Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Miller Practical Experiment, Peterson and Peterson Practical Experiment, Conrad Practical Experiment
Uploaded by
lloyd evansOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Miller Practical Experiment, Peterson and Peterson Practical Experiment, Conrad Practical Experiment
Uploaded by
lloyd evansCopyright:
Available Formats
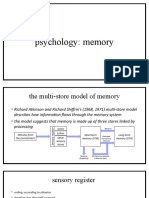
Memory: encoding, capacity and duration of STM
Miller practical experiment, Peterson and Peterson practical experiment, Conrad practical
experiment
STM
Capcity is limted 1-2 seconds
Limted duration
Acoustic codes
Miller (1956)
Magic number 7 (plus or minus 2)
The amount of slots
Didnt specify how much information could be held in each slot
If we he chunk we can hold more information
Peterson and Peterson (1959)
- lab experiment
- 24 participants `(psychology students`)
- recall trigrams
- count backwards in 3s or 4s
- recall after 3,6,9,12,15
- Findings
- Longer interval less trigrams recalled
- 80% after 3 seconds
- 10% after 18
Memory: encoding, capacity and duration of LTM, differences between STM and LTM
LTM capcity potentially unlimted
LTM-POTENIALLY unlimted
Semanctic code
LTM is usually through elaborative rehersal of STM
Memory: Multi store model of memory
Information is detected by the senory dectory and enters sensory
memory
If attended to the this enters the STM
If the information is rehersed then it can entre the LTM
Memory retrieval happens through LTM TO STM
If not rehersed or retrieved the memory is lost through
displacement or decay
Evaulaiton
-
HM SUPPORTS THIS . He lost his LTM after brain surgery , he
remeberred little or none of personal or public events in the past 45
years but LTM is still intact
The model is over simplified , this model suggests that LTM and
STM work in one uniform fashion . It has been shown in the
Working memoery model that STM is a lot more complicated and
consists of many other componenets
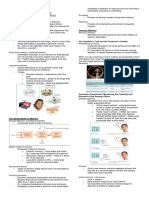
Working memory model: description (consolidation) and evaluation
Centeral executive Drive system
Allocates data to sub-syestems
Mental math and problem solving
Viso spatial stores and process information visually orr
spatially
Navigation
The phonological loop
The phonological store stores information as sound for 1-2
seconds
Articulatory Control Process
Specch production
Used to reherse and store information from the phonological store
Baddley and Hitch
Multiple parts of working memory at the
same time
Participants had to take part In 2 tasks at the
same time dual task technique
Digit span task repeat numbers and verbal
reasoning answer obvious true or false
questions
Digits increased longer by fractionsd of
seconds
No mistakes
Digit span phonologcsal loop
Verbal central
Evalaution
- KF case study
- Brain damage from bike damaged his stm
- VERBAL AFFECTED
- Visual largely unaffected
Little is known on the central so capacity and what it does can not be tested .
You might also like
- Memory SummaryDocument3 pagesMemory SummaryAnamikaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Level of AnalysisDocument46 pagesCognitive Level of AnalysisDavin Do100% (1)
- Models of MemoryDocument20 pagesModels of Memoryapi-296097282No ratings yet
- Modal Model of The Mind: Long-Term Memory Working or Short-Term Memory Sensory MemoryDocument33 pagesModal Model of The Mind: Long-Term Memory Working or Short-Term Memory Sensory MemoryDan SpitaruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - MemoryDocument22 pagesChapter 6 - Memorycammcbean100% (1)
- Questions About Learning and MemoryDocument3 pagesQuestions About Learning and MemoryPoppy HolbenNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Revision PackDocument33 pagesAQA A Level Revision PackLanya OmerNo ratings yet
- Memory Info PackDocument28 pagesMemory Info PackShaty MohamedNo ratings yet
- Psychology NotesDocument40 pagesPsychology Notessharank123100% (1)
- Cognitive PsychDocument68 pagesCognitive Psychmrjaymsu2468No ratings yet
- 1 Short Term and Working MemoryDocument46 pages1 Short Term and Working MemoryAGLDNo ratings yet
- Human CognitionDocument4 pagesHuman CognitionNurullina FajriNo ratings yet
- Memory Booklet 2015-2016Document68 pagesMemory Booklet 2015-2016api-264819644No ratings yet
- The Human: Information I/o ViaDocument36 pagesThe Human: Information I/o ViananikulfatunNo ratings yet
- Multi Store ModelDocument12 pagesMulti Store ModelShanaraBegum16474100% (4)
