Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Immun
Types of Immun
Uploaded by
Chiqui Lao DumanhugCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Microbiology Chapter 17 Spring 07Document3 pagesMicrobiology Chapter 17 Spring 07fallingupward312No ratings yet
- Name : .. Chapter 2 - Cell As A Unit ofDocument17 pagesName : .. Chapter 2 - Cell As A Unit ofRozaini Othman82% (28)
- Immunology PDFDocument1 pageImmunology PDFTanushree Pal0% (1)
- Classification of BacteriaDocument2 pagesClassification of BacteriaMuhammad Umer100% (1)
- Physiology of LactationDocument18 pagesPhysiology of LactationPreeti Sawant100% (2)
- Basic ImmunologyDocument57 pagesBasic ImmunologyRonalyn UgatNo ratings yet
- Immunology OverviewDocument83 pagesImmunology OverviewHARIS KKNo ratings yet
- T - Cell DifferentiationDocument24 pagesT - Cell DifferentiationAnand Prakash YadavNo ratings yet
- Humoral & Celullar ImmunityDocument60 pagesHumoral & Celullar ImmunityHaziq KamardinNo ratings yet
- BCH444 PDFDocument232 pagesBCH444 PDFYaseen Ahmad100% (1)
- Antigen (Immunogen) : Prepared By: Victor B. Perlas JR., RMTDocument25 pagesAntigen (Immunogen) : Prepared By: Victor B. Perlas JR., RMTEduardo MedinaceliNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument27 pagesBiologyAnand GNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument24 pagesAntiviral DrugsBurhan Nabi0% (1)
- ImmunityDocument44 pagesImmunityHam Za100% (1)
- Topic: Cytokine and Their Roles in The Immune Regulation: Md. Jiyaul MustafaDocument21 pagesTopic: Cytokine and Their Roles in The Immune Regulation: Md. Jiyaul MustafaAisha Siddiq100% (1)
- ANTIBODYDocument22 pagesANTIBODYapi-19916399100% (1)
- Antigen-Antibody InteractionsDocument13 pagesAntigen-Antibody Interactionsمصطفى رسول هاديNo ratings yet
- Immunity (Lecture Notes)Document5 pagesImmunity (Lecture Notes)Anisha NishanthNo ratings yet
- The Immune SystemDocument31 pagesThe Immune SystemYesiana Lilis Sugiarti100% (1)
- Antigen and Its PropertiesDocument20 pagesAntigen and Its Propertiestusharpremin92% (12)
- Vaccination: Yunus Ariyanto FKM - Univ. JemberDocument11 pagesVaccination: Yunus Ariyanto FKM - Univ. JemberDian WidyaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Cellular and Molecular Immunology Module1: IntroductionDocument32 pagesCellular and Molecular Immunology Module1: IntroductionAygul RamankulovaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic ResistanceDocument29 pagesAntibiotic ResistanceDian Aditama100% (1)
- AntigenDocument11 pagesAntigenAnushka Sharma0% (1)
- Lecture 10 AutoimmunityDocument78 pagesLecture 10 AutoimmunitytimcarasNo ratings yet
- Antigen Presenting CellDocument26 pagesAntigen Presenting CellSurja DasNo ratings yet
- Innate Immunity: Dr. Prasanna Honnavar, PHDDocument44 pagesInnate Immunity: Dr. Prasanna Honnavar, PHDmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 Quiz ReviewerDocument2 pagesBio 2 Quiz ReviewerAlexandra RoderoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 - Beta-LactamDocument7 pagesChapter 43 - Beta-LactamErika De JesusNo ratings yet
- Types of VaccinesDocument21 pagesTypes of VaccinesAtoillah IsvandiaryNo ratings yet
- Is PPT CompleteDocument456 pagesIs PPT CompleteCelso Rodil IIINo ratings yet
- Major Complex: HistocompatabilityDocument42 pagesMajor Complex: HistocompatabilityAshikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 (Hemoglobin Metabolism)Document3 pagesChapter 10 (Hemoglobin Metabolism)Joannah Marie100% (1)
- Innate Immunity: - Properties of Innate Immunity - Components of Innate ImmunityDocument39 pagesInnate Immunity: - Properties of Innate Immunity - Components of Innate Immunityrima melliaNo ratings yet
- Cellular ImmunityDocument13 pagesCellular ImmunityPragya100% (1)
- Innate ImmunityDocument9 pagesInnate Immunitynascha dumpNo ratings yet
- Basic Immunology: Dr. Fitriyah Mayorita, SP - PKDocument46 pagesBasic Immunology: Dr. Fitriyah Mayorita, SP - PKFadhila RizkiNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument4 pagesImmunityBritanya East100% (1)
