Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Step by Step: Tutorial For Axisvm 11
Uploaded by
Adam OdomOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Step by Step: Tutorial For Axisvm 11
Uploaded by
Adam OdomCopyright:
Available Formats
Step by Step
Tutorial for AxisVM 11
Author: Somogyi Zsolt
Edited by: Inter-CAD Kft.
2012 Inter-CAD Kft.
All rights reserved
All brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks.
Blank page
Step by step tutorial
TARTALOM
1.
BEAM MODEL ....................................................................................................................... 5
2.
FRAME MODEL................................................................................................................... 23
3.
SLAB MODEL ....................................................................................................................... 53
4.
MEMBRANE MODEL ......................................................................................................... 93
4.1.
4.2.
4.3.
4.4.
5.
START ............................................................................................................................... 93
GEOMETRY DEFINITION USING PARAMETRIC MESH ........................................................... 94
GEOMETRY DEFINITION USING DOMAINS ........................................................................ 100
DEFINE SUPPORTS AND LOADS ........................................................................................ 105
SHELL MODEL .................................................................................................................. 117
AxisVM 11
Blank page
Step by step tutorial
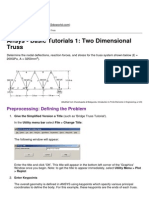
1. BEAM MODEL
Objective
The objective of this design example is to determine the internal forces,
longitudinal reinforcement and shear links of the two-span continuous
reinforced concrete beams illustrated below.
The loads on the beams will be presented subsequently.
Cross-section of both spans is a 600 x 400 mm rectangle and designed
in accordance with Euro Code.
Start
Start AxisVM 11 by double-clicking the AxisVM11 icon in the
AxisVM11 folder, found on the Desktop or in the Start - Programs
Menu.
New
Create a new model by clicking on the New icon.
Click on Front View icon for the modeling view. In the dialogue
window that pops up, replace the Model Filename with Beam. Select
the appropriate Design Code: Eurocode.
Click OK to close the dialog window.
Change view
The left-bottom corner of the main window shows the symbol of the
global coordinate system. The positive direction is marked by the
corresponding capital letter (X, Y or Z). The default view of a new
model is in X-Z plane.
It is important to note that unless changed the gravity acts along the
Z direction.
Define of
Geometry
Select the Elements tab to bring up the Elements Toolbar.
AxisVM 11
Draw objects
directly
Clicking on the draw objects directly icon shows following window:
Horizontal beam
Click on the Horizontal Beam icon, which is the second from left to
specify the axis of the two beams. The following window shows after
clicking:
Select Browse cross-section libraries and click on OK.
Cross-section
editor
The following window shows after clicking:
Step by step tutorial
Rectangular
shape
The following window shows after clicking on Rectangular shape
icon:
Enter 60 for h (height) then click on place button. Click anywhere in
the window to place the shape.
The following window shows up afterwards:
By clicking on OK shows a dialog box asking for cross-sections name:
Click on OK to close window.
AxisVM 11
The following message shows up:
Clicking on OK shows following window:
Roll down in the list of Materials by using vertical sliding bar (or roll
mouse wheel) and click on C25/30, then clik on OK.
Reference
By leaving Local z Reference on Auto the beams local x axis will be in
center of the beam and local z axis in vertical plane of the beam.
The following window will be displayed:
Beam polyline
Draw the continuous beams centre line!
Press key x on your keyboard x coordinate will highlighted in the
Coordinates window. Type in 0 then press key y and type 0 then press
z and type 0 and press Enter.
Click on left d button on the Coordinates window to switch typing
from relative to global coordinates.
Step by step tutorial
Relative
coordinate
system
Add next 2 nodes by pressing keys:
x
x
12
10
y
y
0
0
z
z
0 [Enter]
0 [Enter]
Then right-click and select Cancel from the quick menu:
You can change to the global coordinate values by pressing the d labeled button on the left of the Coordinate Window. If d button is
down (pressed) it denotes relative coordinates.
(Hint: In the right column of the coordinate window you can specify
points in cylindrical or spherical coordinate systems). The origin of the
relative coordinate system is marked by a thick blue X (cross turned by
45 deg.).
Zoom
To bring up the Zoom Icon Bar, move the mouse on the Zoom icon in
the Icon bar (left side of the main window). It contains six icons. Lets
choose the third icon (Zoom to fit) from the Zoom Icon Bar, or press
Ctrl-W (or double-click on mouse wheel), which has the same effect.
An alternative way of zooming is to press the + or keys on your
numerical keypad.
The following will be displayed:
10
Geometry Check
AxisVM 11
Click the Geometry Check icon on the top of the desktop,
to check for geometric ambiguities. The program will ask for
the maximum tolerance (distance) for merging points.
After the geometry check a summary of actions appears.
Perspective
Chek the models location in space!
Click on the Perspective icon on the Icon bar (left side of the main
window).. If you want to rotate the view , click on the left mouse
button and hold to rotate the view.
You can also hold Alt + mouse wheel and rotate the view anytime.
Closing this palette the view mode is preserved.
Step by step tutorial
11
Display Options
Click on Display Options icon for showing our models local coordinate
system, node numbers, graphical symbols, etc. (For quick acces to these
settings click on the same icon in mouse right-click menu.)
On the Symbols tab Local Systems group check Beam box and on
Labels tab check Cross-Section Name in Properties group.
Close the window with OK button. The local system of the beam and
the cross-section is shown on the beam. If mouse is rolled over this
beam further properties show up.
After rolling the mouse over the beam info box shows up with beam
number, length, material type, cross-section name, self-weight and
reference.
Select view from perspective to X-Z plane.
Fit in window
Click on Fit in window function for best view.
Nodal support
Click on Nodal support icon and select central node, then click on OK
button. Window shows up where stiffness of the support in each
direction can be set. Select Global direction and set support stifness.
Rx, Ry, Rz are for translation stifnness in kN/m. Default value for these
stifnessse are 1E+10 kN/m for fixed and 0 kN/m for free to move in
subject direction. Rx is for translation stifness in x direction.
Rxx, Ryy, Rzz are for rotational stifnness in kNm/rad. Default value for
these stifnessse are 1E+10 kNm/rad for fixed and 0 kNm/rad for free to
rotate support about subject direction. Rxx is for rotational stifness
about x direction.
Set rotational stiffnesses to 0 and fix the support only in X and Z
dirrection.
12
AxisVM 11
Click on OK to apply settings.
Select two end nodes and the same way create rolling vertical support
setting values as follow:
If everything is set correctly the translation support is a brown line and
rotational support is a orange line.
Loads
To apply loads and movements select Loads tab.
Step by step tutorial
Loadcases and
Load groups
13
Various loads and movements should be separated into load cases.
Click on Loadcases and Load groups icon.
The following window shows:
Program automatically generates load case ST1 which is shown in top
left coner. Click on ST1and rename it to SELF WEIGHT. Then click on
OK button what closes the window and we can specify the self weight
load into SELF WEIGHT load case. Check if the SELF WEIGHT load
case is selectged in the status window which in top left corner
(default).
Display Options
Self weight
Static load case
Click on Display Options icon. Unselect Object contours in 3D and
Beam box on the Symbols tab in Local Systems group and on Labels
tab unselect Cross-Section Name in Properties group.
Click on Self weight icon then select all elements with All (
)
button. After clicking on OK button both beams will have an offseted
blue dashed line indicaing that self weight was added indeed
(considering g=9.81 m/s2 gravity in negative Z direction).
Open Loadcases and Load groups window again and click on Static
icon in New case top icon row. Create load cases with names LIVE 1,
LIVE 2, LIVE 3 and SUPPORT DISPLACEMENT. Click on LIVE 1 load
case then close with OK.
14
Load along line
elements
AxisVM 11
After clicking on Load along line elements icon click on beam at left
hand side, then click on OK. Following window shows up:
Type in -17.5 into fields pz1 and pz2 then confirm with OK.
Step by step tutorial
15
Loadcases and
Load groups
After clicking on down arrow next to Loadcases and Load groups icon
following list shows up:
List shows all load cases. The actual load case is highlighted. Select
load case LIVE 2 with mouse or arrow keys.
Same way apply -17,5 kN/m line load on both beams.
Support
Displacement
Change load case to SUPPORT DISPLACEMENT then click on Support
Displacement icon. Then select central support and click on OK. The
following window shows up:
Type in value 20 into filed ez.
Load
Combinations
Activate Load Combinations function by clicking on its icon. The Table
Browser shows up:
New Row
Create new ULS (ultimate limit state) load combination by clicking on
New Row icon. Load factors foe each load cases must be set.
Set load factors as follow:
SELF WEIGHT 1,35 [Enter];LIVE1 1,5 [Enter];LIVE2 0 [Enter];
SUPPORT DISPLACEMENT 1,0 [Enter]
Type in all these values, then create another ULS load combination
and type in:
SELF WEIGHT 1,35 [Enter];LIVE1 0 [Enter];LIVE2 1,50 [Enter];
SUPPORT DISPLACEMENT 1,0 [Enter]
The 3rd load combination is SLS Quasipermanent with following
factors:
SELF WEIGHT 1,0 [Enter];LIVE1 0,6 [Enter];LIVE2 0,6 [Enter];
SUPPORT DISPLACEMENT 0 [Enter]
16
AxisVM 11
Click on OK to finish.
Static
Click on Static tab for running analysis:
Linear static
analysis
Click on Linear static analysis icon to run analysis.
Nodal DOF
Degrees of freedom must be set before analysis. Program checks nodal
degrees of freedom and offers automatic settings:
Check Save model with these settings and these dialog box will not
appear in the next run. Accept the Beam with multiple support in
plane X-Z option and click on Yes to close.
Statistics
The following message shows up after analysis:
Click on Statistics to see more information about the analysis:
Step by step tutorial
17
Click on OK after analysis. Automatically Staic tab is activated with ez
vertical deformations from SELF WEIGHT load case as Isosurface 2D.
Result display
parameters
The following windows shows up after clicking on Result display
parameters icon:
Select SELF WEIGHT load case. If we leave Display shape on
undeformed the results are drawn to undeformed model. Select eZ
component and Diagram as display mode. Select Lines and Nodes for
Write Values to setting.
After click on OK the following diagram will be displayed:
Check and look through all deformations from all load cases. To do
this, click on list right next to Result display parameters icon. Select the
first load combination Co #1.
18
Min, max values
AxisVM 11
To find minimal and maximal values click on Min, Max Values icon.
The following window shows up:
Select eZ and click on OK. After that new window shows up highest
negative deformation then after click on OK the highest positive
deformation. Click again on OK to close.
