Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Narrative Elements in English
Uploaded by
calliope0080 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesNarrative Elements used in English
Brief summary of :
Setting
Tone
Characters
Theme
Plot
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNarrative Elements used in English
Brief summary of :
Setting
Tone
Characters
Theme
Plot
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesNarrative Elements in English
Uploaded by
calliope008Narrative Elements used in English
Brief summary of :
Setting
Tone
Characters
Theme
Plot
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
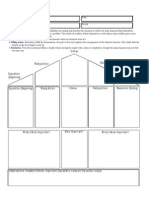
Narrative elements
5 narrative elements in a short story
Character
Theme
Plot
Point of view
Setting
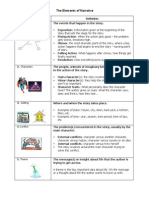
CHARACTER
Important areas to consider when character is revealed INDIRECTLY by
the writer:
Actions
Dialogue
Physical description
Reactions (to other characters and events)
THEME
A central idea that runs through the literary work
Emerges in and through the development of characters, settings, plot
movement and changes
The theme(s) are usually expressed as a general observation of people
or the world we live in
The theme may be stated or implied
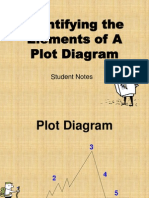
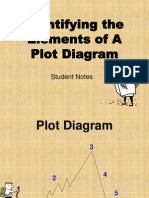
PLOT
A series of related events selected by the author to present and bring
about the resolution of some conflict or problem
The events in a story follow a pattern.
1. Exposition: the story begins, introduction of characters, setting and
scene are revealed, action & conflict begin
2. Complication: conflict or problem developed from the problems
characters encounter
3. Rising action: several events, which show the character wrestling with
the storys main conflict.
4. Climax: usually the turning point in the story eg . Character makes a
decision, high point in action etc.
5. Resolution: Conflict is resolved / solution is introduced, ending can be
positive or negative
POINT OF VIEW
Also known as narrative view point
Some common narrative viewpoints:
First person subjective: narrator (the person who tells the story) is major /
minor character; reader knows more than the narrator uses I eg. in
Phone Call
Third person omniscient: narrator (the person who tells the story) is a
person outside the story who knows all the events and characters eg.
in After You, My Dear Alphonse; The Rainbow Bird & The Invaders
SETTING
Place
Time
Physical environment
Social environment
You might also like
- Structuring Your Novel: Essential Keys for Writing an Outstanding StoryFrom EverandStructuring Your Novel: Essential Keys for Writing an Outstanding StoryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)
- Elements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Document27 pagesElements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Quanitum ExpressNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH - Elements-Of-Short-StoryDocument11 pagesENGLISH - Elements-Of-Short-StoryElthea PascuaNo ratings yet
- Short Story - Elements of Short StoryDocument27 pagesShort Story - Elements of Short Storyapi-261452312No ratings yet
- Elements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Document25 pagesElements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Alaa YasienNo ratings yet
- 5 Narrative Elements in A Short StoryDocument2 pages5 Narrative Elements in A Short Storycalliope008No ratings yet
- Grade 7Document47 pagesGrade 7Adelaide RefugioNo ratings yet
- Short StoryDocument10 pagesShort StoryDany SaintNo ratings yet
- Plot Elements Vocabularyy 2012Document21 pagesPlot Elements Vocabularyy 2012api-237333070No ratings yet
- PlotDocument9 pagesPlotapi-262711797No ratings yet
- Elements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Document28 pagesElements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Claudette Lindsay LabagnoyNo ratings yet
- 0212 PlotnotesDocument1 page0212 Plotnotesdrgayen6042No ratings yet
- Elements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Document28 pagesElements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Ashly Kim E. RadazaNo ratings yet
- 5 Elements of A Short Story PDFDocument16 pages5 Elements of A Short Story PDFHanahjane Atuel0% (1)
- Soul of The Great BellDocument41 pagesSoul of The Great BellBryllNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Narrative Part 2Document16 pagesElements of A Narrative Part 2sophia stephanie ruizNo ratings yet
- The Elements of Narrative-1Document1 pageThe Elements of Narrative-1devorehumanitiesNo ratings yet
- Elements of NarrativeDocument39 pagesElements of Narrativeshazrah salamNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1A: Horror and Suspense: 1.1 Story ElementsDocument43 pagesUNIT 1A: Horror and Suspense: 1.1 Story Elementsbabyu1No ratings yet
