Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hal 5
Hal 5
Uploaded by
kartikaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hal 5
Hal 5
Uploaded by
kartikaCopyright:
Available Formats
M- Yadav et al. / Awlied Catalysis A: dffieral425-426 {2012) 11/r.
1 16
114
+l
rtt
()
b
4*
s
ti
rar
Jri
X,r'lr:sc
la
art
2t 3S 4U 5t 5C' 70
i*t,9'o)
8C
26/ degree
Fig.2. Theeffectofxyloseconcentrationontheconversionofxyloseandtheselectivity ta xylitol.
Fig.4. )(q! profile ofNiO ishown for reference peaks) (a). Tio2 {b), {}Jio-Tiaz) (c).
Ru (1.o%)/NiO {5.0%j-TiO2 (fiesh sample) (d), and Ru {1.0%llNi0 (5.C%)-TiO2 (after
hydrog:nationj
(e,l-
ir4
1(1f\9^ O,n {rrrther
n.1r+r1n
incro:<inctha{amnar:(rrre
{n tLA
t-Eqmffiffihough
the corlversion af xylose rached 1002;,
the sel-ettiviry to xylitol decreased since it is known that higher
the temperatilre, ihe mcre promiflent is formation cf by-products
--,,\ l.r/o.)l Iz / I,
----.-_-P4cY4tr
ULIICI Uy-[AUuuLL5
IdldUlillLUl tU,J/o, dltd
3.4. Characteristic properties of the catalyst
48
$
The X-ray
9*
t8s
12{}
lerlrpsl[turel
Frg.
3.
135
15$
L,
The effect of temperature on the corlveIsion of xylose and the selectivity to
xylitol.
The efiect of temperature on hydragenation ofxylose was studied by varying the reaction temperature from 10Oto 140 "C and the
results are showfi irt Fig. 3 where hoth conversion and the selectivity values are plotted against reactaon temperature. lt is seen fuom
the figure that the xylose conversion
'rnm
tha
fiorrra
fhrf
rr6sr
!
!rrq!
fhp
Lrrr
n
v
very close to 120'c as both
and selectiviE/ values
Fig-
5.
diffraction patterns ofneat NiO (a); given as for refer-
ence, neat Ti02 {b), modified NiO-TiO2 (c), catalyst Rul(NiO-TiO2)
{d) and catalyst Ru (1.0%)lNiO !,5.O%}-TiAz (after hydrogenation){e)
:rp chr.,*,n i* Eis -4 !i ic c.+n trnm thlc fra,,ro ther tha YPfl nr-nfrlec
of TiO2 suppnrt (b: red colour) and NiO modified TiOz supForr (c;
blue colour) have ohirious
riifferences. The presence ol charactert,to{
'
igirs NiC pe4ks (iffilofiIe.i *t.,ict.,
+) .o/. . tJ dtlu /J illulLdLE 5ulttsstul tlluulll(dilull ul llur 5uu+
pqrt r*,ithlli.kel .hlq!ide. In additiorr, the ltRD proEles of NiCt-TiO2
{c, blue color) and its catalyst of Ru (d, green color} look alike. The
metallic Ru in the catalyst could not be detected as Ru loadings iess
than 5.O% are aiways covereti by NiO modifieci IiO2 support making
it diificult to rieteimine [28 j. The xRD profile of liesh catalyst sample i.e, before hydrogenation Ru/(NiO-TiO2) (d: green color) and
nflicr hydiogcnation (e: pinl< color) unambiguously de.1po_rtsfiat s_ rhar rhe caratysr is absolutety stauteaurtri$ilarog"nal8,t F&tlt1$,fa'
Fig. 5 presents TEM irnages ofthe catalysts Ru (1.0%)/TiO2 and
lRu {1.O%)lNiO {5.0%)-TiO2l. The dark portion of the image (Fig.5a)
TEM images ofthe catalysts Ru {1.o%)ftioz (a) and Ru (1-0%)/NiO (5-0%)-TiO, (b}.
