Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research
Uploaded by
Sachin JainCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Research
Uploaded by
Sachin JainCopyright:
Available Formats
Bustro_100322_TriFold.
qxp
5/3/2005
8:56 AM
Page 2
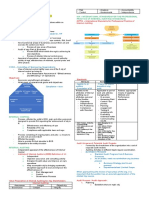
Standard & Poors Equity Research Methodology
BOTTOM-UP COMPANY ANALYSIS
Company Fundamental Analysis1
MACRO AND ECONOMIC
ANALYSIS
When conducting bottom-up
company analysis, analysts are
expected to incorporate Macro
and Economic Analysis.
Investment Policy
Committee (IPC)
Step 1
Review public
information
10Ks
10Qs
Annual Reports
Conference
Calls
Meets weekly and is
responsible for determining
Standard & Poors analytical
views on investment trends
Mission:
Ensure Standard & Poors
views are reached through a
deliberative, consistent process
that involves input from a
diverse group of Standard &
Poors senior analytic personnel
Step 2
Conversations with
company management for detailed
information
Establish relationships
with new companies
Most meetings with
companies done via
phone; some in-person
meetings
Obtain a better
understanding of:
Trends
Leverage/margins
Efficiency programs
Costs - current,
changes
Step 3
EPS Growth Rate
Earnings Prospects
Balance sheet
and cash flows
Interest rate forecasts
Market performance forecasts
Economic, political and related
developments of interest to
investment community
Consensus concerning effect
of such developments on S&Ps
view of financial markets,
including recommended
percentage asset allocation
among stocks, bonds and cash
Sector Strategy
and Guidance
Review financial
assumptions
Assess:
with company as
appropriate for company guidance (e.g.
earnings comparisons)
Management team
Competitive
environment
Suppliers
Buyers
Substitutes
Barriers to entry
Regulatory
environment
Standard & Poors Core Earnings Calculation
Analysis includes:
Step 5
Step 4
Prepare 3-Year
Preliminary
Earnings Model
Included
Excluded
Employee stock option grant expense
Restructuring charges from ongoing
operations
Write-downs of depreciable or
amortizable operating assets
Pension costs
Purchased research and
development expenses
Merger/acquisition related expenses
Unrealized gains/losses from
hedging activities
Finalize Earnings
Model
Determine earnings
quality
Evaluate corporate
governance
Project Standard
& Poors Core
Earnings, S&Ps
more accurate,
proprietary representation of the
true performance
of a firms ongoing
operations
Step 8
Step 7
Step 6
Goodwill impairment charges
Gains/losses from asset sales
Pension gains
Litigation or insurance settlements
and proceeds
Reversal of prior-year changes
and provisions
Analyst uses multiple criteria for valuing
Establish Intrinsic Value
a company, including:
Intrinsic Value Analysis
Relative Valuation
Sum of the Parts
Risk Assessment Analyst incorporates a
risk premium to derive a valuation
Target Price over 12 months
Analyst assigns a Risk Ranking
Assessment (High/Medium/Low) of
projected share volatility and risk of
capital loss
Criteria / Definition
Intrinsic Value Analysis
Determine securitys intrinsic value based on discounted
free cash flow (DCF) analysis. Estimates of future free cash
flows are discounted back to current dollars, including variables
like risk assessment and capital structure
Present value of shares vs. current share price
10-15 year projection
Defined parameters around DCF to make it more reasonable
(e.g. interest rate inputs)
Relative Valuation
Assessing a securitys relative value by comparing appropriate
financial ratios across peer groups
Comparison with industry group
Price/Earnings (P/E)
Efficiency
Margins
Step 9
Decide STARS recommendation
(refer to inside panel for details on S&Ps
5 STARS Ranking System)
Incorporate risk assessment rating
into overall STARS ranking (For
more details on Standard & Poors
Risk Ranking Assessment, call
1-800-523-4534.)
