Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What's A Body Plan?
Uploaded by
api-2885560120 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views6 pagesAnimals have primitive body plans but then e discovered that they developed into complex ones having true tissue and bilateral symmetry. Tissues are groups of cells that have the same structure and work together to perform a specific function. Organs help you do the things that you want such as moving around We have primitive animals and complex animal. Primitive animals perform radial symmetry because you can cut them from every direction ass long as it passes the central axis but still get the same result. Complex animals have bilateral symmetry can only be
Original Description:
Original Title
doc (15)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnimals have primitive body plans but then e discovered that they developed into complex ones having true tissue and bilateral symmetry. Tissues are groups of cells that have the same structure and work together to perform a specific function. Organs help you do the things that you want such as moving around We have primitive animals and complex animal. Primitive animals perform radial symmetry because you can cut them from every direction ass long as it passes the central axis but still get the same result. Complex animals have bilateral symmetry can only be
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views6 pagesWhat's A Body Plan?
Uploaded by
api-288556012Animals have primitive body plans but then e discovered that they developed into complex ones having true tissue and bilateral symmetry. Tissues are groups of cells that have the same structure and work together to perform a specific function. Organs help you do the things that you want such as moving around We have primitive animals and complex animal. Primitive animals perform radial symmetry because you can cut them from every direction ass long as it passes the central axis but still get the same result. Complex animals have bilateral symmetry can only be
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
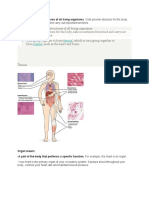
Whats a body plan?
Its the animals shape, symmetry and internal
organization.
We thought the animal only had primitive body plans but
then e discovered that they developed into complex ones
having true tissue and bilateral symmetry.
Tissues are groups of cells that have the same structure
and work together to perform a specific function
(ex:muscle tissue for producing movement due to
contraction of the muscles) (ex:nerve tissue for
conducting signals)
Different tissues work together and are organized into
structure called organs
(sponges arent organized into tissues just cell)
(coral are organized into tissues but not in organs)
Function of both tissue and organ=help you do the things
that you want such as moving around
We have primitive animals and complex animal
Primitive animals perform radial symmetry because you
can cut them from every direction ass long as it passes
the central axis but still get the same result; they all do
the same function. Radial symmetry animals central axis
plane can be divided equally into halves(ex:jellyfish)
Animals that dont move or depend on water current for
transport have radial symmetry.
Complex animals have bilateral symmetry can only be cut
book half. Bilateral symmetry optimizes the animal from
moving fast and quickly in a very specific direction.
Animals that move have a bilateral symmetry.(more
specialized like having an interior sensory structure and
nerves called cephalization) Cephalization allow the
animals to get food and escape predators.
Asymmetry is for animals that cant be divided into
smaller pieces (ex:sponges)
Bilateral symmetry is a symmetry for complex
animals with complex body plan. The plane passes
down the middle of the animal from head to
tail(vertically) into book halves or mirror image
halves (ex:human or butterfly)
Radial symmetry is a for primitive animals with
primitive body plan,The plane passes the central axis
and divides the organism into equal
halves(ex:jellyfish and sea star)
Early embryonic development(sexual reproduction)
Stage 1 is the zygote. A zygote is a fertilized egg
produced by the union of a sperm and an egg cell
Stage 2 is called cleavage. During cleavage the zygote
undergoes cell division by mitosis . 3 divisions= 8 cells
(Meaning: the series of cell division by mitosis occurring
immediately after an egg is fertilized)
1 division= 2 cells 2 division=4 cells
cells
3 division=8
Stage 3 is called the blastula. When cleavage ends,
blastula is the result where as a hollow ball is formed due
to growing mass of dividing cells( Meaning: the stage of
an embryo before gastrulation)The blastula has a fluid
interior called the blastocoels.
Stage 4 is gastrulation. The hollow ball or the blastula
begins to collapse inward and form a cup shaped pocket
or pouch; this pouch is called the blastopore.
