Professional Documents
Culture Documents
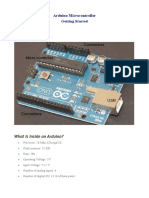
Arduino
Uploaded by
s.b.v.seshagiri1407Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arduino
Uploaded by
s.b.v.seshagiri1407Copyright:
Available Formats
Arduino :
Introduction &
Programming
Anurag Dwivedi & Rudra Pratap Suman
What is an Arduino ?
Open Source electronic prototyping
platform based on flexible easy to use
hardware and software.
Uses of Arduino
Getting started with
Programming
Bare minimum code
voidsetup(){
// put your setup code here, to run once:
}
voidloop(){
// put your main code here, to run
repeatedly:
}
Bare minimum code
setup : It is called only when the Arduino is
powered on or reset. It is used to initialize
variables and pin modes
loop : The loop functions runs continuously
till the device is powered off. The main logic
of the code goes here. Similar to while (1)
for micro-controller programming.
PinMode
A pin on arduino can be set as input or
output by using pinMode function.
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // sets pin 13 as
output pin
pinMode(13, INPUT); // sets pin 13 as input
pin
Reading/writing digital values
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Makes the output
voltage on pin 13 , 0V
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Makes the output
voltage on pin 13 , 5V
intbuttonState=digitalRead(2); // reads
the value of pin 2 in buttonState
Analog to Digital Coversion
What is analog ?
It is continuous range of voltage values (not
just 0 or 5V)
Why convert to digital ?
Because our microcontroller only
understands digital.
ADC in Arduino Uno
Converting Analog Value to
Digital
Quantanization the signal
ADC in Arduino
The Arduino Uno board contains 6 pins for
ADC
10-bit analog to digital converter
This means that it will map input voltages
between 0 and 5 volts into integer values
between 0 and 1023
Reading/Writing Analog Values
analogRead(A0); // used to read the analog
value from the pin A0
analogWrite(2,128);
ADC Example
// These constants won't change. They're used to give names to the pins used:
constintanalogInPin=A0;// Analog input pin that the potentiometer is attached to
constintanalogOutPin=9;// Analog output pin that the LED is attached to
intsensorValue=0; // value read from the pot
intoutputValue=0; // value output to the PWM (analog out)
voidsetup(){
// initialize serial communications at 9600 bps:
Serial.begin(9600);
}
voidloop(){
// read the analog in value:
sensorValue=analogRead(analogInPin);
// map it to the range of the analog out:
outputValue=map(sensorValue,0,1023,0,255);
// change the analog out value:
analogWrite(analogOutPin,outputValue);
// print the results to the serial monitor:
Serial.print("sensor = ");
Serial.print(sensorValue);
Serial.print("\toutput = ");
Serial.println(outputValue);
// wait 2 milliseconds before the next loop
// for the analog-to-digital converter to settle
// after the last reading:
delay(2);
}
You might also like
- Exploring Arduino: Tools and Techniques for Engineering WizardryFrom EverandExploring Arduino: Tools and Techniques for Engineering WizardryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- (Arduino) Pranav Computer Branch - BDocument14 pages(Arduino) Pranav Computer Branch - BVIPER VALORANTNo ratings yet
- ArduinoDocument14 pagesArduinowmarasigan2610No ratings yet
- Arduino TutorialDocument26 pagesArduino TutorialsrujanNo ratings yet
- Arduino LectureDocument52 pagesArduino LectureSỹ RonNo ratings yet
- Function and SyntexDocument8 pagesFunction and SyntexSifatNo ratings yet
- Coding TurbidityDocument1 pageCoding TurbidityOkky Agassy FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Arduino & RPiDocument33 pagesArduino & RPiiemct23No ratings yet
- Arduino IDE Setup & Blinking LEDDocument6 pagesArduino IDE Setup & Blinking LEDRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Controler PDFDocument15 pagesControler PDFKhoiril HudaNo ratings yet
- Arduino Lab2Document89 pagesArduino Lab2sarvodayasingh100% (1)
- EnergiaDocument15 pagesEnergiaDaniel V Sam100% (1)
- Arduino Microcontroller ProgrammingDocument21 pagesArduino Microcontroller ProgrammingmawaddahNo ratings yet
- Arduino: BY Salih MahmodDocument25 pagesArduino: BY Salih MahmodrbenseghierNo ratings yet
- Light Detection and Measurement: Dr. Eng. Endrowednes KuantamaDocument20 pagesLight Detection and Measurement: Dr. Eng. Endrowednes KuantamaAman RayNo ratings yet
- Arduino - AnalogInOutSerialDocument4 pagesArduino - AnalogInOutSerialAhmed JafarNo ratings yet