Step 10
Supervisory
analyst review
for regulatory
and compliance
purposes
Company value
P/E trading history
High/low in cycle
Current P/E level justification
Valuation vs. appropriate index
Sum of the Parts
Products
and Services
Retail
Advisor Insight
Custom Newsletters
Equity Liaison Desk
Industry Surveys
Market Insight
MarketScope
Model Portfolios
NetAdvantage
Pocket Guides
Portfolio Advisor
Sector Scorecard
Stock Guides
Stock Reports
The Outlook
Institutional
Determining fair value of a stock by determining private
market values for a firms individual units
No clear comparison and/or conglomerate
Break divisions up as stand-alone business units
Calculate a relative value for each division
Arrive at a blended valuation
Compustat Data
Equity Insights
Industry Surveys
Institutional Equity Reports
IPC Notes
Monthly Investment Review
Sector Watch
US Financial Notes
Risk Assessment
Technicals
Insider buying
Beta
Ongoing Analytical Review
Step 11
Step 1
Repeat Steps 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9
Step 2
Ongoing Analytical Review
Continuous committee-based evaluation of STARS recommendation Constant updates for covered companies from primary sources. Goal: 7-8 updates per year
Quarterly updates published and distributed Material events Changes in recommendations
Step 3
Step 7
Chief Investment Strategist
provides guidance on past and
current sector trends and
forecasts top and bottom
performing sectors.
Group Sector Heads meet
regularly with Global and
Regional Research Directors to
incorporate input from equity
analysts from all sectors to
formulate a collective bottom-up
investment strategy. This
bottom-up input, in the context
of past and current sector
trends and macro-economic
projections, support S&Ps
holistic sector weight strategy
and recommendations.
Review
Company Valuation Analysis
Stock Report updates
Step 8
MarketScope updates
First Call notes
Step 9
Company Coverage Criteria
Core STARS Coverage Criteria
Additional Coverage Criteria
Deletions to Equity Coverage
All S&P 500 Index 2
S&P Composite 1500 Index constituent
Negative corporate actions
300 of the S&P MidCap 400 Index
Significant trading volume
200 of the S&P SmallCap 600 Index
Market capitalization
Dropped from S&P Composite 1500 Index
Key non-U.S. stocks
Corporate actions (mergers/acquisitions, spin-offs)
Stock price < $5/share
Emerging growth companies
Lack of investor interest
(bankruptcy, mergers and acquisitions)
Number of Companies Covered Per Analyst
20-25 companies
1 Standard & Poors analysts access to information will
always be subject to applicable legal requirements concerning
fair disclosure.
2 Excluding Standard & Poors parent, the McGraw-Hill
Companies.
The equity research reports and recommendations provided by
Standard & Poors Equity Research are performed separately from
any other analytic activity of Standard & Poors. Standard & Poors
Equity Research has no access to non-public information received
by other units of Standard & Poors. Standard & Poors does not
trade on its own account.
You might also like
- Bank of America Global Equity ValuationDocument56 pagesBank of America Global Equity Valuationrichard100% (1)
- Operations Management Stevenson 11th Edition Test BankDocument10 pagesOperations Management Stevenson 11th Edition Test BankAries Gonzales Caragan50% (2)
- Training The Street PrimersDocument30 pagesTraining The Street PrimersRyan MarloweNo ratings yet
- Norman K. Denzin - The Cinematic Society - The Voyeur's Gaze (1995) PDFDocument584 pagesNorman K. Denzin - The Cinematic Society - The Voyeur's Gaze (1995) PDFjuan guerra0% (1)
- Equity Research Methodology 031604Document1 pageEquity Research Methodology 031604vardashahid100% (1)
- Fundamental Analysis of Dr. Reddys LabDocument66 pagesFundamental Analysis of Dr. Reddys LabAvinash Kandoi0% (1)