Differentiation
When the gastrula keeps increasing in cells, The cells
start to become increasingly different than each other .So
they are separated in 3 types of cells that would form
primary tissue layers:
Ectoderm:The outer layer of the body,sense organs,and
the nervous system
Endoderm: forms the gut, the respiratory system, and
many glands
Mesoderm: form the most of the skeleton, the muscle, the
circulatory system, and the organs of reproduction and
excretion
Patterns of development
The gastrula as you know form a pouch near the
blastopore this puch keeps going inward until it breaks in
a passage. The passage is then lined with endoderm (the
gut formation)
If the blastopore develops a mouth then its a protostome
(ex:flat worm, spiders,clam)
If the blastopore develops an anus then its a
deuterostome (ex:vertebrates, sea star)
Body Cavity
Bilateral symmetry animals have internal body plans(3
kinds of body plans )
Function of a fluid filled coelom is that it protects internal
organs from movement of surrounding muscles/allows an
animal to move without damaging its organ or interfering
with the organs functions.
A coelom is a fluid filled cavity surrounded by mesoderm.
Aceolmates body plan: means without a body
cavity= no coelom(the space between the gut and
the aceolomate wall is filled with tissue)(primitive)
(Ex:flatworm)
Pseudocoelomate body plan : false coelom where as
the it is filled with a liquid that acts like a skeleton for
support. A cavity with 1 lining of mesoderm.
(complex body system formation)(Ex:roundworm)
Coelomate body plan: true coelom with 2 lining of
mesoderm(most complex;advanced body system
formation) (Ex:segmented worm)
Two evolutionary trend are the body segmentation and
the jointed appendages
Body segmentation
Body segmentation has to do ceolmate animals where as
they are composed of series of repeating, similar units
called segments.
Segment can either be seen easily like lobsters, spiders,
and insects and either cannot be seen except during early
developments. For example, the muscles of the
vertebrates that develop segments of tissues called
somites. Function of segmentation is great mobility and
flexibility
A small change in a segment can produce another new
segment with a different function
Jointed appendages
Arthropods were the first to have jointed appendages.
Joints function=permit powerful movement and aid in
locomotion
Joint appendages function=allow animals to perform
complex movement such as defensive display of mantis.
You might also like
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- General Biology 2 Organs and Organ System: APRIL 13, 2021Document6 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Organs and Organ System: APRIL 13, 2021Patrick VerroyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Kingdom Animalia PDFDocument29 pagesLecture 2 - Kingdom Animalia PDFJordan LewisNo ratings yet
- Animal Body Plans1Document25 pagesAnimal Body Plans1ivan domingoNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom and Biomolecules Class11Document64 pagesAnimal Kingdom and Biomolecules Class11Ribhu MehraNo ratings yet
- Apanimal Form SshakerDocument20 pagesApanimal Form Sshakerkhoffman4180No ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 4Document17 pagesAnimal Kingdom Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 4dharun0704No ratings yet
- Understanding Higher InvertebratesDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Higher InvertebratesIzzy ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory (Outline)Document6 pagesCell Theory (Outline)Sheila Mae VeralNo ratings yet
- Zelfstudie Van Blastula Naar 3 KiemlagenDocument18 pagesZelfstudie Van Blastula Naar 3 KiemlagenCheyenne ProvoostNo ratings yet
- Animal blueprints overviewDocument14 pagesAnimal blueprints overviewmia perezNo ratings yet
- Pembentukan Lapisan-Lapisan Bakal Dan SelomDocument35 pagesPembentukan Lapisan-Lapisan Bakal Dan SelomRosihan Husnu MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument95 pagesKingdom AnimaliaAmeena BegumNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF FARM ANIMALSDocument8 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF FARM ANIMALSAshley Tanya GilbertNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Assignment 1Document8 pagesAnatomy Assignment 1Ashley Tanya GilbertNo ratings yet
- Lesson IV The General Plan of The Animal BodyDocument6 pagesLesson IV The General Plan of The Animal BodyMarifer FiguracionNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Coelom and MetamerismDocument19 pagesEvolution of Coelom and MetamerismAnupam GhoshNo ratings yet
