Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Take Any Two Paths C and C Fromatob in D and Define C To Be The Curve Consisting Ofc Followed by - C
Take Any Two Paths C and C Fromatob in D and Define C To Be The Curve Consisting Ofc Followed by - C
Uploaded by
gthulasi7871260 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesVC
Original Title
Vc-15
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVC
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesTake Any Two Paths C and C Fromatob in D and Define C To Be The Curve Consisting Ofc Followed by - C
Take Any Two Paths C and C Fromatob in D and Define C To Be The Curve Consisting Ofc Followed by - C
Uploaded by
gthulasi787126VC
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
INDEPENDENCE OF PATH
Take any two paths C1 and C2 from A to B
in D and define C to be the curve consisting
of C1 followed by C2.
INDEPENDENCE OF PATH
Then,
0 F dr F dr
C
C1
C2
F dr
F dr F dr
C1
C2
Hence, F dr F dr
C1
C2
So, we have proved the following theorem.
INDEPENDENCE OF PATH
Theorem 3
F dr is independent of path in D
if and only if:
F dr 0
for every closed path C in D.
INDEPENDENCE OF PATH
We know that the line integral of any
conservative vector field F is independent
of path.
It follows that
F dr 0 for any closed path.
PHYSICAL INTERPRETATION
The physical interpretation is
that:
The work done by a conservative force field
(such as the gravitational or electric field in
Section 16.1) as it moves an object around
a closed path is 0.
You might also like
- Vector CalculusDocument89 pagesVector Calculusxxaliceliuxx100% (1)
- Position Vector:: C A P A C I T O RDocument41 pagesPosition Vector:: C A P A C I T O RRajeev Ranjan0% (1)
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersFrom EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- A Curve Is Called Closed If Its Terminal Point Coincides With Its Initial Point, That IsDocument6 pagesA Curve Is Called Closed If Its Terminal Point Coincides With Its Initial Point, That Isgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- With This Terminology, We Can Say That:: Line Integrals of Conservative Vector Fields Are Independent of PathDocument6 pagesWith This Terminology, We Can Say That:: Line Integrals of Conservative Vector Fields Are Independent of Pathgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- The Physical Interpretation Is ThatDocument6 pagesThe Physical Interpretation Is Thatgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- W D FD F F MMG MMG: So, by Theorem 2, The Work Done IsDocument6 pagesW D FD F F MMG MMG: So, by Theorem 2, The Work Done Isgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Conservative Fields: Domain D Domain EDocument5 pagesConservative Fields: Domain D Domain EAbha SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Ii-9: Wilson Loops,'T Hooft'S Loops, and 'T Hooft'S Model of Confinement Edward WittenDocument6 pagesLecture Ii-9: Wilson Loops,'T Hooft'S Loops, and 'T Hooft'S Model of Confinement Edward WittenluisdanielNo ratings yet
- Section 10.2 Path Independence of Line IntegralDocument23 pagesSection 10.2 Path Independence of Line IntegralKrishna ChaituNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - DeflectionsDocument101 pagesUnit 4 - DeflectionsksrsunilNo ratings yet
- Stokes Theorem Ii Maths21a, O. Knill: y Z Z X X y X y ZDocument1 pageStokes Theorem Ii Maths21a, O. Knill: y Z Z X X y X y Zmartim_martinsNo ratings yet
- 17.4 Green's Theorem: NotationDocument3 pages17.4 Green's Theorem: NotationbobNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis 1 Elastic Beam Theory-1Document20 pagesStructural Analysis 1 Elastic Beam Theory-1TrevorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25: Electric PotentialDocument11 pagesChapter 25: Electric PotentialAlexNo ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument18 pagesVector CalculuseshetNo ratings yet
- CauchygoursatDocument2 pagesCauchygoursatSaid Liger AldásNo ratings yet
- projected conic C ceiling plane directrix: r V d β LDocument1 pageprojected conic C ceiling plane directrix: r V d β LlinghuchongNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential Capacitance - Free PDFDocument34 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential Capacitance - Free PDFKrrish DabasNo ratings yet
- Slopes of Limited Height Taylor Analysis: R AD F C O O RDocument4 pagesSlopes of Limited Height Taylor Analysis: R AD F C O O RpkNo ratings yet
- C 6 DeflectionDocument35 pagesC 6 DeflectionSuyash ToshniwalNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics L-2Document26 pagesApplied Physics L-2Farhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Also, The Domain of F Is The Entire Plane (D ), Which Is Open and Simply-ConnectedDocument6 pagesAlso, The Domain of F Is The Entire Plane (D ), Which Is Open and Simply-Connectedgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- PHY481 - Lectures 7 and Part of 8Document3 pagesPHY481 - Lectures 7 and Part of 8Sameen MarufNo ratings yet