- Immunology & Serology Week 1Document2 pagesImmunology & Serology Week 1Romie SolacitoNo ratings yet
- Elisa: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent AssayDocument12 pagesElisa: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent AssayAmit100% (1)
- Immunoglobulins ClassDocument16 pagesImmunoglobulins ClassKoushali BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Immune System 2020Document31 pagesOverview of The Immune System 2020mehakNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 and 12: Students LecturesDocument17 pagesCh. 2 and 12: Students LecturesBasma RagabNo ratings yet
- Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism (18 Oct)Document14 pagesPhenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism (18 Oct)api-19824406100% (6)
- Elisa (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbant Assay)Document4 pagesElisa (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbant Assay)Linette GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Antibodies Structure and FunctionDocument16 pagesAntibodies Structure and Functionياسين احمد علي الشيخNo ratings yet
- Antibodies CHPT 4Document16 pagesAntibodies CHPT 4AmitAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Antigen & AntibodiesDocument16 pagesAntigen & AntibodiesYing Ming TangNo ratings yet
- Bacterial and Viral GeneticsDocument52 pagesBacterial and Viral GeneticsPradeep Tomar100% (1)
- Allergy and HypersensitivityDocument73 pagesAllergy and HypersensitivityAdi PomeranzNo ratings yet
- Mediators of InflammationDocument43 pagesMediators of InflammationNatasha Baloch100% (2)
- Chapter 3 PowerPointDocument73 pagesChapter 3 PowerPointJohn NikolaevichNo ratings yet
- Types of ImmunityDocument35 pagesTypes of ImmunityKailash NagarNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Factor Latex Test PartolanDocument15 pagesRheumatoid Factor Latex Test Partolanchocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- ImmunotoxicityDocument6 pagesImmunotoxicitysuba_n23100% (1)
- Ig Structuer and FunctionsDocument34 pagesIg Structuer and FunctionsDentist Dina SamyNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid OxidationDocument28 pagesFatty Acid OxidationEmm NomanNo ratings yet
- Immunology PDFDocument1 pageImmunology PDFTanushree PalNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Rods of Enteric TractDocument2 pagesGram Negative Rods of Enteric TractJohn TerryNo ratings yet
- Et Al. Immunology, 6th Ed., pp7, 132-134 Et Al. Medical Microbiology, 4th Ed., PP 102-103Document7 pagesEt Al. Immunology, 6th Ed., pp7, 132-134 Et Al. Medical Microbiology, 4th Ed., PP 102-103Cristina Georgiana100% (1)
- Antigens & Antigen Presentation: Prof Anura WeerasingheDocument21 pagesAntigens & Antigen Presentation: Prof Anura Weerasinghesiva100% (1)
- NP1 Dec 2012Document8 pagesNP1 Dec 2012Tatiana's CoutureNo ratings yet
- Keeping The Peace Conflict Management Strategies.13Document5 pagesKeeping The Peace Conflict Management Strategies.13Chiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis SampleDocument15 pagesAppendicitis SampleChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Breast CancerChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- NCLEX RN CramsheetDocument2 pagesNCLEX RN CramsheetChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- Date/Timecuesneeddiagnosisobjective of Carenursing InterventionsevaluationDocument3 pagesDate/Timecuesneeddiagnosisobjective of Carenursing InterventionsevaluationChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- From Bedside To Classroom: From Expert Back To Novice: Cheryl Spencer PHD, RNDocument4 pagesFrom Bedside To Classroom: From Expert Back To Novice: Cheryl Spencer PHD, RNChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- Deaver Ovum Suture BasinDocument1 pageDeaver Ovum Suture BasinChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Intern: Iris Parcon Clerks: Karen Bianca Espinola Anna Sophia Lim Leo Salvador VedanaDocument50 pagesCase Presentation: Intern: Iris Parcon Clerks: Karen Bianca Espinola Anna Sophia Lim Leo Salvador VedanaKaren Bianca Matampale EspinolaNo ratings yet