- Basis For Animal Kingdom ClassificationDocument31 pagesBasis For Animal Kingdom ClassificationIan AlpaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organisation-2Document19 pagesLevels of Organisation-2Joanna Susan JojiNo ratings yet
- Animal Basis of Classification PDFDocument5 pagesAnimal Basis of Classification PDFhop_parasher100% (1)
- ANATHOMYDocument92 pagesANATHOMYFloresan BagayawaNo ratings yet
- What Is Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesWhat Is Anatomy and PhysiologyDen LinaoNo ratings yet
- 2304 Intro AnatomyDocument6 pages2304 Intro AnatomyLiezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Ap LC1Document12 pagesAp LC1DanelleNo ratings yet
- Chapter3-Animal Architecture NotesDocument4 pagesChapter3-Animal Architecture Notesapi-195601294No ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument22 pagesKingdom AnimaliaPrarthanaSudeepNo ratings yet
- About Human BodyDocument16 pagesAbout Human BodyApril Lavenia BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Biology For TeachersDocument106 pagesBiology For TeachersKeishaAaliyahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy IntrodactionDocument48 pagesAnatomy IntrodactionYasin AbassNo ratings yet
- ANIMAL KINGDOM - NON-CHORDATADocument25 pagesANIMAL KINGDOM - NON-CHORDATASona JithinNo ratings yet
- Non ChordataDocument24 pagesNon Chordataadithyakrishnahn007No ratings yet
- Veterinary Gross Anatomy IntroductionDocument51 pagesVeterinary Gross Anatomy IntroductionFira'ol BogalaNo ratings yet
- Phylum AnimaliaDocument28 pagesPhylum Animaliaapi-310714826No ratings yet
- Anatomy Exploring The Human BodyDocument15 pagesAnatomy Exploring The Human BodyZack Aarton100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 41 Introduction to Body Structures and FunctionsDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 41 Introduction to Body Structures and FunctionsDaniel GuadarramaNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom: Basis of ClassificationDocument15 pagesAnimal Kingdom: Basis of ClassificationChaitali Deshmukh100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyDanelleNo ratings yet
- Topic: AnatomyDocument10 pagesTopic: AnatomyTess TessNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom ClassificationDocument11 pagesAnimal Kingdom ClassificationcharminemarideNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Basis of ClassificationDocument34 pages4.1 Basis of ClassificationDivyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- JI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 1-2Document2 pagesJI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 1-2Shubham PawadeNo ratings yet
- VB (TR), Bodies, Bodying or BodiedDocument6 pagesVB (TR), Bodies, Bodying or BodiedRaduNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Animl KingdomDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 4 Animl KingdomAnushka MishraNo ratings yet
- Frog anatomy vs human anatomy comparison under 40 charsDocument13 pagesFrog anatomy vs human anatomy comparison under 40 charsMark Tolentino100% (1)
- A&P Chapter 1 Overview: Anatomy, Physiology, and Structural OrganizationDocument10 pagesA&P Chapter 1 Overview: Anatomy, Physiology, and Structural OrganizationRustin John ReaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organization and SkeletonDocument3 pagesCell Organization and SkeletonNina NassarovaNo ratings yet
- Bodily Shape and Support For Internal OrgansDocument2 pagesBodily Shape and Support For Internal OrgansChrisNo ratings yet
- CH 3 CellsDocument6 pagesCH 3 CellsHend HamedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: The Study of the Human BodyDocument32 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: The Study of the Human BodyTrifena Prisca MosseNo ratings yet
- VB (TR), Bodies, Bodying or BodiedDocument6 pagesVB (TR), Bodies, Bodying or BodiedAndreiNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument123 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyWilliamMindoro100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument39 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Human AnatomyPramisshila Nurnatasha Abd SamatNo ratings yet
