Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Will India Go Back To 1991
Will India Go Back To 1991
Uploaded by
Maheshkv MahiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Will India Go Back To 1991
Will India Go Back To 1991
Uploaded by
Maheshkv MahiCopyright:
Available Formats
Will India go back to 1991 situation?
Suggest some measure to rescue the economy from its
current state of economic turmoil (To increase the rupee value)
India's present situation of rapid fall in rupee value is caused by
Persistent inflation of past few years
High current account deficit of about $85billion (4.5% of GDP)
1991 situation
Western economies were stronger and looking forward to deepen the process of economic
globalisation
Big bang reforms like LPG worked for India
2013 situation
Major OECD economies are looking much more inward to stabilize their economy
Negative impact of global financial crisis began to affect the emerging nations like India.
After 2010,excess liquidity flowing from west caused the
High international oil prices and commodity
India's mismanage of supply of key resources such as Land, Coal, Iron ore, Critical
food items
All these problems had created India to face the
High inflation
Low growth
Bulging CAD
Key difference between 1991 & 2013 are
Availabilty of global financial inflows to India during 1991 and 2013
US federal reserve withdrawl of liquidity
India needs to understand:
Cheap financial capital inflowing from the west is double edged weapon if not used
judiciously to enhance productivity of domestic economy it leads to external debt trap.
As said before, present situation of the India's economy is different from 1991 situation. So India
will never go back to 1991 situation because Indias fundamentals of economy are stronger.
Measures to revive Indian economy (To increase the rupee value)
1. To contain CAD:
By discouraging imports and supporting exports.
Large amount of CAD is caused by import of coal ($15 billion) - It can be reduced by
increasing domestic coal production because India is having largest coal reserves in Asia.
2. Reducing subsidies:
Reduction in the government consumption / subsidies and a loosening of monetary policy
to increase government saving
3. Import oil from Iran:
Increase oil imports from Iran as we can pay in rupees.
4. Dollar Swap facility to oil companies:
RBI has to give direct access to large dollar buying oil companies -to bypass the spot
market
5. Correcting non-oil trade deficit:
India's biggest trading partner China accounts for half of the non-oil trade deficit.
This can be offset by capital inflows from China into India's infrastructure, such as metro
or road projects.
6. Encouraging Capital Inflows
RBI has removed administrative restrictions on investment schemes offered by banks to
non-resident Indians, and removed ceiling on interest rates on deposit accounts held by
NRIs.
RBI increased the current overseas borrowing limit for banks from 50% to 100%, and
allowed it to be converted into rupees and hedged with the RBI at concessional rate.
RBI also allowed banks to swap fresh NRI dollar deposits with a minimum duration of 3
years with the RBI.
7. Strong push to exports:
Widening the focus market and focus product scheme.
India's iron ore export can be restored to more than $10 billion annually.
8. Selling of gold bonds
Sell a gold bond with a five year maturity, which can act as a gold
substitute just like Kisan Vikas Patras
9. International Cooperation
Government increased its currency swap limit with Japan from
USD15 billion to USD50 billion.
10. National manufacturing policy
To increase the sectoral share of manufacturing in GOP to at least 25% by
2022
To increase the rate of job creation so as to create 100
million additional jobs by 2022;
Industrial townships called National Investment and
Manufacturing Zones (NIMZs)
Effective and rapid implementation of NMP is necessary at this stage to enhance the economic
situation.