Click on the second list (next to load case list) and you can select from
several results: internal forces, stresses. Select internal forces My first
for 1st and 2nd load combination. (Co #1, Co #2)
Step by step tutorial
19
Concrete design
For RC design click on R.C. Design tab:
Beam
reinforcement
design
Click on Beam reinforcement design icon then on All button and finally
OK. The following warning message shows up:
After click on OK window with Beam parameters shows up:
20
Beam
Parameters
AxisVM 11
Select B500B rebar grade for longiutdal rebars and stirrups:
Set Concrete cover to 20mm and top longitudal rebars f to 20 mm:
To consider crack control check Increase reinforcement according to
limiting crack width checkbox:
After click on OK the follwing message shows up:
After click on OK the follwing window with results shows up:
Please note that in addition to My,Ed moment diagram (thin line) also
offseted moment diagram (thick line) which offests in accordance
with national design code.
Step by step tutorial
21
Select Envelope Min, Max in list with load combinations:
Under My,Ed moment diagram there is a As required reinforcement diagram on top and bottom, Vz shear diagram and shear link spacing sw
diagram.
Requred reinforcement in tension is in blue and required
reinforcement in compression in red.
Check
Click on Check in Beam Reinforcement window:
The following window shows up:
This window shows needed number of rebar, actual crack width
considering needed number of rebar and number of rebar rows.
Click on OK to close the window.
22
AxisVM 11
blank page
Step by step tutorial
23
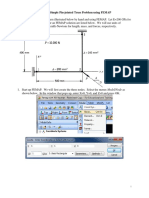
2. FRAME MODEL
Objective
Analyse the following frame and design column A1 and the pad
footing under.
Beams are IPE 400 rolled steel cross-section and columns HE 280 rolled
steel cross-section. Diagonals O 194 x 5 pipe cross-section. Material
grade is S 235 and designed according to Eurocode 2.
Start
Start AxisVM 11 by double-clicking the AxisVM11 icon in the
AxisVM11 folder, found on the Desktop or in the Start - Programs
Menu.
New
Create a new model by clicking on the New icon.
Click on Front View icon for the modeling view. In the dialogue
window that pops up, replace the Model Filename with FRAME.
Select the appropriate Design Code: Eurocode.
Click OK to close the dialog window.
Default global Z direction is upward. This is important for gravity
direction.
24
AxisVM 11
Define of
geometry
Select the Elements tab to bring up the Elements Toolbar.
Draw objects
directly
Clicking on the draw objects directly icon shows following window:
Click on column icon even if it is already selected.
The following window shows after clicking:
Select Browse cross-section libraries and click on OK. The following
window shows after clicking:
Roll down in the list of Cross-Section Tables by using vertical sliding
bar (or roll mouse wheel) and click on HE European wide flange
beams, and then click on HE 280 A . Close with OK.
Step by step tutorial
25
The following message shows up:
Clicking on OK shows following window:
Roll down in the list of Materials by using vertical sliding bar (or roll
mouse wheel) and click on S235, then clik on OK.
Set Height to 3,5 m in the displayed window:
Change view
Change view to top view (X-Y plane)!
Column
Click on Column icon below.
Click on these position in the graphical area:
(0,0) - (6,0) (0,5) (6,5) (0,10) (6,10)
26
AxisVM 11
The following window will be displayed:
Change view
Change view to perspective! Change the values in window as follow:
H= 15 V= 320 P = 0
Horizontal beam
Click on Horizontal beam icon.
Load from
database
Click on Cross-section row in the window, then on Load from
database icon . Select IPE 400 from IPE European I-beams:
Step by step tutorial
27
Click on OK to close window. The following window shows up:
Beam polyline
Click on Beam polyline icon then click on top of columns and draw the
beams. Draw the perimeter beams first then pree Esc to cancel
drawing. Draw central beam the same way. The following will be displayed:
Beam
Click on beam icon in draw objects directly window.
28
Load from
database
AxisVM 11
Click on Cross-section row in the window, then on Load from
database icon . Select ROR 193,70*4,5 form ROR European pipes (Pipe
shapes):
Click on OK to close window. The following window shows up:
Beam polyline
Draw polyline from bottom of A1 column to centre of beam in Y
direction:
Then draw other one into bottom of next column:
Step by step tutorial
29
Press Esc to cancel and draw two braces on the other end the same
way:
Translate
Using function Translate copy the frame in Z direction. Click on
Translate icon then on All icon and OK. The follow window shows
up:
Select Consecutive method then click on OK to confirm. Click on
bottom of column A1 then on top of this column finally press Esc to
cancel.
30
AxisVM 11
The following will be displayed:
Geometry Check
Click the Geometry Check icon which is on Geometry tab:
User can set for the maximum tolerance (distance) for checking points
and show the mesh.
After the geometry check a summary of actions appears.
Fit in window
Select Fit in window from zoom functions for best view.
Step by step tutorial
Rendered view
31
Select Rendered view from view options:
The following will be displayed:
Display Options
Click on Display Options ,Symbols tab and unselect Object Contours
in 3D:
32
AxisVM 11
Wireframe
Change back to Wireframe view:
Nodal support
Supports can be definied with nodal supports function on Elements
tab. Click on the icon, select bottom nodes of columns then confirm
with OK. The following window shows up:
Rotational stiffness set to 0 and translational stiffness leave on 1E+10.
Click on OK to confirm settings.
Loads
To apply loads and movements select Loads tab.
Loadcases and
Load groups
Various loads and movements should be separated into load cases.
Click on Loadcases and Load groups icon to add new load case. The
following window shows up:
Step by step tutorial
33
Program automatically generates load case ST1 which is shown in top
left coner. Click on ST1 and rename it to LIVE1. Click on OK to close
and select LIVE1 load case. The following will be displayed in the status window:
Load along line
elements
Add line loads to all horizontal beams. 50 kN/m to beams at lower level
and 25 kN/m to beams at upper level . Activate the Load along line
elements function and select with selection rectangle the upper beams.
Confirm the selection with OK and the following window shows up:
34
AxisVM 11
Set pZ1 and pZ2 to -25, then confirm with OK. The following will be
displayed:
Step by step tutorial
Display Options
35
Click on Display Options icon, the following window shows up:
Select Labels tab and check the Load Value check box in Properties
group:
36
AxisVM 11
Close with OK and the load values will be displayed:
Load along line
elements
Activate the Load along line elements function and select with selection
rectangle the lower beams, then confirm with OK and set pZ1 and pZ2
to -50.
Step by step tutorial
37
Confirm loads with OK and the following will be displayed:
Loadcases and
Load groups
Click on Loadcases and Load groups icon!
New static load
case
Add new load case by clicking on Static icon in New case top icon row.
Name it as WIND. After confirming with OK all loads will disappear
and Status window is showing load case: WIND.
Load along line
elements
Click on Load along line elements icon then select two columns in the
corner.
38
AxisVM 11
Then apply 6 kN/m line load in x direction (pX1 and pX2). The same
way apply 12kN/m to the central edge column in x direction.
The following will be displayed:
Step by step tutorial
Load
Combinations
New Row
39
Create load combinations from load cases. Using load combinations we
can define load factors to load cases.
Create new ULS (ultimate limit state) load combination by clicking on
New Row icon.
Define following load factors: LIVE1 1,5 ; WIND 1,5
Type in the factors the click on OK to finish.
We have finished data input for analysis.
Display options
Click on Display options icon then on Symbols tab. Uncheck Node,
Cross-section shape and Loads check boxes then on Labels tab
uncheck Load Value checkbox.
Static
Click on Static tab for running analysis:
Linear static
analysis
Click on Linear static analysis icon to run analysis. The following
window shows up:
40
Statistics
Static
AxisVM 11
Click on Statistics to see more information about the analysis:
The following window shows up after analysis:
Click on OK after analysis. Automatically Static tab is activated with ez
vertical deformations for LIVE1 load case as Isosurface 2D view. To see
results of load combinations select combination Co #1 from dropdown list.
Change results view from Isosurface 2D to Diagram:
Step by step tutorial
Change view
41
Change to Z-X view plane!
The following will be displayed:
Parts
Clicking on Parts icon shows the following window:
42
New
AxisVM 11
Clicking on New icon shows the following window:
Type 1 into Part name data field, then click OK.
Select parts of the frame which will be in part name 1. The following
picture shows how to select beams on a right hand side with selection
rectangle:
After click on OK the following window shows up:
Click on OK to close and confirm. Part with name 1 is created.
Step by step tutorial
43
Change view
Change to Z-Y view plane!
Result display
parameters
Click on Result display parameters icon, then check the Write values to:
Lines checkbox in the window.
Clicking on OK shows following window:
Min, max values
To find location of max. deformation use Min, Max values function.
Clicking on icon shows following window:
44
AxisVM 11
Select one of the deformation components. Confirm with OK shows
max. negative value and the location as well:
After click on OK shows the max. positive value and the location of
this value:
Select Beam internal forces Nx from list box in a toolbar:
Step by step tutorial
45
The following Nx axial force diagram will be displayed:
With the same way show moments about local y My:
Show reactions Rz the same way:
46
AxisVM 11
Steel design
For check on column A1 click on Steel design tab:
Design
parameters
For definining design parameters click on design parameters, then
select column A1 and confirm selection with OK.
The following window shoes up:
Define Ky = 1.25 and c2 = 1.0, then confirm with OK.
Axial ForceBending-Shear
Select Analysis - Axial Force-Bending-Shear results from list box in
toolbar:
Step by step tutorial
47
The following diagram will be displayed:
Efficiency
Select Efficiency from the same list box. The following diagram will be
displayed:
Click on column A1 to show all checks on subject column:
48
AxisVM 11
Az OK-ra klikkelve lphetnk ki a funkcibl.
R.C. design
Click on R.C. design tab:
Pad footing
design
Pad footing below column can be designed with Pad footing design
function.
Click on icon then on nodal support and confirm with OK.
Footing design
parameters
Window with Footing design parameters shows up:
Select rectangular pad footing , C30/37 concrete , soil cover t[cm]=170
and max. pad width bmax[cm]=120.
Step by step tutorial
49
Check on Calculate reinforcement on Reinforcement tab.
Soil database
User can read predefined soil characteristics from the soil databes
located on the Soil tab.
Clicking on Soil database icon shows following window:
50
AxisVM 11
Click on Homogenous, coarse and medium sand in dry or damp
column, soild row and soil parameters will be shown in bottom left
corner:
Confirm selection with OK button.
Layer thickness
Type in layer thickness 4.0 m.
Add new soil
layer
Add defined soil layer to the soil profile with this buton.
Soil database
Click on soil database icon in Backfill options to define soil type for soil
fill above pads bottom level. Select Mixed Non-silty, sandy gravel in
dry or damp column and solid row. Then confirm with OK. The
following window will be displayed:
After click on OK, type in name for specified soil profile:
Step by step tutorial
51
Type in name : soil1 and save profile with OK. Program calculates
pads required dimensions and reinforcement. The follwing message
shows up:
Close the message with OK, the following window shows up:
Pads required dimensions are shown on plan and in info window.
