Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Electromechanical Relays: Principal Design
3 Electromechanical Relays: Principal Design
Uploaded by
igorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Electromechanical Relays: Principal Design
3 Electromechanical Relays: Principal Design
Uploaded by
igorCopyright:
Available Formats
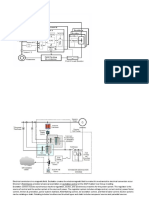
3 ELECTROMECHANICAL RELAYS
fig 3.1
Principal design
POWER RELAYS
3.1 Design
The basic design of electromechanical power relays is the same regardless of whether it is a
miniature PCB relay or an industrial power relay. The most important components are:
Contact system or secondary side
fixed contacts
moving contacts (contacts being moved
by the magnetic system (motor) to
switch the load circuit)
contact springs (holding the contacts
but sufficiently flexible to allow the
contacts to move)
Magnetic system
coil (to generate the necessary
magnetic field to actuate the armature
and the contacts)
core
yoke (to establish the magnetic circuit)
armature (the moving part of the
fig 3.2
magnetic system which closes and
opens the magnetic circuit and acts via a comb or actuator on the moving relay contacts)
return spring (to establish a defined position of the magnetic and contact system in case
the coil is not energized)
Contact/Magnetic System
Mechanical components
case
base (to protect the relay against external influences and for protection against electric
shock)
insulation (within the relay to separate the primary circuit from the secondary side and to
provide the required insulation)
actuator (used in some relay designs to translate the motion of the magnetic system to the
contact system (moving contacts). Must have insulation properties to isolate the primary
circuit (coil, magnetic circuit) from the secondary side (contact system))
pins or terminals (to connect between the contact system and the load)
mounting devices
10
ELECTROMECHANICAL RELAYS
3.2 Subsystems
Relay Subsystems
Contact
System
Magnetic
System
Mechanical
Components
S904
fig 3.3
Relay Subsystems
11
You might also like
- Magnetic Micro RelayDocument4 pagesMagnetic Micro RelayAdarsh Patil100% (1)
- Fire Code 2013 PDFDocument1,033 pagesFire Code 2013 PDFKo PaukNo ratings yet
- Electrical TheoryDocument154 pagesElectrical Theorypatriot4229100% (2)
- Electrical Drive 2015 RegularDocument64 pagesElectrical Drive 2015 Regularkabtamu mamoNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection (Control System) : Protective RelaysDocument29 pagesPower System Protection (Control System) : Protective RelaysBagirath SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- #All About RelayDocument10 pages#All About RelayRitika JainNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Relays and Their Working Principles: A Relay Is A Switching DeviceDocument17 pagesDifferent Types of Relays and Their Working Principles: A Relay Is A Switching DeviceVIPIN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Tribhuvan UniversityDocument14 pagesTribhuvan UniversitySudhakar ShresthaNo ratings yet
- E I (EC 323) : Lectrical NstallationsDocument38 pagesE I (EC 323) : Lectrical NstallationsMalith DeemanthaNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint - Introduction To Protection Relay - RevBDocument44 pagesPowerPoint - Introduction To Protection Relay - RevBGopinath SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Industrial AutomationDocument38 pagesIndustrial Automationvineet ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Bee053 P&S NotesDocument60 pagesBee053 P&S NotesADDIS JOHNNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3wqfr3qvDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 3wqfr3qvKosigar ChelladoraiNo ratings yet
- Documento Sin TítuloDocument2 pagesDocumento Sin TítuloPablo García GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Appliance ProtectorDocument40 pagesThree Phase Appliance ProtectorJeevan PreethuNo ratings yet
- Isolation 62109Document11 pagesIsolation 62109Shahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Various Elements of The Power SystemDocument15 pagesVarious Elements of The Power Systemrohit kumar tiwariNo ratings yet
- Classification of Electrical Wiring DiagramsDocument8 pagesClassification of Electrical Wiring DiagramsSrinivasan RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document22 pagesLecture 2Abdul-halim HafidhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document29 pagesLecture 3Abdul-halim HafidhNo ratings yet
- Isolation in Solar Power Converters: Understanding The IEC62109-1 Safety StandardDocument11 pagesIsolation in Solar Power Converters: Understanding The IEC62109-1 Safety StandardIvan Adair Prado JiménezNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Switch Mechanism For Circuit BreakersDocument6 pagesMagnetic Switch Mechanism For Circuit BreakersAndi KaNo ratings yet
- ExcitationDocument12 pagesExcitationDdumbaNo ratings yet
- Tap ChangerDocument6 pagesTap ChangermshahidshaukatNo ratings yet