- Ped 2 LP 1 2022 2023Document7 pagesPed 2 LP 1 2022 2023Sherrizah AlidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32 - Unikont Diversity 2 - Professor KeatingDocument9 pagesChapter 32 - Unikont Diversity 2 - Professor KeatingDainyon GreeneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyLy RoseNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Reviewer 1Document18 pagesAnatomy Reviewer 1Jane EbascoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Anatomy, Physiology and The Human Body: Learning OutcomesDocument91 pagesUnit 1 Anatomy, Physiology and The Human Body: Learning OutcomesDeolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- XI 4 Animal KingdomDocument58 pagesXI 4 Animal KingdomDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Intro. To MetazoaDocument30 pagesLecture 3 - Intro. To MetazoaGammee OrNo ratings yet
- Grades of Organization and Body PlanDocument19 pagesGrades of Organization and Body PlanbjkopparNo ratings yet
- Baqri&Coomans 1973 - Dorylaimida Descritos Por Stekhoven y Teunissen 1938Document57 pagesBaqri&Coomans 1973 - Dorylaimida Descritos Por Stekhoven y Teunissen 1938Miguelillo_HernandezNo ratings yet
- Biology of Earthworms PDFDocument297 pagesBiology of Earthworms PDFMiquel Johanes Harianja100% (2)
- Report TextDocument5 pagesReport TextsantiNo ratings yet
- Sounds Great 1Document91 pagesSounds Great 1Monica Rose Lacuesta-SnyderNo ratings yet
- 113 Bugs USDocument22 pages113 Bugs USLâm TùngNo ratings yet
- To Study The Development of Cockroach 1.0Document6 pagesTo Study The Development of Cockroach 1.0Utkarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Costa, 2006. Relationships and Taxonomy of The Killifish Genus Rivulus 29-48 PDFDocument20 pagesCosta, 2006. Relationships and Taxonomy of The Killifish Genus Rivulus 29-48 PDFFábio Origuela de LiraNo ratings yet
- BBO 2013 Round 2 PaperDocument25 pagesBBO 2013 Round 2 PapermartynapetNo ratings yet
- Class11 Biology Unit19 NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionDocument12 pagesClass11 Biology Unit19 NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionUdit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- B2+ Test Series (36Document4 pagesB2+ Test Series (36Ngân Nguyễn Bùi HoaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet. 4. Asexual ReproductionDocument3 pagesWorksheet. 4. Asexual ReproductionLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Fish ClassificationDocument12 pagesEvolution and Fish Classificationlajola.gershonNo ratings yet
- Eric's Talking Ears PDFDocument27 pagesEric's Talking Ears PDFSuciati Anandes100% (1)
- (Research Progress in Botany) Philip Stewart - Sabine Globig-Reproductive Physiology in Plants-Apple Academic Press (2011)Document321 pages(Research Progress in Botany) Philip Stewart - Sabine Globig-Reproductive Physiology in Plants-Apple Academic Press (2011)Heruko Fatimah100% (1)
- Introduction To Eumetazoa: The True Animals'Document22 pagesIntroduction To Eumetazoa: The True Animals'jeanette8riosNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary Consequences of Skeletal DifferentiationDocument22 pagesEvolutionary Consequences of Skeletal Differentiationjulio7345No ratings yet
- Animal Classification GuideDocument4 pagesAnimal Classification GuideKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- ReadingDocument2 pagesReadingLinh ThùyNo ratings yet
- Document on skin changes associated with hypothyroidismDocument3 pagesDocument on skin changes associated with hypothyroidismKrystal VallesNo ratings yet
- 2006 Tomlinson - The Uniqueness of PalmsDocument10 pages2006 Tomlinson - The Uniqueness of PalmsDavidFernandoSantamaríaMaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Genetic DriftDocument4 pagesGenetic DriftjscribdscribdNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules Revision NotesDocument49 pagesBiological Molecules Revision NotesAyaz Nasih88% (8)
- Zoo HandoutsDocument22 pagesZoo HandoutsPaul Caesar0% (1)
- PROTOCHORDATESDocument4 pagesPROTOCHORDATESapi-26570979100% (1)
- U3-Test ANIMALS PDFDocument2 pagesU3-Test ANIMALS PDFJesus LopezNo ratings yet
- Adenuga TemitopeDocument2 pagesAdenuga TemitopeebenyallenNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Action 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol (Bronopol)Document6 pagesAntibacterial Action 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol (Bronopol)lokesh1331No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellDocument49 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellArthe RajarajanNo ratings yet
- MT Assignment, Muscles of MasticationDocument5 pagesMT Assignment, Muscles of MasticationSyeda MunazzaNo ratings yet
- Biology Dry Practical Dichotomous Key AnimalsDocument16 pagesBiology Dry Practical Dichotomous Key Animalsjudithguya18No ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)