Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MENG3306 - Chapter 1 CEP-Class Example Problems
Uploaded by
Mike Linhorst0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pageschap 1 questions
Original Title
CEP Chapter1 (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentchap 1 questions
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesMENG3306 - Chapter 1 CEP-Class Example Problems
Uploaded by
Mike Linhorstchap 1 questions
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
MENG3306 Chapter 1
CEP-Class Example Problems
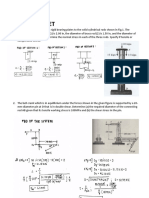
1. Determine the resultant internal torque acting on the cross sections through points C
and D of the shaft shown in Fig 1. The shaft is fixed at B (1.2).
2. Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section through point D of
Fig 2 (1.19).
3. The pipe has a mass of 12 kg/m. If it is fixed to the wall at A as shown in Fig 3,
determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section through B (1.30).
4. The lever is held to the fixed shaft using a tapered pin AB, which has a mean diameter
of 6 mm. If a couple is applied to the lever, determine the average shear stress in the pin
between the pin and lever. See Fig 4 (1.39).
5. The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional area of 1.25 in 2 as shown in Fig 5. If
the maximum average normal stress in any bar is not to exceed 20 ksi, determine the
maximum magnitude P of the loads that can be applied to the truss (1.59).
6. The fillet weld size a = 0.25 in as shown in Fig 6. If the joint is assumed to fail by
shear on both sides of the block along the shaded plane, which is the smallest cross
section, determine the largest force P that can be applied to the plate. The allowable
shear stress for the weld material is allow = 14 ksi (1.85).
7. The bar in Fig 7 is held in equilibrium by the pin supports at A and B. Note that the
support at A has a single leaf and therefore it involves single shear in the pin, and the
support at B has a double leaf and therefore it involves double shear. The allowable shear
stress for both pins is allow = 125 MPa. If x = 1m and w = 12 kN/m, determine the
smallest required diameter of pins A and B. Neglect any axial force in the bar (1.108).
Fig 2
Fig 1
Fig 3
Fig 4
Fig 6
Fig 5
Fig 7
You might also like
- Module 1 Assignment Questions PDFDocument5 pagesModule 1 Assignment Questions PDFSaravanakumar PNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document6 pagesTutorial 4Ysgn MysgnNo ratings yet
- BAUTISTA, DARLENE JOY C. - 2CE-C - Activity 1-Prelim TermDocument24 pagesBAUTISTA, DARLENE JOY C. - 2CE-C - Activity 1-Prelim TermDARLENE JOY C. BAUTISTA67% (3)
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1NayefGhazaliNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheets SOMDocument20 pagesTutorial Sheets SOMPriyanshu Sharma100% (1)
- Strength of MaterialsDocument61 pagesStrength of MaterialsEkajara JoshNo ratings yet
- First Project ExamplesDocument49 pagesFirst Project ExamplesMeleti Meleti MeletiouNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Stress1 PDFDocument18 pagesConcepts of Stress1 PDFCarl Malone Lotivio LorillaNo ratings yet
- IINEEA1 Tutorial 1Document6 pagesIINEEA1 Tutorial 1michaeljxmesNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 4-IiDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 4-IiMilton CobaNo ratings yet
- 1-3 Simple Stresses 1-3-1 Axial StressDocument32 pages1-3 Simple Stresses 1-3-1 Axial StressHazim KhalilNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsDocument7 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsadrianNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials PDFDocument35 pagesStrength of Materials PDFromeo08100% (1)
- Normal Stress Stress: Simple StressesDocument24 pagesNormal Stress Stress: Simple StressesJake Tuwa MiguelNo ratings yet
- Mechanical stress problemsDocument7 pagesMechanical stress problemsDhenil ManubatNo ratings yet
- Asign1 MomDocument4 pagesAsign1 MomAmru AwangNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document7 pagesProblem Set 1Percival ArcherNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 3Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- SoM -AM2200 Assignment - Stresses in Rods, Links, and Shear WallDocument3 pagesSoM -AM2200 Assignment - Stresses in Rods, Links, and Shear WallSai naveenNo ratings yet
- Assignment For IPEDocument4 pagesAssignment For IPEAbirHasanNo ratings yet