Close the window with OK.
52
AxisVM 11
blank page
Step by step tutorial
53
3. SLAB MODEL
Objective
Calculate max. deflection, max. moment, and max. reinforcement of
slab shown below.
Define slab thickness to 200 mm using C20/25 concrete from norm
Eurocode 2.
Start
Start AxisVM 11 by double-clicking the AxisVM11 icon in the
AxisVM11 folder, found on the Desktop or in the Start - Programs
Menu.
New
Create a new model by clicking on the New icon.
Click on Front View icon for the modeling view. In the dialogue
window that pops up, replace the Model Filename with Slab. Select
the appropriate Design Code: Eurocode.
54
Change view
AxisVM 11
The left-bottom corner of the main window shows the symbol of the
global coordinate system. The positive direction is marked by the
corresponding capital letter (X, Y or Z). Global Z direction is always
upwards. It is important to note that unless changed the gravity acts
along the Z direction.
Click on Change view and following row of icons show up:
Change view to top view (X-Y plane)!
Using geometry functions draw the slab.
Elements
Select the Elements tab to bring up the Elements Toolbar.
Draw objects
directly
Clicking on the draw objects directly icon shows following window:
Slab
Select slab element even if it is already selected.
The following window shows up:
Material
database
The following window shows after clicking on OK:
Select C20/25 concrete and confirm with OK.
Step by step tutorial
55
Type and
Thickness
Change type in Draw objects directly window from Shell to Plate and
thickness to 200 mm.
Complex slab
Click on Complex slab icon.
User can draw the slab directly or define the coordinates.
Use the global coordinates (d labeled button is not pressed).
Define coordinates of first point by pressing keys:
x
Relative coordinate system
0 [Enter]
You can change coordinate system by pressing the d labeled button
on the left of the Coordinate Window.
If d button is down (pressed) it denotes relative coordinates. X turns to
dX and so on indicating that we are defining relative ccordinates. The
relative point of origin is shown as thick blue X (cross turned by 45
deg.) Press d again for global coordinates.
Relative coordinate system
Continue defining next point with relative coordinates.
Press following keys:
7.9
0 [Enter]
On computers where , is set as decimal separator type 7,9 instead of
7.9
Arc by three
points
Click on Arc by three points under Draw objects directly tool palette:
Press following keys to define next contour points:
x
x
Line
0.5
0
y
y
z
z
3.4
6.8
0 [Enter]
0 [Enter]
Click on Line under Draw objects directly tool palette:
Press following keys to define next contour points:
-7.9
0 [Enter]
Then press [Enter] again to finish (close) contour definition.
Exit from Draw objects directly by pressing Esc.
56
AxisVM 11
The following will be displayed in the main window:
To move the origin of the local coordinate system to the bottom left
corner of the slab. Move cursor over the bottom left corner of the slab
and press Insert.
Geometry
Click on Geometry tab:
Create nodes
Click on Create nodes icon and type in the following:
x
x
6.4
0
y
y
2.2 [Enter]
2.4 [Enter]
Exit from Create nodes by pressing Esc.
The following will be displayed in the main window:
Step by step tutorial
57
Please note the thin red line which denotes
the domains contour. Moving the cursor
over the contour of the domain shows
domains properties:
Fit in window
Click on Fit in window function for best view.
Mesh
Click on Mesh tab!
Domain meshing
Click on Domain meshing then click on * to select all and confirm with
OK.
Then select quad mesh (in centre) and define Average mesh element
size to 0.65 m:
After click on OK the mesh is
Progress bar shows the meshing progress:
generated
automatically.
58
AxisVM 11
The following will be displayed in the main window:
Moving the cursor over the centre of
finite elements (red dot) shows finite
elements properties:
Refinement
Click on Refinement by bisection icon:
Domain
refinement
Then select following elements:
Step by step tutorial
59
After click on OK the following will be displayed:
Display options
Switch on surface elements local coordinate systems!
Click on Symbols tab in the Display options, following window will be
displayed:
Check the Surface checkbox in the Local Systems group and confirm
with OK.
Surface properties are accesible after definition. When local
coordinates of the surface are shown, the red line denotes x direction,
yellow for y direction and green for z direction.
60
AxisVM 11
Display Options
Switch off surface elements local coordinate systems the same way!
Elements
Click on Elements tab!
Nodal support
Define nodal supports. Click on Nodal support icon then select
column central nodes and confirm with OK. The following window
shows up:
Calculation...
Click on Calculation... button and he following window shows up:
Here you can calculate support stiffnes based on columns supports
and dimensions.
Step by step tutorial
61
New crosssection
Clicking on New cross-section icon shows following window:
Rectangular
shape
Clicking on Rectangular shape icon shows following window:
Type in 30 into two top input fields (b[cm]= ;h[cm]= ), then click on
Place button and click anywhere in the window to place the new
cross-section.
The following window will be displayed:
62
AxisVM 11
Click on OK and dialog box shows up whare you can type in new
cross-sections name:
Type 3 into L [m]= input field, then click on OK. Calculated values will
be automatically filled in the Nodal support window.
After click on OK nodal supports will be definied.
The following will be displayed:
Step by step tutorial
Line supports
63
To define line supports lick on Line supports icon, then select lines on
slabs perimeter. Select the two paralell edges and the one on left:
Confirm selection with OK and the following will be displayed:
Claculation
Click on Calculation... button.
Set these values in the window: L [m]= 3 and d[cm]=30
To set End Releases to pinned, click on both icons:
64
AxisVM 11
Confirm settings with OK and the calculated stiffness values will be
automatically filled in Line support window.
Click on OK to close the window and the following will be displayed:
Loads
Next sted is adding loads on slab.Click on Loads tab:
Step by step tutorial
65
Load cases and
Load groups
Various loads and movements should be separated into load cases.
Click on Loadcases and Load groups icon to add new load case. The
following window shows up:
Program automatically generates load case ST1 which is shown in top
left coner. Click on ST1 and rename it to SELF-WEIGHT, then clicking
on OK selects the SELF-WEIGHT loadcase. The Status window
informs us about the selected loadcase:
Self Weight
Click on Self Weight icon then select all
(*) . Confirming with OK applies self on
all selected elements. Thin dotted red
line indicates applied self weight:
Display options
Click on Display options then on Symbols tab in the Display options
window then uncheck Mesh and Surface centre in the Graphics
Symbols group. Close with OK.
New loadcase,
static
Open Loadcases and Load groups window and create new static
loadcase. Name it FINISHES, this loadcase will contain loads from slab
finishes. Close with OK.
66
Distributed Load
on Domain
AxisVM 11
Define load corresponding to 10 cm thick layer of concrete say 2.5
kN/m2. Click on Distributed Load on Domain icon and the following
window shows up:
Type in -2.5 to pZ [kN/m2] field (negative value denotes opposite
direction to local direction).
Distributed
domain load
Define load by clicking on Distributed domain load , then click to the
area of domain. Close with close button.
Domain Line
Load
To define load from balustrade click on Domain Line Load icon and the
following window shows up:
Type -1 into fields pZ1 and pZ2.
Arc by three
points
Select Arc by three points icon from bottom row, then click bottom,
central and top point of the curved edge. Then again on top point of
edge. Press Esc to exit.
Step by step tutorial
Load value
67
Switch on load intensity using
Numbering function in the
bottom right corner.
Click on Numbering icon and the
following window shows up:
Check the Load Value and Units
checkbox.
The following will be displayed:
New Loadcase,
static
Create new loadcase and name it LIVE.
Specify live load on slab in this loadcase. Define Distributed load on
Domain with pz=-1,5kN/m2 as shown previously.
Load
combinations
Loadcase are defined, now define two load combinations which we
will use for design and checking.
Click on Load combinations icon.
New Row
Create first load combination by clicking on New Row icon. Leave the
name on default Co#1. Select SLS Quasipermanent as type of load
combinaton.
Use following load factors for the new load combinaton:
SELF-WEIGHT 1,0
FINISHES 1,0
LIVE 0,3
68
New Row
AxisVM 11
Create the second load combination by clicking on New Row icon.
Leave the name on default Co#2. Select ULS as type of load
combinaton.
Use following load factors for the new load combinaton:
SELF-WEIGHT 1,35
FINISHES 1,35
LIVE 1,5
Click on OK to close the window.
We have finished with data input for slab design.
Static
Click on Static tab for running analysis:
Linear static
analysis
Click on Linear static analysis icon to run analysis.
Degrees of
freedom
Set degree of freedom of models nodes. Program checks the model
and offers one type in the dialog box:
Check the Save model with these settings checkbox and degree of
freedom settings will be saved. Click on Yes to confirm and close the
dialog box.
Analysis continus and the following progress bar shows up:
Step by step tutorial
69
Click on Statistics to see more information about the analysis:
The top progres bar shows progress of the actual task. The progress bar
bellow is showing the total pogress.
Estimated Memory Requirement shows size of used virtual memory
for analysis. If the PCs memory size is smaller than this, error message
regarding size of virtual memory will be displayed.
Click on Messages to see the detailed list of analysiss messages.
The following window will be displayed:
70
Static
AxisVM 11
After click on OK program automatically activates vertical deformations ez on Static tab in Isosurface 2D view of SELF-WEIGHT loadcase.
Select load combination Co#1 (SLS) to check service limit states:
Deformation values are negative because they are in opposite direction
of local z.
Min, Max Values
To find location of max. deformation use Min, Max values function.
Clicking on icon shows following window:
Select one of the deformation components. Confirm with OK shows
max. negative value and its location as well:
Step by step tutorial
71
After click on OK shows the max. positive value and the location of
this value :
Colour legend
The Colour legend window shows boundary values of each colour.
Adjust number of boundary values by moving the bottom edge of this
window:
Find areas with deflections larger than 2.1mm! Boundary values can be
changed by clicking on Colour legend window:
72
AxisVM 11
Click on a bottom value of the table on a left hand side. Change the
deafault value (-2,423) to 2,1.
Press [Enter] and Auto interpolate function calculates other boundary
values.
After click on OK the following will be displayed:
Area with deflection larger than 2,1mm is hatched.
Step by step tutorial
Isoline
73
See the results using Isolines. Click on arrow right to Isosurface 2D
title and select Isoline:
After selecting Isoline the following will be displayed:
Change view
Change view to perspective! Click on Setting Perspective View:
Change perspective values in window as follow:
Click on X in top right corner to close the window with perspective
settings.
Result
display
parameters
To change to deformed shape click on Result display parameters icon.
