Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Steps To Selecting The Right Accelerometer
Steps To Selecting The Right Accelerometer
Uploaded by
Bogdan NeagoeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Steps To Selecting The Right Accelerometer
Steps To Selecting The Right Accelerometer
Uploaded by
Bogdan NeagoeCopyright:
Available Formats
Steps to selecting the right accelerometer
TP 327
Steps to selecting the right accelerometer
At first look, an accelerometer manufacturers catalog or web
site can be intimidating to both the novice and often the more
experienced user. Accelerometers are offered in a variety of
technologies, shapes, sizes, ranges, etc.
This article will provide a trail that the user can follow that will
lead to the optimum accelerometer for the application.
Technology selection
narrow bandwidth and outstanding temperature stability.
The first step in the selection process is to determine the
These devices are highly desirable for measuring low
type of measurement to be made. The measurement type
frequency vibration, motion and steady state acceleration.
will be the first step in the technology selection. There
are three widely used technologies used for acceleration
Type of measurement
measurements.
In this section, the basic measurement types will be
described and then, later in this article, more detail will
Piezoelectric (PE) accelerometers are the most widely used
be provided. For the purposes of this article, acceleration
accelerometers for test and measurement applications.
measurements will be divided into the following categories:
These devices offer a very wide measurement frequency
range (a few Hz to 30 kHz) and are available in a wide
Vibration: An object is said to vibrate when it executes an
range of sensitivities, weights, sizes and shapes. These
oscillatory motion about a position of equilibrium. Vibration
accelerometers should be considered for both shock and
is found in the transportation and aerospace environments
vibration measurements. PE accelerometers are available
or as simulated by a shaker system.
with a charge or voltage (IEPE) output, discussed later in
this article.
Shock: A sudden transient excitation of a structure that
generally excites the structures resonances.
Piezoresistive (PR) accelerometers generally have low
sensitivity making them desirable for shock
Motion: For the purpose of this article, motion is a slow
measurements. They are also used extensively in
moving event such as the movement of a robotic arm or an
transportation crash tests. Because of the low sensitivity,
automotive suspension measurement.
they are being used less for vibration measurements. PR
accelerometers generally have a wide bandwidth and the
Seismic: This is more of a motion or a low frequency
frequency response goes down to zero Hz (often called
vibration. This measurement usually requires a specialized
DC responding) or steady state, so they can measure
low noisehigh resolution accelerometer.
long duration transients.
Once the measurement type is determined, the reader can
Variable capacitance (VC) is among the newer accelerometer
go directly to the measurement section (in this article) of
technologies. Like PR accelerometers, they are DC
interest, or review the different measurement types.
responding. VC accelerometers have high sensitivities, a
General considerations
IEPE piezoelectric
Prior to going into the technologies and applications, here
In recent years, the IEPE type has become the most
are a few general considerations.
commonly used accelerometer type. IEPE sensors are
often sold under different trade marked names, but all
The frequency response is an important parameter when
virtually comply with a pseudo industry standard and are
considering any accelerometer. This parameter is usually
interchangeable between brand names.
specified within 5% of the reference frequency (usually
100 Hz). Many devices will have the specifications extended
Basically, an IEPE accelerometer is a device with the
to 1 dB and in some cases 3 dB. Most data sheets will
charge amplifier built-into the accelerometer. They require
have a typical frequency response curve to assist the user.
no external charge amplifiers and use ordinary low cost
The frequency range will usually be determined by the test
cable. The accelerometer does require a constant current
specifications or as determined by the user.
power source and many data acquisition systems have
built-in power sources. If the user knows the vibration
Another consideration is the number of axes to be
range and the operating temperature is in the range of
measured. Accelerometers are available in single and
-55C (-67F) to 125C (257F) then an IEPE device should
triaxial (see Figure 1) versions. Another approach to
be considered. Note that high temperature versions are
making a three axis measurement is to mount three
available in some models that have a maximum operating
accelerometers on a triaxial mounting block. Both methods
temperature of 175C (350F).
allow for the measurement of three orthogonal axes
simultaneously.