- Riley Strain CODDocument10 pagesRiley Strain CODLeigh EganNo ratings yet
- B.SC Botany (H) Sem II Paper-CC-04 Question Bank Dr. (MRS.) A. S. Khalkho Bryophytes Objective Type QuestionsDocument13 pagesB.SC Botany (H) Sem II Paper-CC-04 Question Bank Dr. (MRS.) A. S. Khalkho Bryophytes Objective Type QuestionsVinay Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- ACT 5 - Skeletal - Lab Sheet 2 Copy KoDocument12 pagesACT 5 - Skeletal - Lab Sheet 2 Copy KoMariah Ray Rint100% (1)
- The Respiratory System (Handouts)Document6 pagesThe Respiratory System (Handouts)EdNo ratings yet
- 338 Stretching PDFDocument7 pages338 Stretching PDFsage porterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09. Host Response To InfectionDocument51 pagesChapter 09. Host Response To InfectionZin LimNo ratings yet
- Approach To Hepatomegaly, Splenomegaly and HepatosplenomegalyDocument43 pagesApproach To Hepatomegaly, Splenomegaly and HepatosplenomegalyLee Jun Xiong100% (2)
- CHP 07 0610 (2023)Document9 pagesCHP 07 0610 (2023)eanheng123No ratings yet
- Intracranial TumorsDocument31 pagesIntracranial TumorsRadio ResidentNo ratings yet
- Direction: Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesDirection: Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answerariel agos100% (1)
- 3 Exam: KUB Anatomy: OS206: AbdomenDocument3 pages3 Exam: KUB Anatomy: OS206: AbdomendocaliNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesDigestive SystemTana OquendoNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument5 pagesNutritionk,srikanthNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cyst FinalDocument26 pagesOvarian Cyst FinalReicy Aquino SacularNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic Shock PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesHypovolemic Shock PathophysiologyKAYCEENo ratings yet
- Biology Question BankDocument5 pagesBiology Question BankAamna AnsariNo ratings yet
- BiopotentialsDocument35 pagesBiopotentialsramyarakiNo ratings yet
- MPSC Rajyaseva Syllabus 2023Document74 pagesMPSC Rajyaseva Syllabus 2023PravinNo ratings yet
- REFLECTIONDocument2 pagesREFLECTIONDaniel Angelo ArangoNo ratings yet
- Herbal Cosmetics - Introduction and Scope: Prepared By-Zuli Shingala Faculty of Pharmacy, Msu BarodaDocument20 pagesHerbal Cosmetics - Introduction and Scope: Prepared By-Zuli Shingala Faculty of Pharmacy, Msu BarodaZuli Shingala100% (1)
- BiologyDocument48 pagesBiologyNitin KhodifadNo ratings yet
- The Human Renal SystemDocument8 pagesThe Human Renal SystemRobert CaseyNo ratings yet
- Cytology I - Techniques and Application: Peter NG Cyto Lab Ic, MT, PYNEHDocument201 pagesCytology I - Techniques and Application: Peter NG Cyto Lab Ic, MT, PYNEHbusiness onlyyouNo ratings yet
- Oral Biology CurriculumDocument5 pagesOral Biology Curriculumjunaid34No ratings yet
- The CellDocument4 pagesThe CellOlerato NtsimaneNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of A Rabbit Diagram - Google SearchDocument1 pageThe Anatomy of A Rabbit Diagram - Google SearchmaddieasmythNo ratings yet
Types of Immun
Types of Immun
Uploaded by
Chiqui Lao DumanhugCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Immun
Types of Immun
Uploaded by
Chiqui Lao DumanhugCopyright:
Available Formats
TYPES
OF
IMMUNITY
Natural
Immunity
-
also
called
in
born/
inherent
immunity
- Physical
barrier:
skin,
Chemical
barrier:
substance
produced
by
the
body
Cellular
barrier:
T
&
B
lymphocytes
Acquired
Immunity
Herpes
zoster
-
follows
the
nerve
endings;
very
painful
because
its
on
top
of
nerves
ACQUISITION
OF
IMMUNITY
ACTIVE
PASSIVE
Acquired
Immunity
A.
Natural
exposed
to
antigen
by
having
the
disease
Ex.
Chickenpox
B.
Artificial
immunization
with
antigen
Ex.
Vaccines,
toxoids
A.
Natural
transplacental
&
colostrums
transfer
from
mother
to
child
Ex.
Breastfeeding
B.
Artificial
ready-made
antibodies
Ex.
