Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Fizz Martin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
127 views5 pagessolid mechanic
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsolid mechanic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
127 views5 pagesChapter 1
Uploaded by
Fizz Martinsolid mechanic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
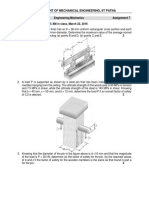
Tutorial-1
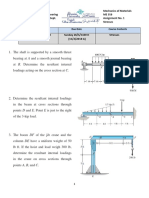
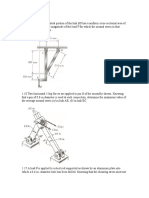
1. Determine the resultant internal loadings on the cross section
through point D. Assume the reactions at the supports A and B
are vertical.
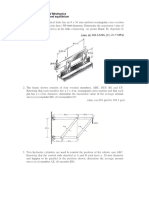
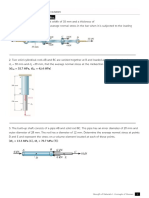
2. The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings A and B and is
subjected to the forces applied to the pulleys fixed to the shaft.
Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross
section located at point C. The 300-N forces act in the -z direction
and the 500-N forces act in the +x direction. The journal bearings
at A and B exert only x and z components of force on the shaft.
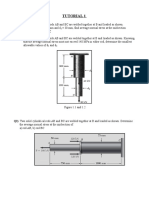
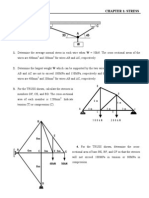
3. The built-up shaft consists of a pipe AB and solid rod BC. The pipe
has an inner diameter of 20 mm and outer diameter of 28 mm.
The rod has a diameter of 12 mm. Determine the average normal
stress at points D and E and represent the stress on a volume
element located at each of these points.
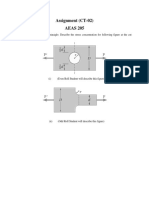
4. The 150-kg bucket is suspended from end E of the frame.
Determine the average normal stress in the 6-mm diameter wire
CF and the 15-mm diameter short strut BD.
5. The 150-kg bucket is suspended from end E of the frame. If the
diameters of the pins at A and D are 6 mm and 10 mm,
respectively, determine the average shear stress developed in
these pins. Each pin is subjected to double shear.
6. The tension member is fastened together using two bolts, one on
each side of the member as shown. Each bolt has a diameter of
7.5 mm. Determine the maximum load P that can be applied to
the member if the allowable shear stress for the bolts is allow =
84MPa. and the allowable average normal stress is allow =
140MPa.
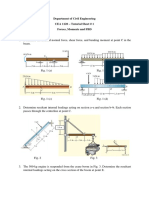
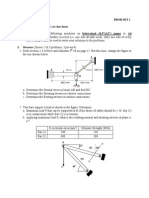
7. The frame is subjected to the load of 4 kN which acts on member
ABD at D. Determine the required diameter of the pins at D and C
if the allowable shear stress for the material is allow = 40MPa. Pin
C is subjected to double shear, whereas pin D is subjected to
single shear.
You might also like
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies - Supplementary ProblemsDocument7 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies - Supplementary ProblemsDhenil ManubatNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document7 pagesTutorial 5A SкNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering HW 1Document5 pagesMechanical Engineering HW 1DanialNo ratings yet
- Applied Hydrology VT Chow 1988Document3 pagesApplied Hydrology VT Chow 1988kaicaNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 (Allowable Stress)Document5 pagesTugas 1 (Allowable Stress)WAHYU DWI LESTARINo ratings yet
- Stress Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesStress Practice ProblemsSayantan ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set StressDocument4 pagesProblem Set StressChristian RigonNo ratings yet
- Stress and StrainDocument7 pagesStress and StrainAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials QuestionsDocument16 pagesStrength of Materials QuestionsRaymond BaldelovarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Stress ProblemsDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Stress ProblemsKarthik Kalash100% (1)
- ENSC 13 Problem Set 1 (2sem AY 2019-2020)Document5 pagesENSC 13 Problem Set 1 (2sem AY 2019-2020)Sean CrispoNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 4-IiDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 4-IiMilton CobaNo ratings yet
- ES 13 ProbSet 1Document2 pagesES 13 ProbSet 1Sammy Marquez50% (2)
- Solid Mechanics - DM23801Document41 pagesSolid Mechanics - DM23801Michael MeashoNo ratings yet
- ENGG 410 Problem Set 3 - Shear - Torsional StressDocument4 pagesENGG 410 Problem Set 3 - Shear - Torsional StressJoana Rosette TordecillaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document3 pagesSheet 1محمد معوضNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Concept of StressDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 Concept of Stresswilliamgacc11No ratings yet
- Es 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)Document3 pagesEs 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)akosikapitansinoNo ratings yet
- Som - Am2200 Assignment - 2Document3 pagesSom - Am2200 Assignment - 2Sai naveenNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsDocument7 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsadrianNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheets SOMDocument20 pagesTutorial Sheets SOMPriyanshu Sharma100% (1)
- Asign1 MomDocument4 pagesAsign1 MomAmru AwangNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Chapter 1Document17 pagesExercises in Chapter 1Lam TranNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document6 pagesHW 1Mark Louies Mago VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Stress1 PDFDocument18 pagesConcepts of Stress1 PDFCarl Malone Lotivio LorillaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (Group) - 220110 - 003126Document7 pagesAssignment 5 (Group) - 220110 - 003126MOHAMMAD AELEEF BIN PATRICK A20ET0356No ratings yet
- Stress, Strain and Relation ExerciseDocument7 pagesStress, Strain and Relation ExerciseHazeq AzaharNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document3 pagesTutorial Chapter 1ACC SHNo ratings yet
- Practical Problems (Chap 1 Chap 4)Document2 pagesPractical Problems (Chap 1 Chap 4)tevin sessa100% (1)
