Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cholinergic Drug Mnemonics
Cholinergic Drug Mnemonics
Uploaded by
mina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageCholinergic-Drug-Mnemonics
Original Title
Cholinergic-Drug-Mnemonics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCholinergic-Drug-Mnemonics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageCholinergic Drug Mnemonics
Cholinergic Drug Mnemonics
Uploaded by
minaCholinergic-Drug-Mnemonics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
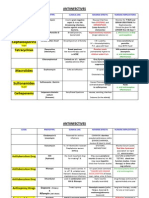
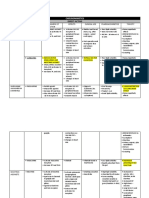
Direct Agonists
Muscarinics = Methacholine
Affect
= Acetylcholine
Cardiac
= Carbachol
Pulse
= Pilocarpene
But
= Bethanechol
Nicotinics
= Nicotine
Clench
= Cevimeline
**This one's a two for one since it also hints at how the diff receptors work (muscarinics
affect the heart rate, while nicotinics affect the neuromuscular junction).
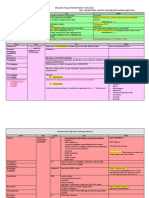
Anti AchE's:
New
Physicians
Endure
Pimping
= Neostigmine
= Physostigmine
= Edrophonium
= Pyridostigmine
Alzheimer's Drugs (also Anti-AChE's):
Grandma
= Galantamine
Doesn't
= Donepezil
Remember
= Rivastigmine
Today
= Tacrine
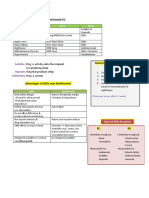
Hints:
1. For the Ach antagonists, just remember that most of them look similar to atropine
(they have trop, rop, or pine in them). Exceptions are scopolamine, tolterodine, and
oxybutynin.
2. For skeletal muscle relaxants (neuromuscular inhibitors), they all look similar to
tubocurarine (have a cur in them). Exception is mecamylamine, which has a different
mechanism anyways.
3. ACh agonists generally elicit the "rest and digest" response from the body, such as
slower HR, increased secretions, increased GI motility, etc.
4. ACh antagonists (atropine) do the opposite: the "fight or flight" response. This
includes increased HR, decreased secretions and motility, pupil dilation, etc.
You might also like
- Adrenergic AgentsDocument45 pagesAdrenergic AgentsAmit ShahNo ratings yet
- Drug Cards CNSDocument23 pagesDrug Cards CNSChristine Schroeder100% (2)
- Pharmacology Final Study GuideDocument28 pagesPharmacology Final Study GuideAnthony Palladeno100% (1)
- Opioids PDFDocument2 pagesOpioids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters and Psychiatry PDFDocument22 pagesNeurotransmitters and Psychiatry PDFcapriciousbelal93% (14)
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Document48 pagesNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNo ratings yet
- Antiinfectives Drug TableDocument5 pagesAntiinfectives Drug Tablecdp1587100% (3)
- Pharmacology Study Notes - Adrenergic DrugsDocument2 pagesPharmacology Study Notes - Adrenergic Drugsstuckaluck83% (6)
- Comprehensive Pharmacy Review - NotesDocument143 pagesComprehensive Pharmacy Review - NotesDina Osama75% (4)
- Unit 8. Cholinergic and AnticholinergicsDocument50 pagesUnit 8. Cholinergic and AnticholinergicsApril Mergelle LapuzNo ratings yet
- ANS PharmacologyDocument58 pagesANS Pharmacologyalemu100% (1)
- Introduction To ANS PharmacologyDocument34 pagesIntroduction To ANS PharmacologySebontu HasenNo ratings yet
- The Heart of Flow PDFDocument72 pagesThe Heart of Flow PDFBenjamin Rüffin100% (2)
- Mechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiDocument146 pagesMechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiReynaldo RiveraNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY Anti Microbial DrugsDocument17 pagesPHARMACOLOGY Anti Microbial DrugsLeilani Sablan100% (2)
- Adrenergic & Cholinergic DrugsDocument1 pageAdrenergic & Cholinergic DrugsMina Minawy100% (1)
- DrugsDocument10 pagesDrugsJoyVee Pillagara-De LeonNo ratings yet
- Drug ChartDocument8 pagesDrug Chartstudentalwaysstudy100% (1)
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument36 pagesPHARMACOLOGYjanr123456100% (1)
- DiureticsDocument4 pagesDiureticsNazmul Islam AbirNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic and Anti-Adrenergic DrugsDocument54 pagesAdrenergic and Anti-Adrenergic DrugsChittaranjan Padhy100% (1)
- Muscarinic and Anti-MuscarinicsDocument3 pagesMuscarinic and Anti-MuscarinicsElleJBNo ratings yet
- Cholinergics and AnticholinergicsDocument5 pagesCholinergics and AnticholinergicscatislandbigredNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology HandoutDocument5 pagesPharmacology HandoutMark Elben Teodoro100% (1)
- Pharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetPattyNo ratings yet
- MCQs With Key 50 Qs On ANSDocument10 pagesMCQs With Key 50 Qs On ANSshhahhmurad6592% (12)
- Onco PharmacologyDocument9 pagesOnco Pharmacologyarn0ld21No ratings yet
- Drug KenalogDocument1 pageDrug KenalogSrkocherNo ratings yet