Charge mode piezoelectric
Charge mode piezoelectric accelerometer advantages
include high temperature operation and an extremely wide
amplitude range. A typical charge mode accelerometer
will have an operating temperature range of -55C to
288C (-67 to 550F). Special purpose accelerometers
are available for extreme environments as low as -269C
(-452F) to as high as 760C (1400F). Special radiation
hardened charge mode accelerometers are available for
use in a nuclear environment.
Figure 1 A miniature triaxial accelerometer that incorporates three
accelerometers in a single package for the measurement of three
orthogonal axes simultaneously.
Unlike the IEPE accelerometer, the charge type
accelerometer requires the use of special low noise cable.
The low noise cable is expensive compared to the standard
Vibration
commercial coaxial cable. A charge amplifier, or an in-line
Piezoelectric accelerometers are the first choice for most
charge converter is also required.
vibration measurements since they have a wide frequency
response, good sensitivity and resolution and are easy
Variable capacitance
to install. There are two subdivisions of piezoelectric
In instances where vibration measurements at very low
accelerometers which include the basic charge-mode
frequencies are required, a variable capacitance (VC)
accelerometer and the voltage mode Internal Electronic
accelerometer is a choice to consider. VC accelerometers
Piezoelectric (IEPE) types.
have a frequency response from 0 Hz to 1 kHz, depending
on the sensitivity required. When making very low
frequency measurements, a VC accelerometer with a
Automotive crash testing is a rather specialized area of
frequency range from 0 Hz to 15 Hz will provide a high
shock testing. Piezoresistive accelerometers are usually
sensitivity of 1 Volt/g. VC accelerometers are useful on
used (see Figure 3).
electro hydraulic shakers, flutter measurements and many
transportation applications.
Figure 3 Automotive crash test accelerometer shown in an industry
standard package.
For far field shock measurements, a special shear mode
Figure 2 Variable capacitance accelerometer shown with a popular
mounting configuration. Models are available with a 10-32 stud mount.
accelerometer with a built-in electronic filter is often
adequate. These are usually lightweight IEPE types with
solder connections. The electronic filter electronically
Shock
attenuates the resonance frequency of the accelerometer
Two technologies are available for shock measurements
to prevent overloading of the data acquisition equipment.
and a variety of accelerometers are available depending on
the levels and final data required. It is important to know
Near field measurements are usually very high levels often
the expected shock level, since this will determine the type
in excess of 20 000 g. Here the choice of accelerometers
of accelerometer to be used. Here is a rough guide to assist
is dependent upon the type of test being conducted.
the reader in choosing the proper accelerometer.
Specialized accelerometers of either piezoelectric (charge
mode and IEPE) or piezoresistive may be appropriate.
Low level
< 500 g
Typically, an IEPE with characteristics similar to the far-
Crash
< 2000 g
field accelerometer is appropriate, but with the addition
Far field
500 g to 1000 g sensor located 2 meters
of an internal mechanical filter. The mechanical filter
from the point of impact
will ensure the survivability of the accelerometer and will
Near field
> 5000 g with the sensor located < 1 meter
generally eliminate zeroshift.
from the point of impact
For low-level shock measurements, a general purpose
accelerometer will generally do the job. The accelerometer
will need a linear range of at least 500 g and a shock
survivability rating of 500 g. An IEPE type is usually
preferred since they are less susceptible to producing
erroneous results from cable motion. The user should
use an amplifier with a low-pass filter to attenuate the
accelerometer resonance.
Figure 4 Example of a near field shock accelerometer with built-in
mechanical filter and rugged -28 mounting stud
A detailed discussion of zeroshift is beyond the scope of
Environment
this article. In general terms, the zeroshift phenomenon
Once the technology has been selected and the test type
appears with the time history not returning to the zero
determined, there are a number of other factors to be
acceleration level following the shock event. This shifting
considered. As a starting point, the environment is to be
results in distortion of data when performing integration. If
considered.
a piezoresistive accelerometer is selected, zeroshift is rare.