Click on Deformed Display shape in Display Parameters window and
confirm with OK. The deformed shape will be displayed:
74
Change view
AxisVM 11
Change view to top view!
See the internal forces.
Select load combination Co#2 (ULS). Click on arrow next to ez [mm]
title and the following list of components will be displayed:
Select Surface Internal Forces mx. Isolines of mx moments will be
displayed. The mx moments are moments in local x direction which
are used for design reinforcement in x local direction. The similar way
we can select moments in y direction, torsional moments and shear
forces.
Select Nodal Support Intenal Forces Rz which shows vertical
reactions of the nodal support.
Step by step tutorial
Result display
parameters
75
Click on Result display parameters icon and the following window
will be displayed:
Check the Write Values To Nodes checkbox and click on OK. The
following vertical reactions will be displayed:
Select Line Support Intenal Forces Rz [kN/m] which shows vertical
reactions of the line support. Click on Result display parameters icon
and the following window and check the Write Values To Lines
checkbox and click on OK:
76
AxisVM 11
R. C. Design
Click on R.C. Design tab. Here you can calculate required area of
reinforcement for surface elements (domains).
Reinforcement
parameters
Click on Reinforcement
parameters icon then select all
(*) and confirm with OK. The
following message shows up:
Close with OK and the
following window will be
displayed:
Step by step tutorial
77
Set Exposition classes on Materials tab. Set XC1 for Top and Bottom
surface. Set Primary direction of reinforcement as x for Top and
Bottom surface on Reinforcement tab. Check Apply minimum cover
checkbox:
Close the window with OK.
Change view to Isosurface 2D!
Now you can see axb [mm2/m] results, which is required amount of
reinforcemnt in local x direction at bottom of the slab. See
Reinforcement Values in the list of results where you can also select
required area of reinforcement for other directions.
Change boundary values to cross-sectional areas for specific spacings
(e.g 1005 mm2/m for T16@200)for each colour in the colour legend
window.Select axt [mm2/m] results, which is required amount of
78
AxisVM 11
reinforcemnt in local x direction at top of the slab.
Min, Max Values
To find location of max. req. area of reinforcement use Min, Max
values function. Clicking on icon shows following window:
Click on OK shows max. req. area of reinforcement and its location:
Click on OK to exit.
Reinforce with 0,3% using 12 diameter at 180 mm c/c bars
(628mm2/m) double reinforcement locally to 12 at 90 mm c/c (1257
mm2/m).
Max. required reinforcement value is (942mm2/m) what is less then
doubled reinforcement (1257 mm2/m).
To find the area which need double reinforcement set number of
isoarea values on Colour legend window to 3.
Click on Colour legend window and change boundary values to these
reinforcement values:
Step by step tutorial
79
Click on OK and isosurfaces will be updated using new boundary
values:
Hatched area denotes that center of the slab doesnt need any top
reinforcement in x direction. On the edge 12 @ 180 c/c reinforcement
is needed while around columns 12 @ 90 c/c reinforcement is
needed.
To design reinforcement above columns click on Static tab and select
Surface Internal Forces - mxD+ [kNm/m] results which considers also
mxy forces.
80
Section Line
AxisVM 11
Click on Section Line icon.
Click on New section plane button and type in column1:
Aftre click on OK define the section plane. First click on top nodal
support then on bottom nodal support
The following window will be diplayed:
Change view
Click on OK to see moments in x direction in plane section column1..
Change to side view (Z-Y plane)
and change results view from Isosurface 2D to Section Line then you
can see section of moment diagra:
Step by step tutorial
81
Turn off sections! Click on Section Liness Planes speed button.
(bottom right corner)
Speed buttons
Click on Numbering icon (see Speed Buttons)
and uncheck Write Values to Lines and Units
checkbox:
Change view to Perspective and Section Line
view to Isosurface 3D.
The following will be displayed which shows design moments in x
direction:
Change view
Change view back to Top View (X-Y plane)!
R.C. Design
Click on R.C. Design tab!
Actual
Reinforcement
Click on Actual Reinforcement icon! The following window shows up:
82
AxisVM 11
Set x direction for Primary direction of reinforcement on top and
bottom surface on Parameters tab and check the Apply minimum
cover checkbox.
Set diameter to 12 for [mm]= and Spacing [mm] to 180 on
Reinforcement tab. Check the Calculate rebar positions checkbox then
select x Direction Top Reinforcement in top left box and click on
Add button.
The following will be displayed:
The same way define Bottom Reinforcement in x and also in y
direction. The following will be displayed:
Reinforcement
over an existing
domain
Click on Reinforcement over an existing domain icon then click
somewhere inside the domain. Click on Close button to exit.
The following will be displayed:
Step by step tutorial
Reinforcement
difference
83
Select Reinforcement difference / xb axa results component:
Change view to Isosurface 2D!
Check Write values to Surfaces checkbox in Numbering from Speed
Buttons The following will be displayed:
84
AxisVM 11
Only positive values denotes that bottom actual (defined)
reinforcement is sufficient in x direction for load combination Co #2.
Same applies for ya-aya component.
Change to xt-axt component:
Here you can see that values around nodal supports are negative, this
areas reinforcement has to be increased.
Actual
Reinforcement
Using Actual Reinforcement function increase reinforcement around
column in 2x2m square area!
Click on Actual Reinforcement icon and select Reinforcement tab.
Set 12 at 180 c/c check Calculate rebar positions then select x
direction / Top reinforcement and click on Add button.
Rectangular
reinforcement
domain
Additional reinforcement can be defined using Rectangular
reinforcement domain. Click on the icon then move the cursor over
lower nodal support
press Ins key to move the origin of the local coordinate system.
Step by step tutorial
85
Type in the following sequence of keys :
x -1 y -1 z 0 [Enter]
x 2 y 2 z 0 [Enter]
Then press Esc twice to exit.
The following will be displayed:
The xt axt results around lower nodal support are positive so actual
(defined) reinforcement is sufficient above lower nodal support.
Translate
Click on Translate icon:
Then move the cursor over reinforcement domains contour and click
on it to select. Confirm with OK to finish selection. In the Translate
window select Incremental Method and set N=1:
Close the window with OK and define translation vector by clicking
on lower then on upper nodal support.
86
AxisVM 11
This way you have copied the actual domain reinforcement, the
following will be displayed:
There arent any negative xt axt values so the actual (defined)
reinforcement is sufficient at top in x direction.
Change to results to yt- ayt !
There are still negative values around nodal supports but now at top in
y direction. You need to increase the reinforcement in these areas.
Actual
Reinforcement
Press and hold SHIFT key then click then click on actual reinforcement
above columns then click on Actual Reinforcement icon.
Set x direction for Primary direction of reinforcement on top and bottom
surface on Parameters tab and check the Apply minimum cover
checkbox. Select Reinforecement tab and the following window shows
up:
Step by step tutorial
87
Click on field under x direction - Top Reinforcement (12 mm / 180
mm) then on y direction - Top Reinforcement and finally on Add
button. The following settings will be displayed:
Click on OK to exit.This way we have defined the same actual
reinforcement in y direction as it is in x direction. The following will
be displayed:
The yt ayt results around nodal supports are now also positive, so
the actual (defined) reinforcement is sufficient for all 4 components.
Ellenrizzk a szerkezet repedstgassgt a hasznlhatsgi hatrllapotra!
88
Crack widths
AxisVM 11
Select load combination Co #1 (SLS), then select Cracking wk(b)
result component which is showing crack widths in local x direction at
bottom surface of the domain (slab).
The following will be displayed:
Domain is hatched what denotes that there are no cracks at bottom
surface of domain from load combination Co #1.
Select Cracking wk(t) result component which is showing crack
widths in local x direction at top surface of the domain. Crack widths
above nodal supports is up to 11mm:
Step by step tutorial
89
To determine the deflection of the cracked slab you need to run
Nonlinera static analysis of the load combination Co #1 (SLS).
Static
To run the analysis click on the Static tab.
Nonlinera static
analysis
Click on Nonlinear static analysis icon and the following window
shows up:
Az OK-ra klikkelve megkezddik a szmts s a kvetkez ablak jelenik meg:
Check Use reinforcement in calculation checkbox and select Actual
Reinforcement. Click on OK to run analysis.
Messages
Click on Messages to see more information about the analysis:
90
Iterations
AxisVM 11
Click on Iterations to see how the calculations are converging for each
increment:
After click on OK program automatically activates vertical
deformations ez on Static tab in Isosurface 2D view of load
combination Co #1 with nonlinear analysis. The following will be displayed:
R. C. Design
Click on R.C. Design tab.
Plate punching
analysis
To check shear punching click on R.C. Design tab and select load
combination Co #2 (ULS). Click on Plate punching analysis icon then
select upper nodal support and click on OK.
The following window will be displayed:
Step by step tutorial
91
Material grades will be selected according to used types and other
values will be set in accordance with used design code.Click on OK to
close the window and the following check results will be displayed:
No punching reinforcement is necessary according to the check.
92
Result summary
AxisVM 11
Click on Result summary icon to see detailed results of the check:
Click on Close to exit from Punching analysis results and click on Close
to exit from Plate punching analysis.
Step by step tutorial
93
4. MEMBRANE MODEL
4.1.
Start
Objective
The objective of the analysis is to determine the internal forces and
reinforcements of the following wall structure.
Assume wall thickness to be 200 mm, the concrete grade: C20/25, and
the reinforcement grade: B500A and designed in accordance with Eurocode-2.
Start
Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder,
found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu.
New
Create a new model by clicking on the New icon.
Click on Front View icon for the modeling view. In the dialogue
window that pops up, replace the Model Filename with Membrane1.
Select the appropriate Design Code: Eurocode:
The first step is to create the geometry of structure.
Change view
In the lower left corner of the graphics area is, in blue colour, the
coordinate system beginning point marked with a blue X. The view
can be changed from the Icons Menu with the Views Icon. Move the
cursor over that icon and the following Icon bar is displayed:
Global Z direction is always upwards.
Change view to Front View (X-Z plane)!
94
4.2.
AxisVM 11
Geometry definition using parametric mesh
Geometry
If not already selected, click on Geometry tab:
Quad/Triangle
Division
The geometry of the wall is created with the Quad/Triangle Division
icon. Hold down the left mouse button to display the sub-menu. Click
on the first icon on the left.
To create the upper part enter N1=20, N2=8 :
Close the dialog window with Ok. Now you have to specify the corners of the Quad. They can be specified graphically or by entering the
coordinates. Enter them with coordinates :
To enter the first corner, type in the following sequence of keys:
x 0 y0
z 3 [Enter]
Specify the relative coordinates of the next corners in a similar way.
Type in the following sequence of keys :
x
x
x
12
0
-12
y
y
y
0
0
0
z
z
z
0 [Enter]
3 [Enter]
0 [Enter]
Exit from drawing quads by pressing Esc.