- (Ans) 138 MCQ With Key Answer: by DR - Giuma SuliemanDocument27 pages(Ans) 138 MCQ With Key Answer: by DR - Giuma SuliemanTofik Mohammed100% (1)
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocument19 pagesPharmacology MnemonicsAl-nazer Azer Al100% (5)
- Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs IIDocument12 pagesPharmacology Trans ANS Drugs IIPrincess Mara DuranNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1.3 NeurotransmittersDocument10 pagesBiochemistry 1.3 Neurotransmitterslovelots1234No ratings yet
- Adrenergics & Adrenergic BlockersDocument5 pagesAdrenergics & Adrenergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (4)
- Pharmacology Mnemonics PDFDocument27 pagesPharmacology Mnemonics PDFHasanAli100% (2)
- Ethics Codes For Any Pharmacists in Details. With MCQDocument12 pagesEthics Codes For Any Pharmacists in Details. With MCQsunshine151100% (1)
- Nursing Pharmacology Perfusion Study GuideDocument9 pagesNursing Pharmacology Perfusion Study GuideChelsea SmithNo ratings yet
- Psyche 2Document10 pagesPsyche 2Nicole Mae0% (1)
- Git Drugs TablesDocument3 pagesGit Drugs TablesSulochan Ssplendid Splinterr Lohani100% (1)
- 1-Adrenocorticosteroids Chapter39Document94 pages1-Adrenocorticosteroids Chapter39hamidNo ratings yet
- Drug Cards 1Document20 pagesDrug Cards 1Keying Chen100% (1)
- Alif Mudh - Say Practice PDFDocument7 pagesAlif Mudh - Say Practice PDFarham200864% (11)
- Pharmacy Mcqs 1Document18 pagesPharmacy Mcqs 1sunshine151No ratings yet
- Pharmacy Mcqs 1Document18 pagesPharmacy Mcqs 1sunshine151No ratings yet
- Psycho PharmaDocument8 pagesPsycho PharmaMark JosephNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 1 Lecture Notes PharmacologyDocument165 pagesUSMLE Step 1 Lecture Notes PharmacologyAris OverallNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocument17 pagesPharmacology MnemonicsJuvenis SampangNo ratings yet
- 13 How To Survive - PharmacologyDocument34 pages13 How To Survive - Pharmacologysophiesurvivalguides100% (1)
- Pharmacology A ReviewDocument15 pagesPharmacology A ReviewKathrynne MendozaNo ratings yet
- (PHARMA) 1.12 Cholinergic Drugs (LReyes) v2 PDFDocument15 pages(PHARMA) 1.12 Cholinergic Drugs (LReyes) v2 PDFNoreenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Inflammation Study GuideDocument11 pagesNursing Pharmacology Inflammation Study GuideChelsea Smith100% (1)
- Drug Study Catapres. Losartan, Nootropil Cefuroxime, ArcoxiaDocument2 pagesDrug Study Catapres. Losartan, Nootropil Cefuroxime, Arcoxiajoy_monterubioNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Test 1Document39 pagesPharmacology Test 1Niki BolinNo ratings yet
- Cholinergics and Cholinergic BlockersDocument5 pagesCholinergics and Cholinergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (3)
- Antidepressants: Depression Is One The Most Treatable Mental IllnessDocument40 pagesAntidepressants: Depression Is One The Most Treatable Mental IllnessMohammed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Autonomic DrugsDocument107 pagesAutonomic DrugsMaria Mercedes LeivaNo ratings yet
- Complete Drug GuideDocument225 pagesComplete Drug GuideJessica 'Baker' IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Table of Sedative, Hypnotic, AntianxietyDocument4 pagesTable of Sedative, Hypnotic, AntianxietyirfanzukriNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)Document2 pagesPharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)graycorypNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs XL Chart 3Document2 pagesRespiratory Drugs XL Chart 3cdp1587100% (1)
- Anti-Infective Pharmacology ReviewerDocument5 pagesAnti-Infective Pharmacology ReviewerArianne Pearl PrimeroNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Receptors ChartDocument1 pageAdrenergic Receptors ChartLeon ChenNo ratings yet
- Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsDocument6 pagesHmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, Interactionswaste78No ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System DrugsDocument11 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Drugssbjon984924100% (1)
- Ati Medication Template CodeineDocument1 pageAti Medication Template CodeineSharee HaywoodNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument44 pagesCholinergic Drugskhuzaima9100% (1)
- OB Drug ChartsDocument2 pagesOB Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics Flash CardsDocument17 pagesPharmacology Pharmacokinetics Flash Cardsbobiome100% (1)
- Drug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherDocument4 pagesDrug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherCess Lagera YbanezNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocument1 pageAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88No ratings yet
