Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shapes of Molecules
Shapes of Molecules
Uploaded by
api-2968338590 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesThe shape of a molecule depends on the number of bonding pairs, lone pairs, and orbital overlap, with lone pair-lone pair repulsion greatest and bonding pair-bonding pair repulsion least. Bonds can be sigma bonds from overlapping s and p orbitals end-on, or pi bonds from overlapping p orbitals sideways. Single bonds have one sigma bond, double bonds have one sigma and one pi bond, and triple bonds have one sigma and two pi bonds. Metallic bonding involves ions packed in a lattice with delocalized electrons forming a sea, attracted to the ions via powerful forces related to ion charge. Intermolecular forces also hold molecules together apart from intramolecular covalent bonds.
Original Description:
Original Title
shapes of molecules
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe shape of a molecule depends on the number of bonding pairs, lone pairs, and orbital overlap, with lone pair-lone pair repulsion greatest and bonding pair-bonding pair repulsion least. Bonds can be sigma bonds from overlapping s and p orbitals end-on, or pi bonds from overlapping p orbitals sideways. Single bonds have one sigma bond, double bonds have one sigma and one pi bond, and triple bonds have one sigma and two pi bonds. Metallic bonding involves ions packed in a lattice with delocalized electrons forming a sea, attracted to the ions via powerful forces related to ion charge. Intermolecular forces also hold molecules together apart from intramolecular covalent bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesShapes of Molecules
Shapes of Molecules
Uploaded by
api-296833859The shape of a molecule depends on the number of bonding pairs, lone pairs, and orbital overlap, with lone pair-lone pair repulsion greatest and bonding pair-bonding pair repulsion least. Bonds can be sigma bonds from overlapping s and p orbitals end-on, or pi bonds from overlapping p orbitals sideways. Single bonds have one sigma bond, double bonds have one sigma and one pi bond, and triple bonds have one sigma and two pi bonds. Metallic bonding involves ions packed in a lattice with delocalized electrons forming a sea, attracted to the ions via powerful forces related to ion charge. Intermolecular forces also hold molecules together apart from intramolecular covalent bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
The shape depends on:
- Number of bonding pairs
- Number of lone pairs
- Repulsion: lone pair-lone pair> lone pair-bonding pair> bonding pairbonding pair
In a covalent bond, atomic orbitals overlap forming a molecular orbital.
There are 2 types of shapes that these bonds can have:
1) Sigma bonds: take place when 2 S orbitals, 2 P orbitals or 1 S and 1
P orbital overlap end-on.
2)Pi bonds: take place only when 2 P orbitals overlap sideways.
Single bonds have a sigma bond.
Double bonds have 1 sigma and 1 pi bond.
Triple bonds have 1 sigma and 2 pi bonds.
- In metallic bonding, metallic ions are packed in a lattice and the
electrons from their outer shells form a sea of electrons.
- Between the ions in the lattice and the delocalized electrons, there
are powerful attraction forces.
- The bigger the charge on the ion, the greater the attraction.
- Apart from the covalent bonding inside molecules, there are
intermolecular forces holding them together.