by SUTHAN S.P
REFERENCES:
The Hindu editorial
Prsindia.org
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5811)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- (Revised) Officer of Bank Financial Institution AffidavitDocument1 page(Revised) Officer of Bank Financial Institution Affidavitin1or100% (8)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Emergence of The Asian TigersDocument4 pagesThe Emergence of The Asian TigersShepherd Cha'abataNo ratings yet
- Click Here To Play:: Plant TissuesDocument2 pagesClick Here To Play:: Plant Tissuestarun_mishra876No ratings yet
- Click Here To Play:: Plant TissuesDocument2 pagesClick Here To Play:: Plant Tissuestarun_mishra876No ratings yet
- Railways and Tourism: Steam TrainDocument2 pagesRailways and Tourism: Steam Traintarun_mishra876No ratings yet
- Guide4BankExams SyllogismDocument23 pagesGuide4BankExams SyllogismShiv Ram Krishna67% (3)
- Signals SystemsDocument22 pagesSignals Systemstarun_mishra876No ratings yet
- Banks N HeadquartersDocument1 pageBanks N Headquarterstarun_mishra876No ratings yet
- Indian TribesDocument5 pagesIndian Tribestarun_mishra876No ratings yet
- International Banking Finance RegularDocument11 pagesInternational Banking Finance Regularprathmesh surveNo ratings yet
- ACC 330 Final Project Two Tax Planning Template - 2020Document3 pagesACC 330 Final Project Two Tax Planning Template - 2020BREANNA JOHNSONNo ratings yet
- My PDFDocument37 pagesMy PDFAnDaLeEb IrFaAn KashmiriNo ratings yet
- CSPL22121565Document2 pagesCSPL22121565ABALUNo ratings yet
- Assignmentkarla Company Provided The Following Information For 2016 PDF FreeDocument1 pageAssignmentkarla Company Provided The Following Information For 2016 PDF FreePatrisha Carpio BeleyNo ratings yet
- Great Depression Research Paper by Marcus DiorDocument7 pagesGreat Depression Research Paper by Marcus DiorRegular Ol'MärcusNo ratings yet
- Report 20220307115041Document38 pagesReport 20220307115041Phani PrakashNo ratings yet
- FSA Analysis 3Document1 pageFSA Analysis 3Tamo AndguladzeNo ratings yet
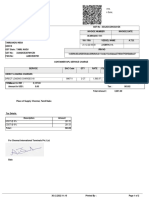
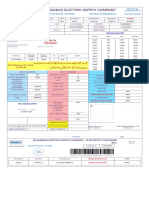
- Iesco Online BillDocument1 pageIesco Online BillRaheel TariqNo ratings yet
- The Kotak Mahindra Group An Overview: #DiscoverkliDocument6 pagesThe Kotak Mahindra Group An Overview: #DiscoverkliNalla ThambiNo ratings yet
- Econ South Korea VS ArgentinaDocument2 pagesEcon South Korea VS ArgentinaJuan Miguel DosonoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Government Influence On Exchange RatesDocument6 pagesChapter 6-Government Influence On Exchange Ratesnguyễnthùy dươngNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Class NotesDocument2 pagesIncome Tax Class NotesMr. BachooNo ratings yet
- 2406 Tata Group - 386382390366395Document8 pages2406 Tata Group - 386382390366395Jeffrey YudiartaNo ratings yet
- GDP RRLDocument4 pagesGDP RRLAru KimNo ratings yet
- Anti Dumping CaseDocument5 pagesAnti Dumping CaseKate PamularNo ratings yet
- Kinds of TradeDocument1 pageKinds of TradeBianca TapangNo ratings yet
- 0946010b0000000605622 ESTATEMENT 062021 0946010b00000006Document3 pages0946010b0000000605622 ESTATEMENT 062021 0946010b00000006Umesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Print Payment AdviceDocument14 pagesPrint Payment AdviceDTO HailakandiNo ratings yet
- Absolute Cost and Comparative Cost AdvantagesDocument11 pagesAbsolute Cost and Comparative Cost AdvantagesmohdportmanNo ratings yet
- Abrapa Cotton Brazil Report - 2024 01Document9 pagesAbrapa Cotton Brazil Report - 2024 01Akib KhanNo ratings yet
- 1.10 International Organization NewDocument14 pages1.10 International Organization NewArbind YadavNo ratings yet
- Form C PDFDocument1 pageForm C PDFS M Labu HassanNo ratings yet
- Indian EconomyDocument4 pagesIndian EconomyLoveleen GargNo ratings yet
- BPODocument7 pagesBPOGenelle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Hatton National BankDocument1 pageHatton National Bankerica jayasunderaNo ratings yet
- Current Analysis of NAFTADocument6 pagesCurrent Analysis of NAFTAFarhan ArshadNo ratings yet
- National Accounts of Tanzania Mainland Publication 2021Document13 pagesNational Accounts of Tanzania Mainland Publication 2021Omari MaugaNo ratings yet