- MS Final 49 UrinaryDocument3 pagesMS Final 49 UrinaryZachary T HallNo ratings yet
- (OS 213) LEC 03 Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System (1) - 1Document16 pages(OS 213) LEC 03 Drugs Acting On The Respiratory System (1) - 1Yavuz DanisNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocument37 pagesPharmacology FirecrackerRehan Usman100% (1)
- Acetylcholine Agonist and Antagonist DrugsDocument5 pagesAcetylcholine Agonist and Antagonist DrugsQamar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Subject: Pharmacology Topic: ANS 2 Lecturer: Maria Luisa D. Delacruz, M.D. Date of Lecture:August 3, 2011 Transcriptionist: Anonymous Pages: 16Document16 pagesSubject: Pharmacology Topic: ANS 2 Lecturer: Maria Luisa D. Delacruz, M.D. Date of Lecture:August 3, 2011 Transcriptionist: Anonymous Pages: 16dtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Materi KolinergikDocument62 pagesMateri KolinergikWira KrisnaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Pharmacology (Document1 pageCardiovascular System Pharmacology (sunshine151No ratings yet
- Jeem - Khay PracticeDocument4 pagesJeem - Khay Practicesunshine15175% (4)
- NuthingDocument37 pagesNuthingsunshine151No ratings yet
- Introduction To PE - chp1Document18 pagesIntroduction To PE - chp1Catalina DumitruNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument6 pagesCholinergic Drugssunshine151No ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agonists Drug Action Receptor Pharmacologic UseDocument1 pageAdrenergic Agonists Drug Action Receptor Pharmacologic Usesunshine151No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Skeletal SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Skeletal Systemsunshine151No ratings yet
- CC Is A Clinical Condition That Results From An Insufficient Supply of Healthy RedDocument8 pagesCC Is A Clinical Condition That Results From An Insufficient Supply of Healthy Redsunshine151No ratings yet
- Biostatistics and PharmacoeconomicsDocument20 pagesBiostatistics and Pharmacoeconomicssunshine151100% (1)
- AsthmaDocument9 pagesAsthmasunshine151No ratings yet
- Fisiologi Saraf OtonomDocument32 pagesFisiologi Saraf OtonomNiaNo ratings yet
- PHC 513 Flipped Class QuestionDocument17 pagesPHC 513 Flipped Class QuestionALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISNo ratings yet
- Cardiolab NotesDocument14 pagesCardiolab NotesEmmanuel MensahNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Use of Nicotine Based Insecticides in Insect Pest Management 1Document4 pagesA Review On The Use of Nicotine Based Insecticides in Insect Pest Management 1Rakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Emmetropization 2 2006Document57 pagesEmmetropization 2 2006permataNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Respiratory DiseasesDocument11 pagesDrugs Used in Respiratory DiseasesDH DipuNo ratings yet
- Semester A Final Exam ReviewDocument46 pagesSemester A Final Exam ReviewMadison MauckNo ratings yet
- CHOLINOMIMETICSDocument4 pagesCHOLINOMIMETICSMicah James MaravillasNo ratings yet
- Formulir Review Judul Skripsi 2019 (Update 28 Maret 2019) Kevin ThenediDocument2 pagesFormulir Review Judul Skripsi 2019 (Update 28 Maret 2019) Kevin ThenediKevin ThenediNo ratings yet
- Onuaguluchi1996 1Document10 pagesOnuaguluchi1996 1IkaSugihartatikNo ratings yet
- The MDSiteDocument12 pagesThe MDSitealex_pitigoi100% (1)
- Cvs Adjustments During Exercise by DR Sadia ZafarDocument23 pagesCvs Adjustments During Exercise by DR Sadia ZafarMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Chapter 14 (Autonomic Nervous System) PDFDocument60 pagesLecture Notes For Chapter 14 (Autonomic Nervous System) PDFdwataNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Urticaria Subtype Classification and Clinical ApproachDocument14 pagesCholinergic Urticaria Subtype Classification and Clinical ApproachKikin RizkynnisaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocument37 pagesPharmacology FirecrackerRehan Usman100% (1)
- Guyton Physiology Trang 784 796Document13 pagesGuyton Physiology Trang 784 796Bùi Nguyễn Yến VyNo ratings yet
- Cholinoceptor-Activating, Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs and Cholinoceptor-Blocking DrugsDocument6 pagesCholinoceptor-Activating, Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs and Cholinoceptor-Blocking DrugsCarlos NiñoNo ratings yet
- GI Long Notes PDFDocument88 pagesGI Long Notes PDFQueenie WongNo ratings yet
- Organophosphate Poisoning GuidelineDocument5 pagesOrganophosphate Poisoning Guidelinelamoleverde9297No ratings yet
- Abstract & Program Book - 31082022Document273 pagesAbstract & Program Book - 31082022prasetyo gantengNo ratings yet