The following will be displayed:
Quad/Triangle
Division
The haunches are created in a similar way. Click on Quad/Triangle Divison icon. Enter the following values: N1=3, N2=6 :
Close the dialog window with Ok. Now you have to specify the corners
of the walls left haunch.
Step by step tutorial
95
Type in the following sequence of keys :
x
x
x
x
0
1
0,8
-1,8
y
y
y
y
0
0
0
0
z
z
z
z
-6 [Enter]
0 [Enter]
3 [Enter]
0 [Enter]
Exit from drawing quads by pressing Esc.
The following will be displayed:
Mirror
Create the other haunch by mirroring the first one with respect to the
centre of structure (X=6). Click on the Mirror icon.
The Selection bar is displayed:
Select with a selection window all nodes of the haunch.
The selected elements will be highlighted:
96
AxisVM 11
Finish the selection with Ok and the following dialog will be displayed:
Set Mirror: Copy, Nodes to connect: None, check Copy elements. Now
you have to specify the mirror plane. First select any central point, then
select any point vertically above or below it.
Step by step tutorial
97
The following will be displayed:
The geometry of the wall has been successfully created.
Zoom
Fit in window
Geometry
Check
Let's zoom to the structure. Move the cursor over the Zoom icon and
the Zoom Icon bar pops up:
Click on the Fit In Window icon.
In the top Icon bar click on Geometry Check icon to check for possible
duplicate entries. The following window will be displayed:
In the dialog window specify the Tolerance for merging the nodes. If
the distance between two nodes is less than this value then these nodes
will be merged. Check Geometry Check checkbox only and set
Tolerance[m] = 0.001.
Click on OK and a check summary is displayed when completed:
98
AxisVM 11
Elements
The next step is to create the finite elements. Click on Elements tab.
Surface
Elements
Click on Surface Elements icon. After selecting All (* button) elements
and confirming with OK the following dialog window is displayed:
Set the type of the element to Membrane (plane stress).
Material Library
Import
Click on Material Library Import icon. The following dialog window is
displayed:
Select C25/30 from the list, then confirm with Ok.
Thickness
Type in the Thickness edit box 200 [mm], then close the dialog window with Ok.
Step by step tutorial
Display
Options
99
To view the local coordinate system of the surface elements click on
the Display Options icon on the icons menu on the left side. The following dialog window is displayed:
Check the Surface checkbox in the Local Systems panel group. Accept
the change with Ok.
If the Mesh, Node, Surface Centre is switched on among the Graphics
Symbols in the Display Options, you can see that the program uses 9node membrane elements. These 9 nodes are the 4 corners, 4 midpoints and the centre point of surface element. If you move the cursor
over the surface centre symbol (a filled square), a hint window is displayed with the properties of the surface element: its tag, material,
thickness, mass and references, as shown on the next picture:
The red line shows the x axis of the local coordinate system, the yellow
one the y axis and the green one the z axis.
100
4.3.
AxisVM 11
Geometry definition using domains
Define of
Geometry
Elements
If not already selected, click on Elements tab. The Geometry toolbar
will be displayed:
Draw objects
directly
Clicking on the draw objects directly icon shows following window:
Domain
Click on domain icon! The following window shows up:
Material
database
The following window shows after clicking on OK:
Select C25/30 concrete and confirm with OK.
Type
Change type in Draw objects directly window from Shell to
Membrane (plane stress) and thickness to 200 mm (20 cm).
Step by step tutorial
Complex slab
101
Click on Complex slab icon.
User can draw the slab directly or define the coordinates.
Define coordinates of first point by pressing keys:
0 [Enter]
You can change to the global coordinate values by pressing the d labeled button on the left of the Coordinate Window.
If d button is down (pressed) it denotes relative coordinates. X turns to
dX and so on indicating that we are defining relative ccordinates. The
relative point of origin is shown as thick blue X (cross turned by 45
deg.)
Continue defining next points of the domain with relative coordinates.
Press following keys:
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
1
0,8
8,4
0,8
1
0
-12
0
y
y
y
y
y
y
y
y
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
0 [Enter]
3 [Enter]
0 [Enter]
-3 [Enter]
0 [Enter]
6 [Enter]
0 [Enter]
-6 [Enter]
Exit from Draw objects directly by pressing Esc twice.
102
AxisVM 11
The following will be displayed in the main window:
Translate
Click on the Translate icon!
Select the top horizontal line and finish the selection with Ok. Choose
Incremental from the Method panel, N=1, Nodes to Connect: None,
then close the dialog window with Ok. Now specify the translation
vector. Click on any empty place in the Graphics Area, then type in the
following sequence:
-0,75 [Enter]
The following will be displayed in the main window:
It is easy to observe the symbol of the domain - a blue line on the inner
contour of the domain. Moving the cursor over it shows a hint window
with the properties of the domain:
Step by step tutorial
103
Click on Mesh tab for meshing:
Domain
Meshing
Click the Domain Meshing Icon. Select the domain with the All button (*) and finish the selection with Ok. The following dialog window
will be displayed:
Type in 0.7 [m] for the Average mesh element size. After closing this
dialog window with Ok the automatic mesh generation is started. The
progress of mesh generation is shown in a window.
104
AxisVM 11
After the mesh generation is completed, the following will be displayed:
If you move the cursor on the surface centre symbol (a filled square), a
hint window is displayed with the properties of the surface element:
it's tag, material, thickness, mass and references as shown in the next
drawing.
Step by step tutorial
4.4.
105
Define supports and loads
Line Support
To create the supports click on the Line Support icon and select the
bottom lines of the haunch with a selection box.
Finish the selection with Ok.
To define a pinned support use the following settings:
After closing the window with OK you can see this :
You have finished with finite element definition.
106
AxisVM 11
Loads
Click the Loads tab:
Surface Edge
Load
Assume a 50kN/m vertical distributed load. Click on the Surface Edge
Load icon, then select the second line from top (created with the
translate command if defined using domain):
Finish the selection with Ok, and type in: a py [kN/m] = 50 :
Press Ok and the load is applied.
The following drawing is displayed:
Step by step tutorial
107
Static
The next step is the analysis and post processing. Click on Static tab:
Linear Static
Analysis
Click on Linear Static Analysis icon. The model will be saved with its
current name.
Nodal DOF
To proceed with the analysis you must set degrees of freedom (DOF).
The program checks the model and offers a DOF setting:
Check the Save model with these settings checkbox and degree of
freedom settings will be saved. Accept the Membrane in plane X-Z
setting and close with Yes button.
Analysis continus and the following progress bar shows up:
Messages,
Statistics
Click on Messages and Statistics to see more information about the
analysis.
The following window will be displayed after analysis:
108
AxisVM 11
After click on OK program automatically activates
deformations ez on Static tab in Isosurface 2D view .
Display options
Switch off Loads in Display options on Symbols tab for clarity.
Fit in window
Click on Fit in window function for better view.
vertical
The following will be displayed :
Select Surface Internal Forces nx by clicking on arrow next to
eZ[mm] on Static tab:
The nx diagram are the local normal forces in the membrane.
Min, Max Values
To find location of max. deformation use Min, Max values function.
Clicking on icon shows following window:
Step by step tutorial
109
Select one of the surface force components. Confirm with OK shows
the max. negative value and its location as well:
After click on OK shows the max. positive value and the location of
this value.
Colour legend
The Colour legend window shows boundary values of each colour.
Adjust number of boundary values by moving the bottom edge of this
window:
110
Colour legend
AxisVM 11
Find areas with surface forces over -100 kN/m! Boundary values can
be changed by clicking on Colour legend window. Click on a bottom
value of the table on a left hand side. Change the deafault value (291,86) to 100:
Press [Enter] and the Auto interpolate function calculates other
boundary values.
After click on OK the following will be displayed:
Areas with surface forces over -100 kN/m are hatched.
Step by step tutorial
Isoline
111
See the results using Isolines. Click on arrow right to Isosurface 2D
title and select Isoline:
After selecting Isoline the following will be displayed:
View the internal forces of the supports. Select Line Support Internal
Forces Rz in the Result Component combo box.
Result Display
Parameters
Click on Result Display Parameters icon, and check the Lines checkbox in the Write Values To panel and set the Display Mode to Diagram:
Close the dialog window with Ok and the values of vertical support
forces will be displayed on the screen:
112
AxisVM 11
R.C. Design
The next step is to calculate the reinforcement. Click on R.C. Design
tab:
Reinforcement
Parameters
Click on Reinforcement Parameters icon, and select all surface elements with All (*) button. Complete the selection with OK, and the
following dialog window is displayed:
Close the dialog box with OK and the following will be displayed:
Close the dialog window with OK and the axb diagram is displayed:
Step by step tutorial
113
The area of reinforcement in the x direction is the sum of the axt and
axb values.
114
AxisVM 11
blank page
Step by step tutorial
115
5. SHELL MODEL
Objective
Determine the specific forces and the amount of reinforcement for the
shown reservoir filled with water.
Thickness of the walls and the raft is 250 mm; ribs on the upper edge
are 30x60. The structure is made of C25/30 concrete and B500B rebar.
Use Euro code 2 for design.
Start
Start AxisVM 11 by double-clicking the AxisVM11 icon in the
AxisVM11 folder, found on the Desktop or in the Start - Programs
Menu.
New
Create a new model by clicking on the New icon.
Click on Front View icon for the modeling view. In the dialogue
window that pops up, replace the Model Filename with reservoir.
Select the appropriate Design Code: Eurocode:
116
AxisVM 11
Settings
Click Settings / Options / Grid & Cursor in the menu.
Replace each value under Cursor Step to 0.2:
This way you made sure that the mouse cursor moves in 0.2 m steps so
you can avoid geometric imperfections while drawing the model.
Define of
Geometry
Now you create the geometry using enhanced editing functions.
Elements
Select the Elements tab to bring up the Elements Toolbar.
Draw
directly
Domain
objects
Clicking on the draw objects directly icon shows following window:
Click on domain icon! The following window shows up:
Step by step tutorial
Material
database
117
The following window shows after clicking on OK:
Select C25/30 concrete and confirm with OK.
Thickness
Set Thickness mm] to 250
Complex slab
Click on Complex slab icon.
User can draw the contour directly or define the coordinates.
Draw the wall of the reservoir in X-Z plane!
Change view
Change view to Front View (X-Z plane):
Choose the global origin as the first point of the
polygon. It is at the bottom left where the horizontal and the vertical brown lines (representing
the global X and Z axes) are intersecting. The
blue X shows the current origin of the actual coordinate-system.
Relative coordinate system
You can change to the relative coordinate values by pressing the d labeled button on the left of the Coordinate Window. If d button is
down (pressed) it denotes relative coordinates.
