Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circuits Worksheet
Circuits Worksheet
Uploaded by
daregumacal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesreviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentreviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCircuits Worksheet
Circuits Worksheet
Uploaded by
daregumacalreviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
CIRCUITS WORKSHEET
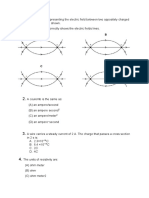
1. Determine the equivalent (total) resistance for each of the following circuits below.
2. Determine the total voltage (electric potential) for each of the following circuits below.
3. Fill out the table for the circuit diagramed at the right.
Circuit
Position
1
2
3
Total
Voltage (V)
Current (A)
Resistance ()
10.0
20.0
30.0
6.00
4. Fill out the table for the circuit diagramed at the right.
Circuit
Position
1
2
3
Total
Voltage (V)
Current (A)
Resistance ()
10.0
20.0
30.0
6.00
5. Fill out the table for the circuit diagramed at the right.
Circuit
Position
1
2
3
Total
Voltage (V)
Current (A)
Resistance ()
10.0
20.0
30.0
6.00
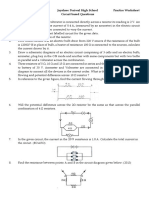
Questions 6 and 7 refer to the following:
The diagram to the right represents an electric
circuit consisting of four resistors and a 12-volt
battery.
6) What is the equivalent resistance of the circuit shown?
7) What is the current measured by ammeter A shown in the diagram?
8) A 6.0-ohm lamp requires 0.25 ampere of current to operate. In which circuit below would the lamp operate
correctly when switch S is closed?
Questions 9 and 10 refer to the following:
A 50.-ohm resistor, an unknown resistor R, a 120-volt source, and an ammeter are connected in a complete
circuit. The ammeter reads 0.50 ampere.
9) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit shown.
10) Determine the resistance of resistor R shown in the diagram.
Questions 11 through 13 refer to the following:
A 3.0-ohm resistor, an unknown resistor, R, and two ammeters, A1 and A2, are connected as shown below with a
12-volt source. Ammeter A2 reads a current of 5.0 amperes.
11) Determine the equivalent resistance of the circuit shown.
12) Calculate the current measured by ammeter A1 in the diagram shown.
13) Calculate the resistance of the unknown resistor, R in the diagram shown.
You might also like
- 00 Practice On Right Hand Rule and Flemings Left Hand RuleDocument3 pages00 Practice On Right Hand Rule and Flemings Left Hand Rule王施甯50% (2)
- Physics Worksheet Lesson 19 Electric Circuits PDFDocument5 pagesPhysics Worksheet Lesson 19 Electric Circuits PDFMuhammad Tauseef50% (2)
- Transformers Worksheet G9Document6 pagesTransformers Worksheet G9Prayogo DidiNo ratings yet
- 9 Electricity Test - CircuitsDocument5 pages9 Electricity Test - CircuitsRahmonGreen100% (1)
- Ohms Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesOhms Law WorksheetdoctshNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits (Grade 9) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingDocument2 pagesElectric Circuits (Grade 9) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingMOHDFADZLY8475% (4)
- Series Parallel Circuits Worksheet 02Document4 pagesSeries Parallel Circuits Worksheet 02Kimverly Jane Millan Javier50% (2)
- Buoyancy WorksheetDocument2 pagesBuoyancy WorksheetMahmudul Hasan MonirNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Lab Write-UpDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic Lab Write-Upapi-375748727No ratings yet
- Resistance Voltage and Current With AnswersDocument3 pagesResistance Voltage and Current With AnswersAli Raza25% (4)
- Coulomb Law Practice With Answers 1 (1) KJHDocument2 pagesCoulomb Law Practice With Answers 1 (1) KJHJaden Moniez100% (1)
- Electrical Energy and Power WorksheetDocument5 pagesElectrical Energy and Power WorksheetCris BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuizDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice QuizMHLS68No ratings yet
- Static Electricity Worksheet 1Document1 pageStatic Electricity Worksheet 1Oksana MandrykNo ratings yet
- 08 Dynamics-Newton's 2nd LawDocument9 pages08 Dynamics-Newton's 2nd Laweltytan100% (1)