- ArduinoDocument34 pagesArduinoLukeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ArduinoDocument22 pagesIntroduction To ArduinoSourabh BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Arduino BootcampDocument47 pagesArduino Bootcampvinod varmaNo ratings yet
- 02 ArduinoUNODocument58 pages02 ArduinoUNOZavorra ZavorratoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Arduino and IdeDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Arduino and IdeDhanashree ThoratNo ratings yet
- Modul 5: Analog Input PotensiometerDocument18 pagesModul 5: Analog Input PotensiometerHANDRI ZALILNo ratings yet
- Arduino Boards NotesDocument73 pagesArduino Boards Noteskangirene9705No ratings yet
- Arduino Uno Microcontroller Guide for IoT BeginnersDocument73 pagesArduino Uno Microcontroller Guide for IoT BeginnersGr RanjereNo ratings yet
- Arduino Lesson 9-Analog ReadingsDocument4 pagesArduino Lesson 9-Analog ReadingsBill ChenNo ratings yet
- Arduino Programming For ESD: by MD - Dedarul HasanDocument38 pagesArduino Programming For ESD: by MD - Dedarul HasandedarulNo ratings yet
- IOT ARduino PDFDocument84 pagesIOT ARduino PDFKuppan Chetty RamanathanNo ratings yet
- Arduino Workshop Code HandoutDocument4 pagesArduino Workshop Code HandoutshanreiNo ratings yet
- Arduino Einfuehrung SchulzeDaniel SS2010Document28 pagesArduino Einfuehrung SchulzeDaniel SS2010Fernando MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Introducing the Arduino Microcontroller PlatformDocument46 pagesIntroducing the Arduino Microcontroller PlatformCassio PazNo ratings yet
- Mikrokontroller ArduinorariefDocument101 pagesMikrokontroller ArduinorariefDio Izqhaq Risky SasongkoNo ratings yet
- EMS ArduinoTutorialDocument7 pagesEMS ArduinoTutorialMOHAMMED MUFEED MOHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- ADC in ArduinoDocument6 pagesADC in ArduinoNishantNo ratings yet
- 1253 Iot PRG 1 2 3Document7 pages1253 Iot PRG 1 2 3xyz abcNo ratings yet
- RFID Learning Kit For ArduinoDocument92 pagesRFID Learning Kit For Arduinoic3_2kNo ratings yet
- IOT PracticalsDocument28 pagesIOT PracticalsmuskanbandariaNo ratings yet
- Final Year DjangoDocument11 pagesFinal Year DjangoKaustubh SawantNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document65 pagesModule 5Shilpa ShridharNo ratings yet
- RE2101A179Document12 pagesRE2101A179Lingampalli AbhijithNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital WriteDocument9 pagesAnalog and Digital WriteJun HastNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document73 pagesModule 5JyothsnaNo ratings yet
- 03 Program Structure and IODocument10 pages03 Program Structure and IOsfleandro_67No ratings yet
- Arduino Uno Start Document 5 2022Document14 pagesArduino Uno Start Document 5 2022Eashvar SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 4 Arduino ProgrammingDocument32 pages4 Arduino Programmingncqphuong.20it2No ratings yet
- Robots Need Sensory Input - Guide to Arduino Sensors and ProgrammingDocument4 pagesRobots Need Sensory Input - Guide to Arduino Sensors and ProgrammingHema hreeNo ratings yet
- ArduinoDocument35 pagesArduinoAashrey JainNo ratings yet
- Arduino: Introduction & Programming: Course InstructorDocument29 pagesArduino: Introduction & Programming: Course InstructorHuma Qayyum MohyudDin100% (1)
- lab 1Document9 pageslab 1Malik YousafNo ratings yet
- Week#2 - C Data Types and Arduino PlatformDocument27 pagesWeek#2 - C Data Types and Arduino PlatformMade KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Arduino Handouts and ReviewerDocument8 pagesArduino Handouts and ReviewerEliane DadoNo ratings yet
- Flame Sensor2Document3 pagesFlame Sensor2ShameerNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Lab Manual - Simulation With ThinkerCADDocument12 pagesDay 1 Lab Manual - Simulation With ThinkerCADinfo.learninglabsonlineNo ratings yet
- Flame Sensor Arduino PDFDocument3 pagesFlame Sensor Arduino PDFSyaiful RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2 Serial ComDocument13 pages2 Serial ComShang Divina Ebrada100% (1)
- Round Two GuideDocument13 pagesRound Two GuideSarmad AhmadNo ratings yet
- HKBK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING SYLLABUS IOT TECHNOLOGYDocument78 pagesHKBK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING SYLLABUS IOT TECHNOLOGYSavanNo ratings yet
- Ardunio Language ReferenceDocument25 pagesArdunio Language ReferenceAlamcoNo ratings yet
- Intro To ArduinoDocument38 pagesIntro To ArduinoANTONIO MIGUEL DAYNONo ratings yet