Move the mouse cursor to the following locations and click once to enter each vertex: 11.0 right and 0.2 down, down 0.4, right 1.0, up 3.6, left
12.0, down 3.0 (or by keyboard: x 11 z 0,2 [Enter] z 0.4 [Enter] x 1
[Enter] z 3.6 [Enter] x 12 [Enter] z 3 [Enter]).
Double-click at the last vertex to quit the drawing function.
The following will be displayed in the main window:
118
Change view
AxisVM 11
Change view to Perspective:
After changing values in window as follow:
H= 30 V= 320 P = 0
Click on X at top right corner to close the Perspective window.
Mirror
Create the wall on other side by mirroring the first one with respect to
the centre of structure (Y=4). Click on the Mirror icon.
The Selection bar is displayed:
Select the domain with the All button (*) and finish the selection with
Ok. The following dialog window will be displayed:
Select Mirror: Multiple and Nodes to Connect: All
Then close with OK.
Step by step tutorial
119
Define the plane of mirroring. Type in the following sequence of keys :
x 0
y 4
z 0 [Enter]
x 1
y 0
z 0 [Enter]
Press Esc to exit.
The following will be displayed :
Fit in window
Click on Fit in window function for better view.
Numbering
Click on Numbering icon in the bottom right corner
and the following check boxes will be displayed:
Here you can turn numbering on or off. Turn on the
check box before Node and node numbers appear immediately.
Translation
(move)
To shape up the grip slope move the line between Node 3 and 4 down
by 0.2 m.
Paralell move of
line
Drag a selection rectangle around Node 3 and 4:
All elements within the rectangle will be selected (Node 3, Node 4 and
the line between them).
Move the cursor onto the selected line and start dragging it.
120
AxisVM 11
Select the Paralell move of line icon from the Icon bar on the left and
choose the first icon from the fly out toolbar.
Now you have to specify the translation vector.
To specify the exact distance type in the following:
X 0
Y0
Z -0.2 [Enter]
Geometry
Select the Geometry tab to bring up the Geometry Toolbar.
Geometry Check
Click the Geometry Check icon which is on Geometry tab, the following
window shows up:
User can set for the maximum tolerance (distance) for checking points
and show the mesh.
Check the Select unattached nodes or lines checkbox and click on OK.
After clicking OK a check report message will be displayed:
Elements
Clicking the Elements tab you can specify the element types, material
properties, cross-sections and references determining local systems of
the elements:
Step by step tutorial
121
Reference point
The local system of finite elements can be set by references. In this example a reference point is used to define the orientation of the local Z
direction of the domains and a reference plane to define the in-plane X
and Y axes.
Click the reference point icon then click the centre point of the line between Node 5 and 11. To locate the centre point move the cursor along
the line and check if the cursor shape changes from / to .
Press Esc to exit from function.
Numbering
Move the cursor over the Numbering icon on the speed button toolbar.
Turn on the Reference checkbox. Now an R2 label appears beside the
reference symbol.
Reference plane
To set the local system of domains create a reference plane. Click the
Reference plane icon on the Elements toolbar. You need three points to
define the plane.
Click Node 6, then click anywhere on the line between Node 1 and 2
finally click on Node 2.
The following will be displayed :
Press Esc to exit from function.
Domain
Define a domain to create structural surface elements.
Click the Domain icon. The Selection palette appears. Click on the following lines to select domain contours:
12 6; 12 8, following 2 lines 8-2 and 6-2 are automatically selected.
8 - 7;1 - 7, following 2 lines 1 - 2;2 8 are automatically selected.
11 - 10;10 - 4 following 2 lines 4 - 5;5 - 11 are automatically selected.
122
AxisVM 11
Click OK on the Selection palette. The Domains dialog will be displayed:
Thickness
Enter 250 mm(or 25 cm) into the edit field Thickness[mm].
Reference
Set the Local x Reference to R3:
Close the window with OK button.
You will see a green contour along the domain boundary showing the
shape of the domain. The colour depends on the element type. Shell
domains always have a green contour.
Local systems
A Gyorspalettn a jobb oldalrl 4. ikonra klikkelssel kapcsoljuk be a
Loklis rendszerek szimblumot.
Turn on the display of the local systems by clicking on the Local systems speed button in the bottom right speed button toolbar.
Step by step tutorial
Domain
123
Define a domain to create structural surface elements. Click the Domain icon. The Selection palette appears.
Click on the following lines to select domain contours:
7 9 ; 9 3, following 2 lines 3 1and 1 7, are automatically selected.
Click OK on the Selection palette. You get to the Domains dialog.
Choose Shell as element type, 250 mm as Thickness, R3 as Local x Reference, R2 as Local z Reference and click OK.
Domain
Define a domain to create structural surface elements. Click the Domain icon. The Selection palette appears. Click on the following lines to
select domain contours:
9-10; 10-4, following 2 lines 4-3and 3-9, are automatically selected.
Click OK on the Selection palette. You get to the Domains dialog.
Set 250 mm as Thickness and leave references on Auto and click on
OK.
The following will be displayed:
124
Speed buttons
Line elements
New CrossSection
AxisVM 11
Turn off Numbering / Node and Local systems using speed buttons.
To define ribs on the upper edges click on Line elements on the Elements toolbar. The Selection palette appears. Click on the 4 edges. Click
OK on the Selection palette. You get to the Line elements dialog:
Click on New Cross-Section icon to define new cross-section. The
following window shows up:
Step by step tutorial
Rectangular
shape
125
To define a 30 x 60 rectangular shape click on Rectangular shape icon
.The following window shows up:
Type 300 into the b[mm] edit field and 600 into h[mm] then click the
Place button. You get back to the main window. Click anywhere to
place the shape. The following will be displayed:
The cross-section 1st and 2nd principal direction, centre of gravity and
other cross-section parameters are displayed within the property info
window. Click More parameters if you want to see all parameters calculated automatically by a finite element analysis of the cross-section.
Click OK to close the Cross-section change default name of crosssection if required. Click on OK again to confirm.
126
Bottom rib
AxisVM 11
Set the excentricity to Bottom rib then confirm settings with OK. Rib
centrelines are displayed as blue lines and the contour of actual crosssection is shown in yellow.
Move the cursor over a rib and wait for the tooltip to appear displaying
element properties:
Rendered view
A bal oldali ikonsoron fellrl a negyedik ikon az brzolsi md. Vlasszuk ki a jobboldali Ltvnyterv funkcit!
Move the cursor over the View mode icon on the left Icon bar. A fly out
toolbar appears. Select the third icon to choose Rendered view.
This way you can check element definitions.
Rotate view
Click the Rotate view icon on the Zoom toolbar at the bottom left corner of the main window. Drag the model to rotate it. A special Rotation
toolbar appears. You can control the way view rotation works by selecting from the options.
You can also hold Alt + mouse wheel and rotate the view anytime.
View undo
Select View undo from the Zoom toolbar to restore the previous view.
Fit in window
Click on Fit in window function for best view.
Wireframe
Select Wireframe from the view mode fly out toolbar.
Step by step tutorial
127
Surface support
To define supports for the structure click the Surface support icon on
the Elements toolbar. The Selection palette appears. Click on the two
horizontal domains. Click OK on the Selection toolbar. The following
window shows after clicking:
Change Rx and Ry to 1E+3 and click OK.
The following will be displayed in the main window:
Loads
To define loads click the Loads tab:
Load cases and
load groups
To define load cases and load groups click Load cases and load groups
icon on the Loads toolbar. The following window will be displayed:
128
AxisVM 11
Click on the selected load case ST1 to rename it to Self-Weight. Click
OK to close the dialog.
Self weight
To define self weight, click on Self weight icon. On the Selection palette click the Select all (*) icon or press grey * on the keyboard. Click
OK to close the Selection palette.
Dashed lines along the domain contours represent the self weight.
Moving the cursor to a domain you get a tooltip like this:
Static Load Case
To create another load case click the Load cases and load groups icon on
the Loads toolbar and click the Static button in the New Case group
box.
Enter Water as the name of the new load case in the tree view.
Click OK to close the dialog.
Fluid loads
To define the water load click the Fluid loads icon. On the Selection
palette click the Select all (asterisk) icon or press grey * on the keyboard. Click OK to close the Selection palette. The following window
will be displayed:
Step by step tutorial
129
To define water level 30 cm under the top edge of the reservoir change
Z1 [m]=3.000 to 2.7, and set the bottom pressure value p(Z2) [kN/m2]=
35 (pressure is in the negative local z direction) and click OK.
The following will be displayed:
Load
combinations
To create load combinations click the Load combinations icon. You get
to the load combinations table in the Table Browser:
New row
To create new combinations click the New row icon. Leave the name
on default Co #1 then select (user defined combination) . Then enter
1.35 into the Self Weight column and 1.00 into the Water column. Use
[Tab] or [Enter] to jump to the next cell. Click OK to close the dialog.
130
AxisVM 11
Speed buttons
Using the speed button and turn off Supports, Reference and Object
contours in 3D from the Graphic symbols fly out.
Mesh
To create finite element mesh click the Mesh tab.
Speed buttons
Using the speed button turn off Load display.
Domain Meshing
Click on the Domain meshing icon. On the Selection palette click the
Select all (*) icon or press grey * on the keyboard. Click on OK to close
the Selection palette. Select rectangular mesh type (in centre) and set
Average Mesh Element Size to 0.600 m.
Click on OK to close the dialog. You get a visual feedback on the meshing process:
Step by step tutorial
131
After completing you get the following:
Green points at the centre of surface elements are the symbols of shell
centre points. Moving the mouse over a centre point you get a hint
with the elements properties:
Speed buttons
Static
Linear analysis
Turn off Nodes, Surface centre and Domains in the Graphic Symbols
then turn off also the Mesh Display.
This way we have finished modelling and model can be analysed.
To run the analysis and display the results click the Static tab.
Click on Linear static analysis to run the linear analysis.
You get to the dialog which gives you a feedback on the process of the
analysis. Click Details to know more about it.
The following progress bar shows up:
132
Messages and
Statistics
AxisVM 11
Click on Messages and Statistics to see more information about the
analysis:
The Estimated Memory Requirement shows the necessary amount of
memory to run the analysis. If this value is higher than the available
physical memory AxisVM uses the hard disk to swap memory blocks
during the calculation. If the system of equations fits into the physical
memory the calculation is considerably faster.
The following window shows up after analysis:
Numbering
After click on OK the Static tab is activated with ez vertical
deformations for Self Weight load case as Isosurface 2D view.
Click the Numbering speed button and turn on Write Values to Surfaces
and Min./Max. only.
To see the result for the Water load case click
on the dropdown button of the combo box
displaying Self Weight and select Water:
You can change the result component the
similar way, select eY.