HTIG
NATURAL
ACTIVE
(infection)
Temporary,
several
weeks
Temporary,
several
months
PASSIVE (maternal)
ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
IMMUNITY
ARTIFICIAL
PASSIVE (antibody transfer)
INNATE IMMUNITY
ACTIVE (immunization)
immediate
Several
years;
extended
protection
with
booster
doses
Duration
Long
term,
often
lifetime
Development
Develops
slowly,
protective
level
reached
in
a
few
weeks
Develops
slowly,
protective
levels
reached
in
a
few
weeks
immediate
THE IMMUNE RESPONSE
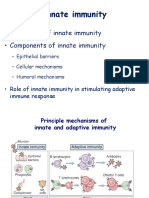
1. HUMORAL IMMUNITY (antibody mediated immunity)
Dominated by B lymphocytes
Works mainly against:
- Antigens dissolved in body fluids
- Extracellular pathogen (bacteria)
Presence of antigen recognized by T helper cells activated by B cells become plasma cells - ANTIBODIES
Antibodies are specific gamma globulins; also called immunoglobulin
TYPES OF ANTIGEN ANTIBODY REACTION
Agglutination clumping of cells
Precipitation soluble antigens, when crossed with antibodies, may become insoluble;
phagocytic cells more readily ingest insoluble materials
Neutralization antibodies combine with the toxins, neutralizing their effects
Lysis antibodies attack cell membrane of antigens
Opsonization fixation of complement and Ig particles
2. CELL
MEDIATED
IMMUNITY
Dominated
by
T
lymphocytes
Needs
the
signal
of
TCR
and
APC
for
immune
response
to
occur
When
you
insert
a
correct
key
(antigen)
in
the
ignition
(TCR)
and
turn
it,
the
car
starts
(recognition),
but
the
car
does
not
move
forward
until
you
move
the
gear
shift
into
the
drive
(co-stimulation)
You might also like
- Microbiology Chapter 17 Spring 07Document3 pagesMicrobiology Chapter 17 Spring 07fallingupward312No ratings yet
- Name : .. Chapter 2 - Cell As A Unit ofDocument17 pagesName : .. Chapter 2 - Cell As A Unit ofRozaini Othman82% (28)
- Immunology PDFDocument1 pageImmunology PDFTanushree Pal0% (1)
- Classification of BacteriaDocument2 pagesClassification of BacteriaMuhammad Umer100% (1)
- Physiology of LactationDocument18 pagesPhysiology of LactationPreeti Sawant100% (2)
- Basic ImmunologyDocument57 pagesBasic ImmunologyRonalyn UgatNo ratings yet
- Immunology OverviewDocument83 pagesImmunology OverviewHARIS KKNo ratings yet
- T - Cell DifferentiationDocument24 pagesT - Cell DifferentiationAnand Prakash YadavNo ratings yet
- Humoral & Celullar ImmunityDocument60 pagesHumoral & Celullar ImmunityHaziq KamardinNo ratings yet
- BCH444 PDFDocument232 pagesBCH444 PDFYaseen Ahmad100% (1)
- Antigen (Immunogen) : Prepared By: Victor B. Perlas JR., RMTDocument25 pagesAntigen (Immunogen) : Prepared By: Victor B. Perlas JR., RMTEduardo MedinaceliNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument27 pagesBiologyAnand GNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument24 pagesAntiviral DrugsBurhan Nabi0% (1)
- ImmunityDocument44 pagesImmunityHam Za100% (1)
- Topic: Cytokine and Their Roles in The Immune Regulation: Md. Jiyaul MustafaDocument21 pagesTopic: Cytokine and Their Roles in The Immune Regulation: Md. Jiyaul MustafaAisha Siddiq100% (1)
- ANTIBODYDocument22 pagesANTIBODYapi-19916399100% (1)
- Antigen-Antibody InteractionsDocument13 pagesAntigen-Antibody Interactionsمصطفى رسول هاديNo ratings yet
- Immunity (Lecture Notes)Document5 pagesImmunity (Lecture Notes)Anisha NishanthNo ratings yet
- The Immune SystemDocument31 pagesThe Immune SystemYesiana Lilis Sugiarti100% (1)
- Antigen and Its PropertiesDocument20 pagesAntigen and Its Propertiestusharpremin92% (12)
- Vaccination: Yunus Ariyanto FKM - Univ. JemberDocument11 pagesVaccination: Yunus Ariyanto FKM - Univ. JemberDian WidyaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Cellular and Molecular Immunology Module1: IntroductionDocument32 pagesCellular and Molecular Immunology Module1: IntroductionAygul RamankulovaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic ResistanceDocument29 pagesAntibiotic ResistanceDian Aditama100% (1)
- AntigenDocument11 pagesAntigenAnushka Sharma0% (1)
- Lecture 10 AutoimmunityDocument78 pagesLecture 10 AutoimmunitytimcarasNo ratings yet
- Antigen Presenting CellDocument26 pagesAntigen Presenting CellSurja DasNo ratings yet