The environmental characteristics include temperature,
As is the case with vibration, the frequency response is
maximum acceleration levels and humidity.
an important parameter for shock. In general, a shock
accelerometer should have a wide frequency response
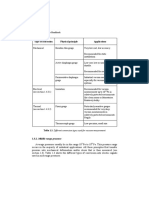
Below is a table, showing typical values to assist with
range (10 kHz is typical), depending on what is being tested.
temperature selection:
Motion, constant acceleration and
low frequency vibration
Technology
Temperature range
Comments
Piezoelectric - general
-55 C to 260C
The range is extended
in some cases
This category is where variable capacitance (VC)
Piezoelectrichigh temperature
-55 C to 650C
Special high temperature
accelerometers
Cryogenic piezoelectric
-184C to 177C
IEPE general types
-55 C to 125C
vibration with a high output level. They also provide a high
IEPE high temperature
-55 C to 175C
degree of stability over a broad temperature range.
Piezoresistive
-55 C to 66C
accelerometers should be considered. This technology
allows for the measurement of low level, low frequency
When a VC accelerometer is placed in a position where
The specified g range is often confusing to the new
the sensitive axis is parallel to the earths gravity, an
accelerometer user since this parameter appears twice
output equal to 1 g will be produced. This phenomenon
in the specifications. The actual usable range, of the
is often referred to as DC responding. Because of this
accelerometer is found in the dynamic specifications. For
characteristic, VC accelerometers are very useful for
example, an IEPE accelerometer might have a Range of
measuring centrifugal force or for the measurement of
500 g, and, under the environmental characteristics the
acceleration and deceleration of devices such as elevators.
device has a shock limit of 1000 g and a shock limit of 2000
g. In the above example, 500 g is the maximum range of
In the realm of vibration testing, VC accelerometers are
linear operation of the accelerometer. The parameters
used in applications where low frequency events are to be
specified in the environmental section are indicative of the
studied and preservation of phase data is important.
maximum survivable shock and/or sine acceleration levels.
VC accelerometers have found their niche in the area of
In the case of charge mode piezoelectric devices, a range
aircraft flutter testing. They are also valuable tools for
is not specified under the dynamic characteristics since
measuring vehicular ride quality.
it is largely determined by the charge amplifier. The user
should refer to the amplitude linearity specifications, in
The low frequency characteristics make VC accelerometers
the dynamic characteristics section of the data sheet. As
ideal for ride quality measurements in automobiles, trucks
above, the maximum range specified in the environmental
and railroad equipment. These are low frequency devices
characteristics section is a maximum survivability figure.
and a wideband frequency response is not a characteristic
of VC devices.
The humidity specification is usually given as Hermetic,
Epoxy seal, or Environmental seal. Most of these seals
will withstand high levels of moisture. If the accelerometer
Mounting
is being used in the space environment, underwater or
There are a number of ways to mount an accelerometer to
very long exposures to excessive humidity, an hermetic
the unit under test (UUT). Methods include everything from
seal is recommended. It should be noted that continuous
permanent mounting to temporary methods. This article
temperature cycling can make an epoxy seal fail.
will discuss the most common mounting methods.
If accelerometers are designed to operate within a nuclear
By far the best mounting method is the use of a
radiation environment, the data sheets will so indicate.
threaded stud, or screw. Stud/screw mounting provides
the best transmissibility at high frequencies since the
Magnetic susceptibility is seldom specified since it is
accelerometer is virtually fused to the mounting surface.
usually not a problem with newer accelerometers. Non-
High frequency response can be enhanced by the
magnetic materials are used in modern accelerometers
application of light oil between the accelerometer and
thus reducing this problem.