Step by step tutorial
133
Parts
To hide the front wall of the reservoir create a part. Click the Parts icon
on the Icon bar on the left. You get to the Parts dialog:
New
Define a part containing everything but the front wall click on New
icon and specify the name as 1:
Click on OK then select all (*) on the Selection palette.
After this Remove selection icon (-) will be activated.
Change view
Change to Z-X view plane (front view)!
Press and hold wheel of the mouse pan the view so the right part of
model is fully visible. Use the botom slider if your mouse doesnt have
a wheel button.
Using selection rectangle unselect the wall on right hand side from the
selection:
134
AxisVM 11
Click on OK on the Selection palette then close the Parts dialog window with OK.
View Undo
Undo the view (or select Perspective view by [Ctrl+4]) and you will
see that the front wall is hidden.
Step by step tutorial
135
Min, max Values
To determine the extreme values of the horizontal displacements click
the Min, max Values icon. Clicking on icon shows following window:
Select one of the deformation components. Click on OK to show max.
negative value with its location:
Click on OK to show max. posititive value with its location:
Close the window with OK.
Select the load combination (Co #1) and the eR resultant displacement!
136
Display
Parameters
AxisVM 11
Click on the Display Parameters icon, set Display Shape to Deformed,
Display Mode to Diagram and Scale By to 2 :
Close the window with OK!
Hidden line removal
Go to the bottom of the screen, turn on the Mesh Display speed button
and change the display mode on the Icon bar to Hidden line removal :
Rotate view
Click the Rotate view icon on the Zoom toolbar at the bottom left corner
of the main window. Drag the model to rotate it and check the
deformed shape. A special Rotation toolbar appears. You can control
the way view rotation works by selecting from the options.
You can also hold Alt + mouse wheel and rotate the view anytime.
Press Esc to exit.
View undo
Select View undo from the Zoom toolbar to restore the previous view.
Result Display
Parameters
Click on Result Display Parameters icon and change Display shape to
Undeformed , Display Mode to Isosurfaces 2D and Scale to 1.
Using the speed button turn off Mesh display.
Change result component to Surface Internal Forces mxD+
Colour legend
The Colour legend window shows boundary values of each colour.
Adjust number of boundary values by moving the bottom edge of this
window, set it to 22:
Step by step tutorial
137
Change result component to Surface Internal Forces myDSection Lines
To see section of myD- diagram click on Section Lines icon on the Icon
bar. The following window will be diplayed:
138
AxisVM 11
To define a new section plane click the New section plane button in the
dialog. The following message box will be diplayed:
Type in 1 as the name of the section plane and confirm with OK, then
close the window with OK.
Change view
Select the X-Z view (Front view) from the fly out toolbar or press
[Ctrl+1]:
A section plane can be defined by two points in side, front of top view.
Being
in front view click the rib at 6.0 m (e.g. typing: x 6 [Enter]) and enter
the second point somewhere under the first on a vertical line (e.g. typing: z 3 [Enter]).
You get back to the Section Lines dialog. Click on OK.
Change view
Select the Z-Y view (side view) from the fly out toolbar or press
[Ctrl+3]. Change Display Mode to Section Line.
Numbering
Click Numbering speed button and turn on Write Values to Lines.
You get the following diagram:
Speed buttons
Turn off Section Lines Planes !
Perspective
Click on the Perspective icon on the Icon bar (left side of the main
window). Close the perspective settings window.
Change view to Isosurface 2D! Select Surface Support Intenal Forces
Rz which shows vertical reactions of the surface support and the
following will be displayed:
Step by step tutorial
139
R. C. Design
Click on R.C. Design tab.:
Reinforcement
parameters
Click on Reinforcement parameters icon then select all (*) and confirm
with OK. The following message shows up:
Close with OK and the following window will be displayed:
140
AxisVM 11
Set Exposition classes on Materials tab. Set XC2 for Top and Bottom
surface. Set Primary direction of reinforcement as x for Top and
Bottom surface on Reinforcement tab. Check Apply minimum cover
checkbox:
Close the window with OK.
Numbering
Click the Numbering speed button and turn off Write Values to Surfaces
and Lines. The following will be displayed:
Check ayb, axt, ayt reinforcement values!
Check crack widths for load combination Co #1 using actual
reinforcement 12 @ 150mm c/c in both direction at top and bottom!
Step by step tutorial
Actual
Reinforcement
141
Click on Actual Reinforcement icon! The following window shows up:
Set x direction for Primary direction of reinforcement on top and
bottom surface on Parameters tab and check the Apply minimum
cover checkbox.
Click on Reinforcement tab.
Set reinforcement rebar on right hand side and assign it to 4
reinforcement layers on left hand side.
Set diameter to 12 for [mm]= and Spacing [mm] to 150 on
Reinforcement tab. Check the Calculate rebar positions checkbox then
select x Direction Top Reinforcement in top left box and click on
Add button.
The following will be displayed:
The same way define Bottom Reinforcement in x and also in y
direction.
Selection
Assign defined actual reinforcement to domains. Click Selection icon
then select all domains with the All button (*) and finish the selection
with Ok.
Click on Close button to close the window.
The following will be displayed:
142
Crack widths
AxisVM 11
Select Cracking wk(b) result component which is showing crack
widths in local x direction at bottom surface of domains (outter face of
reservoir):
All domains are hatched what denotes that there are no cracks on
outter face of domains.
Check crack widths on the inner face of the reservoir!
Select Cracking wk(t) result component which is showing crack
widths in local x direction at top surface of domains. The following will
be displayed:
Step by step tutorial
143
Here you can see cracks on some inner corners of the domains.
Beam
reinforcement
design
To design reinforcement in the rib, click on Beam reinforcement design icon, then click on the shorter rib on top of the end wall and
finally click on OK. The following warning message shows up:
After click on OK next warning message shows up:
Beam
parameters
After click on OK window with Beam parameters shows up.
Select rectangular cross-section beloor Cross-section title (at top). then
select B500B rebar grade for longiutdal rebars and stirrups.
Set Concrete cover to 20mm and top longitudal rebars f to 35 mm. For
crack control check Increase reinforcement according to limiting crack
width checkbox:
144
AxisVM 11
After click on OK the follwing window with results shows up:
Click on Check tab in Beam Reinforcement window and you can see:
needed number of rebar, actual crack width considering needed
number of rebar and number of rebar rows.
Click on OK to close the window.
Step by step tutorial
Notes
145
146
Notes
AxisVM 11
Step by step tutorial
Notes
147
You might also like
- RadierDocument10 pagesRadierRazvan BaiceanuNo ratings yet
- Lateral Stability of Long Precast Concrete BeamsDocument12 pagesLateral Stability of Long Precast Concrete BeamsTaiCheong Lee100% (1)
- Integration Robot Structural Analysis Professional With Advance Steel AU 2015 Class HandoutDocument36 pagesIntegration Robot Structural Analysis Professional With Advance Steel AU 2015 Class HandoutmihaidelianNo ratings yet
- A Detaliu Atic Plan Armare Sambure 25x25: Etr Ø8/20 L 0.74m S500Document1 pageA Detaliu Atic Plan Armare Sambure 25x25: Etr Ø8/20 L 0.74m S500Ionut SprancenatuNo ratings yet
- Webinar N°3 Steel DesignDocument39 pagesWebinar N°3 Steel DesigndelkoskeNo ratings yet
- Extras ArmareDocument17 pagesExtras ArmareStaruiala GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Incovoiere: B Ho RC Ra MDocument58 pagesIncovoiere: B Ho RC Ra MConstantin OvidiuNo ratings yet
- Plan Sarpanta A: Produced by An Autodesk Educational ProductDocument1 pagePlan Sarpanta A: Produced by An Autodesk Educational ProductMarius StoicaNo ratings yet
- FEM-Design - Intoduction CourseDocument46 pagesFEM-Design - Intoduction CourseAbulfazl MuhammadiNo ratings yet
- Calcul Scara PisicaDocument18 pagesCalcul Scara PisicaVirginia Elena IordacheNo ratings yet
- Calculul Static Al Halelor Industriale - C. Rusca, D. GeorgescuDocument147 pagesCalculul Static Al Halelor Industriale - C. Rusca, D. GeorgescuMaDGeo100% (2)
- Robot APIDocument105 pagesRobot APIRui Gavina0% (1)
- r9. Plan Rosturi Taiate in Pardoseala.Document1 pager9. Plan Rosturi Taiate in Pardoseala.alexandruNo ratings yet
- Calculul Incarcarilor: B S T B S T 1 2 3 1 2Document31 pagesCalculul Incarcarilor: B S T B S T 1 2 3 1 2Ovidiu CristianNo ratings yet
- Model EtabsDocument17 pagesModel EtabstfemilianNo ratings yet
- Calcul Aria Armatura Longitudinala Perete Mulat Fata InterioaraDocument2 pagesCalcul Aria Armatura Longitudinala Perete Mulat Fata InterioaraBza ZaBugNo ratings yet
- Chapitre 18 Portiques BA-Exemple Calcul-Corr09Document87 pagesChapitre 18 Portiques BA-Exemple Calcul-Corr09Mohamed Bouzidi FSNo ratings yet
- Soficad 162-163 eDocument157 pagesSoficad 162-163 eMario Andres Arias Estrella0% (1)
- Axisvm Manualx6 enDocument650 pagesAxisvm Manualx6 enCernomodiac NicolaeNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Fundatii IzolateDocument32 pagesMathcad - Fundatii IzolateMaris NicuNo ratings yet