apa-
?-rffi-oLl7:,
You might also like
- Roz Marra Ki Masnoon DuainDocument34 pagesRoz Marra Ki Masnoon DuainaamirNo ratings yet
- 9th Urdu Barkat AliDocument2 pages9th Urdu Barkat Alimoxamil khanNo ratings yet
- Stats Test 2 - 20230529 - 0001Document8 pagesStats Test 2 - 20230529 - 0001Ronald McdonaldNo ratings yet
- Assistant ProfessorDocument13 pagesAssistant ProfessorDasapan GopiNo ratings yet
- Physics 2013 UndergraduateDocument9 pagesPhysics 2013 UndergraduatepatriciaNo ratings yet
- 8Document2 pages8muhanadNo ratings yet
- Analisis de RodiozonatoDocument13 pagesAnalisis de RodiozonatoDonaldo HerreraNo ratings yet
- Electrician Question Paper 2016Document12 pagesElectrician Question Paper 2016PADMAKUMAR KUNJUMONNo ratings yet
- 4 PZ Ilr TR Hhru / (,: / (C:a .X (ZX 4lDocument11 pages4 PZ Ilr TR Hhru / (,: / (C:a .X (ZX 4l72屆林振華No ratings yet
- 2009 Sem 2 - CA1 & 2Document8 pages2009 Sem 2 - CA1 & 2Khim YangNo ratings yet
- D2 JPN 2012Document18 pagesD2 JPN 2012Valdi FirstiantoNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of TiCl4 - Initial Steps in The Production of TiO2Document10 pagesHydrolysis of TiCl4 - Initial Steps in The Production of TiO2Cuong Ky NguyenNo ratings yet
- Gujarati NEETDocument45 pagesGujarati NEETrock2903No ratings yet
- AcountDocument28 pagesAcountaamna3082No ratings yet
- Turchi1990 PDFDocument15 pagesTurchi1990 PDFJorge VecinoNo ratings yet
- I T) 4oyat Tzrt":A7-/ Tt. Ro, R-"R" ('-I-.: (6) + E, F Tll.. ( ( (8) Z, I-T - ,: ( ( Ft,,T1L.Document4 pagesI T) 4oyat Tzrt":A7-/ Tt. Ro, R-"R" ('-I-.: (6) + E, F Tll.. ( ( (8) Z, I-T - ,: ( ( Ft,,T1L.Refadul islamNo ratings yet
- G J E S R: Lobal Ournal of Ngineering Cience and EsearchesDocument15 pagesG J E S R: Lobal Ournal of Ngineering Cience and EsearchesYousif Husain AzeezNo ratings yet
- 'stz0tt: G) 6rulDocument12 pages'stz0tt: G) 6rulubyisismayilNo ratings yet
- .S!E Ighii: 35T2076 'Eit - R. C.Lis !. E Pil (C) C@ T, TTW! Iurygm (C) Oiln4 A. LRD M.4Ui4Tt (O 6. @ue DD DDDocument12 pages.S!E Ighii: 35T2076 'Eit - R. C.Lis !. E Pil (C) C@ T, TTW! Iurygm (C) Oiln4 A. LRD M.4Ui4Tt (O 6. @ue DD DDbijukumargNo ratings yet
- RAC Mechanical EngineeringDocument15 pagesRAC Mechanical EngineeringGiridhar BasavarajNo ratings yet
- Calculus Formulas PDFDocument11 pagesCalculus Formulas PDFKyleAntonSenoAlignoNo ratings yet
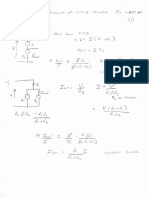
- Problems of Laplace Transform (Cont.)Document8 pagesProblems of Laplace Transform (Cont.)Nguyễn Doãn KhảiNo ratings yet
- S1 Phy 2013Document9 pagesS1 Phy 2013Daniel MontillaNo ratings yet
- J 66 Seriesvalves JDocument21 pagesJ 66 Seriesvalves JTrần Duy TânNo ratings yet
- EMT Bolum 3 UygulamaDocument14 pagesEMT Bolum 3 Uygulamagamer girlNo ratings yet
- Unit Load BeamDocument6 pagesUnit Load BeamKEVIN NATHANAELNo ratings yet
- Scan 24-Apr-2021 C10Document3 pagesScan 24-Apr-2021 C10asishNo ratings yet
- Departm T of Textile Industries, National Taipei Institute of Twhnology, Taipei, Taiwan (Received 18 April 1994 Aceqted 3 June 1994)Document10 pagesDepartm T of Textile Industries, National Taipei Institute of Twhnology, Taipei, Taiwan (Received 18 April 1994 Aceqted 3 June 1994)Manthan JainNo ratings yet
- The Synthesis and Structural Properties of (M (Dippe) (G - C H S) ) Complexes of PD and PT and Comparison With Their Ni AnalogDocument8 pagesThe Synthesis and Structural Properties of (M (Dippe) (G - C H S) ) Complexes of PD and PT and Comparison With Their Ni AnalogHưng LucaNo ratings yet
- S1 CHM 2012Document7 pagesS1 CHM 2012Daniel MontillaNo ratings yet