- Packing List For GermanyDocument2 pagesPacking List For GermanyarjungangadharNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Ordinal NumbersDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Ordinal Numbersapi-329663096No ratings yet
- Manual CAT 345C LDocument20 pagesManual CAT 345C LRicardo SotoNo ratings yet
- Process: For Institutional One-On-One Use OnlyDocument16 pagesProcess: For Institutional One-On-One Use OnlyABermNo ratings yet
- CygnusDocument34 pagesCygnuskskumarr100% (1)
- Corporate Ratings MethodologyDocument3 pagesCorporate Ratings MethodologykrupakaranNo ratings yet
- New QuestionsDocument13 pagesNew QuestionsNaman JainNo ratings yet
- Brand Finance Global 500 2023 PreviewDocument99 pagesBrand Finance Global 500 2023 Previewneusdiez36No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 SMHDocument66 pagesChapter 12 SMHsalman parvezNo ratings yet
- 768760870587security Frameworks NIST CSF As An Enabler and Incident Response ApproachDocument33 pages768760870587security Frameworks NIST CSF As An Enabler and Incident Response ApproachggcvbcNo ratings yet
- DBSTR SustainabilityESG Phase3 FADocument3 pagesDBSTR SustainabilityESG Phase3 FA陳岱佑No ratings yet
- ISO-TC 176-TF - APG-Effectiveness2015Document32 pagesISO-TC 176-TF - APG-Effectiveness2015Mayra RiosNo ratings yet
- Comprehansive Process. TamerDocument2 pagesComprehansive Process. TamerMarco IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Hotels & Resorts: Analytics at TheDocument2 pagesHotels & Resorts: Analytics at TheridwanhakimNo ratings yet
- DR - Kavita Sasidharan Kulkarni, Supervisor, NMIMS School of Business, HyderabadDocument10 pagesDR - Kavita Sasidharan Kulkarni, Supervisor, NMIMS School of Business, HyderabadSaransh KansalNo ratings yet
- Basecamp Whitepaper Profitability AnalysisDocument21 pagesBasecamp Whitepaper Profitability AnalysisYano FélixNo ratings yet
- Accenture Banking On BlockchainDocument10 pagesAccenture Banking On BlockchainFernando MiyazakiNo ratings yet
- Paper 20 IcmaiDocument452 pagesPaper 20 IcmaiAksaya S100% (1)
- Business Analytics: With Certification From NSE AcademyDocument8 pagesBusiness Analytics: With Certification From NSE AcademyTanuj SinghNo ratings yet
- SIP SummaryDocument6 pagesSIP SummaryNishiNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 Auditing Practices Group: Aligning The QMS With The Achievement of Organizational and Business SuccessDocument32 pagesISO 9001 Auditing Practices Group: Aligning The QMS With The Achievement of Organizational and Business SuccessSelvaraj SimiyonNo ratings yet
- BusinessValuationModelingCoursePresentation 200527 140843Document93 pagesBusinessValuationModelingCoursePresentation 200527 140843Maruthi Sabbani100% (2)
- Seminar 10 Valuation Theory and Implementation 2016Document29 pagesSeminar 10 Valuation Theory and Implementation 2016mattNo ratings yet
- Operations Auditing: - o o - o - o oDocument9 pagesOperations Auditing: - o o - o - o oLORI-LYN GUICONo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 Auditing Practices GroupDocument31 pagesISO 9001 Auditing Practices GroupphucakjNo ratings yet
- IBank Coaching - Investment Banking Valuation Methodology (2020) (1) - CompressedDocument23 pagesIBank Coaching - Investment Banking Valuation Methodology (2020) (1) - CompressedcherryNo ratings yet
- K Faid - Master PDVSA - Module 12 - 2009Document49 pagesK Faid - Master PDVSA - Module 12 - 2009Franklin RevillNo ratings yet
- Why Is S&OP Important: Case Study 1: An End To End S&OP SolutionDocument1 pageWhy Is S&OP Important: Case Study 1: An End To End S&OP Solutionsam662223No ratings yet
- Topic 1 - 2023 - Introduction To BA - STDDocument11 pagesTopic 1 - 2023 - Introduction To BA - STDVũ Ngọc HàNo ratings yet
- Rating Methodology - Manufacturing Companies - 16sept2019Document10 pagesRating Methodology - Manufacturing Companies - 16sept2019Siddhant SinghNo ratings yet