UUT. If this method of mounting is desired, accelerometers
should be purchased that are designed for stud and/or
If the accelerometer is going to be mounted on a highly
screw mounting.
flexible surface, the base strain specification becomes
important. A flexile surface tends to bend inducing strain on
Adhesive mounting is often required, especially on small
the accelerometers base. The resulting strain can appear
surfaces and PC boards. A cyanoacrylate is the preferred
as vibration in the accelerometers output.
mounting adhesive since it can be easily removed if the
proper removal techniques are used. The user has a couple
Accelerometer weight
of accelerometer choices for adhesive mounting. Many
When an accelerometer is attached to the test article, the
accelerometers are available that are specifically designed
measured acceleration will be altered. These effects can
for adhesive mounting and this fact will be noted on the
be reduced to an insignificant amount by being mindful of
data sheet. A stud-mount accelerometer may be mounted
the accelerometers weight. As a rule-of-thumb, the weight
using an adhesive, but a cementing stud should be used
of the accelerometer should be no greater than 10% of the
to prevent the adhesive from damaging to the
weight of the test article.
accelerometers threads.
Ground isolation
Accelerometers are available with ground isolation or
with the ground connected to the accelerometers case.
Accelerometers with ground isolation usually have an
isolated mounting base and, where applicable, an isolated
mounting screw, or in some cases the entire accelerometer
case is ground isolated.
Figure 5 Shown on the left is a popular side connector accelerometer
that weighs 7.8 grams and is used on heavy test articles. The unit on
the right is a miniature accelerometer that weighs 0.5 grams that can
be mounted on lightweight structures and PC boards.
Ground isolation becomes important when the test
articles surface is conductive and at ground potential. A
difference in ground voltage levels between the electronic
instrumentation and the accelerometer may cause a
ground loop resulting in erroneous data.
Sensitivity and resolution
Other considerations
An accelerometer is a transduction device that converts
The above information will help the potential user to make
mechanical energy into an electrical signal (the output).
a preliminary decision as to which accelerometers can
The output is expressed in terms of millivolts per g, or in
potentially perform the measurement task. There are
the case of a charge mode accelerometer the output is
other parameters that are equally important that should be
expressed in terms of pC per g. Accelerometers are offered
discussed with potential suppliers. These important items
in a wide range of sensitivities and the optimum sensitivity
may include:
is dependent on the level of the signal to be measured
e.g., in the case of a high g shock test, low sensitivity is
Signal conditioning and powering
desirable.
Transverse sensitivity
Temperature response
In the case of low level signals, it is desirable to use an
Cable types
accelerometer of high sensitivity in order to provide an
output signal well above the amplifiers noise level. For
It is recommended that once the questions in this
example, suppose the expected vibration level is 0.1 g
article have been answered, further discussion with the
and the accelerometer has a sensitivity of 10 mV/g, then
manufacturer is recommended.
the voltage level of the signal would 1 mV, thus a higher
sensitivity accelerometer may be desirable.
In the instance where either a low level signal and/or a
wide dynamic range is required, then the accelerometers
resolution and sensitivity become important.
Resolution is related to the accelerometers minimum
discernable signal. This parameter is based on the noise
floor of the accelerometer (and in the case of an IEPE type,
the internal electronics) expressed in terms of g rms.