- Physiologi LearnDocument46 pagesPhysiologi LearnDaniel Edward Ricardo MalauNo ratings yet
- Human-Computer Interaction: Cognitive Processes - Part IDocument43 pagesHuman-Computer Interaction: Cognitive Processes - Part ISammar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Memory Exam Questions PractiseDocument11 pagesMemory Exam Questions PractiseThe Anger of RIVALSNo ratings yet
- Information - Processing Theory Atkinson & ShiffrinDocument20 pagesInformation - Processing Theory Atkinson & ShiffrinytengkuNo ratings yet
- Memory - MSM (16 Marks)Document1 pageMemory - MSM (16 Marks)AnamikaNo ratings yet
- CognitiveDocument4 pagesCognitiveBlessingNo ratings yet
- Psychology Memory RevisionDocument13 pagesPsychology Memory RevisionGeorge NoorlandNo ratings yet
- KMF1023 Module 5 Human Memory - Edited 300810Document32 pagesKMF1023 Module 5 Human Memory - Edited 300810Naqiah PuaadNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument10 pagesMemoryGrace HanhanNo ratings yet
- Memory Revision 1Document2 pagesMemory Revision 1api-219687122No ratings yet
- Chp.8 MemoriesDocument7 pagesChp.8 MemoriesEmma MahoneyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document42 pagesChapter 5tatafishcatngNo ratings yet
- Memory and Models of MemoryDocument31 pagesMemory and Models of MemoryAdesh Nidhi Tiwary100% (1)
- Information Processing ModelDocument17 pagesInformation Processing ModelRohayanti Binti YaakopNo ratings yet
- Study of Memory in Psychology: Dr. Magda Fahmy Professor of Psychiatry Suez Canal UniversityDocument137 pagesStudy of Memory in Psychology: Dr. Magda Fahmy Professor of Psychiatry Suez Canal UniversityMuhammad SufyanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes: Cognitive Approach To Undersatding BehaviourDocument38 pagesUnit 2 Notes: Cognitive Approach To Undersatding BehaviourAdvait MadanalNo ratings yet
- COGNITIVEPSYCHOLOGYNOTES23Document24 pagesCOGNITIVEPSYCHOLOGYNOTES23shristiNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument47 pagesMemoryRameen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 MemoryDocument6 pagesLesson 7 MemoryTin BautistaNo ratings yet
- IB Psych COG APCH REV SESDocument46 pagesIB Psych COG APCH REV SESNIRUPAMA G11No ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT NO4 STMDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT NO4 STMArnold SolomonNo ratings yet
- Human Memory: Atkinson-Shiffrin ModelDocument4 pagesHuman Memory: Atkinson-Shiffrin ModelNuraishah KamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Atkinson-Shiffrin Model of MemoryDocument25 pagesAtkinson-Shiffrin Model of MemoryFelicia NikeNo ratings yet
- 2.1-Memory-Multi-store-model - Psychology A Level AqaDocument14 pages2.1-Memory-Multi-store-model - Psychology A Level Aqanarjis kassamNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument24 pagesMemoryAnamikaNo ratings yet
- Class1human MemoryDocument1 pageClass1human MemoryAnonymous I78Rzn6rSNo ratings yet
- Summary Samples Exercises 1Document11 pagesSummary Samples Exercises 1Ehab HouraniNo ratings yet
- Psych148 Week 5 NotesDocument4 pagesPsych148 Week 5 NotesjaelaescalonaNo ratings yet
- Multi StoreDocument4 pagesMulti Storethe active channel try Home have vidoes every dayNo ratings yet
- 12-Interaction Design Models - Model Human Processor - Principles-31-Jul-2020Material - I - 31-Jul-2020 - Interaction - Design - ModelsDocument22 pages12-Interaction Design Models - Model Human Processor - Principles-31-Jul-2020Material - I - 31-Jul-2020 - Interaction - Design - ModelsMAHENDRANo ratings yet
- Human-Computer Interaction: Termin 3: The Human Movement, Memory, Attention, Thinking, EmotionDocument48 pagesHuman-Computer Interaction: Termin 3: The Human Movement, Memory, Attention, Thinking, EmotionviswaNo ratings yet
- MSM EssayDocument1 pageMSM EssayWilliamNo ratings yet
- Memory Encoding: Cognitive Psychology Class 7Document58 pagesMemory Encoding: Cognitive Psychology Class 7Li CarinaNo ratings yet
- Psychology Essay Notes PDFDocument1 pagePsychology Essay Notes PDFGwyneth CHUANGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 MemoryDocument63 pagesChapter 7 MemoryPDF BooksNo ratings yet
- PY1101 Lecture 4 NotesDocument11 pagesPY1101 Lecture 4 NotesSeah Fu MeiNo ratings yet
- Memory Booklet Part ONEDocument35 pagesMemory Booklet Part ONEatuna joeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 MemoryDocument67 pagesChapter 7 MemoryDemuel Dee L. BertoNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument35 pagesMemoryMuskanNo ratings yet
