Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 06
Assignment 06
Uploaded by
riddler_0070 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThis document outlines four problems related to analog integrated circuit design:
1. Calculate currents and differential resistance in a transistor circuit and determine the condition for infinite output resistance.
2. Calculate the input impedance of another circuit and note anything special about the result.
3. Calculate small signal impedance in a third circuit and determine the condition and frequency for infinity. Model transistors using transconductance.
4. Calculate the stability condition of an inverter chain by modeling gain and finding the root that yields the lowest value for instability.
Original Description:
assign
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines four problems related to analog integrated circuit design:
1. Calculate currents and differential resistance in a transistor circuit and determine the condition for infinite output resistance.
2. Calculate the input impedance of another circuit and note anything special about the result.
3. Calculate small signal impedance in a third circuit and determine the condition and frequency for infinity. Model transistors using transconductance.
4. Calculate the stability condition of an inverter chain by modeling gain and finding the root that yields the lowest value for instability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageAssignment 06
Assignment 06
Uploaded by
riddler_007This document outlines four problems related to analog integrated circuit design:
1. Calculate currents and differential resistance in a transistor circuit and determine the condition for infinite output resistance.
2. Calculate the input impedance of another circuit and note anything special about the result.
3. Calculate small signal impedance in a third circuit and determine the condition and frequency for infinity. Model transistors using transconductance.
4. Calculate the stability condition of an inverter chain by modeling gain and finding the root that yields the lowest value for instability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
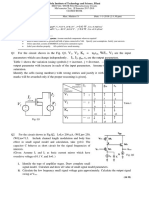
EE5390: Analog Integrated Circuit Design; HW6
Nagendra Krishnapura (nagendra@iitm.ac.in)
due on 13 April 2011
Vdd
Rs
L
Vdd
Rs
Rdiff
Rs
vom
C
vop
Vdd
vx
Rs
ix
vom
L
C
ix
Rs
vop
I0
I0
(a)
C1
C2
I0
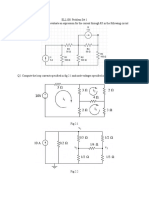
Figure 3:
N inverters(N: odd)
(b)
Figure 1:
Vdd
Figure 4:
Zin
C1
C2
3. Calculate the small signal impedance vx /ix . What is
the condition for this to be infinity? What is the fre-
I0
quency at which this happens? Model the transistor
using only its gm .
Figure 2:
4. In Fig. 4, assume that all nodes are at the self bias
voltage of the inverter. Model the small signal gain
of each inverter as A0 /(1 + s/p1 ) and calculate the
1. Calculate the current flowing in each transistor in
Fig. 1(a) in the quiescent condition. Calculate the
condition for instability (i.e. when the loop gain becomes 1). Hint: Among the roots of 1, pick the
one which satisfies the above for the lowest value of
small signal differential resistance Rout looking into
the drains of the two transistors.
In Fig. 1(b), calculate (vop vom )/ix . What is the
condition for this to be infinity? What is the frequency at which this happens?
A0 .
2. Calculate the input impedance Zin in Fig. 2. Is there
anything special about it? Model the transistor using
only its gm .