- Islamic Studies 2018Document65 pagesIslamic Studies 2018Asad Ali KhokharNo ratings yet
- Application FormDocument1 pageApplication Formmertra246No ratings yet
- Lampiran PraktikumDocument3 pagesLampiran PraktikumAhmad Fahmi IrfandaNo ratings yet
- سكشن ٢ تحكمDocument3 pagesسكشن ٢ تحكمHossam kunNo ratings yet
- Free Time Around The WorldDocument26 pagesFree Time Around The WorldFleur Une MyosotisNo ratings yet
- Tffi#"li Ffi Ff66i Uil,'ll$tq Ry .'!$FT G: (' "6o U,,oftt:k (."1hDocument7 pagesTffi#"li Ffi Ff66i Uil,'ll$tq Ry .'!$FT G: (' "6o U,,oftt:k (."1hAlice TamNo ratings yet
- Lot Lot of Ni, of R Lot LRT of NLR T U. R !u To Li To: of of of of Pallty of of Itne LtneDocument1 pageLot Lot of Ni, of R Lot LRT of NLR T U. R !u To Li To: of of of of Pallty of of Itne LtneGeorgeMarcusNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0925838823006862 mmc1Document25 pages1 s2.0 S0925838823006862 mmc1J MrNo ratings yet
- Doctor's ReportsDocument13 pagesDoctor's ReportsIHN ITNo ratings yet
- EXP101 DataSheet B1 Grp6Document2 pagesEXP101 DataSheet B1 Grp6Elijah FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Trocedue: Mogk Practical TestDocument2 pagesTrocedue: Mogk Practical Testscientia est potentiaNo ratings yet
- Calculated Lamellar Binding I. Van Der Waals Bonding in Talc and PyrophylliteDocument6 pagesCalculated Lamellar Binding I. Van Der Waals Bonding in Talc and Pyrophyllite7kkqg42m6cNo ratings yet
- Al-Mu'Jam Al-Kabir Tabarani Jild 3Document784 pagesAl-Mu'Jam Al-Kabir Tabarani Jild 3Sarfraz HussainNo ratings yet
- JLPT Shiken Mondai To Seikai 4 KyuuDocument35 pagesJLPT Shiken Mondai To Seikai 4 KyuuMd Najmul IslamNo ratings yet
- DT Fi D..peitd (O Di - Lo! T.: (B) @) Hin - LM.RDocument12 pagesDT Fi D..peitd (O Di - Lo! T.: (B) @) Hin - LM.RbijukumargNo ratings yet
- Cmic See SolnDocument35 pagesCmic See SolnDerek scottNo ratings yet
- 10.1016/j.catcom.2016.01.023: Catalysis CommunicationsDocument18 pages10.1016/j.catcom.2016.01.023: Catalysis Communicationsmanuel lozanoNo ratings yet
- Metals: Tantalum and Niobium Selective Extraction by Alkyl-AcetophenoneDocument11 pagesMetals: Tantalum and Niobium Selective Extraction by Alkyl-AcetophenoneDai Nguyen100% (1)
- 6 Compressor Air System Units & Components PDFDocument336 pages6 Compressor Air System Units & Components PDFAgus KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 2 Nvfs 2 Yui 4844 Ok 4 CoDocument104 pages2 Nvfs 2 Yui 4844 Ok 4 CowaqasNo ratings yet
- Niobium IV QUI Pub v2Document28 pagesNiobium IV QUI Pub v2KATIA VANESSA BERRIO HENAONo ratings yet
- NENYNlBrZzlQc2c0ZC0hX2pLZE1DRHpnPT0 PDFDocument2 pagesNENYNlBrZzlQc2c0ZC0hX2pLZE1DRHpnPT0 PDFShourjyo biswasNo ratings yet
- 2223 - X TAV Resistor 1 Arus CabangDocument1 page2223 - X TAV Resistor 1 Arus Cabangkiryusetsuna112No ratings yet
- Moza - Tugas MTK - 18-10-2021Document7 pagesMoza - Tugas MTK - 18-10-2021dewiandreanNo ratings yet
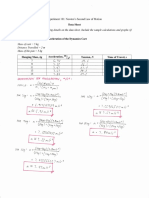
- Fourier Transform TableDocument1 pageFourier Transform TableSansaniNo ratings yet
- The Periodictable 17Document4 pagesThe Periodictable 17Gregorio ValllejoNo ratings yet
- Maths 04: 'F Exânen Finâlde Probâbilités Er Sratisriqùer'IiDocument9 pagesMaths 04: 'F Exânen Finâlde Probâbilités Er Sratisriqùer'Iilydiiia bNo ratings yet
- Journal of Molecular Structure: M. Bakavoli, F. Moeinpour, A. Davoodnia, A. MorsaliDocument6 pagesJournal of Molecular Structure: M. Bakavoli, F. Moeinpour, A. Davoodnia, A. Morsaliمحمد بلحوتNo ratings yet
- Copper and ZincDocument6 pagesCopper and ZincWilson LiangNo ratings yet