Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 1: D D D D
Uploaded by
atenhyunaeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 1: D D D D
Uploaded by
atenhyunaeCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 1
Objective
To study the characteristics of a silicon (Si) diode and a germanium
(Ge) diode.
Equipment
Variable DC power supply
2 Digital Multi meters (DMM)
Project board
Silicon diode (D1N4002)
Germanium diode (D1N4148)
1k Resistor
Procedure
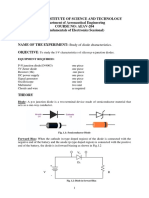
Part A: Forward-bias Diode Characteristics
The circuit shown below is constructed as follows using a Si diode.
The diode voltage is set to VD = 0 V by varying the DC supply voltage
and the diode current ID is measured and recorded in Table 1.1.
Then the diode voltage VD = 0.1 V is also set by varying the DC
supply voltage. The corresponding diode current I D is measured and
recorded in Table 1.1.
Step 3 is repeated for the remaining settings of V D shown in Table 1.1.
Si diode is replaced by a Ge diode and Table 1.2 is completed
afterwards.
ID versus VD characteristic curves are plotted on a graph paper for
both silicon and germanium diodes.
Part B: Reverse-bias Diode Characteristics
The circuit shown below is constructed as follows using a Si diode.
The diode voltage is set to VD = 0 V by varying the DC supply voltage
and the diode current ID is measured and recorded in Table 1.3.
Then the diode voltage VD = -5 V is also set by varying the DC supply
voltage. The corresponding diode current I D is measured and recorded
in Table 1.3.
Step 3 is repeated for the remaining settings of V D shown in Table 1.3.
Si diode is replaced by a Ge diode and Table 1.4 is completed
afterwards.
ID versus VD characteristic curves are plotted on a graph paper for
both silicon and germanium diodes.
You might also like
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Exp No2 ChekDocument3 pagesExp No2 ChekFahim UsmanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Elce221 Lab 1Document6 pagesElce221 Lab 1Little VoiceNo ratings yet
- Silicon Diode VI CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesSilicon Diode VI CharacteristicsM. Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument3 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering Departmentrahul.23eez0004No ratings yet
- ElectronicsLab - Manual March2010Document64 pagesElectronicsLab - Manual March2010pnarendrareddy.mscNo ratings yet
- Project 1 I V Curve of A DiodeDocument6 pagesProject 1 I V Curve of A DiodeBắc LêNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Diodes and Theirs ApplicationsDocument9 pagesSemiconductor Diodes and Theirs Applicationsamerican dxb memesNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Diode Characteristics: ObjectiveDocument8 pagesExperiment 1 Diode Characteristics: Objectivebirla_sNo ratings yet
- Exp 45Document11 pagesExp 45tanmay sonawaneNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 For B.electronicDocument11 pagesExperiment 3 For B.electronicUmmu Umar Wa AisyahNo ratings yet
- LAB1 - Adib EqalDocument15 pagesLAB1 - Adib EqalAdib BakhtiarNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Engineering Honours Degree in Telecommunications EngineeringDocument9 pagesBachelor of Engineering Honours Degree in Telecommunications EngineeringBRIGHT TZZZY CHINGWENANo ratings yet
- Exp - 1 - PN JUNCTION ZENER DiodeDocument13 pagesExp - 1 - PN JUNCTION ZENER DiodekishorebabNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronic Lab (MCE3013) : Experiment 1: Diode CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesAnalogue Electronic Lab (MCE3013) : Experiment 1: Diode CharacteristicsAmirul InNo ratings yet
- Diode Characteristics ExperimentDocument12 pagesDiode Characteristics ExperimentAirell Francis de VeraNo ratings yet
- Osmania University BE 2/4 Electronic Devices Lab ManualDocument88 pagesOsmania University BE 2/4 Electronic Devices Lab ManualAbdulShehzadNo ratings yet
- Lab DiodDocument5 pagesLab DiodidasyarmilaNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 2Document13 pagesLab Activity 2Kyle GuarinNo ratings yet
- 19ECE281: Electronics Circuits Lab: ObjectiveDocument7 pages19ECE281: Electronics Circuits Lab: ObjectiveMadhav SNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 2Document12 pagesLab Activity 2Jayvee Honorio0% (1)
- Diode Lab: Study Normal and Zener CharacteristicsDocument17 pagesDiode Lab: Study Normal and Zener CharacteristicsAnjan SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Study_of_Diode_CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesStudy_of_Diode_CharacteristicsBhavyaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2: Objective: Study of Characteristics of Silicon DiodeDocument5 pagesExperiment No.2: Objective: Study of Characteristics of Silicon DiodeUday BhartiyaNo ratings yet