- Elements of A Plot DiagramDocument9 pagesElements of A Plot Diagrammeiles2350No ratings yet
- Elements of A Short StoryDocument20 pagesElements of A Short Storyafrooz456No ratings yet
- The Elements of FictionDocument22 pagesThe Elements of Fictiongayoilac100% (2)
- Story ElementsDocument29 pagesStory ElementsJake Aldred CabelaNo ratings yet
- Story Elements Flipbook Project NotesDocument45 pagesStory Elements Flipbook Project NotesManalo S. ZhelNo ratings yet
- Plot - Elements of A Plot DiagramDocument9 pagesPlot - Elements of A Plot Diagramapi-260254769No ratings yet
- Elements of A Plot DiagramDocument9 pagesElements of A Plot Diagramapi-237774918No ratings yet
- Elements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Document28 pagesElements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Shilpa SoodNo ratings yet
- Identifying The Elements of A Plot Diagram: Feel Free To Take Brief Notes!Document9 pagesIdentifying The Elements of A Plot Diagram: Feel Free To Take Brief Notes!socadriNo ratings yet
- PlotDocument9 pagesPlotMiki melNo ratings yet
- Material of Story (Narrative TextsDocument30 pagesMaterial of Story (Narrative TextsAfifah 12No ratings yet
- Features of Narrative TextDocument20 pagesFeatures of Narrative TextMicah Eunice FanoNo ratings yet
- Features of Narrative TextDocument20 pagesFeatures of Narrative TextDiana OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Presentation 17Document18 pagesPresentation 17Salahuddin MemonNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Plot Diagram 1Document10 pagesElements of A Plot Diagram 1api-261931897No ratings yet
- Story ElementsDocument26 pagesStory ElementsKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Elements of A StoryDocument28 pagesElements of A StoryJoseph Napod AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Story: What You Need To Know!Document19 pagesElements of A Story: What You Need To Know!kenana sharanekNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Short StoryDocument25 pagesElements of A Short StoryDevorah Mae Filipino100% (1)
- Features of Narrative TextDocument20 pagesFeatures of Narrative TextAnne ChristinaNo ratings yet
- Elements of A StoryDocument14 pagesElements of A StoryJanine Dana TurlaNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Short StoryDocument23 pagesElements of A Short StoryIrene Tumamak PortezNo ratings yet
- Literature Shorten - Second SubjectDocument2 pagesLiterature Shorten - Second SubjectMikel ScoutNo ratings yet
- Elements of FictionDocument25 pagesElements of Fictionapi-261181145No ratings yet
- Hazel Project-BasedDocument16 pagesHazel Project-BasedRica YtangNo ratings yet
- Elements of FictionDocument17 pagesElements of FictionsaadNo ratings yet
- Module 2. Lesson 2. Short Story ElementsDocument18 pagesModule 2. Lesson 2. Short Story ElementsApril Rose SantosNo ratings yet
- Short Story Terms 2Document3 pagesShort Story Terms 2Abdul HadiNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Short StoryDocument2 pagesElements of A Short StoryJuliet Anne Buangin AloNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1666612769834 6990280606969714042Document14 pagesOrca Share Media1666612769834 6990280606969714042Peach KimNo ratings yet
- 5 Elements of A Short StoryDocument20 pages5 Elements of A Short StoryCris S. DisongloNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Short StoryDocument16 pagesElements of A Short Storyfordsantiago01No ratings yet
- The Five Essential Elements of A StoryDocument9 pagesThe Five Essential Elements of A StoryNataliaNo ratings yet
- Elements of The Short StoryDocument16 pagesElements of The Short StoryKhalil AbdulhameedNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document9 pagesLesson Plan 1Ney Ney Alba50% (2)
- Elements of A Short StoryDocument22 pagesElements of A Short Storyirish03niceNo ratings yet
- Five Elements of Fiction Detailed ExplanationDocument13 pagesFive Elements of Fiction Detailed ExplanationjhonNo ratings yet
- Higher Writing Folio: Creative Writing 1Document32 pagesHigher Writing Folio: Creative Writing 1Iva SivarajaNo ratings yet
- Landscapes of short stories for Gr 10 Second Additional LanguageFrom EverandLandscapes of short stories for Gr 10 Second Additional LanguageNo ratings yet
- Story Development: A comprehensive guide to get your writing started the right wayFrom EverandStory Development: A comprehensive guide to get your writing started the right wayNo ratings yet
- Summary of Types of Natural VegetationDocument4 pagesSummary of Types of Natural Vegetationcalliope008No ratings yet
- Diagrams - Formation of River FeaturesDocument2 pagesDiagrams - Formation of River Featurescalliope008No ratings yet
- The River SystemDocument4 pagesThe River Systemcalliope008No ratings yet
- Consequences of DeforestationDocument5 pagesConsequences of Deforestationcalliope008No ratings yet