Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics II Crib
Uploaded by
AbuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics II Crib
Uploaded by
AbuCopyright:
Available Formats
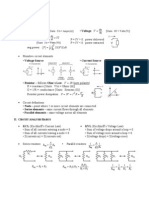
PHYSICS II Electricity and Magnetism, Thermodynamics
Coulombs Law
Dipoles
Electric Flux
(on axis)
to
(Gausss Law)
Potential Energy
when
surface
when to
surface
( plane)
Charge Densities
(
(
Electric Field
r from Point
( )
r from Line
Electric Potential (Voltage)
Capacitors
Plane
(independent of r)
Hoop with radius a,
distance x along axis
Disk with radius R ,
distance x along axis
(Uniform E Field)
-
+
+
+
+
Vhigh
Vlow
(V is constant along
equipotential lines)
)
(
Spherical Conductor
L
Spherical Insulator
Inside
(Charge stored in parallel
capacitors)
Constants
Outside a (Filled)
Cylinder
z
b
a
Kinematics
E inside conductor is 0.
PHYSICS II Electricity and Magnetism, Thermodynamics
B Fields Due to Wire
B Field from Moving Charge
Faradays Law
(Direction from right hand rule)
Ohms Law
Magnetic Force
Right Hand Rules
B Field From Loop of Wire
Biot-Savart Law
(at center)
(
)
(along axis)
| |
Resistors
Capacitors
Amperes Law
EM Waves
(Total Current Enclosed by Loop)
(Poynting VectorEnergy Transfer in
Direction of Travel)
, turns per length
Cyclotron
RC Circuits
Kirchoffs Laws
Power
(
Constants
Induced EMF
Solenoid
Polarization
(Natural Light when Polarized)
PHYSICS II Electricity and Magnetism, Thermodynamics
Specific Heat
Ideal Gas Law
Unit Conversions
TK = TC + 273.15
TF = TC 1.8 + 32
Cv = Molar Specific Heat at constant
volume
Cp = Cv + R = Molar Specific Heat at
constant pressure
1 L = 0.001 m3 = 1000 cm3
1 atm = 101.325 kPa
( )
BASIC GAS PROCESSES
Process:
Definition:
Stays Constant:
Isochoric
V and p/T
Isobaric
p and V/T
Isothermal
T and pV
Work:
Heat:
( )
Adiabatic
All gas processes
First law
Ideal-gas law
Heat Engine
Refrigerator
Specific Heats of Common Gases
Gas
Cp
CV
He
20.8
12.5
1.67
Ne
20.8
12.5
1.67
Ar
20.8
12.5
1.67
H2
28.7
20.4
1.4
N2
29.1
20.8
1.4
O2
29.2
20.9
1.4
You might also like
- Iintroduction & Overview of Electrode Processes (Ch. 1)Document48 pagesIintroduction & Overview of Electrode Processes (Ch. 1)GIRMA SELALE GELETANo ratings yet
- 4-Electrochemical Kinetics of CorrosionDocument84 pages4-Electrochemical Kinetics of Corrosion이선엽No ratings yet
- Current Electricity Part 01Document120 pagesCurrent Electricity Part 01Vishal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Multiphase Arc Plasma For Material ProcessingDocument49 pagesModeling and Simulation of Multiphase Arc Plasma For Material ProcessingbaruaeeeNo ratings yet
- AI 12 ElectrochemistryDocument23 pagesAI 12 ElectrochemistryLintangNurAnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 25Document14 pagesLecture 25iggyNo ratings yet
- AtomicHandWrittenNotes BulutayDocument222 pagesAtomicHandWrittenNotes BulutaySwashy Yadav50% (2)
- Resistive Plate Chambers For Experiments at India Based Neutrino ObservatoryDocument42 pagesResistive Plate Chambers For Experiments at India Based Neutrino Observatoryvarunk8275No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringDocument46 pagesFundamentals of Electrical EngineeringRaza SikandarNo ratings yet
- Circuit AnalysisDocument15 pagesCircuit AnalysisoffnruninNo ratings yet