- Innate Immunity: Dr. Prasanna Honnavar, PHDDocument44 pagesInnate Immunity: Dr. Prasanna Honnavar, PHDmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 Quiz ReviewerDocument2 pagesBio 2 Quiz ReviewerAlexandra RoderoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 - Beta-LactamDocument7 pagesChapter 43 - Beta-LactamErika De JesusNo ratings yet
- Types of VaccinesDocument21 pagesTypes of VaccinesAtoillah IsvandiaryNo ratings yet
- Is PPT CompleteDocument456 pagesIs PPT CompleteCelso Rodil IIINo ratings yet
- Major Complex: HistocompatabilityDocument42 pagesMajor Complex: HistocompatabilityAshikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 (Hemoglobin Metabolism)Document3 pagesChapter 10 (Hemoglobin Metabolism)Joannah Marie100% (1)
- Innate Immunity: - Properties of Innate Immunity - Components of Innate ImmunityDocument39 pagesInnate Immunity: - Properties of Innate Immunity - Components of Innate Immunityrima melliaNo ratings yet
- Cellular ImmunityDocument13 pagesCellular ImmunityPragya100% (1)
- Innate ImmunityDocument9 pagesInnate Immunitynascha dumpNo ratings yet
- Basic Immunology: Dr. Fitriyah Mayorita, SP - PKDocument46 pagesBasic Immunology: Dr. Fitriyah Mayorita, SP - PKFadhila RizkiNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument4 pagesImmunityBritanya East100% (1)
- Immunology & Serology Week 1Document2 pagesImmunology & Serology Week 1Romie SolacitoNo ratings yet
- Elisa: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent AssayDocument12 pagesElisa: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent AssayAmit100% (1)
- Immunoglobulins ClassDocument16 pagesImmunoglobulins ClassKoushali BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Immune System 2020Document31 pagesOverview of The Immune System 2020mehakNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 and 12: Students LecturesDocument17 pagesCh. 2 and 12: Students LecturesBasma RagabNo ratings yet
- Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism (18 Oct)Document14 pagesPhenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism (18 Oct)api-19824406100% (6)
- Elisa (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbant Assay)Document4 pagesElisa (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbant Assay)Linette GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Antibodies Structure and FunctionDocument16 pagesAntibodies Structure and Functionياسين احمد علي الشيخNo ratings yet
- Antibodies CHPT 4Document16 pagesAntibodies CHPT 4AmitAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Antigen & AntibodiesDocument16 pagesAntigen & AntibodiesYing Ming TangNo ratings yet
- Bacterial and Viral GeneticsDocument52 pagesBacterial and Viral GeneticsPradeep Tomar100% (1)
- Allergy and HypersensitivityDocument73 pagesAllergy and HypersensitivityAdi PomeranzNo ratings yet
- Mediators of InflammationDocument43 pagesMediators of InflammationNatasha Baloch100% (2)
- Chapter 3 PowerPointDocument73 pagesChapter 3 PowerPointJohn NikolaevichNo ratings yet
- Types of ImmunityDocument35 pagesTypes of ImmunityKailash NagarNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Factor Latex Test PartolanDocument15 pagesRheumatoid Factor Latex Test Partolanchocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- ImmunotoxicityDocument6 pagesImmunotoxicitysuba_n23100% (1)
- Ig Structuer and FunctionsDocument34 pagesIg Structuer and FunctionsDentist Dina SamyNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid OxidationDocument28 pagesFatty Acid OxidationEmm NomanNo ratings yet
- Immunology PDFDocument1 pageImmunology PDFTanushree PalNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Rods of Enteric TractDocument2 pagesGram Negative Rods of Enteric TractJohn TerryNo ratings yet
- Et Al. Immunology, 6th Ed., pp7, 132-134 Et Al. Medical Microbiology, 4th Ed., PP 102-103Document7 pagesEt Al. Immunology, 6th Ed., pp7, 132-134 Et Al. Medical Microbiology, 4th Ed., PP 102-103Cristina Georgiana100% (1)
- Antigens & Antigen Presentation: Prof Anura WeerasingheDocument21 pagesAntigens & Antigen Presentation: Prof Anura Weerasinghesiva100% (1)
- NP1 Dec 2012Document8 pagesNP1 Dec 2012Tatiana's CoutureNo ratings yet