TP 327
0809
You might also like
- Vibration TransducerDocument7 pagesVibration TransducerPrakash Kumar100% (1)
- TN16 - Sensor Selection GuideDocument13 pagesTN16 - Sensor Selection GuideAsitha KulasekeraNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Right Accelerometer White Paper PDFDocument6 pagesChoosing The Right Accelerometer White Paper PDFRahulNo ratings yet
- Mkm1133 Instrumentation and Control SystemDocument19 pagesMkm1133 Instrumentation and Control SystemNurul Nadia Mohd ZawawiNo ratings yet
- 3 Axis AccelerometerDocument10 pages3 Axis AccelerometerTechqualcerNo ratings yet
- TurbineSupervisoryGuide PDFDocument28 pagesTurbineSupervisoryGuide PDFCormac MyersNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To AccelerometersDocument3 pagesPractical Guide To AccelerometersShelton Raja100% (1)
- Vibration and Monitoring Terms GlossaryDocument12 pagesVibration and Monitoring Terms Glossaryyaniprasetyo12No ratings yet
- Accelerometer Selection and InstallationDocument16 pagesAccelerometer Selection and InstallationLake HouseNo ratings yet
- REDUCTION of The SKI SLOPE EFFECTDocument8 pagesREDUCTION of The SKI SLOPE EFFECTEnzo MarquesNo ratings yet
- Accelerometer Selection Based On ApplicationsDocument8 pagesAccelerometer Selection Based On Applicationspatilrushal824No ratings yet
- Industrial Sensors PDFDocument11 pagesIndustrial Sensors PDFGrace MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageNo ratings yet
- Vibration Measurement ProceduresDocument8 pagesVibration Measurement ProceduresEclipse Shu100% (1)
- Vibration Measurement Handbook MideDocument14 pagesVibration Measurement Handbook MideJason DrakeNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Accelerometer SelectionDocument3 pagesA Guide To Accelerometer SelectionSathiendran RkNo ratings yet
- NOTES 4 Sensors For Vibration MeasurementDocument77 pagesNOTES 4 Sensors For Vibration MeasurementmanishpaliNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT2 Mech Vibration F2019Document27 pagesASSIGNMENT2 Mech Vibration F2019AbdulrehmanNo ratings yet
- Proper Selection of Accelerometer Sensitivity To Avoid Saturation in Vibration MeasurementsDocument12 pagesProper Selection of Accelerometer Sensitivity To Avoid Saturation in Vibration MeasurementsJHON ANGEL VARGAS HUAHUASONCCONo ratings yet
- How Does A Piezo-Electric Accelerometer Work?Document19 pagesHow Does A Piezo-Electric Accelerometer Work?Sri SaiNo ratings yet
- Sensor Selection Guide: Common Vibration SensorsDocument9 pagesSensor Selection Guide: Common Vibration SensorsMajid TorabiNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Commercial Accelerometers of Different TechnologiesDocument6 pagesPerformance Analysis of Commercial Accelerometers of Different TechnologiesEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- AcceleromtereDocument8 pagesAcceleromtereSV TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Familiarization With and Performance Check Of, Vibration Testing & Measuring EquipmentDocument33 pagesFamiliarization With and Performance Check Of, Vibration Testing & Measuring EquipmentOmar Saleem100% (1)
- Vib - AccelerometerDocument16 pagesVib - AccelerometerMahmoud SobhyNo ratings yet
- Accelerometer TypesDocument12 pagesAccelerometer TypesNitin MaliNo ratings yet
- Describe Different Types of AccelerometersDocument7 pagesDescribe Different Types of AccelerometersRotin PierreNo ratings yet
- Vibrational Sensors For Sensing Energy Through VibrationsDocument21 pagesVibrational Sensors For Sensing Energy Through VibrationsvijayrajanaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Sensors 1 - 2021-22Document55 pagesWeek 7 Sensors 1 - 2021-22KrisNo ratings yet
- Data Acquisition: Detectors: TransducersDocument11 pagesData Acquisition: Detectors: TransducersVasile RaduNo ratings yet
- Vibration Measurement ProceduresDocument8 pagesVibration Measurement ProceduresEclipse ShuNo ratings yet
