Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NC CNC Conventional
Uploaded by
Abhinav ChaudharyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NC CNC Conventional
Uploaded by
Abhinav ChaudharyCopyright:
Available Formats
Conventional
S K Mondals
NC, CNC Machines
Q1.
What are a manipulator, wrist and end effectors for a robot? Why has the
wire EDM process become so widely accepted in industry?
[IES 2010; 5 Marks]
Ans.
Manipulator: - Manipulator are built as series chains or parallel chains or
occasionally a combination of both. Links and joints (revolute and prismatic) that
are mostly used in manipulators. In spatial manipulators (open chains) adjacent
axes are parallel or perpendicular to each other.
Wrists: - Wrists roll, yaw and pitch. There are 3 motions and 3 actuators are
required for motion.
End effectors: - continuous path motion painting application are an example when
the end effector has to move over a desired curve in space. The robot end effector is
required to reach the centre of circle the target point. The circle on extreme left
shows the situation when the robot has poor accurancy and poor repeatability. The
circle in the middle shows the EE had been repeatedly reaching positions which are
closely together through way from the target point.
Wire EDM :- Electric discharge wire cutting or more commonly called wire EDM is
a process of producing complex two and three dimensional shapes using a simple
wire ending the material from a electrically conducting material, wire EDM is used
for matching sheet metal dies/extrusion dies and proto type part it is relatively a
very slow process (line travels of the order of 100 m/hr 25 mm thick sheet utilizing
computer controlled machines, thats why wire EDM is widely accepted in industry.
Q2.
In FMS define the terms : Automatic Guided Vehicle (AGV) and DNC.
Explain the terms chucking reamers and climb milling. What effect does
the helix angle have on drill performance. Explain the terms combined
cuts and multiple cuts.
[IES 2010; 15 Marks]
Ans.
Automatic guided vehicle (AGV) :- It is mobile robot that follows markers or wire
in the floor or uses vision or lasers. They are most often used in industrial
application to move material around a manufacturing facility or a warehouses. AGV
system lareliable horizontal transportation when spacels at a premium and
flexibility is critical e.g Aerospace, Automotive, clean room.
Direct numerical control (DNC):- It is commonly manufacturing term for
networking CNC machine tool. On some CNC machine controllers the available
memory is too small to contain the machine programmed. So in this case the
programme is stored in separate computer and sent directly to the machine. If the
computer connected to a number of machines it can distribute programme to
different machine required. DNC networking or DNC communication is always
required when CAM programme are run or some CNC machine control.
Helix angle effect:- An increase in the helix angle to more quickly remove chips but
a decrease in helix angle in the interest of greater strength of cutting edges, in the
drilling performance.
Q3.
Expand the following :
(i) ASCII
(ii) BCD
(iii) MDI
(iv) RAM
[IES 2010; 10 Marks]
Conventional
S K Mondals
NC, CNC Machines
(v) ROM
Ans.
ASCII American standard code for information interchange
BCD binary code decimal
MDI multiple document interface
RAM random access memory
ROM read only memory
Q4.
What is the function of manipulator in a robot? Classify robots as per their
path control.
[IES 2008; 2 Marks]
Ans.
The function of manipulator in a robot is to permit relative motion with certain
degree of freedom. Robots are classified on the basis of their path of control as:
(i)
Point to point (PTP): Point to point programming causes the robot to shift from a
programmed point to next programmed point, with a pause between each
movement.
(ii) Continuous path: Continuous path programming causes the robot to move in a
smooth continuous manner along a defined trajectory.
Name the four types of statements in a complete APT part program.
Prepare part program for geometry description of the contour shown in
the figure below:
[IES-2008, 15-Marks]
20
P2
L1
80
20
30
L2
135
L5
L3
40
C2
20
20
C1
P1
L4
Q5.
Ans.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
Four types of statements in complete APT part program are given below.
Motion statement describes the path of cutting tool
Geometry statement- describes configuration of surface
Post Processor Statement-function of particular machine tool
Auxiliary Statement that arentt covered by the above three statements.