- 21bme8037 D S S R Venkat ProjectDocument24 pages21bme8037 D S S R Venkat Projectvenkat deeviNo ratings yet
- Excitation SystemsDocument15 pagesExcitation SystemsSahiti DarikaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Solar Tracking SystemDocument82 pagesAutomatic Solar Tracking SystemDebashishParidaNo ratings yet
- Charging System NotesDocument5 pagesCharging System Notesmoyocarnage409No ratings yet
- LopDocument4 pagesLopD SNo ratings yet
- Relay: Fig 6.1: Automotive-Style Miniature Relay, Dust Cover Is Taken OffDocument12 pagesRelay: Fig 6.1: Automotive-Style Miniature Relay, Dust Cover Is Taken OffmichealNo ratings yet
- Section: CSC 2 BSMAR-E: Name: Calunangan, Ollin Fel EDocument3 pagesSection: CSC 2 BSMAR-E: Name: Calunangan, Ollin Fel EJerry PinongpongNo ratings yet
- Undip Analisa Ganguan Hubung Singkat Transmisi 150 KVDocument19 pagesUndip Analisa Ganguan Hubung Singkat Transmisi 150 KVTatang FestiyawanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mechatronics SystemsDocument13 pagesAdvanced Mechatronics Systemssaleem razaNo ratings yet
- Numerical RelayDocument19 pagesNumerical RelayRajesh Naik Dharavath100% (1)
- DC Motor: Motors Motor Motors Motors Motors MotorDocument6 pagesDC Motor: Motors Motor Motors Motors Motors MotorAvd KishoreNo ratings yet
- Motor Current Signal AnalysisDocument13 pagesMotor Current Signal Analysissureshnfcl100% (1)
- ContactorDocument21 pagesContactorNaty SeyoumNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromechanical Assembly in Printed Circuit Board AssemblyDocument14 pagesWhat Is Electromechanical Assembly in Printed Circuit Board AssemblyjackNo ratings yet
- Elements DescriptionDocument16 pagesElements DescriptionNARENDER SINGHNo ratings yet
- LG 4-Install Wiring System Using Rigid Steel Metalic ConduitDocument28 pagesLG 4-Install Wiring System Using Rigid Steel Metalic ConduitSol GamesNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection (EE-523) Lecture-01: Samiya Zafar Assistant Professor, EED NEDUET M.Engg Fall Semester 2017Document47 pagesPower System Protection (EE-523) Lecture-01: Samiya Zafar Assistant Professor, EED NEDUET M.Engg Fall Semester 2017JaleesNo ratings yet
- Electrical System: Systems OperationDocument9 pagesElectrical System: Systems OperationMbahdiro KolenxNo ratings yet
- Contactors and Motor StartersDocument5 pagesContactors and Motor StartersZdan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Excitation System: Neelum Jehlum Hydro Power CompanyDocument12 pagesExcitation System: Neelum Jehlum Hydro Power CompanyAmeer Hamza100% (1)
- Lec 1Document43 pagesLec 117b-012-peNo ratings yet
- Tatva Institute of Technological Studies, Modasa Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument33 pagesTatva Institute of Technological Studies, Modasa Department of Electrical EngineeringTirgar VipulNo ratings yet
- Switchgear NTCCDocument21 pagesSwitchgear NTCCHoney Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- EEE309 Lecture 1 and 2 NotesDocument17 pagesEEE309 Lecture 1 and 2 NotesDivine MekongNo ratings yet
- 9 Final-Bhu PDFDocument8 pages9 Final-Bhu PDFGuru MishraNo ratings yet
- Relay Technologies (2) - 2 PDFDocument34 pagesRelay Technologies (2) - 2 PDFItumeleng Tumi LamolaNo ratings yet
- ProfPathakProblems - Modeling of Transformer Internal FaultsDocument6 pagesProfPathakProblems - Modeling of Transformer Internal Faultslbk50No ratings yet
- Lecture 18 System StabilityDocument33 pagesLecture 18 System StabilityTEMIDAYONo ratings yet
- Circuit BreakersDocument14 pagesCircuit BreakersrichierichNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Analysis of The Synchronous Generators Excitation SystemsDocument7 pagesModeling and Analysis of The Synchronous Generators Excitation Systemsni60No ratings yet
- JURNAL2 - Fachrul Rozi Ramadhan - 201971039 - B - B1Document12 pagesJURNAL2 - Fachrul Rozi Ramadhan - 201971039 - B - B1Fachrul rozi ramadhanNo ratings yet
- Control System of The Wiredrawing Machine1Document8 pagesControl System of The Wiredrawing Machine1Vadim CazacNo ratings yet
- HVDC - Pat 2 - AnswwersDocument27 pagesHVDC - Pat 2 - AnswwersFundayyy moviesNo ratings yet
- Actuator Principles and ClassificationDocument2 pagesActuator Principles and ClassificationrkNo ratings yet
- Relay ESDDocument5 pagesRelay ESDAditi JadhavNo ratings yet
- Natural Mode of Synchronous Operation. It Implies ThatDocument20 pagesNatural Mode of Synchronous Operation. It Implies ThatTana AzeezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Solid State Relays and The Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Solid State Relays and The Advantages and DisadvantagesKen Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Uploads Product Rishmaster EM3490 1PH Manual PDFDocument2 pagesUploads Product Rishmaster EM3490 1PH Manual PDFKo PaukNo ratings yet
- Ventilation FundamentalsDocument24 pagesVentilation FundamentalsSomnath SenNo ratings yet
- How To Size A Room Air Conditioner PDFDocument3 pagesHow To Size A Room Air Conditioner PDFKo PaukNo ratings yet