- Piezoelectric Accelerometers: Lecture-5 Industrial ElectronicsDocument17 pagesPiezoelectric Accelerometers: Lecture-5 Industrial ElectronicsramprabhakarjNo ratings yet
- ACCELEROMETERDocument9 pagesACCELEROMETERDHAMO DHARANNo ratings yet
- Sensor Classification and How To Choose A SensorDocument7 pagesSensor Classification and How To Choose A SensorAkhilesh Reddy KarraNo ratings yet
- Iot For Engineers Ece3501 Digital Assignment-1: L.Anirudh 18bec0559Document28 pagesIot For Engineers Ece3501 Digital Assignment-1: L.Anirudh 18bec0559anirudh lakshminarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Accelerometer:-: Musical InstrumentDocument14 pagesAccelerometer:-: Musical InstrumentJyotirekha PatiNo ratings yet
- SOURCE1Document10 pagesSOURCE1Samy OuazineNo ratings yet
- Dept. Elective V Biomedical Engineering: Physiological TransducerDocument7 pagesDept. Elective V Biomedical Engineering: Physiological TransducerKumar PranayNo ratings yet
- 2 Sensors and TransducersDocument83 pages2 Sensors and TransducersJEYAVEL PALANISAMYNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Transducers OverviewDocument77 pagesSensors and Transducers OverviewVarunNo ratings yet
- SAT-constancia RFC PDFDocument4 pagesSAT-constancia RFC PDFJulio Eme-ErreNo ratings yet
- Sensors For Biomedical Applications - Part 1Document51 pagesSensors For Biomedical Applications - Part 1Sohira QaziNo ratings yet
- NI Tutorial 13654Document6 pagesNI Tutorial 13654Rodrigo SerranoNo ratings yet
- Proximity - Sensor EI 44Document27 pagesProximity - Sensor EI 44Swarndeep KushariNo ratings yet
- AE - Unit-2-Sensorsand ActuatorsDocument125 pagesAE - Unit-2-Sensorsand ActuatorsShitalPatilNo ratings yet
- Taimoor Inayat Assi 3Document10 pagesTaimoor Inayat Assi 3Charsi 1080No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Nondestructive Testing - Advanced Concepts and ApplicationsDocument7 pagesUltrasonic Nondestructive Testing - Advanced Concepts and ApplicationsDhanasekaran RNo ratings yet
- Control & Measuring InstrumentsDocument50 pagesControl & Measuring InstrumentscmcNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge Based AccelerometerDocument13 pagesStrain Gauge Based Accelerometeranandakumarmts0% (1)
- DJM3052 Industrial Electronic (UNIT 5) : SensorDocument22 pagesDJM3052 Industrial Electronic (UNIT 5) : SensorShazryl DanielNo ratings yet
- Sensor PDFDocument8 pagesSensor PDFConstanzaNo ratings yet
- Ty Oskkfud Lajpukvksa Rfkk E'Khuksa Ij Hkwdai Osq Vykok Daiu Vè;;Uksa Osq Fy;S ;A=Kksa Dk Lalfkkiu) Vuqlj.K Vksj Voyksdu Μ Dk;Z LafgrkDocument13 pagesTy Oskkfud Lajpukvksa Rfkk E'Khuksa Ij Hkwdai Osq Vykok Daiu Vè;;Uksa Osq Fy;S ;A=Kksa Dk Lalfkkiu) Vuqlj.K Vksj Voyksdu Μ Dk;Z LafgrkdipNo ratings yet
- MSD Presentation On 5 SensorsDocument25 pagesMSD Presentation On 5 Sensorsmeraj aliNo ratings yet
- Robotic End EffectorDocument38 pagesRobotic End Effector13311A0341 S SHIVA SAI KIRANNo ratings yet
- Accelerometer Application Focus On Seismic Sensors: Home Rental Excitation Electronics Industrial NDTDocument2 pagesAccelerometer Application Focus On Seismic Sensors: Home Rental Excitation Electronics Industrial NDTLake HouseNo ratings yet
- New Sensor Technology For Measuring Torsional Shaft Vibration in Turbine GeneratorsDocument8 pagesNew Sensor Technology For Measuring Torsional Shaft Vibration in Turbine GeneratorssebastianNo ratings yet
- Lec 15Document3 pagesLec 15jkmaroNo ratings yet
- A Low Power Bioimpedance Module For Wearable Systems: SciencedirectDocument4 pagesA Low Power Bioimpedance Module For Wearable Systems: SciencedirectDmitriyNo ratings yet
- MEMS Accelerometers: Testing and Practical Approach For Smart Sensing and Machinery DiagnosticsDocument23 pagesMEMS Accelerometers: Testing and Practical Approach For Smart Sensing and Machinery DiagnosticsRafael Lemanski Dos SantosNo ratings yet