Program in APT
PARTNO CONTOUR
MACHIN/MILL, 1
CLPRNT
Conventional
S K Mondals
UNITS/MM
P0 = POINT/0.0, 0.0, 0.0
P1 = POINT/110.0, 20.0, 0.0
P2 = POINT/20.0, 20.0, 0.0
P3 = POINT/90.0, 110.0, 0.0
P4 = POINT/20.0, 100.0, 0.0
P5 = POINT/50.0, 130.0, 0.0
L1 = LINE/P2, ATANGL, 90, XAXIS
L2 = LINE/P4, ANTNGL, 45, XAXIS
L3 = LINE/P5, ATANGL, 135, L2
L4 = LINE/P1, PERPTO, L3
L5 = LINE/P1, PERPTO, L4
C1=CIRCLE/CENTER, P3, RADIUS, 20.0
C2=CIRCLE/CENTER, P1, RADIUS, 20.0
PL1=PLANE/P1, P2, P3
CUTTER/10.0
TOLER/0.1
INTOL/0.005
OUTTOL/0.005
SPINDL/500, CLW
COOLNT/ON
FEDRAT/200
FROM/P0
GO/TO, L1, TO, PL1, TO, L5
GOLFT/L1, PAST, L2
GORGT/L2, PAST, L3
GORGT/L3, PAST, C1
GORGT/C1, PAST, L4
GORGT/L4, PAST, C2
GORGT/C2, PAST, L5
GORGT/L5, PAST, L1
RAPID
GOTO/P0
COOLNT/OFF
SPINDL/OFF
END
FINI
NC, CNC Machines
Conventional
S K Mondals
NC, CNC Machines
Q6.
State any four basic elements of a Robot. Give one line statement for each.
[IES 2007; 2 Marks]
Ans.
The vast majority of todays commercially available robots possess one of the four
basic configurations
(i) Polar configuration
(ii) Cylindrical configuration
(iii) Cartesian coordinate configuration
(iv) Jointed arm configuration
The four basic configurations are illustrated in the schematic diagrams of figure.(i)
(a to d)
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Figure (i) (a): Polar configuration uses a telescopic arm that can be raised or
lowered about a horizontal pivot. The pivot is mounted on a rotating base. These
various joints provide the robot with capacity to move its arm within a spherical
space, and hence its name spherical coordinate robot.
Figure (i) (b): Uses a vertical column and a slide that can be moved up or down
along the column. The robot arm is attached to the slide so that it can be moved
radially with respect to the column. By rotating the column, the robot is capable of
achieving a work space that approximates a cylinder.
Figure (i) (c): Uses three perpendicular slides to contruct the x, y and z-axes. By
moving the three slides relative to one another, the robot is capable of working in a
rectangular work envelope.
Figure (i) (d): Its configuration is similar to that of the human arm. It consists of
two straight components corresponding to the human forearm and upper arm
mounted on a vertical pedestal. These components are connected by two rotary
joints corresponding to the shoulder and elbow. A wrist is attached to the end of the
forearm, thus providing several additional joints.
Q7.
Prepare part using APT language for milling the contour shown in Fig. in
a single pass.
[IES-2007, 20-Marks]
Conventional
S K Mondals
NC, CNC Machines
110
C
B
R30
Q
110
120
E
R40
40
+ 40
100
P
Material : M S.
8 mm
Answer:
PARTNO CONTOUR
MACHIN/MILL, 2
CLPRNT
UNITS/MM
P0 = POINT/0.0, 0.0, 10.0
PTA = POINT/0.0, 0.0, 0.0
PTB = POINT/0.0, 120.0, 0.0
PTC = POINT/30.0, 150.0, 0.0
PTD = POINT/140.0, 150.0, 0.0
PTE = POINT/140.0, 40.0, 0.0
PTF = POINT/100.0, 0.0, 0.0
PTQ = POINT/30.0, 120.0, 0.0
Conventional
S K Mondals
NC, CNC Machines
PTP = POINT/140.0, 0.0, 0.0
LAB = LINE/PTA, PTB
LCD = LINE/PTC, PTD
LDE = LINE/PTD, PTE
LAF = LINE/PTA, PTF
CBC = CIRCLE/CENTRE, PTQ, RADIUS, 30.0
CEF = CIRCLE/CENTRE, PTP, RADIUS, 40.0
PL1=PLANE/PTA, PTB, PTC
CUTTER/10.0
TOLER/0.1
INTOL/0.005
OUTTOL/0.005
SPINDL/500, CLW
COOLNT/ON
FEDRAT/200
FROM/P0
GODOWN/0.0, 0.0, -8.0
GO/TO, LAB, TO, PL1, TO, LAF
GO/TO, LAB, PAST, CBC
GORGT/CBC, PAST, LCD
GORGT/LCD, PAST, LDE
GORGT/LDE, PAST, CEF
GORGT/CEF, PAST, LAF
GORGT/LAF, PAST, LAB
RAPID
GOTO/P0
COOLNT/OFF
SPINDL/OFF
END
FINI
Q8.