- Exercises Lecture 3 - Answers: Climbing and Descending FlightDocument9 pagesExercises Lecture 3 - Answers: Climbing and Descending FlightBaptisteNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Xii HDHW Vsa &VS 2023Document6 pagesElectrostatics Xii HDHW Vsa &VS 2023mishra.sanskar12345No ratings yet
- Circular Coil DerivationDocument1 pageCircular Coil DerivationClaudiu Anton VitanNo ratings yet
- A Proof of The Jordan Curve Theorem: Received 5 February, 1979Document5 pagesA Proof of The Jordan Curve Theorem: Received 5 February, 1979Vijayssc SivaNo ratings yet
- Bracket-Problem PpsDocument9 pagesBracket-Problem PpsLovely NegreNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Electrostatic ProblemsDocument16 pagesSolutions of Electrostatic ProblemsMochamad Rizal JauhariNo ratings yet
- Feuille de Calcul .Shape Control of Cables Under Vertical Static Loads - Example de CalculDocument9 pagesFeuille de Calcul .Shape Control of Cables Under Vertical Static Loads - Example de CalculStefan SorinNo ratings yet
- B 2 Ps 3Document4 pagesB 2 Ps 3Sifei ZhangNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 SolnDocument35 pagesChap 5 SolnPawanKumar BarnwalNo ratings yet
- 정역학 13판 11장Document63 pages정역학 13판 11장leejingpNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Ncert ch02 Electrostatic Potentia and Capacitance Part 1 QuesDocument35 pages12 Physics Ncert ch02 Electrostatic Potentia and Capacitance Part 1 QuesManish PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Eemf 1Document1 pageEemf 1rupesh1000No ratings yet
- Two-Dimensional Airfoils: 1 DefinitionsDocument5 pagesTwo-Dimensional Airfoils: 1 DefinitionsKing MassNo ratings yet
- Stokes TheoremDocument2 pagesStokes TheoremNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Current ElectricityDocument21 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Current ElectricityK_S_Krishna0001No ratings yet
- 4 Jacob Lewis Bourjaily: Q D W DDocument2 pages4 Jacob Lewis Bourjaily: Q D W DNori FuentesNo ratings yet
- The Theorems of Green, Stokes, and GaussDocument112 pagesThe Theorems of Green, Stokes, and Gaussabha singhNo ratings yet
- Universidad de Cartagena Departamento de Física: ε fills half of the space betweenDocument2 pagesUniversidad de Cartagena Departamento de Física: ε fills half of the space betweenKeiila ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Bending Stress in Beams: Basic AssumptionsDocument9 pagesBending Stress in Beams: Basic AssumptionspidotnasirNo ratings yet
- Conductors and Electrical Screening: ConductorDocument1 pageConductors and Electrical Screening: ConductorEddieNo ratings yet
- Electromotive Force: A Guide For The PerplexedDocument11 pagesElectromotive Force: A Guide For The PerplexedSivakumar SarmaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential: Q Located atDocument21 pagesElectrostatic Potential: Q Located atDeepa Mary SobhaNo ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument29 pagesVector CalculusRohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: Physics 15bDocument10 pagesElectromagnetism: Physics 15bnalliminiNo ratings yet
- Let Use ThisDocument1 pageLet Use ThisFanlipto GusnandaNo ratings yet
- E DL and We Have A Conducting Path, So We May ActuallyDocument1 pageE DL and We Have A Conducting Path, So We May ActuallyHanif Caesar RachmadNo ratings yet
- V. A. Kotel'nikov, "On The Transmission Capacity of The "Ether" and Wire in Electrocommunications", Izd. Red. Upr. Svyazi RKKA, Moscow, 1933Document19 pagesV. A. Kotel'nikov, "On The Transmission Capacity of The "Ether" and Wire in Electrocommunications", Izd. Red. Upr. Svyazi RKKA, Moscow, 1933Javier Lozada RojasNo ratings yet
- H2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsDocument19 pagesH2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsonnoezNo ratings yet
- Important Questions of Class Xii Physics Ist BookDocument45 pagesImportant Questions of Class Xii Physics Ist BookTEJAS JAINNo ratings yet
- Permittivity of AirDocument6 pagesPermittivity of AirOthmane CharmatNo ratings yet
- Levine1970 Article GeneralizedClosedSetsInTopologDocument8 pagesLevine1970 Article GeneralizedClosedSetsInTopologAlfonso David Rios SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper 25 Ques of Charges and Fields, Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument18 pagesExam Paper 25 Ques of Charges and Fields, Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDeviNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Capacities, Charging and Discharging of CapacitorsDocument15 pagesMeasurement of Capacities, Charging and Discharging of CapacitorsLeila CheropNo ratings yet