- ECEN460 2017 Lect1Document39 pagesECEN460 2017 Lect1hurNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Lec01 1Document63 pagesLec01 1awabnasirahmednasirNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Transducers: The Thermal Energy DomainDocument25 pagesSensors and Transducers: The Thermal Energy Domainpajarillo0No ratings yet
- Mj2411 Renewable Energy Technology - 1Document27 pagesMj2411 Renewable Energy Technology - 1Kazim RazaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Midterm Exam Phy-113-01 Spring 2024Document9 pagesStudy Guide Midterm Exam Phy-113-01 Spring 2024fhhdghgjfggNo ratings yet
- PDO Course 2Document67 pagesPDO Course 21MM1R HL'No ratings yet
- Hydronamic MethodDocument20 pagesHydronamic MethodSeho SunNo ratings yet
- Ee 213Document22 pagesEe 213ALLADO, ALBERT JR. G.No ratings yet
- Time Dependent Currents in RC CircuitsDocument20 pagesTime Dependent Currents in RC Circuitsmurali_j17No ratings yet
- An-Najah University: Electrical Circuits LabDocument7 pagesAn-Najah University: Electrical Circuits LabAdel AtawiNo ratings yet
- HighVoltageEngineering PDFDocument46 pagesHighVoltageEngineering PDFBruno LopesNo ratings yet
- CHEG320 Electrochemistry LecturesDocument114 pagesCHEG320 Electrochemistry LecturesqalanisNo ratings yet
- Plasma Discharge FundamentalsDocument74 pagesPlasma Discharge Fundamentalsgamarino48No ratings yet
- Disorder and Magnetic Field Tuned Insulating State in A-Ino Superconducting FilmsDocument54 pagesDisorder and Magnetic Field Tuned Insulating State in A-Ino Superconducting FilmsMaoz OvadiaNo ratings yet
- SKF3013 Physical Chemistry I: Prof. Dr. Ramli Ibrahim Dr. Norlaili Abu BakarDocument24 pagesSKF3013 Physical Chemistry I: Prof. Dr. Ramli Ibrahim Dr. Norlaili Abu BakarAisha NajihaNo ratings yet
- CAPE U2 LAB#2 Azariah BarrettDocument6 pagesCAPE U2 LAB#2 Azariah BarrettazaribarrNo ratings yet
- HT1 Solution Home Mid ExamDocument4 pagesHT1 Solution Home Mid ExambodeNo ratings yet
- ET4117 Electrical Machines and Drives Lecture2 PDFDocument36 pagesET4117 Electrical Machines and Drives Lecture2 PDFAnonymous AMjDOJ0lNo ratings yet
- Things To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Document20 pagesThings To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Arif SolmazNo ratings yet
- Personal Formula Sheets Phy JeeDocument2 pagesPersonal Formula Sheets Phy JeeA human BeingNo ratings yet
- 6 Vacuum GaugesDocument89 pages6 Vacuum Gaugesapi-3856548100% (1)
- w14d2 Class 35Document72 pagesw14d2 Class 35eviroyerNo ratings yet
- Assignment TheoryDocument11 pagesAssignment TheoryChomfwix VlogsNo ratings yet
- Physics 1220/1320: Electromagnetism - Part One: ElectrostaticsDocument70 pagesPhysics 1220/1320: Electromagnetism - Part One: ElectrostaticsbeckerinskiNo ratings yet
- Phys 122 Equation Sheet Exam 3Document3 pagesPhys 122 Equation Sheet Exam 3zxc100311No ratings yet
- Summary of The Rad CourseDocument132 pagesSummary of The Rad CourseYonatan6248No ratings yet
- Cheg320 Electrochemistry LecturesDocument114 pagesCheg320 Electrochemistry Lecturesapi-259261742100% (1)
- PN Junction Diode Characteristics - FinalDocument6 pagesPN Junction Diode Characteristics - FinalHARSH AGNIHOTRINo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory-ECE305 - Chapter5 Current and ConductorsDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic Theory-ECE305 - Chapter5 Current and ConductorsabdullahNo ratings yet
- EIS BoukampDocument97 pagesEIS BoukampMiraldaNo ratings yet
- Summary w05d1Document2 pagesSummary w05d1hamrobeknurullayev21No ratings yet