Prepare part program to machine the contour shown in the figure using
APT on CNC milling machine.
[IES-2006, 15-Marks]
Conventional
S K Mondals
NC, CNC Machines
R30
R20
100 mm
80
50
60
200 mm
Material: MS
Thickness: 8.0 mm
Answer:
PARTNO CONTOUR
MACHIN/MILL, 3
CLPRNT
UNITS/MM
P0 = POINT/0.0, 0.0, 10.0
P1 = POINT/0.0, 0.0, 0.0
P2 = POINT/60.0, 80.0, 0.0
Conventional
S K Mondals
P3 = POINT/150.0, 100.0, 0.0
P4 = POINT/200.0, 0.0, 0.0
C1 = CIRCLE/ CENTRE, P2, RADIUS, 20
C2 = CIRCLE/CENTRE, P3, RADIUS, 30
L1 = LINE/P1, LEFT, TANTO, C1
L2 = LINE/RIGHT, TANTO, C1, RIGHT, TANTO, C2
L3 = LINE/P4, RIGHT, TANTO, C2
L4 = LINE/P1, P4
PL1=PLANE/P1, P2, P3
CUTTER/10.0
TOLER/0.1
INTOL/0.005
OUTTOL/0.005
SPINDL/500, CLW
COOLNT/ON
FEDRAT/200
FROM/P0
GODOWN/0.0, 0.0, -8.0
GO/TO, L1, TO, PL1, TO, L4
GO/TO, L1, PAST, C1
GORGT/C1, PAST, L2
GORGT/L2, PAST, C2
GORGT/C2, PAST, L3
GORGT/L3, PAST, L4
GORGT/L4, PAST, L1
RAPID
GOTO/P0
COOLNT/OFF
SPINDL/OFF
END
FINI
NC, CNC Machines
You might also like
- Radio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftFrom EverandRadio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Line Controlled RobotDocument27 pagesLine Controlled RobotchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCFrom EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- CNC Basic & Prog.Document89 pagesCNC Basic & Prog.Christine BrownNo ratings yet
- Terex PDFDocument48 pagesTerex PDFmovie hunter100% (1)
- The CNC Handbook: Digital Manufacturing and Automation from CNC to Industry 4.0From EverandThe CNC Handbook: Digital Manufacturing and Automation from CNC to Industry 4.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Line Follower Robot-ICCAE 2010Document6 pagesA Line Follower Robot-ICCAE 2010Ioan DorofteiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics P K Nag Exercise Unsolved Problems SolvedDocument265 pagesThermodynamics P K Nag Exercise Unsolved Problems SolvedRavinder Antil90% (40)
- Robotics Unit-5 Question BankDocument6 pagesRobotics Unit-5 Question BankveerapandianNo ratings yet
- Design of A Full Adder Using PTL and GDI TechniqueDocument6 pagesDesign of A Full Adder Using PTL and GDI TechniqueIJARTETNo ratings yet
- Heidenhain TNC BasicDocument175 pagesHeidenhain TNC BasicReymondo Bundoc100% (2)
- Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) Full TextDocument62 pagesAutomated Guided Vehicle (AGV) Full Textazriffaris100% (2)
- Industrial RoboticsDocument30 pagesIndustrial RoboticssoniyagoyalNo ratings yet
- TNC 430 HeidenhainDocument362 pagesTNC 430 HeidenhainCao ThanhNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 NC CNC DNC FMS Automation and RoboticsDocument143 pagesCh-11 NC CNC DNC FMS Automation and RoboticsshafiqNo ratings yet
- Material HandlingDocument39 pagesMaterial Handlingbathinsreenivas100% (1)
- 6788 Flexsim 1710 Manual ArialDocument1,657 pages6788 Flexsim 1710 Manual ArialQonitaHaulaKinantiNo ratings yet
- Swisslog WarehouseOfTheFuture PDFDocument16 pagesSwisslog WarehouseOfTheFuture PDFAkash_C1992No ratings yet
- FV609-Simulation Using ProModel - Charles HarrellDocument703 pagesFV609-Simulation Using ProModel - Charles HarrellRheza Nugraha PrabareswaraNo ratings yet
- Computer Assisted Part ProgrammingDocument21 pagesComputer Assisted Part ProgrammingSanthan SalaiNo ratings yet
- BullseyeDocument4 pagesBullseyeRuben CuevasNo ratings yet
- Robot Specifications - Robot ProgrammingDocument54 pagesRobot Specifications - Robot ProgrammingPriyanshu NainNo ratings yet
- Scope:: Last and First Name: Student IdDocument4 pagesScope:: Last and First Name: Student Idb7663664No ratings yet
- Autocad Lab ManualDocument24 pagesAutocad Lab Manualmadhu.ammu112No ratings yet
- NC, CNC & Robotics PDFDocument100 pagesNC, CNC & Robotics PDFSiddhrajsinh ZalaNo ratings yet