- Exp#1 Diode Characteristics V2Document12 pagesExp#1 Diode Characteristics V2Shehda ZahdaNo ratings yet
- EEE206 Device Lab ManualDocument117 pagesEEE206 Device Lab ManualGiaa RahmanNo ratings yet
- A51c146 29c4 11ed b197 02b17be2b734 - 20220910132547Document4 pagesA51c146 29c4 11ed b197 02b17be2b734 - 20220910132547narayanas1807No ratings yet
- DJM2032 - Electronic SystemDocument19 pagesDJM2032 - Electronic SystemphyrdowsNo ratings yet
- 5.semiconductor Diodes 2014Document10 pages5.semiconductor Diodes 2014Bogdan ZenecanNo ratings yet
- EE Lab Manuls Fast NuDocument88 pagesEE Lab Manuls Fast NuMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Eng NaderDocument8 pagesExperiment 1 Eng Naderياسر العويطيNo ratings yet
- Ece 425. Labreport 2 LeynesDocument8 pagesEce 425. Labreport 2 LeynesRaymond LomerioNo ratings yet
- ClaireDocument15 pagesClaireClaireNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Diode CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesExperiment 1 Diode CharacteristicsAnas AzamNo ratings yet
- ECE 202 - Exp 1Document4 pagesECE 202 - Exp 1Nusrat FatemaNo ratings yet
- Device Exp 1 Student ManualDocument4 pagesDevice Exp 1 Student Manualgg ezNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits EE 359-Lecture 2: Prof. Uf Tureli Dept. of ECE Stevens Institute of TechnologyDocument32 pagesElectronic Circuits EE 359-Lecture 2: Prof. Uf Tureli Dept. of ECE Stevens Institute of Technologysakthi099No ratings yet
- DiodeDocument32 pagesDiodeVijay Kumar100% (2)
- Expt 3 - Diode CharaDocument5 pagesExpt 3 - Diode Charaokay gNo ratings yet
- Electronic 1st 7 8Document22 pagesElectronic 1st 7 8mohsindalvi87No ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document4 pagesExperiment 2tarekabdelhalimsedik555No ratings yet
- 6V to 12V Converter Circuit AnalysisDocument8 pages6V to 12V Converter Circuit AnalysisPruthvi C mNo ratings yet
- Small and Large Signal Diodes CircuitsDocument5 pagesSmall and Large Signal Diodes CircuitsKhalid Abedrabo100% (1)
- ID AND NAME OF THE STUDENT: 3420987 - Katia Santiago Del Rio 2. TOPIC AND NUMBER OF THE LAB: V-I Characteristics of A SemiconductorDocument4 pagesID AND NAME OF THE STUDENT: 3420987 - Katia Santiago Del Rio 2. TOPIC AND NUMBER OF THE LAB: V-I Characteristics of A SemiconductorKati SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Diode ExperimentDocument4 pagesDiode ExperimentShubham GoelNo ratings yet
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 2 - Diode CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 2 - Diode Characteristicsdonatello84100% (3)
- ECE 2201 - Measure diode V-I characteristics & explore signal clippingDocument8 pagesECE 2201 - Measure diode V-I characteristics & explore signal clippingAreeba MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Eee 111 Lab Manual 2-8 (Latest)Document32 pagesEee 111 Lab Manual 2-8 (Latest)Ismot Jahan MoniNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits-Manual - August 2018Document92 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits-Manual - August 2018Qasim LodhiNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering EE363: Power ElectronicsDocument11 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering EE363: Power ElectronicsTalha RiazNo ratings yet
- Diode CircuitDocument4 pagesDiode CircuitJane Arleth Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Part1 ElectronicsDocument48 pagesPart1 ElectronicsRalph NakadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-QB-Semicond Diodes& ApplicsDocument3 pagesChapter 1-QB-Semicond Diodes& ApplicsRamyaNo ratings yet
- Name: Etuk, Jesse Imoh Matric No: 18CJ024119 Program: Computer Engineering Course: GEC 226 Engineering Lab. Date: 19 July, 2020Document5 pagesName: Etuk, Jesse Imoh Matric No: 18CJ024119 Program: Computer Engineering Course: GEC 226 Engineering Lab. Date: 19 July, 2020David OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Exp 01Document6 pagesExp 01Captain Jack SparrowNo ratings yet
- Diod RectifierDocument35 pagesDiod RectifierRizalNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument20 pagesReportMy SunNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document8 pagesExperiment 1Qusai BakerNo ratings yet
- Diodes: Diode VI CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesDiodes: Diode VI CharacteristicsJoel Pou FeblesNo ratings yet
- 180 HybridDocument10 pages180 HybridatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- 481 Lecture 6Document15 pages481 Lecture 6KuldeepMalikNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument1 pageReferencesatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- 481 Lecture 5Document9 pages481 Lecture 5KuldeepMalikNo ratings yet