- Satyaki Dey ResumeDocument2 pagesSatyaki Dey Resumesatyaki.d.deyNo ratings yet
- Ismail Industries Limited: Rating ReportDocument5 pagesIsmail Industries Limited: Rating ReporthelloNo ratings yet
- World-Class Functionality For All Business Users' NeedsDocument20 pagesWorld-Class Functionality For All Business Users' NeedsBalaji MugunthanNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument1 pageSodapdfMarcos WilkerNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PMP Domain ProcessDocument427 pagesModule 3 PMP Domain ProcessKhawla AlsalehNo ratings yet
- Internal EnvironmentDocument10 pagesInternal Environmentthabithadube844No ratings yet
- Esg Materiality Assessment 2017 KPMG NZDocument6 pagesEsg Materiality Assessment 2017 KPMG NZsherwynNo ratings yet
- SM Chapter 3 Key Words - PDFDocument48 pagesSM Chapter 3 Key Words - PDFVikramNo ratings yet
- How To Use Preseen Material March2015 2Document3 pagesHow To Use Preseen Material March2015 2Ayesha HaroonNo ratings yet
- How To Use Preseen Material March2015 2Document3 pagesHow To Use Preseen Material March2015 2Ayesha HaroonNo ratings yet
- Pa Ifpp IcisaDocument34 pagesPa Ifpp IcisafreddyNo ratings yet
- SBL Revision Question Guidance Sept 22 To June 23Document5 pagesSBL Revision Question Guidance Sept 22 To June 23Tran ThangNo ratings yet
- ToolsDocument42 pagesToolsAhmed LotfyNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1 Financial Performance RatiosDocument135 pages1.2.1 Financial Performance RatiosGary ANo ratings yet
- Summary of BABOK Knowledge AreasDocument18 pagesSummary of BABOK Knowledge Areasogunfowotesegun35No ratings yet
- ANTAM KPI Weighting and LinkageDocument9 pagesANTAM KPI Weighting and LinkageJonathan Pratama SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Implementing Business Process Reengineering (Example Model)Document18 pagesImplementing Business Process Reengineering (Example Model)amitsharma1103No ratings yet
- S2-3 Marketing Research - Environment Scanning PrintDocument15 pagesS2-3 Marketing Research - Environment Scanning PrintTrương Việt TuấnNo ratings yet
- Business ValuationDocument431 pagesBusiness ValuationAnonymous 7zUBWZZfy50% (2)
- Performance Appraisal H R Project 2Document74 pagesPerformance Appraisal H R Project 2The Dark KnightNo ratings yet
- Khushpreet MbaDocument55 pagesKhushpreet MbaKaran SandhuNo ratings yet
- PAPER Employee Performance Appraisal at Sri Veerabhadreshwar Motors BidarDocument13 pagesPAPER Employee Performance Appraisal at Sri Veerabhadreshwar Motors BidarDr Bhadrappa HaralayyaNo ratings yet
- 7 - Job Analysis and Job Benchmarking To Improve The Performances of Sales and Marketing EmployeesDocument4 pages7 - Job Analysis and Job Benchmarking To Improve The Performances of Sales and Marketing Employeessushil.tripathiNo ratings yet
- Factset Presentation: Bonnie & MelodyDocument14 pagesFactset Presentation: Bonnie & MelodyBonnie AuNo ratings yet
- Financial Modeling 5 Jan 2023Document5 pagesFinancial Modeling 5 Jan 2023Archit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Strategy Chapter 3 - External - AnalysisDocument34 pagesStrategy Chapter 3 - External - AnalysisVân Anh Nguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- Owner Cost Estimate Reviews: Allen C. Hamilton PMP CCP DIFDocument18 pagesOwner Cost Estimate Reviews: Allen C. Hamilton PMP CCP DIFyan energiaNo ratings yet
- ICTSAD609 Student Assessment Tasks Project Portfolio V2.0Document47 pagesICTSAD609 Student Assessment Tasks Project Portfolio V2.0akashpandet6No ratings yet
- A Study of the Supply Chain and Financial Parameters of a Small BusinessFrom EverandA Study of the Supply Chain and Financial Parameters of a Small BusinessNo ratings yet
- Use Cases - An Introduction: Jason GormanDocument16 pagesUse Cases - An Introduction: Jason GormanminhnascribdNo ratings yet