- Hobby Servo Motor Control Via PIC Pulse Width Modulation: Nathan Markey April 4, 2003Document7 pagesHobby Servo Motor Control Via PIC Pulse Width Modulation: Nathan Markey April 4, 2003Luciana Gutierrez Salazar100% (1)
- NC and CNC MachinesDocument25 pagesNC and CNC MachinesSabiha Hajdarbegović-HafizovićNo ratings yet
- Project Construction: 3.1 HC-05 Bluetooth To Serial Port ModuleDocument8 pagesProject Construction: 3.1 HC-05 Bluetooth To Serial Port Moduleanugya sharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit - III CNC Part ProgrammingDocument39 pagesUnit - III CNC Part ProgrammingNarayana PerumalNo ratings yet
- Computer Assisted Part Programming (APT, Automatically Programmed Tool)Document40 pagesComputer Assisted Part Programming (APT, Automatically Programmed Tool)kumareshNo ratings yet
- Marcin SZAREK, Gözde ÖZCAN (Biped Robot)Document13 pagesMarcin SZAREK, Gözde ÖZCAN (Biped Robot)Mspavan RaoNo ratings yet
- Robotics: Sections: Robot Anatomy Robot Control Systems End Effectors Industrial Robot Applications Robot ProgrammingDocument30 pagesRobotics: Sections: Robot Anatomy Robot Control Systems End Effectors Industrial Robot Applications Robot Programmingmksamy2021No ratings yet
- Numerical ControlDocument36 pagesNumerical ControlsaishvNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Robotics Working With Abb Irb 120 Robot: Robotics & Industrial Automation (Conestoga College)Document20 pagesIntroduction To Robotics Working With Abb Irb 120 Robot: Robotics & Industrial Automation (Conestoga College)thanh_cdt01No ratings yet
- An Intelligent Line-Following Robot Project For Introductory Robot CoursesDocument7 pagesAn Intelligent Line-Following Robot Project For Introductory Robot CoursesAmla SingNo ratings yet
- A Line Follower Robot From Design To Implementation - Technical Issues and ProblemsDocument5 pagesA Line Follower Robot From Design To Implementation - Technical Issues and ProblemsAhmad AfnanNo ratings yet
- UNIT II System SoftwareDocument11 pagesUNIT II System SoftwareArulmozhi ManoharanNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Industrial RoboticsDocument39 pagesCH 8 Industrial RoboticsDeepak PathakNo ratings yet
- Welcome !!! METE 284 P3-C1Document20 pagesWelcome !!! METE 284 P3-C1Shane Michael BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Part ProgrammingDocument19 pagesComputer Aided Part ProgrammingPiyush Aggarwal100% (4)
- AutoCad Basic Commands PDFDocument34 pagesAutoCad Basic Commands PDFspacejuyNo ratings yet
- Apt PDFDocument45 pagesApt PDFJignesh Rohit0% (1)
- Wireless Robot and Robotic Arm Control With Accelerometer Sensor ProjectDocument51 pagesWireless Robot and Robotic Arm Control With Accelerometer Sensor ProjectAmandeep Singh KheraNo ratings yet
- CNC Project FullDocument22 pagesCNC Project FullDebabrata NandaNo ratings yet
- Omron Cp1e PDFDocument45 pagesOmron Cp1e PDFSuzaini SupingatNo ratings yet
- Short Range Radar SystemDocument14 pagesShort Range Radar SystemHoomi ShbNo ratings yet
- Harshit Robotics 10Document13 pagesHarshit Robotics 10harshitkargathara21No ratings yet
- NC CNC DNC FMS TheoryDocument21 pagesNC CNC DNC FMS Theorykamleshyadavmoney100% (1)
- XrotorDocument21 pagesXrotorFrancesco ReaNo ratings yet
- 3 Waukesha Gas Engine Maintenance ManualDocument75 pages3 Waukesha Gas Engine Maintenance ManualMamunNo ratings yet
- Design Implementation and Control of A H PDFDocument11 pagesDesign Implementation and Control of A H PDFNikhil HasabiNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Manufacturing (EME031)Document4 pagesComputer Aided Manufacturing (EME031)Hemant PalNo ratings yet
- RoboticsDocument26 pagesRoboticsmkmnawaz972No ratings yet
- An Instruction Set For The Efficient Implementation of The Cordic AlgorithmDocument4 pagesAn Instruction Set For The Efficient Implementation of The Cordic AlgorithmNaveen JainNo ratings yet