1
You might also like
- ECX3230 - Electronics Assignment No. 02 (Due Date: See The Activity Diary)Document3 pagesECX3230 - Electronics Assignment No. 02 (Due Date: See The Activity Diary)Lalantha Munasinghe ArachchiNo ratings yet
- Method of (Circuit) AnalysisDocument36 pagesMethod of (Circuit) AnalysisA.K.M.TOUHIDUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Basic Question BankDocument4 pagesBasic Question Bankmanju.dsatmNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Exam1Document8 pagesProblem Set Exam1Danny CabralesNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Exam1Document8 pagesProblem Set Exam1Danny CabralesNo ratings yet
- Analog Guide RajaReddyDocument30 pagesAnalog Guide RajaReddyKirti Susan VargheseNo ratings yet
- V, V, K U C W/L, V I, I, G, R: Unless Given SpecificallyDocument2 pagesV, V, K U C W/L, V I, I, G, R: Unless Given SpecificallyraghavbhatiaNo ratings yet
- Analog Integrated Circuits Exercise 4: Common-Source and Differential AmplifiersDocument9 pagesAnalog Integrated Circuits Exercise 4: Common-Source and Differential Amplifiersubuntu 13.04No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Name: ID NumberDocument18 pagesMidterm Exam Name: ID NumberpskumarvlsipdNo ratings yet
- EEC501Document2 pagesEEC501raviNo ratings yet
- ECE 5317-6351 Microwave Engineering: Notes 14Document59 pagesECE 5317-6351 Microwave Engineering: Notes 14Kiran Kumar B MNo ratings yet
- LAB 11-PE-LabDocument10 pagesLAB 11-PE-LabLovely JuttNo ratings yet
- BE 1st Midterm Sep2009Document3 pagesBE 1st Midterm Sep2009YASHNo ratings yet
- EE 214 Electric Circuits Laboratory: Midterm Examination April 15, 2002Document11 pagesEE 214 Electric Circuits Laboratory: Midterm Examination April 15, 2002Yavuz SahbazNo ratings yet
- Activity 8Document2 pagesActivity 8Tim Jeff RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Training Questions in Electronics/F 6, Gths K'Bo Paper Two: January 2010Document6 pagesTraining Questions in Electronics/F 6, Gths K'Bo Paper Two: January 2010NGOUNENo ratings yet
- A Low-Voltage Current Conveyor Using Inverter-Based Error Amplifier and Its Oscillator ApplicationDocument7 pagesA Low-Voltage Current Conveyor Using Inverter-Based Error Amplifier and Its Oscillator ApplicationAshin AntonyNo ratings yet
- Charoli 26Document7 pagesCharoli 26Hakimuddin BohariNo ratings yet
- Analogue ElectronicsDocument7 pagesAnalogue ElectronicsrizwanahbNo ratings yet
- 15 Electric Circuit Analysis: If The Source Is... The Analysis Type Is..Document26 pages15 Electric Circuit Analysis: If The Source Is... The Analysis Type Is..Suresh NikalajeNo ratings yet
- STI PAC1 2019 Fall SolvedDocument3 pagesSTI PAC1 2019 Fall SolvedMarta Bordonaba Del RioNo ratings yet
- Relation Between V and V in Continuous Conduction: EE462L, Power Electronics, DC-DC Buck ConverterDocument16 pagesRelation Between V and V in Continuous Conduction: EE462L, Power Electronics, DC-DC Buck Converterbill gatesNo ratings yet
- Electrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: Second Sequence ExamDocument4 pagesElectrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: Second Sequence ExamNGOUNENo ratings yet
- Analog Sample Interview QuestionsDocument30 pagesAnalog Sample Interview QuestionsSampoornaGonellaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2: Single Stage Amplifier Design: EMT479 Analogue Ic DesignDocument4 pagesLab 2: Single Stage Amplifier Design: EMT479 Analogue Ic DesignBendera Hitam Dari TimurNo ratings yet
- Da2 271222Document4 pagesDa2 271222rh457707No ratings yet
- hw5 2008Document2 pageshw5 2008Joo JubNo ratings yet
- TE2006 Applied Electronics: Simulation Project 2Document3 pagesTE2006 Applied Electronics: Simulation Project 2Jorge AguirreNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Problem SheetDocument20 pagesUnsolved Problem SheetDeveshNo ratings yet
