichromate(VI) and warm
gently
Solution turns from
orange to blue/green
Orange Cr2O72- ions
are reduced to green
Cr3+ ions
Tertiary alcohols
Add acidified potassium
dichromate(VI) and warm
gently
No colour change
Tertiary alcohols
cannot be oxidised
Alkenes
1. Add bromine water
2. Add acidified potassium
manganate(VII)
1. Turns from orange to
colourless
2. Turns from purple to
colourless
Addition reactions
occur across double
bond
Add Bradys reagent (or 2,4
DNP)
Orange or yellow ppt
seen with aldehydes and
ketones
Distinguishing
between aldehydes
and ketones
Add Benedicts reagent or
Fehlings solution and warm
Aldehydes are
Brick red ppt seen with
reducing agents
aldehydes; no change for
whereas ketones are
ketones
not
Carboxylic acid
Add sodium carbonate
solution
Effervescence
Acids react with
carbonates to
release CO2 gas
Halogenoalkanes
0.5 cm3 of suspected
halogenoalkane is added to a test
tube, followed by 1 cm3 of
ethanol and 1 cm3 of sodium
hydroxide solution. The tube is
heated in a boiling water bath
for a few minutes. Dilute nitric
acid is added until the mixture is
acidic then a few drops of 0.02 M
silver nitrate solution is added.
A precipitate is formed,
the colour of which can
be used to identify the
halogen present.
White ppt = chlorine
Cream ppt = bromine
Yellow ppt= iodine
Substitution reaction
takes place where
OH- replaces halogen
to release a halide
ion. Halide ion then
tested for in usual
way.
Carbonyl, C=O
In A2 course
You might also like
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- James Ruse 2009 Chemistry Trials & SolutionsDocument56 pagesJames Ruse 2009 Chemistry Trials & SolutionsHenry JenkinsNo ratings yet
- A Facile Synthesis of Alkyl Substituted Maleic Anhydrides Radical ApproachDocument4 pagesA Facile Synthesis of Alkyl Substituted Maleic Anhydrides Radical ApproachShaik SameerNo ratings yet
- The Systematic Identification of Organic Compound, PDFDocument135 pagesThe Systematic Identification of Organic Compound, PDFriniteke100% (5)
- Hem Actsheet: Organic Chemistry 4: Carbonyl CompoundsDocument3 pagesHem Actsheet: Organic Chemistry 4: Carbonyl CompoundsDaniel C. WalshNo ratings yet
- Sodium and Potassium Chlorate The Complete Guide v1.0 PDFDocument7 pagesSodium and Potassium Chlorate The Complete Guide v1.0 PDFDavid MartinNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument4 pagesAldehydes and KetonesAnonymous GO6JVW9Wud50% (2)
- Biochemical Test of BacteriaDocument33 pagesBiochemical Test of BacteriaGuna SheelaNo ratings yet
- Classification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsDocument5 pagesClassification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsAcener Padua100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Lab Report (Final Editied)Document8 pagesLab Report (Final Editied)Alexia Channer100% (4)
- AS-Level Chemistry Unit:3 NotesDocument14 pagesAS-Level Chemistry Unit:3 NotesMehreenSaeedNo ratings yet
- 12Document6 pages12NathaLie Sta ElenaNo ratings yet
- Pre Laboratory AssignmentDocument44 pagesPre Laboratory AssignmentJr Montero100% (3)
- P&D AlcoholsDocument5 pagesP&D AlcoholsBrandon RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8Document85 pagesExperiment 8Are-nim Hanim100% (1)
- Chem-No.-13 2Document5 pagesChem-No.-13 2ho laNo ratings yet
- Files-3-Lecture Notes CHEM-303 (Classification Tests)Document56 pagesFiles-3-Lecture Notes CHEM-303 (Classification Tests)mmiliyasNo ratings yet
- C C C C C C CCC: CCC C C CCCCCCCC C C CCCC CCCCC CC CCC CC C CCC CCC CC CCCCC C CCC C CCCC CCC C CCCCCC CDocument5 pagesC C C C C C CCC: CCC C C CCCCCCCC C C CCCC CCCCC CC CCC CC C CCC CCC CC CCCCC C CCC C CCCC CCC C CCCCCC CShan TiNo ratings yet
- I. Tittle: Aldehyde and Ketone II. Date of Experiment: 13th Mart 2013 Iii. PurposeDocument27 pagesI. Tittle: Aldehyde and Ketone II. Date of Experiment: 13th Mart 2013 Iii. PurposeNurel HidayahNo ratings yet
- Qualitative TestDocument4 pagesQualitative TestSwati KaushalNo ratings yet
- Praktikum#5 Dan 6Document34 pagesPraktikum#5 Dan 6Nur BillahNo ratings yet