- Arduino: The Ultimate Guide to Arduino for Beginners Including Arduino Basics, Tips & Tricks, Projects, and More!From EverandArduino: The Ultimate Guide to Arduino for Beginners Including Arduino Basics, Tips & Tricks, Projects, and More!No ratings yet
- Gowda2019 ECU Inter - Processor Data CommunicationDocument11 pagesGowda2019 ECU Inter - Processor Data Communications.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- George2016 Writing Good Techincal Safety RequirementsDocument9 pagesGeorge2016 Writing Good Techincal Safety Requirementss.b.v.seshagiri14070% (1)
- ICCE Presentation On VESA Display PortDocument40 pagesICCE Presentation On VESA Display Porthithot2008No ratings yet
- Pmic Safety Detroit TechdayDocument61 pagesPmic Safety Detroit Techdays.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- Gowda2019 ECU Inter - Processor Data CommunicationDocument11 pagesGowda2019 ECU Inter - Processor Data Communications.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- Quality requirements for samples: Schematic presentation for the use of samples according to the degree of maturityDocument3 pagesQuality requirements for samples: Schematic presentation for the use of samples according to the degree of maturitys.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- ZD 007 Sample Definition Project Management ENDocument1 pageZD 007 Sample Definition Project Management ENs.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- AURIX MultiCore Lauterbach HandoutDocument56 pagesAURIX MultiCore Lauterbach Handouts.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- Analytical Study of Sense AmplifierDocument5 pagesAnalytical Study of Sense Amplifiers.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- Adc Student: Andrew Brown Jonathan Warner Laura StricklandDocument51 pagesAdc Student: Andrew Brown Jonathan Warner Laura Stricklands.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- 320 Lecture 3Document10 pages320 Lecture 3s.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- Reliability and Failure Analysis of Electronic Components: by Dr. Charles Surya, ENC CD 636, ×6220 Ensurya@polyu - Edu.hkDocument61 pagesReliability and Failure Analysis of Electronic Components: by Dr. Charles Surya, ENC CD 636, ×6220 Ensurya@polyu - Edu.hkhariprasad_pentiNo ratings yet
- Automatic ASIL DecompositionDocument18 pagesAutomatic ASIL Decompositions.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- Slyt 581Document5 pagesSlyt 581ajoaomvNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 MOS Transistor Circuit AnalysisDocument22 pagesLecture10 MOS Transistor Circuit AnalysisKartika MunirNo ratings yet
- Elec Chap 3Document28 pagesElec Chap 3Giezel RevisNo ratings yet
- H Da Barth Functional Safety On MulticoreDocument23 pagesH Da Barth Functional Safety On Multicores.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument254 pagesAnalog ElectronicsNithindev GuttikondaNo ratings yet
- P11Document22 pagesP11s.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- Elec Chap 3Document28 pagesElec Chap 3Giezel RevisNo ratings yet
- L17 FET DC AnalysisDocument19 pagesL17 FET DC Analysiss.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- LFI 2015 - DL Lunch Learn SlidesDocument61 pagesLFI 2015 - DL Lunch Learn Slidess.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- S2P5 Gyu Myoung LeeDocument20 pagesS2P5 Gyu Myoung Lees.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- EMI Design TipsDocument3 pagesEMI Design Tipss.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- Automotive Mosfets in Linear Applications: Thermal InstabilityDocument6 pagesAutomotive Mosfets in Linear Applications: Thermal Instabilitys.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- 07 DRITSANOS IoT-Conference Schneider-ElectricDocument13 pages07 DRITSANOS IoT-Conference Schneider-Electrics.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- Sensors Used in Power Sources For IoEDocument33 pagesSensors Used in Power Sources For IoEKiran KirruNo ratings yet
- AppNote - ProfetOperatingModes - V1 0 - 07-2011 PDFDocument16 pagesAppNote - ProfetOperatingModes - V1 0 - 07-2011 PDFs.b.v.seshagiri1407100% (1)
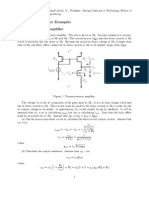
- Lect 22 MOSFET Current Mirror and CS Amplifier PDFDocument10 pagesLect 22 MOSFET Current Mirror and CS Amplifier PDFs.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- FET Current-Mirror Examples Common-Source Amplifier: 1 2 3 REF 3 2 2 3 2 REFDocument5 pagesFET Current-Mirror Examples Common-Source Amplifier: 1 2 3 REF 3 2 2 3 2 REFManpreet SinghNo ratings yet