- Memory in PsychologyDocument35 pagesMemory in PsychologyMuskan100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Short-Term and Working MemoryDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Short-Term and Working MemoryJean GuirnaldoNo ratings yet
- Psychology 101 Chapter 7Document3 pagesPsychology 101 Chapter 7lmaoheartsNo ratings yet
- Eopm Mba Unit4 MemoryDocument28 pagesEopm Mba Unit4 Memoryshubhamlosalka.riim2325No ratings yet
- Cognitive Psych Chap 5Document6 pagesCognitive Psych Chap 5kjgitalioNo ratings yet
- WMS IvDocument12 pagesWMS IvAnaaaerobios100% (1)
- Inspirational Quotes ActivityDocument3 pagesInspirational Quotes ActivityErica Mae VistaNo ratings yet
- TH e Birth of Myth: Mihály HoppálDocument27 pagesTH e Birth of Myth: Mihály HoppáloscarNo ratings yet
- Huntington'S Disease: Update and Review Neuropsychiatric AspectsDocument20 pagesHuntington'S Disease: Update and Review Neuropsychiatric AspectsDewi NofiantiNo ratings yet
- ConsScale A Plausible Test For Machine ConsciousnessDocument9 pagesConsScale A Plausible Test For Machine ConsciousnessFiuttenNo ratings yet
- Reflection. Sleeping Brain at WorkDocument3 pagesReflection. Sleeping Brain at WorkRikki GardoceNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 - Philosophy and Values in Music EducationDocument16 pagesGROUP 3 - Philosophy and Values in Music EducationReynalyn Gozun100% (1)
- Manuscript Draft 5Document117 pagesManuscript Draft 5Jezel Ann CapitanNo ratings yet
- Advance in Cognitive TheoryDocument72 pagesAdvance in Cognitive TheoryBRAIN TRAINING CLUBNo ratings yet
- Basic IntelligenceDocument9 pagesBasic IntelligenceGiselle SigueNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Anti Stress Effects of Nardostachys Jatamansi DC Root Extract On Clinical Patients A Psycological EstimationDocument8 pagesEvaluation of Anti Stress Effects of Nardostachys Jatamansi DC Root Extract On Clinical Patients A Psycological EstimationESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and ConservaionNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Piano PracticeDocument346 pagesFundamentals of Piano Practicemtrespi100% (1)
- PBF GrammarDocument35 pagesPBF GrammarANANo ratings yet
- Research PaperrDocument28 pagesResearch PaperrJohn ManciaNo ratings yet
- Đề 33Document7 pagesĐề 33quynhmai060209No ratings yet
- Psychology IA 2Document21 pagesPsychology IA 2Saadia NomanNo ratings yet
- Dudai - The Consolidation and Transformation of Memory PDFDocument13 pagesDudai - The Consolidation and Transformation of Memory PDFCami Sánchez SalinasNo ratings yet
- Braverman Personality Type Assessment - Online TestDocument16 pagesBraverman Personality Type Assessment - Online TestKomkor GuyNo ratings yet
- Web2.0 in TchrEdDocument12 pagesWeb2.0 in TchrEdSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- The Process of Speech ComprehensionDocument5 pagesThe Process of Speech ComprehensionAnisa Safitri100% (1)
- The Application of Schema Theory in The Process of InterpretationDocument9 pagesThe Application of Schema Theory in The Process of Interpretation汪嘉楠No ratings yet
- Memory Training ManualDocument43 pagesMemory Training ManualRay Leon86% (7)
- LET Reviewer Professional Education Prof. Ed.: Foundations of Education Part 1Document90 pagesLET Reviewer Professional Education Prof. Ed.: Foundations of Education Part 1Gladys GasgaNo ratings yet
- Transient Global AmnesiaDocument3 pagesTransient Global AmnesianoNo ratings yet
- KEY STUDY - Bartlett 1932 - War of The Ghosts 4Document2 pagesKEY STUDY - Bartlett 1932 - War of The Ghosts 4Byron Rodriguez100% (8)
- 5 2021 Learning, Memory and Product PositioningDocument32 pages5 2021 Learning, Memory and Product Positioningabdulbasith amarullohNo ratings yet
- The Human Brain - Discovery Science: Watch The Video and Answer The Questions That FollowDocument2 pagesThe Human Brain - Discovery Science: Watch The Video and Answer The Questions That FollowDonna LLerandi0% (1)
- Practice Test #9: For The Toefl® Listening SectionDocument39 pagesPractice Test #9: For The Toefl® Listening SectionAngeline Mary MarchellaNo ratings yet
- Sadia Tanin ID 111 141 251 - Internship Report On Bangladesh ICT Sector & Nascenia IT LimitedDocument11 pagesSadia Tanin ID 111 141 251 - Internship Report On Bangladesh ICT Sector & Nascenia IT LimitedMahamudul HasanNo ratings yet
- PYC2602 Oct 2018Document13 pagesPYC2602 Oct 2018Anri van ZylNo ratings yet