- 254464.1 Car Mikac VezaDocument6 pages254464.1 Car Mikac VezaengrodeNo ratings yet
- What Are The Storage Devices in CAD?Document23 pagesWhat Are The Storage Devices in CAD?shunmugeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - NC ProgrammingDocument12 pagesChapter 3 - NC ProgrammingnidhidarklordNo ratings yet
- Automation and Robotics AssignmentDocument13 pagesAutomation and Robotics AssignmentMoHit LalNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 6 Political ScienceDocument80 pagesNCERT Class 6 Political ScienceNITIN KUMAR SHARMANo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Question and Answers For GATE IAS PDFDocument37 pagesEngineering Mechanics Question and Answers For GATE IAS PDFshiv kr dubey100% (1)
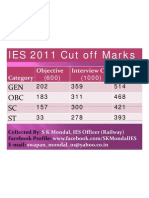
- IES 2011 Cut Off Marks Engineering Service Cutoff MarksDocument1 pageIES 2011 Cut Off Marks Engineering Service Cutoff MarksKBSMANITNo ratings yet
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemsDocument18 pagesFlexible Manufacturing SystemsVijay Kumar100% (1)
- What Is An FMS?: Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocument20 pagesWhat Is An FMS?: Flexible Manufacturing SystemUlyviatrisnaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Chapter 7 Process ManagementDocument68 pagesWeek 3 - Chapter 7 Process Managementarthaprabawa2005No ratings yet
- Agvs: Bridging The Gap in Automation: Brian Keiger, CsoDocument36 pagesAgvs: Bridging The Gap in Automation: Brian Keiger, Csobodeks dexNo ratings yet
- Pedal Operated ForkliftDocument56 pagesPedal Operated Forkliftfahamith ahamed100% (1)
- ExhibitorlistDocument17 pagesExhibitorlistAmazing PranavNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering Project IdeasDocument3 pagesAutomobile Engineering Project IdeasAditya ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Positioning and Obstacle Avoidance of Automatic Guided Vehicle in Partially Known EnvironmentDocument10 pagesPositioning and Obstacle Avoidance of Automatic Guided Vehicle in Partially Known EnvironmentLord VolragonNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology BookDocument42 pagesResearch Methodology BookRicardo AntequeraNo ratings yet
- Major ProjectDocument70 pagesMajor ProjectMujtaba AliNo ratings yet
- New RAH Floor Plans Level 1 Updated 120115Document1 pageNew RAH Floor Plans Level 1 Updated 120115Budi KusumaNo ratings yet
- Practical Applications For Mobile Robots Based On Mecanum Wheels - A Systematic SurveyDocument13 pagesPractical Applications For Mobile Robots Based On Mecanum Wheels - A Systematic SurveyFlorentina AdascaliteiNo ratings yet
- Fork Truck For - Paper Roll Press DeliveryDocument1 pageFork Truck For - Paper Roll Press Deliveryservice9046No ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Material HandlingDocument56 pagesKlasifikasi Material HandlingKenny GurningNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Design of An Automatic Guided Vehicle (AGV) SystemDocument68 pagesPreliminary Design of An Automatic Guided Vehicle (AGV) SystemDanil KhardniNo ratings yet
- JBT General BrochureDocument5 pagesJBT General BrochureDeschepgNo ratings yet
- OS32C SensorsDocument2 pagesOS32C SensorsArjun SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Transfer Line System (TLS) : Essential Components of TLS AreDocument10 pagesTransfer Line System (TLS) : Essential Components of TLS Areburhanuddin bhavnagarwalaNo ratings yet
- Process StrategyDocument65 pagesProcess StrategyPoojitha VallabhaneniNo ratings yet
- PIANC Event Container Terminal QADocument1 pagePIANC Event Container Terminal QAFay NandaNo ratings yet
- Company Presentation en HighDocument39 pagesCompany Presentation en HighDuy Phạm VănNo ratings yet
- Tle9 Agricrop q2 m1 Handlingmaterialsequipment v2Document32 pagesTle9 Agricrop q2 m1 Handlingmaterialsequipment v2Bernadeth Torres LibradoNo ratings yet