- Stoichiometry Worksheet+AnswersDocument2 pagesStoichiometry Worksheet+AnswersAnonymous 6MSekAxCnZ0% (3)
- Quiz ElectricityDocument4 pagesQuiz ElectricityMaestro Pisika LptNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law WorksheetDocument1 pageOhms Law WorksheetMohmmed Ahmed100% (1)
- Questions About Electric CircuitsDocument49 pagesQuestions About Electric Circuitsashok50% (2)
- CAPE Physics Physical QuantitiesDocument3 pagesCAPE Physics Physical QuantitiestuvvacNo ratings yet
- CAPE Physics Unit 2 Module 1 QuestionsDocument6 pagesCAPE Physics Unit 2 Module 1 QuestionstuvvacNo ratings yet
- Circuits Worksheet ResistanceDocument3 pagesCircuits Worksheet ResistanceelchinNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Jayshree Periwal High School Practice Worksheet Physics Circuit Based Questions 2 MarkersDocument4 pagesScience-10 Jayshree Periwal High School Practice Worksheet Physics Circuit Based Questions 2 MarkersMihika MathurNo ratings yet
- Physics 12 Worksheet Circuitry KEYDocument3 pagesPhysics 12 Worksheet Circuitry KEYIna KasimNo ratings yet
- 1 - Circuits WorksheetDocument7 pages1 - Circuits WorksheetPakorn WinayanuwattikunNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity Question PaperDocument4 pagesStatic Electricity Question Papertheja sudarshaniNo ratings yet
- Physics 3204: Worksheet4: Solenoids and Magnetic FieldDocument4 pagesPhysics 3204: Worksheet4: Solenoids and Magnetic FieldVasile Nicoleta50% (2)
- Static Electricity Worksheet 2Document2 pagesStatic Electricity Worksheet 2ashok100% (2)
- Quiz Module 4 Electric FieldDocument6 pagesQuiz Module 4 Electric FieldMaestro Pisika LptNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of The Elements: Unit 3Document2 pagesPeriodic Table of The Elements: Unit 3Maristela Paraan Macaranas100% (1)
- APEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFDocument2 pagesAPEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFFirdausia Rahma PutriNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism WorksheetDocument3 pagesElectromagnetism WorksheetGuan Jie KhooNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Electric FieldsDocument4 pagesWorksheet - Electric FieldsPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics MCQ 6 Mains ElectricityDocument6 pagesIGCSE Physics MCQ 6 Mains ElectricityTessa KNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Static ElectricityDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper Static Electricityproodoot100% (1)
- Electrostatics - Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF - Preparation For EngineeringDocument19 pagesElectrostatics - Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF - Preparation For EngineeringRamaprasad Panda75% (4)
- Electric Circuits Answer KeyDocument2 pagesElectric Circuits Answer KeySabu Lazer50% (2)
- Worksheet For Grade 9 PhysicsDocument3 pagesWorksheet For Grade 9 Physicssamuel zelaelmNo ratings yet
- Static Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesStatic Worksheet AnswersSun RuangkajohnNo ratings yet
- 1 Electricity Student Worksheet PackageDocument50 pages1 Electricity Student Worksheet PackageAnita Chan100% (2)
- 1 .2013 El Force and El Field Hw-PracticeDocument12 pages1 .2013 El Force and El Field Hw-PracticerbgrossNo ratings yet
- Part A - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPart A - Multiple Choice QuestionsBryan SutantoNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Work, Energy, and PowerDocument2 pagesQuiz On Work, Energy, and PowerNathaniel DimaocorNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law and Basic Circuit TheoryDocument7 pagesOhms Law and Basic Circuit TheoryMinji LeeNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument50 pagesHeat and TemperaturealienlightningNo ratings yet
- Honors Physics Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference WorksheetDocument5 pagesHonors Physics Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference WorksheetDesadaNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Flows in Only One Direction Through A WireDocument3 pagesElectricity: Flows in Only One Direction Through A WiresaintEmNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Coulomb's LawDocument4 pagesMCQ On Coulomb's LawDorego Taofeeq100% (1)