You might also like
- Chem 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesChem 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingKuo SarongNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Vs Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding Vs Metallic BondingsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- There Are Only Two Known Species ofDocument7 pagesThere Are Only Two Known Species ofmuhammad aslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2mehrunnisaqaisar111No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chapter # 04Document2 pagesChemical Bonding: Chapter # 04AimanNo ratings yet
- W) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXDocument10 pagesW) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXSav OliNo ratings yet
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNo ratings yet
- Notes On Bonding IDocument38 pagesNotes On Bonding IEdem DumashieNo ratings yet
- Notes On Bonding IDocument38 pagesNotes On Bonding INika ReleniNo ratings yet
- Theory Notes On Chemical Bonding-IVDocument2 pagesTheory Notes On Chemical Bonding-IVRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument122 pagesChemical BondingSergioNo ratings yet
- Hemical Onding: Saman Kotigala BSC MSCDocument24 pagesHemical Onding: Saman Kotigala BSC MSCSaman Bharatha Kotigala100% (1)
- Lo5 1) Chemical BondsDocument9 pagesLo5 1) Chemical BondsabdogamreNo ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument3 pagesForces of AttractionMoya-Dean WalcottNo ratings yet
- Hndout IntroDocument3 pagesHndout IntroMarxlen EndicoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding-04 PDFDocument2 pagesChemical Bonding-04 PDFTushar GaurNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Webquest Background EssayDocument1 pageChemical Bonding Webquest Background Essayapi-303294518No ratings yet
- Enc Encoded ex7XDZYZXOqmbH1FNJmXNKobRl vzOD3CVnwfk7ZNedEJAZXdKoLTMWdDocument49 pagesEnc Encoded ex7XDZYZXOqmbH1FNJmXNKobRl vzOD3CVnwfk7ZNedEJAZXdKoLTMWdSri VanyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument14 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument14 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- First Topic - Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesFirst Topic - Chemical BondingSymonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding1Document35 pagesChemical Bonding1drchewieNo ratings yet
- 000valence Bond TheroyDocument26 pages000valence Bond TheroyTincy mol ckNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document37 pagesChemical Bonding 1palal123No ratings yet
- Ch3 Inch 2101Document80 pagesCh3 Inch 2101liyou eshetuNo ratings yet
- Article (Bonding&Structure)Document3 pagesArticle (Bonding&Structure)Fawzan Fahad MDNo ratings yet
- Liquids and SolidsDocument107 pagesLiquids and SolidsMorgan BowersNo ratings yet
- Bonds in SolidsDocument729 pagesBonds in Solids1553No ratings yet
- Presented By:: Section: A Group No.: 4Document56 pagesPresented By:: Section: A Group No.: 4Bela GhummanNo ratings yet
- Bonding Question AnswersDocument23 pagesBonding Question Answersgyogi1989No ratings yet
- Topic 1.3 Bonding Types of Bond States of Matter Structure and Physical Properties Molecular Shapes Intermolecular ForcesDocument31 pagesTopic 1.3 Bonding Types of Bond States of Matter Structure and Physical Properties Molecular Shapes Intermolecular Forcesfunkykid80No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding LectureDocument7 pagesChemical Bonding LectureSymonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: - Ionic Bonds - Covalent Bonds - Hydrogen Bonds - Metallic BondsDocument112 pagesChemical Bonding: - Ionic Bonds - Covalent Bonds - Hydrogen Bonds - Metallic BondsgokulNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding NotesShaswat PattnayakNo ratings yet
- Review of IB Chem Topics 4 and 14Document10 pagesReview of IB Chem Topics 4 and 14coolpianocatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond and Its TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond and Its TypesKhan NiaziNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Properties of Elements in The Periodic Table The Key Atomic PropertiesDocument8 pagesAn Overview of The Properties of Elements in The Periodic Table The Key Atomic PropertiesMichelle MalabananNo ratings yet
- Sigma and Pi BondingDocument23 pagesSigma and Pi BondingBerlian SitorusNo ratings yet
- Ib PPT 4 SL PDFDocument103 pagesIb PPT 4 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 1105Document51 pagesChemical Bond 1105Abid HasanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document37 pagesChemical Bonding 1Yara GhebariNo ratings yet
- 1.3. BondingDocument10 pages1.3. BondingdodoNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary BondingDocument6 pagesPrimary and Secondary BondingosmondNo ratings yet
- Tanya Touch Assignment #3Document2 pagesTanya Touch Assignment #3TanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document37 pagesChemical Bonding 1ARTICA CASTILLO Fatima ValentinaNo ratings yet