- Business Modeling With UML A Business Process Centred Architecture IntroductionDocument25 pagesBusiness Modeling With UML A Business Process Centred Architecture Introductionapi-3721818No ratings yet
- SSRN Id809107Document36 pagesSSRN Id809107api-3715003No ratings yet
- VaR For Asian Emerging Market Equity PortfoliosDocument6 pagesVaR For Asian Emerging Market Equity Portfoliosapi-3715003No ratings yet
- Incorporating Liquidity Risk in VaR ModelsDocument22 pagesIncorporating Liquidity Risk in VaR Modelsapi-3715003No ratings yet
- Calibrating and Simulating Copula Functions - An Application To The Italian Stock MarketDocument26 pagesCalibrating and Simulating Copula Functions - An Application To The Italian Stock Marketapi-371500375% (4)
- A Threshold Model For Italian Stock Market Volatility Potential of These Models - Comparing Forecasting Performances and Evaluation of Portfolio Risk With Other ModelsDocument42 pagesA Threshold Model For Italian Stock Market Volatility Potential of These Models - Comparing Forecasting Performances and Evaluation of Portfolio Risk With Other Modelsapi-3715003No ratings yet
- Bach Polonaise G Min BWV 119 A4Document1 pageBach Polonaise G Min BWV 119 A4vincenzovaiaNo ratings yet
- Cause List 2.1.2023Document4 pagesCause List 2.1.2023あいうえおかきくけこNo ratings yet
- History of The Hadith, Dr. Muhammad HameedullahDocument0 pagesHistory of The Hadith, Dr. Muhammad HameedullahAMEEN AKBAR100% (4)
- Ultraviolet RadiationDocument3 pagesUltraviolet RadiationbirlacementNo ratings yet
- Cover PageDocument10 pagesCover PageAvijit GhoshNo ratings yet
- Automotive SensorsDocument20 pagesAutomotive SensorsahmedNo ratings yet
- Best S and Nocella, III (Eds.) - Igniting A Revolution - Voices in Defense of The Earth PDFDocument455 pagesBest S and Nocella, III (Eds.) - Igniting A Revolution - Voices in Defense of The Earth PDFRune Skjold LarsenNo ratings yet
- 8 3ThingWorxInstallation 1 0 174675 PDFDocument157 pages8 3ThingWorxInstallation 1 0 174675 PDFAuditio MandhanyNo ratings yet
- Ddec VDocument30 pagesDdec Vllama100% (1)
- Liquid Process Piping - Part 1 General Piping Design PDFDocument33 pagesLiquid Process Piping - Part 1 General Piping Design PDFnitin guptaNo ratings yet
- PC2000-8 Spec SheetDocument20 pagesPC2000-8 Spec SheetNeeraj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Enable Modern Authentication in Exchange OnlineDocument2 pagesEnable Modern Authentication in Exchange Onlinedan.artimon2791No ratings yet
- Cross CultureDocument134 pagesCross CulturePhương AnnhNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire OriginalDocument6 pagesQuestionnaire OriginalJAGATHESANNo ratings yet
- 56257375851Document3 pages56257375851Anneliese FernandesNo ratings yet
- Design of A Low Cost Hydrostatic Bearing: Anthony Raymond WongDocument77 pagesDesign of A Low Cost Hydrostatic Bearing: Anthony Raymond WongRogelio DiazNo ratings yet
- Task 3: New - HTMLDocument12 pagesTask 3: New - HTMLGONELA SAI LOKESH (RA2011028010100)No ratings yet
- AA1 Adventure Anthology One r14Document85 pagesAA1 Adventure Anthology One r14dachda100% (1)
- VectorCAST QA Factsheet ENDocument2 pagesVectorCAST QA Factsheet ENChaos XiaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - Contemporary WorldDocument4 pagesMODULE 1 - Contemporary WorldaapNo ratings yet
- 32 Forms of God GaneshaDocument16 pages32 Forms of God Ganeshasudhakarpk2011100% (2)
- Management Accounting/Series-4-2011 (Code3024)Document18 pagesManagement Accounting/Series-4-2011 (Code3024)Hein Linn Kyaw100% (2)
- Discover India, January 2018Document51 pagesDiscover India, January 2018calebfriesenNo ratings yet
- The English We SpeakDocument2 pagesThe English We Speakcaeronmustai100% (1)
- ADAPT-Builder 2019 GUI Quick Reference GuideDocument103 pagesADAPT-Builder 2019 GUI Quick Reference GuideephremNo ratings yet