- Loads, Load Combinations, Calculation and ResultsDocument30 pagesLoads, Load Combinations, Calculation and ResultsBorce StoilovskiNo ratings yet
- Armare Radier GeneralDocument1 pageArmare Radier GeneralBogdanIng100% (2)
- Plan Taiere Pardoseala: 1 Detaliu Rost ContactDocument1 pagePlan Taiere Pardoseala: 1 Detaliu Rost ContactVlad CiubotaruNo ratings yet
- Advance Design Validation Guide 2023 Volume IVDocument849 pagesAdvance Design Validation Guide 2023 Volume IVkeffy_bfk100% (1)
- Combinatii de IncarcariDocument4 pagesCombinatii de IncarcarilucianduNo ratings yet
- Predimensionare Fundatie IzolataDocument3 pagesPredimensionare Fundatie IzolataVirginia Elena Iordache100% (1)
- Sam Eurocode UK Pretressed Beam Sample ReportDocument176 pagesSam Eurocode UK Pretressed Beam Sample Reportdragos_bogdan1974No ratings yet
- Armare Stalp de BetonDocument1 pageArmare Stalp de BetonAndrei NeațuNo ratings yet
- 3.1.6 SECT A-A - Hala MetalicaDocument1 page3.1.6 SECT A-A - Hala MetalicaCrysty MihalacheNo ratings yet
- Advance Design Validation Guide 2021 Volume IDocument436 pagesAdvance Design Validation Guide 2021 Volume InelucomnelucomNo ratings yet
- Verificare Imbinare Cu Suruburi Grinda-StalpDocument2 pagesVerificare Imbinare Cu Suruburi Grinda-StalpVirginia Elena IordacheNo ratings yet
- Metric Tutorial Revit Structure 2008Document616 pagesMetric Tutorial Revit Structure 2008Fernando GomesNo ratings yet
- Grinda Mixta Otel-BetonDocument6 pagesGrinda Mixta Otel-BetonKalauz EdmondNo ratings yet
- Graitec Advance Concrete Brochure en PDFDocument6 pagesGraitec Advance Concrete Brochure en PDFroly_zerocoolNo ratings yet
- Calcul SarpantaDocument3 pagesCalcul Sarpantacrmn_matNo ratings yet
- Metal. Plansa Nr.3.inima Grinda + Stalp + ContravantuireDocument1 pageMetal. Plansa Nr.3.inima Grinda + Stalp + ContravantuireSergiu NastasNo ratings yet
- Plan Cofraj Planseu Peste ParterDocument1 pagePlan Cofraj Planseu Peste ParterSHaZaMNo ratings yet
- Armare Stalpi 30x30 Dintre Axa 1 Si Axa 3 Armare Stalpi 45x45 Armare Stalpi 40x40 Armare Stalpi 40x50Document1 pageArmare Stalpi 30x30 Dintre Axa 1 Si Axa 3 Armare Stalpi 45x45 Armare Stalpi 40x40 Armare Stalpi 40x50Victor RîndunicaNo ratings yet
- Eurocod 2Document358 pagesEurocod 2777blabla100% (1)
- Eurocode 5 PDF FreeDocument2 pagesEurocode 5 PDF FreeBasilNo ratings yet
- Plan Armare Centuri ExempluDocument1 pagePlan Armare Centuri ExempluVarabiev LucianNo ratings yet
- Spectru ProiectareDocument27 pagesSpectru ProiectareHoria Ionut MihneaNo ratings yet
- Xtract StalpDocument1 pageXtract StalpAndrei TeoNo ratings yet
- Armare Grinda Transversala - 2 PDFDocument1 pageArmare Grinda Transversala - 2 PDFCiprian ShaolinNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Fundatii Continue RigideDocument3 pagesMathcad - Fundatii Continue RigideGîlea ȘtefanNo ratings yet
- Zid de SprijinDocument4 pagesZid de SprijinAnonymous W6WPVDkeNo ratings yet
- Axis VM Step by StepDocument120 pagesAxis VM Step by Stepdoru_enciuNo ratings yet
- Model PlacaDocument29 pagesModel PlacaRadu MihaiNo ratings yet
- AxisVMStepbyStep PDFDocument125 pagesAxisVMStepbyStep PDFpluto_narkoNo ratings yet
- Step by Step: Tutorial For Axisvm X4Document162 pagesStep by Step: Tutorial For Axisvm X4hapsinteNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide To Beam Analysis Using Strand7Document15 pagesQuick Guide To Beam Analysis Using Strand7Tarek AbulailNo ratings yet
- Sap TrussDocument28 pagesSap TrussPoh Yih ChernNo ratings yet
- Asfafjhaf F SDF DSFSD F Sdfs Dfsdfs FSF S Fer SBFDHD GFDGDF G D G DF GDFG DFDocument22 pagesAsfafjhaf F SDF DSFSD F Sdfs Dfsdfs FSF S Fer SBFDHD GFDGDF G D G DF GDFG DFaamirNo ratings yet
- Cantilever Beam Example: Preprocessing: Defining The ProblemDocument8 pagesCantilever Beam Example: Preprocessing: Defining The Problemabdul kareeNo ratings yet
- 2D PROBLEM Using Graphical User Interface Problem 1: Continuous Beam (3 Unequal Spans With Udl)Document32 pages2D PROBLEM Using Graphical User Interface Problem 1: Continuous Beam (3 Unequal Spans With Udl)V.m. RajanNo ratings yet
- Loads Introductory Tutorial For Structural Analysis Part 41Document7 pagesLoads Introductory Tutorial For Structural Analysis Part 41Thomas InsoNo ratings yet
- Ansys Basic TutorialsDocument19 pagesAnsys Basic TutorialsAlex CristeaNo ratings yet
- ETABS LearningDocument8 pagesETABS LearningSai TarunNo ratings yet
- Sap Truess Step by Step ProceduresDocument18 pagesSap Truess Step by Step ProceduresThulasirajan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Simple Rod ProblemDocument22 pagesSimple Rod ProblemhoojzteNo ratings yet
- MS Project Tutorial PDFDocument36 pagesMS Project Tutorial PDFBilal Ahmed Barbhuiya100% (3)
- Engtutorial Bim Toolbox PDFDocument33 pagesEngtutorial Bim Toolbox PDFBelak1No ratings yet
- Hollow PIPE MMDocument12 pagesHollow PIPE MMharabiNo ratings yet
- FRILO - FDC - Basic Operating Instructions - EngDocument9 pagesFRILO - FDC - Basic Operating Instructions - EngBelak1No ratings yet
- Sci A Install Manu AllDocument1 pageSci A Install Manu AllBelak1No ratings yet
- CorelDRAW Object Model DiagramDocument4 pagesCorelDRAW Object Model DiagramAraujo ThiagoNo ratings yet
- Code Combinations According To The Regulation: EN 1990:2002: Parameters of Code Combination GenerationDocument1 pageCode Combinations According To The Regulation: EN 1990:2002: Parameters of Code Combination GenerationBelak1No ratings yet
- Bentley I-Model ODBC DriverDocument28 pagesBentley I-Model ODBC Driverjanice19899No ratings yet
- CYPECAD - User's Manual PDFDocument141 pagesCYPECAD - User's Manual PDFBelak1No ratings yet
- The Values of The Snow&Wind Loads According To BS-EN 1991-1-3/4 NA:2005/2008Document75 pagesThe Values of The Snow&Wind Loads According To BS-EN 1991-1-3/4 NA:2005/2008Belak1No ratings yet
- AC-AxisVM User ManualDocument5 pagesAC-AxisVM User ManualBelak1No ratings yet
- LTE Radio Access, Rel. LTE 17A, Operating Documentation, Issue 03Document54 pagesLTE Radio Access, Rel. LTE 17A, Operating Documentation, Issue 03Nicolás RuedaNo ratings yet
- 2013 GPI Report ES - 0 - GlobalPeaceIndexDocument106 pages2013 GPI Report ES - 0 - GlobalPeaceIndexchristian.lochmuellerNo ratings yet
- Behavior Based SafetyDocument6 pagesBehavior Based Safetyapi-313899066No ratings yet
- Pat-Og, Sr. vs. Civil Service CommissionDocument1 pagePat-Og, Sr. vs. Civil Service CommissionChelle OngNo ratings yet
- College AdministrationDocument13 pagesCollege AdministrationGirmaye HaileNo ratings yet
- W1FB - Design NotebookDocument200 pagesW1FB - Design NotebookHsu100% (1)
- Lucent 5ESS PDFDocument1 pageLucent 5ESS PDFJosue Calebe Rodrigues Machado100% (1)
- Internship LogDocument1 pageInternship Logthedirtydozen98No ratings yet
- Minor ProjectDocument12 pagesMinor ProjectNikitaNo ratings yet
- Newspaper Collection Policy & Appointment Request Form (3/19/14)Document2 pagesNewspaper Collection Policy & Appointment Request Form (3/19/14)HSLBNo ratings yet
- Ejectment JurisprudenceDocument17 pagesEjectment Jurisprudenceeds billNo ratings yet
- PHIMCO Industries vs. PHIMCO Labor AssociationDocument2 pagesPHIMCO Industries vs. PHIMCO Labor Associationbernadeth ranolaNo ratings yet
- Object Detection and Recognition For A Pick and Place Robot: Rahul Kumar Sanjesh KumarDocument7 pagesObject Detection and Recognition For A Pick and Place Robot: Rahul Kumar Sanjesh KumarLuật NguyễnNo ratings yet
- HHS Letter To State Medicaid Directors On Hospice Care For Children in Medicaid and CHIPDocument3 pagesHHS Letter To State Medicaid Directors On Hospice Care For Children in Medicaid and CHIPBeverly TranNo ratings yet
- 2-Behavioral Biases Influencing The Decision Making of Portfolio Managers of Capital Securities and Traders in MoroccoDocument14 pages2-Behavioral Biases Influencing The Decision Making of Portfolio Managers of Capital Securities and Traders in MoroccoBebe Recah SacedaNo ratings yet
- 12port Rosenberger - BA G7G7W8W8W8W8X65V 21 - DEDocument2 pages12port Rosenberger - BA G7G7W8W8W8W8X65V 21 - DESarhento KunehoNo ratings yet
- Ford Ranger ManualDocument266 pagesFord Ranger ManualHerWagner100% (9)
- The Digital Musician Second Edition by ADocument3 pagesThe Digital Musician Second Edition by AEddie IpenzaNo ratings yet
- Max Diff TechDOcDocument21 pagesMax Diff TechDOcNeri David MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ravi Urban Development AuthorityDocument3 pagesRavi Urban Development Authorityaahsan345No ratings yet
- Markes Nicole Resume Online PortfolioDocument2 pagesMarkes Nicole Resume Online Portfolioapi-283615713No ratings yet
- Ruko Twist DrillsDocument80 pagesRuko Twist DrillsPeter NomikosNo ratings yet
- PrmPayRcpt 63169968Document1 pagePrmPayRcpt 63169968nanduriramacharyulu817No ratings yet
- Draw Conclusions and Formulate Recommendations (ABM - BES12-Ia-c-4)Document6 pagesDraw Conclusions and Formulate Recommendations (ABM - BES12-Ia-c-4)Aimee LasacaNo ratings yet
- Seniority List Assistant Engineer Civil As Stood On 28.12.2001Document6 pagesSeniority List Assistant Engineer Civil As Stood On 28.12.2001harideep sharmaNo ratings yet
- PFP Book PDFDocument176 pagesPFP Book PDFYashi MathurNo ratings yet
- Smart Edu 821 Research and Statistics Course NoteDocument9 pagesSmart Edu 821 Research and Statistics Course NoteCelestineNo ratings yet
- Unit 17 Reading Part 123Document2 pagesUnit 17 Reading Part 123Cristina Punta PérezNo ratings yet
- 1 Q2-ConartsDocument22 pages1 Q2-ConartsLorenz TeoNo ratings yet