- ME 212 Tutorial 4Document2 pagesME 212 Tutorial 4Mihir Kumar MechNo ratings yet
- Smat Quiz BeesDocument9 pagesSmat Quiz BeesJayson IsidroNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument3 pagesProblem SetChristian RigonNo ratings yet
- MSE 2212 Mechanics of Materials Assignment 6Document2 pagesMSE 2212 Mechanics of Materials Assignment 6johnNo ratings yet
- ME102: Engineering Mechanics Homework #7Document3 pagesME102: Engineering Mechanics Homework #7RahulAggarwalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Solid Mechanics PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment 2 Solid Mechanics PDFSamiha Maysoon NooriaNo ratings yet
- Axial LoadingDocument4 pagesAxial LoadingAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Simple StressDocument50 pagesSimple StressIvan Manalang50% (4)
- Lecture On Strength of Materials August 2014Document87 pagesLecture On Strength of Materials August 2014Cha Castillo100% (1)
- T 1Document3 pagesT 1Muhamad SyazwanNo ratings yet
- MechanicsDocument5 pagesMechanicsElla ReyNo ratings yet
- Zadaca IptfDocument4 pagesZadaca IptfNermin RedzovićNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.1 and 2.2 PDFDocument4 pagesExercise 2.1 and 2.2 PDFDenver Nieveras0% (1)
- Statics Assignments CompletedDocument9 pagesStatics Assignments CompletedRandhir Ky0% (1)
- Es 13 Prob Set 1Document5 pagesEs 13 Prob Set 1Julian de LaraNo ratings yet
- Review Module: - Strength of Materials 1 Part 1Document2 pagesReview Module: - Strength of Materials 1 Part 1John andre MarianoNo ratings yet
- MENG3306 - Chapter 1 CEP-Class Example ProblemsDocument3 pagesMENG3306 - Chapter 1 CEP-Class Example ProblemsMike LinhorstNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2019 Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Tutorial-3Document2 pagesSolid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2019 Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Tutorial-3Kamini GoyalNo ratings yet
- 34 Assignment 7Document2 pages34 Assignment 7venuNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis LEC2Document9 pagesStress Analysis LEC2Elsaid SalahNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Sample Problems StressDocument2 pagesCH 1 Sample Problems StressRy NeutronNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Bearing and Punching Stress, StrainDocument16 pagesLecture 2 Bearing and Punching Stress, StrainDennisVigoNo ratings yet
- Strenght of Materials (ES-64)Document353 pagesStrenght of Materials (ES-64)api-3836341100% (14)
- 2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsDocument6 pages2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsMartin MugoniNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument4 pagesTutorialvarjith007No ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- How Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityFrom EverandHow Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument2 pagesCombinepdfFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Declining BalanceDocument22 pagesTutorial 1 - Declining BalanceFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Cement DesignDocument10 pagesCement DesignFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Q3 - 24188Document1 pageQ3 - 24188Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Q2 - 24188Document2 pagesQ2 - 24188Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- NPV IRR +payback1Document35 pagesNPV IRR +payback1Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- NPV IRR +payback1Document35 pagesNPV IRR +payback1Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Fyp 1 Fly AshDocument8 pagesFyp 1 Fly AshFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- NPV IRR +payback1Document35 pagesNPV IRR +payback1Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- NPV IRR +payback1Document35 pagesNPV IRR +payback1Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - PSC & Carry ForwardDocument2 pagesTutorial 2 - PSC & Carry ForwardFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - PSC & Carry ForwardDocument2 pagesTutorial 2 - PSC & Carry ForwardFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Economic AssessmentDocument7 pagesEconomic AssessmentFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- MbalDocument4 pagesMbalFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Drilling Simulator: Lab ReportDocument22 pagesDrilling Simulator: Lab ReportFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- GFE Mini Field Development PlanDocument10 pagesGFE Mini Field Development PlanFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Expenses & RisksDocument8 pages7.2 Expenses & RisksFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- MbalDocument4 pagesMbalFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Depth Vs AreaDocument1 pageDepth Vs AreaFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- MbalDocument4 pagesMbalFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Front Page - ITM ProjectDocument1 pageFront Page - ITM ProjectFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Drilling Simulator (16.3.2018)Document23 pagesDrilling Simulator (16.3.2018)Fizz Martin100% (1)
- 1 HoistingSystemDocument42 pages1 HoistingSystemAoun MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 3 CirculatingSystemDocument19 pages3 CirculatingSystemAoun MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document8 pagesBook 2Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Petronas Fdm2063 - Probability and Statistics Chapter 1 Revision Active Learning (Pair Work) - ReflectionDocument2 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Petronas Fdm2063 - Probability and Statistics Chapter 1 Revision Active Learning (Pair Work) - ReflectionFizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (RE)Document13 pagesTutorial 1 (RE)Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 (RE1)Document9 pagesTutorial 2 (RE1)Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- HW#1Document3 pagesHW#1Fizz Martin100% (1)