- Unit - I: Molecular Structure and Theories of BondingDocument13 pagesUnit - I: Molecular Structure and Theories of BondingAthirath VeldandaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument0 pagesChemical BondingAnudeex ShettyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Final PDFDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding - Final PDFKundan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument11 pagesChemical BondingDebasish BagNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesChemical Bondingpream.s1323No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (1) AS1C6Document29 pagesChemical Bonding (1) AS1C6tzeina578No ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Definition: Solid State ChemistryDocument9 pagesBonding in Solids Definition: Solid State Chemistryhaimanot yibeltalNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Bonding 4.1to 4.5 14.1to 14.2Document156 pagesTopic 4 Bonding 4.1to 4.5 14.1to 14.2SujithNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Mysterious World of Fundamental Particles: Cosmic BeginningsFrom EverandThe Mysterious World of Fundamental Particles: Cosmic BeginningsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Inbreeding Interbreeding Outbreeding Inbreeding DepressionDocument1 pageInbreeding Interbreeding Outbreeding Inbreeding Depressionapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Selective AdvantagesDocument2 pagesSelective Advantagesapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Background Genes Progeny TestingDocument1 pageBackground Genes Progeny Testingapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Negative Effects of Growing Herbicide Resistant Crops IncludeDocument3 pagesNegative Effects of Growing Herbicide Resistant Crops Includeapi-296833859No ratings yet
- The Founder Effect: Genetic DriftDocument1 pageThe Founder Effect: Genetic Driftapi-296833859No ratings yet
- PhotolysisDocument1 pagePhotolysisapi-296833859No ratings yet
- TranscriptoneDocument2 pagesTranscriptoneapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Photorespiration: Bundle Sheath CellsDocument1 pagePhotorespiration: Bundle Sheath Cellsapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Coevolution Fitness Natural Selection: Discontinuous VariationDocument2 pagesCoevolution Fitness Natural Selection: Discontinuous Variationapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Selective Advantage Natural Selection Selection Pressure: Speciation SpeciesDocument2 pagesSelective Advantage Natural Selection Selection Pressure: Speciation Speciesapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Absorbance Spectrum Action SpectrumDocument2 pagesAbsorbance Spectrum Action Spectrumapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Selection PressuresDocument1 pageSelection Pressuresapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Photophosphorylation:: PhotoactivationDocument1 pagePhotophosphorylation:: Photoactivationapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Cytoplasm: GlycolysisDocument4 pagesCytoplasm: Glycolysisapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Limiting FactorDocument2 pagesLimiting Factorapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Energy DensityDocument1 pageEnergy Densityapi-296833859No ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument2 pagesAntibioticsapi-296833859No ratings yet
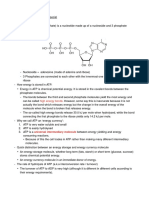
- High Energy Bonds: Universal Intermediary MoleculeDocument2 pagesHigh Energy Bonds: Universal Intermediary Moleculeapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration (In The: CytoplasmDocument1 pageAnaerobic Respiration (In The: Cytoplasmapi-296833859No ratings yet
- GahhDocument1 pageGahhapi-296833859No ratings yet
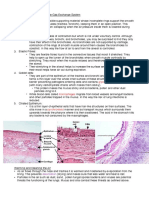
- Gas Exchange: One (1.8 CM) Yes Yes Yes Yes No YesDocument2 pagesGas Exchange: One (1.8 CM) Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yesapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Overcrowded Substandard Housing Low ImmunityDocument2 pagesOvercrowded Substandard Housing Low Immunityapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Passive Smoking: CarcinogensDocument3 pagesPassive Smoking: Carcinogensapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Organic Molecule Respiration Potential Energy Chemical Potential EnergyDocument1 pageOrganic Molecule Respiration Potential Energy Chemical Potential Energyapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle: PacemakerDocument3 pagesCardiac Cycle: Pacemakerapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Cardiac Muscle: MyogenicDocument2 pagesCardiac Muscle: Myogenicapi-296833859No ratings yet
- CholeraDocument1 pageCholeraapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Glycoproteins Called Mucin: DesiccationDocument2 pagesGlycoproteins Called Mucin: Desiccationapi-296833859No ratings yet