- ME 212 Tutorial 8Document2 pagesME 212 Tutorial 8Mihir Kumar MechNo ratings yet
- SMAT Q1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesSMAT Q1 ReviewerEmer Jacob FadriNo ratings yet
- MEC211 Stress and Strain Tutorial QuestionsDocument7 pagesMEC211 Stress and Strain Tutorial Questionsha haNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Deformable BodiesDocument23 pagesEquilibrium of Deformable Bodiesaj filesNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Flexión Mecánica de Materiales: Ing. Miguel Arlenzo Durán Sarmiento, M.EngDocument6 pagesEjercicios Flexión Mecánica de Materiales: Ing. Miguel Arlenzo Durán Sarmiento, M.EngOscar Yesid Monsalve CelisNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document4 pagesTutorial 5Kumar ShivamNo ratings yet
- Stress Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesStress Practice ProblemsSayantan ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Simple StressesDocument39 pagesChapter 1 - Simple StressesJovy Notorio100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Stress ProblemsDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Stress ProblemsKarthik Kalash100% (1)
- Mechanics Prob 2Document3 pagesMechanics Prob 2Paul Angelou CiriacoNo ratings yet
- ES 13 Problem Set 1 SolutionsDocument2 pagesES 13 Problem Set 1 SolutionsSammy Marquez100% (1)
- Questions On Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesQuestions On Strength of MaterialsAiswarya Ramesh me21b011No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document7 pagesTutorial 5A SкNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials, 4th Edition (Solutions Manual) - Singer, PytelDocument286 pagesStrength of Materials, 4th Edition (Solutions Manual) - Singer, PytelSamantha CusiNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesStrength of Materialsjerold_arandiaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Homework SolutionsDocument28 pagesMechanics of Materials Homework Solutionssweet xaramelNo ratings yet
- Stress and Strength CalculationsDocument21 pagesStress and Strength CalculationsMidas Troy VictorNo ratings yet
- Applied Hydrology VT Chow 1988Document3 pagesApplied Hydrology VT Chow 1988kaicaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsDocument6 pages2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsMartin MugoniNo ratings yet
- Prelim Emt313nDocument9 pagesPrelim Emt313npaulineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 (Allowable Stress)Document5 pagesTugas 1 (Allowable Stress)WAHYU DWI LESTARINo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document5 pagesHomework 1danietronico100% (1)
- Fig. P3.129, P3.130Document4 pagesFig. P3.129, P3.130Alen RustemovicNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - Introduction - Concept of Stress - Class ExamplesDocument10 pagesChapter - 1 - Introduction - Concept of Stress - Class ExamplesCandice MdakaNo ratings yet
- Assignment04 (2:11:14)Document2 pagesAssignment04 (2:11:14)Gabriel SmithNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 CRC302Document1 pageTutorial 4 CRC302HarryNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument4 pagesTutorialvarjith007No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Simple StressesDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Simple StressesLalaine RamosNo ratings yet
- Prob SheetDocument20 pagesProb SheetAditya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Steel Tube Stress and Diameter CalculationDocument18 pagesSteel Tube Stress and Diameter CalculationRuth Abegail de VeraNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. 1 Year (Civil) Solid Mechanics (CEN-102) Tutorial Sheet 4: Torsion, Shear Force and Bending MomentDocument4 pagesB. Tech. 1 Year (Civil) Solid Mechanics (CEN-102) Tutorial Sheet 4: Torsion, Shear Force and Bending MomentKumar ShivamNo ratings yet
- STRESS AND STRAIN CALCULATIONSDocument3 pagesSTRESS AND STRAIN CALCULATIONSSaketh BoggavarapuNo ratings yet
- Solid Tutorial 7Document9 pagesSolid Tutorial 7Mohammad Afandi Azmi RaifNo ratings yet
- 34 Assignment 7Document2 pages34 Assignment 7venuNo ratings yet
- 212-Chpt 8Document5 pages212-Chpt 8zainabcomNo ratings yet
- Es 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)Document3 pagesEs 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)akosikapitansinoNo ratings yet
- ME202Document2 pagesME202nitinsparksNo ratings yet
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsFrom EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNo ratings yet