- Idk PDFDocument25 pagesIdk PDFNael NomanNo ratings yet
- Poc One Shot Bounce BackDocument123 pagesPoc One Shot Bounce BackCOOLTEX YTNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Chelatometric Analysis of The Complex For Cobalt Using EDTADocument6 pagesExperiment 8 Chelatometric Analysis of The Complex For Cobalt Using EDTAJosef HiltonNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry Carbonyl CompoundDocument50 pagesMatriculation Chemistry Carbonyl Compoundiki292100% (1)
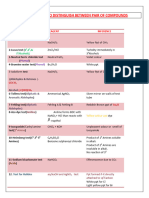
- Chemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of CompoundsDocument5 pagesChemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of CompoundsHarshwardhan100% (1)
- Aldehydes and Ketones: ResultsDocument7 pagesAldehydes and Ketones: ResultsStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols NotesDocument4 pagesAlcohols Notesjohn mNo ratings yet
- The Cerric Nitrate Test: Shows Positive Test ForDocument9 pagesThe Cerric Nitrate Test: Shows Positive Test ForPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDocument44 pagesReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- 2 5352688982180245339Document11 pages2 5352688982180245339حسين محمد مطرود كاظمNo ratings yet
- Organic Qualitative Analysis Aldehydes and KetonesDocument4 pagesOrganic Qualitative Analysis Aldehydes and KetonesNitty MeYa50% (2)
- School of Applied Natural SciencesDocument4 pagesSchool of Applied Natural Sciencesvk100No ratings yet
- Chemical Tests For UnknownsDocument5 pagesChemical Tests For UnknownsKogulan SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Kimling Percobaan Penentuan CLDocument8 pagesKimling Percobaan Penentuan CLRinda As EtaNo ratings yet
- Distiguishing Tests For Pairs of Organic CompoundsDocument7 pagesDistiguishing Tests For Pairs of Organic CompoundsParam SoniNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Chemistry June 2014 Unit-5 Question PaperDocument32 pagesEdexcel IAL Chemistry June 2014 Unit-5 Question PaperAvrinox100% (1)
- CC2 SM Mod 2Document44 pagesCC2 SM Mod 2leahanne141No ratings yet
- Chemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of CompoundsDocument5 pagesChemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of CompoundsIshika Singh100% (2)
- Laboratory Manual CHE102 Chemistry LabDocument41 pagesLaboratory Manual CHE102 Chemistry LabSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- 9701 s12 QP 11 PDFDocument16 pages9701 s12 QP 11 PDFpaanarNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 5: Chemical EquationsDocument3 pagesLecture # 5: Chemical Equationsdanena88No ratings yet
- 31 E23 D 01Document5 pages31 E23 D 01Alou JacintoNo ratings yet
- 4.5 NotesDocument30 pages4.5 NotesMaria OnisorNo ratings yet
- Organic Reactions SummaryDocument3 pagesOrganic Reactions SummaryChun Min ChiaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 9E Ethanol Assay by Dichromate Colorimetric MethodDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 9E Ethanol Assay by Dichromate Colorimetric MethodRachel HechanovaNo ratings yet
- WCH02 01 Que 20150602Document24 pagesWCH02 01 Que 20150602ALorenso SAmNo ratings yet
- 5070 w04 QP 1Document16 pages5070 w04 QP 1mstudy123456No ratings yet
- upload-WCH05 01 Que 201506151446484865Document28 pagesupload-WCH05 01 Que 201506151446484865Sadaf ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 9701 s12 QP 11 PDFDocument16 pages9701 s12 QP 11 PDFHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Full ProjectDocument67 pagesFull ProjectkavilankuttyNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and AlkenesDocument36 pagesAlkanes and AlkenesDaisyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PracticalDocument38 pagesChemistry PracticalMukhtar MalikNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemical Tests (A2)Document3 pagesOrganic Chemical Tests (A2)Kevin The Chemistry TutorNo ratings yet
- Rashid Kanetsa - Organic PracDocument4 pagesRashid Kanetsa - Organic PracRashid KanetsaNo ratings yet