- Activity 2 Let's SimulateDocument3 pagesActivity 2 Let's SimulateResa Consigna MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law WorksheetDocument1 pageOhms Law Worksheetbabyu1100% (1)
- 5 - Ohm's Law WorksheetDocument2 pages5 - Ohm's Law WorksheetNaveed Ahmed100% (1)
- Standing Waves WorksheetDocument2 pagesStanding Waves WorksheetAdib HassanNo ratings yet
- PSI Physics: Electric Field, Potential Energy and Voltage Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesPSI Physics: Electric Field, Potential Energy and Voltage Multiple Choice QuestionsJohn Ace AmbalanNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 8 AnswersDocument44 pagesPhysics Chapter 8 AnswersAbovethesystem95% (22)
- Static Electricity WorksheetDocument6 pagesStatic Electricity WorksheetMastentram Widjaja100% (3)
- Activity 1 CapacitanceDocument1 pageActivity 1 CapacitanceHannah Tabaquero RagudosNo ratings yet
- Show All Work - Multiple Choice Answers "MUST Be Proven" For Full Credit! (Show Your Solution!!!)Document2 pagesShow All Work - Multiple Choice Answers "MUST Be Proven" For Full Credit! (Show Your Solution!!!)Yzelle SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Coulomb's Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesLesson 5 - Coulomb's Law Worksheetdmart033100% (2)
- Circuits WorksheetDocument3 pagesCircuits Worksheetbindu shineNo ratings yet
- Circuits WorksheetDocument4 pagesCircuits Worksheetarshia zabihi yeganehNo ratings yet
- Circuits WorksheetDocument3 pagesCircuits WorksheetTawan PetpaiboonNo ratings yet
- Circuits-Worksheet 101Document5 pagesCircuits-Worksheet 101wassimfakNo ratings yet
- Thermometer WorksheetDocument2 pagesThermometer Worksheettuvvac0% (1)
- AC Theory WorksheetDocument1 pageAC Theory WorksheettuvvacNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism WorksheetDocument1 pageElectromagnetism WorksheettuvvacNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect WorkshetDocument3 pagesPhotoelectric Effect Workshettuvvac0% (1)
- Operations With UncertaintiesDocument5 pagesOperations With UncertaintiestuvvacNo ratings yet
- Logic Gates WorksheetDocument3 pagesLogic Gates Worksheettuvvac100% (1)
- Projectile Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion WorksheettuvvacNo ratings yet
- Completing The Square EquivalentsDocument2 pagesCompleting The Square EquivalentstuvvacNo ratings yet
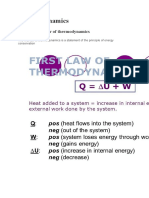
- Thermodynamics: The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument11 pagesThermodynamics: The First Law of ThermodynamicstuvvacNo ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities QuestionsDocument2 pagesElectrical Quantities Questionstuvvac100% (6)
- Capacitors WorksheetDocument2 pagesCapacitors WorksheettuvvacNo ratings yet
- Induction and Transformers WorksheetDocument3 pagesInduction and Transformers WorksheettuvvacNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff Laws WorksheetDocument1 pageKirchhoff Laws WorksheettuvvacNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and Power QuizDocument4 pagesWork Energy and Power Quiztuvvac100% (1)
- Electric Fields QuestionsDocument1 pageElectric Fields QuestionstuvvacNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Algebraic Fractions: To Find The Excluded Value(s) of An Algebraic FractionDocument2 pagesSimplifying Algebraic Fractions: To Find The Excluded Value(s) of An Algebraic FractiontuvvacNo ratings yet
- 9 Worksheet 1: Intermediate LevelDocument3 pages9 Worksheet 1: Intermediate LeveltuvvacNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorems: Name: - DateDocument1 pageCircle Theorems: Name: - DatetuvvacNo ratings yet
- Rational Equations: X 1) (x+3) X X 1 X 1 x+3Document3 pagesRational Equations: X 1) (x+3) X X 1 X 1 x+3tuvvacNo ratings yet
- Multiply and Divide Algebraic FractionsDocument1 pageMultiply and Divide Algebraic FractionstuvvacNo ratings yet
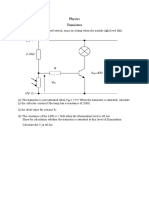
- Physics Transistors: 2.5V When The Transistor Is Saturated, CalculateDocument1 pagePhysics Transistors: 2.5V When The Transistor Is Saturated, CalculatetuvvacNo ratings yet