- 300 Level Alternativev To PracticalDocument6 pages300 Level Alternativev To PracticalDjNo ratings yet
- Module 5: DC-AC Converters: Lecture 14: DC-AC Inverter For EV and HEV ApplicationsDocument34 pagesModule 5: DC-AC Converters: Lecture 14: DC-AC Inverter For EV and HEV ApplicationsNagarajanNo ratings yet
- EEE 234L Spring 2022 - Lab Sheet 3Document6 pagesEEE 234L Spring 2022 - Lab Sheet 3Mahmud Sazzad MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Analog Devices & Circuits: Inst Ruct Ions T O Candidat EsDocument2 pagesAnalog Devices & Circuits: Inst Ruct Ions T O Candidat EsAnmolNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Basic CMOS AmplifiersDocument5 pagesLab 2 Basic CMOS AmplifiersJatinKumarNo ratings yet
- S D S D D D S S D D S: P N N PDocument5 pagesS D S D D D S S D D S: P N N PPankajSinghBhatiNo ratings yet
- PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, / Software Systems SemesterDocument3 pagesPSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, / Software Systems SemesterE.V.TAMIZHVANAN SuryaNo ratings yet
- Compter ModellingDocument7 pagesCompter Modellingahmadgafarov1No ratings yet
- Lab 7Document20 pagesLab 7bugra38785No ratings yet
- ECD Lab 2Document6 pagesECD Lab 2Maryam MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Digi Anal5Document4 pagesDigi Anal5NGOUNENo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis of Three Phase Alternator Sequence Impedance: Apparatus RequiredDocument9 pagesFault Analysis of Three Phase Alternator Sequence Impedance: Apparatus RequiredMohan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- BEE 2273 Electronic Devices and Applications Test 1 Op-Amp and Its Applications ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. Show All Your Work. Time: 1 HourDocument3 pagesBEE 2273 Electronic Devices and Applications Test 1 Op-Amp and Its Applications ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. Show All Your Work. Time: 1 HourYvonne ThienNo ratings yet
- 2015 CXC Elec Paper 2Document19 pages2015 CXC Elec Paper 2api-255989257No ratings yet
- EC212 Assignment 1 Analog Circuits TheoryDocument3 pagesEC212 Assignment 1 Analog Circuits Theorynjfdht24nmNo ratings yet
- Anallysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits QuestionsDocument5 pagesAnallysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits QuestionsshankarNo ratings yet
- Flyback PDFDocument11 pagesFlyback PDFlucianoNo ratings yet
- CE/EE3311 Electronic Circuits HW3Document2 pagesCE/EE3311 Electronic Circuits HW3Get wNo ratings yet
- HW8 PDFDocument2 pagesHW8 PDFGet wNo ratings yet
- Ies 11980 Only BJTDocument7 pagesIes 11980 Only BJTGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Zero Crossing Detector and Window DetectorDocument7 pagesZero Crossing Detector and Window DetectorTimoth Dev50% (2)
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Dr. Balraj SinghNo ratings yet
- SKEE3263Excercise2 (Soln)Document7 pagesSKEE3263Excercise2 (Soln)sawsheng59No ratings yet
- Signal Generator Project StatementDocument16 pagesSignal Generator Project StatementHussain Bin AliNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 01 Maximum Power Transfer Theorem ObjectivesDocument43 pagesExperiment # 01 Maximum Power Transfer Theorem ObjectiveskarachietNo ratings yet
- HITEC University Taxila: Power Electronics LabDocument9 pagesHITEC University Taxila: Power Electronics LabNisar Ahmed RanaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 7 Sinusoidal AC AnalysisDocument6 pagesLaboratory 7 Sinusoidal AC Analysistj1401No ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Functions 2.17 Breaker Failure Protection 50BFDocument1 pageFunctions 2.17 Breaker Failure Protection 50BFriddler_007No ratings yet
- Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced (Acsr) : Characteristics of A1/S1 B Conductors As Per IEC 1089/91 TYPE A1/S1 BDocument12 pagesAluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced (Acsr) : Characteristics of A1/S1 B Conductors As Per IEC 1089/91 TYPE A1/S1 Briddler_007No ratings yet
- Additional Standards: PrefaceDocument1 pageAdditional Standards: Prefaceriddler_007No ratings yet
- Typographic and Symbol Conventions: PrefaceDocument1 pageTypographic and Symbol Conventions: Prefaceriddler_007No ratings yet
- 1 Overview of DIGSI 5: 1.1 What Is DIGSI 5? 12 1.2 Engineering Philosophy and Terms 13 1.3 User Interface 23Document1 page1 Overview of DIGSI 5: 1.1 What Is DIGSI 5? 12 1.2 Engineering Philosophy and Terms 13 1.3 User Interface 23riddler_007No ratings yet
- Overview of DIGSI 5 1.1 What Is DIGSI 5?Document1 pageOverview of DIGSI 5 1.1 What Is DIGSI 5?riddler_007No ratings yet
- Preface: SIPROTEC 5 Engineering Guide, Manual C53000-G5040-C004-1, Release 02.2013 3Document1 pagePreface: SIPROTEC 5 Engineering Guide, Manual C53000-G5040-C004-1, Release 02.2013 3riddler_007No ratings yet
- Monitoring of The Circuit Breaker Auxiliary Contacts: Functions 2.17 Breaker Failure Protection 50BFDocument1 pageMonitoring of The Circuit Breaker Auxiliary Contacts: Functions 2.17 Breaker Failure Protection 50BFriddler_007No ratings yet
- Eg 6Document1 pageEg 6riddler_007No ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument1 pageReferencesriddler_007No ratings yet
- Eg 5Document1 pageEg 5riddler_007No ratings yet
- Siprotec 5 Engineering Guide DIGSI 5Document1 pageSiprotec 5 Engineering Guide DIGSI 5riddler_007No ratings yet
- Note For Your Own Safety, Please Observe The Warnings and Safety Instructions Contained in This ManualDocument1 pageNote For Your Own Safety, Please Observe The Warnings and Safety Instructions Contained in This Manualriddler_007No ratings yet
- Chapter 2) 7SR158 Technical ManualDocument2 pagesChapter 2) 7SR158 Technical Manualriddler_007No ratings yet
- Charging Current in Long Lines and High-Voltage Cables - Protection Application ConsiderationsDocument1 pageCharging Current in Long Lines and High-Voltage Cables - Protection Application Considerationsriddler_007No ratings yet
- Document Release History: Voltage & Frequency RelayDocument2 pagesDocument Release History: Voltage & Frequency Relayriddler_007No ratings yet
- 7SR158 Argus ContentsDocument1 page7SR158 Argus Contentsriddler_007No ratings yet
- Preface: Purpose of This ManualDocument2 pagesPreface: Purpose of This Manualriddler_007No ratings yet
- Siprotec: Preface Functions Mounting and Commissioning Technical Data Appendix Literature Glossary IndexDocument1 pageSiprotec: Preface Functions Mounting and Commissioning Technical Data Appendix Literature Glossary Indexriddler_007No ratings yet
- 1.3 Setting ModeDocument2 pages1.3 Setting Moderiddler_007No ratings yet
- 7SR158 Argus: Answers For EnergyDocument1 page7SR158 Argus: Answers For Energyriddler_007No ratings yet
- 3.4.2 Measurands: FW# FUN INF Description Asdu COTDocument2 pages3.4.2 Measurands: FW# FUN INF Description Asdu COTriddler_007No ratings yet
- USB RS232 Adapter enDocument1 pageUSB RS232 Adapter enriddler_007No ratings yet
- Technical Manual Chapters: 7SR158 Argus ContentsDocument2 pagesTechnical Manual Chapters: 7SR158 Argus Contentsriddler_007No ratings yet
- Minutes of Safety Committee Meeting Held On 24.09.15 of M/s BPPL Conference HallDocument3 pagesMinutes of Safety Committee Meeting Held On 24.09.15 of M/s BPPL Conference Hallriddler_007No ratings yet
- Cired: 21 International Conference On Electricity Distribution Frankfurt, 6-9 June 2011 Paper 915Document4 pagesCired: 21 International Conference On Electricity Distribution Frankfurt, 6-9 June 2011 Paper 915riddler_007No ratings yet
- Ger 3981Document18 pagesGer 3981riddler_007No ratings yet