- 41948179-Strength-of-Materials (Repaired)Document86 pages41948179-Strength-of-Materials (Repaired)Josh HabanNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Field Of A Sheet Of Charge: Adding the effects of all the strips; dy' ρDocument5 pages2.5 Field Of A Sheet Of Charge: Adding the effects of all the strips; dy' ρgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- 01maxwells Equations5Document5 pages01maxwells Equations5gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of ChargesDocument7 pagesMaxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of Chargesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Electromagnetics 1 PDFDocument4 pagesElectromagnetics 1 PDFgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of ChargesDocument3 pagesMaxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of Chargesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Differential Operators: A A A A X y ZDocument3 pagesDifferential Operators: A A A A X y Zgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Displacement Current & Maxwell's EquationsDocument4 pagesDisplacement Current & Maxwell's Equationsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic Fields and UnitsDocument3 pagesElectric and Magnetic Fields and Unitsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell - Equations 2Document6 pagesMaxwell - Equations 2gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Engine Sealing, Gaskets, and Fastener Torque: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument5 pagesEngine Sealing, Gaskets, and Fastener Torque: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learninggthulasi787126No ratings yet
- The Following Theorem Says That The Only Vector Fields That Are Independent of Path Are ConservativeDocument4 pagesThe Following Theorem Says That The Only Vector Fields That Are Independent of Path Are Conservativegthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell - Equations 1Document5 pagesMaxwell - Equations 1gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Choose Any Point (X, Y) in The Disk With X X.: Conservative Vector FieldDocument4 pagesChoose Any Point (X, Y) in The Disk With X X.: Conservative Vector Fieldgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- As Is Independent of Path, It Does Not Matter Which Path C From (A, B) To (X, Y) Is Used To Evaluate F (X, Y)Document5 pagesAs Is Independent of Path, It Does Not Matter Which Path C From (A, B) To (X, Y) Is Used To Evaluate F (X, Y)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Lithium Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013Document5 pagesLithium Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- We Assume That D Is Open - Which Means That, For Every Point P in D, There Is A Disk With Center P That Lies Entirely in DDocument4 pagesWe Assume That D Is Open - Which Means That, For Every Point P in D, There Is A Disk With Center P That Lies Entirely in Dgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Most Computer Algebra Systems (CAS) Have Commands That Compute The Curl and Divergence of Vector FieldsDocument5 pagesMost Computer Algebra Systems (CAS) Have Commands That Compute The Curl and Divergence of Vector Fieldsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Notice The Similarity To What We Know From Section 12.4:: A X A 0 For Every Three-Dimensional (3-D)Document5 pagesNotice The Similarity To What We Know From Section 12.4:: A X A 0 For Every Three-Dimensional (3-D)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- F I J K: X y Z P Q R R Q P R Q P y Z Z X X yDocument6 pagesF I J K: X y Z P Q R R Q P R Q P y Z Z X X ygthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Nickel Metal Hydride (Nimh) Batteries: H) 2 / 1 (Oh E 2 MM O HDocument3 pagesNickel Metal Hydride (Nimh) Batteries: H) 2 / 1 (Oh E 2 MM O Hgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Nickel Cadmium (Nicd) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013Document5 pagesNickel Cadmium (Nicd) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Sodium Sulphur (Nas) BatteriesDocument4 pagesSodium Sulphur (Nas) Batteriesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument6 pagesVector Calculusgthulasi787126No ratings yet
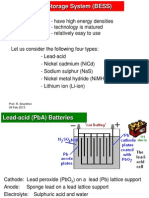
- Lead-Acid (Pba) Batteries: DrawbacksDocument5 pagesLead-Acid (Pba) Batteries: Drawbacksgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Energy Storage 5Document5 pagesEnergy Storage 5gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Battery Electric Storage System (BESS) : - Have High Energy Densities - Technology Is Matured - Relatively Easy To UseDocument6 pagesBattery Electric Storage System (BESS) : - Have High Energy Densities - Technology Is Matured - Relatively Easy To Usegthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Energy Storage 2Document4 pagesEnergy Storage 2gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy Storage (FES)Document6 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage (FES)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Mechanical Energy Storage-1Document4 pagesMechanical Energy Storage-1gthulasi787126No ratings yet