- DSB CDocument3 pagesDSB CatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- Discussion Lab PROJECTDocument1 pageDiscussion Lab PROJECTatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- Islamic Worldview Ungs 2030Document275 pagesIslamic Worldview Ungs 2030deen94No ratings yet
- In The Islamic WorldviewDocument5 pagesIn The Islamic WorldviewatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document80 pagesChapter 2atenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- Homework4 SolutionDocument5 pagesHomework4 SolutionatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- Is Islamic Law Shariah or FiqhDocument4 pagesIs Islamic Law Shariah or FiqhatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- Interpolation - Introduction: NTH n+1Document51 pagesInterpolation - Introduction: NTH n+1atenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: International Islamic University MalaysiaDocument5 pagesCourse Outline: International Islamic University MalaysiaatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- AnovaDocument21 pagesAnovaatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- Discussion AnovaDocument2 pagesDiscussion AnovaatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 5 Vectors in Plane and Space S1 2015-2016Document22 pagesLECTURE 5 Vectors in Plane and Space S1 2015-2016atenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- No 2Document35 pagesNo 2atenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 3 F This ShitDocument3 pagesEXPERIMENT 3 F This ShitatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- Vertical Milling Machine OperationsDocument13 pagesVertical Milling Machine OperationsSalman ShaxShax HeissNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Z Z Z ZDocument2 pagesExperiment 2: Z Z Z ZatenhyunaeNo ratings yet
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesFrom EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Fundamentals of Hydrogen Production and Utilization in Fuel Cell SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Hydrogen Production and Utilization in Fuel Cell SystemsNo ratings yet
- RV Living Collection: RV living for beginners, RV travel for the whole family, RV repair and RV mobile solar power: Experience Freedom on the roads alone or with your family with this collection. Learn how to repair your motorhome while using renewable energy!From EverandRV Living Collection: RV living for beginners, RV travel for the whole family, RV repair and RV mobile solar power: Experience Freedom on the roads alone or with your family with this collection. Learn how to repair your motorhome while using renewable energy!No ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsFrom EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsNo ratings yet
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentFrom EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Renewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandRenewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationFrom EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Grid-Scale Energy Storage Systems and ApplicationsFrom EverandGrid-Scale Energy Storage Systems and ApplicationsFu-Bao WuNo ratings yet
- Industrial Waste Treatment HandbookFrom EverandIndustrial Waste Treatment HandbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Boy Who Harnessed the Wind: Creating Currents of Electricity and HopeFrom EverandThe Boy Who Harnessed the Wind: Creating Currents of Electricity and HopeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (130)
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- DIY Free Home Energy Solutions: How to Design and Build Your own Domestic Free Energy SolutionFrom EverandDIY Free Home Energy Solutions: How to Design and Build Your own Domestic Free Energy SolutionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successFrom EverandThe New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Global Landscape of Renewable Energy FinanceFrom EverandGlobal Landscape of Renewable Energy FinanceNo ratings yet
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridFrom EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Power Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesFrom EverandPower Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Biogas Production: Pretreatment Methods in Anaerobic DigestionFrom EverandBiogas Production: Pretreatment Methods in Anaerobic DigestionNo ratings yet
- ISO 50001: A strategic guide to establishing an energy management systemFrom EverandISO 50001: A strategic guide to establishing an energy management systemNo ratings yet