- Keeping The Peace Conflict Management Strategies.13Document5 pagesKeeping The Peace Conflict Management Strategies.13Chiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis SampleDocument15 pagesAppendicitis SampleChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Breast CancerChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- NCLEX RN CramsheetDocument2 pagesNCLEX RN CramsheetChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- Date/Timecuesneeddiagnosisobjective of Carenursing InterventionsevaluationDocument3 pagesDate/Timecuesneeddiagnosisobjective of Carenursing InterventionsevaluationChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- From Bedside To Classroom: From Expert Back To Novice: Cheryl Spencer PHD, RNDocument4 pagesFrom Bedside To Classroom: From Expert Back To Novice: Cheryl Spencer PHD, RNChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- Deaver Ovum Suture BasinDocument1 pageDeaver Ovum Suture BasinChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Intern: Iris Parcon Clerks: Karen Bianca Espinola Anna Sophia Lim Leo Salvador VedanaDocument50 pagesCase Presentation: Intern: Iris Parcon Clerks: Karen Bianca Espinola Anna Sophia Lim Leo Salvador VedanaKaren Bianca Matampale EspinolaNo ratings yet
- Riley Strain CODDocument10 pagesRiley Strain CODLeigh EganNo ratings yet
- B.SC Botany (H) Sem II Paper-CC-04 Question Bank Dr. (MRS.) A. S. Khalkho Bryophytes Objective Type QuestionsDocument13 pagesB.SC Botany (H) Sem II Paper-CC-04 Question Bank Dr. (MRS.) A. S. Khalkho Bryophytes Objective Type QuestionsVinay Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- ACT 5 - Skeletal - Lab Sheet 2 Copy KoDocument12 pagesACT 5 - Skeletal - Lab Sheet 2 Copy KoMariah Ray Rint100% (1)
- The Respiratory System (Handouts)Document6 pagesThe Respiratory System (Handouts)EdNo ratings yet
- 338 Stretching PDFDocument7 pages338 Stretching PDFsage porterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09. Host Response To InfectionDocument51 pagesChapter 09. Host Response To InfectionZin LimNo ratings yet
- Approach To Hepatomegaly, Splenomegaly and HepatosplenomegalyDocument43 pagesApproach To Hepatomegaly, Splenomegaly and HepatosplenomegalyLee Jun Xiong100% (2)
- CHP 07 0610 (2023)Document9 pagesCHP 07 0610 (2023)eanheng123No ratings yet
- Intracranial TumorsDocument31 pagesIntracranial TumorsRadio ResidentNo ratings yet
- Direction: Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesDirection: Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answerariel agos100% (1)
- 3 Exam: KUB Anatomy: OS206: AbdomenDocument3 pages3 Exam: KUB Anatomy: OS206: AbdomendocaliNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesDigestive SystemTana OquendoNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument5 pagesNutritionk,srikanthNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cyst FinalDocument26 pagesOvarian Cyst FinalReicy Aquino SacularNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic Shock PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesHypovolemic Shock PathophysiologyKAYCEENo ratings yet
- Biology Question BankDocument5 pagesBiology Question BankAamna AnsariNo ratings yet
- BiopotentialsDocument35 pagesBiopotentialsramyarakiNo ratings yet
- MPSC Rajyaseva Syllabus 2023Document74 pagesMPSC Rajyaseva Syllabus 2023PravinNo ratings yet
- REFLECTIONDocument2 pagesREFLECTIONDaniel Angelo ArangoNo ratings yet
- Herbal Cosmetics - Introduction and Scope: Prepared By-Zuli Shingala Faculty of Pharmacy, Msu BarodaDocument20 pagesHerbal Cosmetics - Introduction and Scope: Prepared By-Zuli Shingala Faculty of Pharmacy, Msu BarodaZuli Shingala100% (1)
- BiologyDocument48 pagesBiologyNitin KhodifadNo ratings yet
- The Human Renal SystemDocument8 pagesThe Human Renal SystemRobert CaseyNo ratings yet
- Cytology I - Techniques and Application: Peter NG Cyto Lab Ic, MT, PYNEHDocument201 pagesCytology I - Techniques and Application: Peter NG Cyto Lab Ic, MT, PYNEHbusiness onlyyouNo ratings yet
- Oral Biology CurriculumDocument5 pagesOral Biology Curriculumjunaid34No ratings yet
- The CellDocument4 pagesThe CellOlerato NtsimaneNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of A Rabbit Diagram - Google SearchDocument1 pageThe Anatomy of A Rabbit Diagram - Google SearchmaddieasmythNo ratings yet