- Lecture #1 Introduc - On To Electrochemistry: Kaori SugiharaDocument47 pagesLecture #1 Introduc - On To Electrochemistry: Kaori SugiharaLoga NathanNo ratings yet
- FE Exam Review2011Document53 pagesFE Exam Review2011Juan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Leccion - 07 - Revision - Conceptos - Transmisión de Calor123Document46 pagesLeccion - 07 - Revision - Conceptos - Transmisión de Calor123miriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 KDocument19 pagesLecture 13 KKalyani ChandpurkarNo ratings yet
- Ch.1 DC CircuitsDocument40 pagesCh.1 DC Circuitsaattish100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document41 pagesChapter 4Anil ParmarNo ratings yet
- Hot-Wire Anemometry - With Mathematical ExpresionDocument63 pagesHot-Wire Anemometry - With Mathematical ExpresionKannan RamarajNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electronics and Breadboard CircuitsDocument83 pagesIntroduction To Electronics and Breadboard CircuitsMadhavDhruvNo ratings yet
- Diodes, Triodes, Thermistors, Opto-Isolators, & PhototransistorsDocument46 pagesDiodes, Triodes, Thermistors, Opto-Isolators, & PhototransistorsZorila AlexandruNo ratings yet
- 3 - Electric CircuitsDocument35 pages3 - Electric CircuitsKARTHIK S SNo ratings yet
- Physics U1&2 Sep 2023 VF TsepDocument57 pagesPhysics U1&2 Sep 2023 VF TsepkitsuniesNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Advances in Magnetohydrodynamics: Proceedings of a Colloquium Organized by the Department of Fuel Technology and Chemical Engineering at Sheffield University, October 1961From EverandAdvances in Magnetohydrodynamics: Proceedings of a Colloquium Organized by the Department of Fuel Technology and Chemical Engineering at Sheffield University, October 1961I. A. McGrathNo ratings yet
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsFrom EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNo ratings yet
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonFrom EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IFrom EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields INo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Systems Technology Assignment 10 (Multiple Choice Questions)Document2 pagesManufacturing Systems Technology Assignment 10 (Multiple Choice Questions)NareshJagathkarNo ratings yet
- Bearings 13 PDFDocument48 pagesBearings 13 PDFNareshJagathkarNo ratings yet
- The Kashmir Crisi1Document5 pagesThe Kashmir Crisi1NareshJagathkarNo ratings yet
- 115dx Disaster Management - TextmarkDocument8 pages115dx Disaster Management - TextmarkNareshJagathkarNo ratings yet
- (Donald A.neamen) Semiconductor Physics and Devices Basic Principles (3rd Ed)Document566 pages(Donald A.neamen) Semiconductor Physics and Devices Basic Principles (3rd Ed)NareshJagathkar91% (11)
- Welcome TO APCPDCL PDFDocument1 pageWelcome TO APCPDCL PDFNareshJagathkarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Aerospace Engineering Soler 2014 PDFDocument404 pagesFundamentals Aerospace Engineering Soler 2014 PDFAnousack KittilathNo ratings yet
- 8180CBSE Sample Paper 1 For Session 2015 PDFDocument4 pages8180CBSE Sample Paper 1 For Session 2015 PDFNareshJagathkarNo ratings yet
- AriHant MATHEMATICSDocument15 pagesAriHant MATHEMATICSNareshJagathkar100% (1)
- Chemistry Project On Foaming Capacity of Soaps PDFDocument7 pagesChemistry Project On Foaming Capacity of Soaps PDFNareshJagathkar0% (2)