- Physics Coulomb's Law WorksheetDocument1 pagePhysics Coulomb's Law WorksheettuvvacNo ratings yet
- Internal Resistance IA PDFDocument10 pagesInternal Resistance IA PDFtuvvacNo ratings yet
- Capacitance NotesDocument75 pagesCapacitance NotestuvvacNo ratings yet
- Math Worksheet SubsitutionDocument2 pagesMath Worksheet SubsitutiontuvvacNo ratings yet
- Lattice PLLDocument21 pagesLattice PLLHoracio DorantesNo ratings yet
- Some Problems-3 PDFDocument10 pagesSome Problems-3 PDFMaitraNo ratings yet
- Using Cortex-M3M4M7 Fault ExceptionsDocument18 pagesUsing Cortex-M3M4M7 Fault ExceptionsRobertoNo ratings yet
- mb262 772cx 71131Document288 pagesmb262 772cx 71131Nadeem Ahmad Khan100% (1)
- BEP3 Farbcodierung - ENGDocument1 pageBEP3 Farbcodierung - ENGEva Bart-Kay Sanchez LopezNo ratings yet
- Broadcast SolutionsDocument152 pagesBroadcast SolutionsZoran AsenovNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of Power Quality in Distribution System Using D-StatcomDocument20 pagesEnhancement of Power Quality in Distribution System Using D-StatcomSairam SaiNo ratings yet
- STTA1206D/DI/G: Turboswitch Ultra-Fast High Voltage DiodeDocument9 pagesSTTA1206D/DI/G: Turboswitch Ultra-Fast High Voltage DiodeMarcos AndréNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog: First Edition 2016Document32 pagesProduct Catalog: First Edition 2016phucetau zNo ratings yet
- Loewe Q2500MDocument128 pagesLoewe Q2500Mf17439100% (2)
- Connecting Cypress SPI Serial Flash To Configure Xilinx FPGAsDocument9 pagesConnecting Cypress SPI Serial Flash To Configure Xilinx FPGAsFergus FernNo ratings yet
- An316 Application NoteDocument7 pagesAn316 Application NotemasmoxNo ratings yet
- s7300 Cp341 Manual en en-USDocument248 pagess7300 Cp341 Manual en en-USdavidpornNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone Software Performance: GreendroidDocument2 pagesMobile Phone Software Performance: GreendroidShagunChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Infranor DriveDocument57 pagesInfranor DriveRicardo AbreuNo ratings yet
- Irig-B Decoder Based On Fpga For Synchronization in Pmus by Considering Different Input FormatsDocument6 pagesIrig-B Decoder Based On Fpga For Synchronization in Pmus by Considering Different Input FormatsvitpowerguyNo ratings yet
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio in Power Electronic Digital Control CircuitsDocument10 pagesSignal-to-Noise Ratio in Power Electronic Digital Control CircuitsShiju KumarNo ratings yet
- Methodologies To Determine Fhe Fault Current Through An OPGW (Optical Ground Wire)Document6 pagesMethodologies To Determine Fhe Fault Current Through An OPGW (Optical Ground Wire)mrjack1100% (2)
- Tl022 TexasDocument10 pagesTl022 Texasenzo_60No ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument10 pagesDatasheet PDFViola Safa Nur AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Keysight Radar EqnDocument9 pagesKeysight Radar EqnAnandPrakashSinhaNo ratings yet
- Nuhertz BrochureDocument2 pagesNuhertz BrochureAWR CorporationNo ratings yet
- Dmos Dual Full Bridge Driver: Multipower BCD TechnologyDocument11 pagesDmos Dual Full Bridge Driver: Multipower BCD TechnologyChristian BiancoNo ratings yet
- ZTE UMTS Particular Radio Function Feature Guide - V5.0 - 20110407Document46 pagesZTE UMTS Particular Radio Function Feature Guide - V5.0 - 20110407Poobalan Murugeya100% (2)
- Ranza Fault LocatorDocument72 pagesRanza Fault LocatorNalina YatheeshNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Interface For Time To Digital Converter Chip GP2Document2 pagesMicrocontroller Interface For Time To Digital Converter Chip GP2rmcnis100% (2)
- Erno BorbelyJFETs The New Frontier Part 1and 2 PDFDocument11 pagesErno BorbelyJFETs The New Frontier Part 1and 2 PDFeligeotroNo ratings yet
- B.E Electrical and Electronics Engineering Curriculum 2012 Batch OnwardsDocument7 pagesB.E Electrical and Electronics Engineering Curriculum 2012 Batch Onwardskarthick_mariner92No ratings yet
- Switching Theory and Logic DesignDocument8 pagesSwitching Theory and Logic DesignVenkat ChadalavadaNo ratings yet