Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elasticity and Plasticity
Uploaded by
Finney Wilson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesTheory of Elasticity and Plasticity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTheory of Elasticity and Plasticity
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesElasticity and Plasticity
Uploaded by
Finney WilsonTheory of Elasticity and Plasticity
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
www.examquestionpaper.in
Reg. No.: (#|@|4[wl) 4 47 [3 lolols
~ Question Paper Code: 14036
M.E. DEGREE EXAMINATION, JANUARY 2015.
First Semester
Structural Engineering
ST 7103 — THEORY OF ELASTICITY AND PLASTICITY
(Regulation 2013)
‘Time : Three hours Maximum : 100 marks
Answer ALL questions.
PART A — (10 x 2 = 20 marks)
1. Define hydrostatic state of stress.
What are stress invariants?
3. Check if the function $= Ax®y~Br*y? is a Airy's stress function,
4, Give examples for plane strain problems.
5. Write the Brendt-Batho equation.
6. With a neat sketch represent the shear stress flow in a thin 1- section under
torsion.
a
Write short notes on the multiple parameter method used for simulating
beams on elastic foundation.
8. Write the advantages of finite difference method.
9. Write short notes on Tresca's failure theory.
10. Show the stress-strain behaviour of a material which is rigid with strain
hardening properties.
www.examquestionpaper.in
PART B — (5.x 16 = 80 marks)
i 240 120 -30
The state of stress at a point is given by | 120 160 100] MPa. Find
; [-30 100 75
the principal stress and the orientation of each principal plane.
Or
20 -30 -20
The state of stress at a point is given by |-30 60 50 |MPa.
-20 50 75
Determine the normal shear and resultant stresses on a plane where
normal stress makes an angle of 50° with the X-axis and 70° with the
Y-axis.
Prove that the following are Airy's stress function and examine the stress
distribution represented by them
@ b= Ale'-3x4y*)
Gi) g=Ax°
Gil) g= Ax? - By?
(iv) $= Ax? + Bry+Cy?.
Or
A thick steel cylinder which has an inner diameter of 1 m is subjected to
an internal pressure of 10 MPa. Calculate the wall thickness if the
maximum shearing is not to exceed 40 MPa.
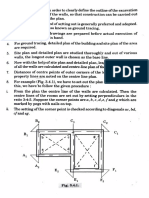
A thin-walled member 1.2 m long has the cross-section shown in
Fig. Q 13(a). Determine the maximum torque which can be carried by the
section if the angle of twist is limited to 10". What will be the maximum
shear stress when this maximum torque is applied? G = 80 GN/m?.
Figure Q.13 (a)
Or
Give a detailed account of Prandtl's membrane analogy explaining the
principle of analysis of a thin-walled member under torsion.
2 14036
Md.
1b.
(a)
()
(a)
(>)
www.examquestionpaper.in
An infinite beam on a Winkler foundation has the following properties:
= 0.3 kN/mm/mm, E = 200 GPa. A concentrated load of intensity 25 kN
is applied to the beam. Compute the maximum deflection, shear force,
bending moment and slope acting in the beam. The beam cross-section is
I-shaped (flanges: 100 x 10 mm and web 150 x 8mm).
Or
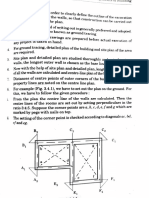
Determine the deflection of the built-in beam on an elastic foundation
shown in Figure Q14(b) using finite difference method. The beam is
subjected to a udl of intensity, p = 250 kN/m. L = 4m. Take modulus of
the foundation as 2.0 MPa, EI = 550 x 10? Nmm®. Compare the results
assuming the node interval, h as 2m and Im.
Figure Q. 14 (b)
‘A rectangular beam of 230mm x 350mm of 3m long carries a central
concentrated load of 50 KN. The stress strain curve of the beam material
is given by ¢=7002***. Determine the maximum stress induced in the
beam and compare the results when the stress strain curve is a linear
one.
Or
A solid circular shaft of 90mm radius is subjected to a twisting couple so
that the outer 40mm deep sheet of the shaft yields plastically. If the yield
stress in shear for the shaft material is 150 MPa, determine the value of
twisting couple applied and associated angle of twist. G = 80 GPa.
o ¢ oe
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Unit 3 - 2 Materials TestingDocument8 pagesUnit 3 - 2 Materials TestingFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Fossils and The Flood Title 01111Document44 pagesFossils and The Flood Title 01111Finney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Carbon 14Document41 pagesCarbon 14doxorubicin100% (1)
- English Songs 2019Document1 pageEnglish Songs 2019Finney WilsonNo ratings yet
- MTech SyllDocument1 pageMTech SyllFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Calculate strength of ISA section as tie memberDocument26 pagesCalculate strength of ISA section as tie memberFinney Wilson0% (1)
- Bridges Failures in Extreme Flood EventsDocument10 pagesBridges Failures in Extreme Flood EventsFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - 1 Materials TestingDocument6 pagesUnit 3 - 1 Materials TestingFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia of FlywheelDocument3 pagesMoment of Inertia of FlywheelFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Land Surveying ProgrammeDocument7 pagesDiploma in Land Surveying ProgrammeFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Design Arguments For The Existence of God Part 2Document2 pagesDesign Arguments For The Existence of God Part 2Finney WilsonNo ratings yet
- IITK-GSDMA Wind Codes Project ReportDocument106 pagesIITK-GSDMA Wind Codes Project ReportFung MakNo ratings yet
- Design Arguments For The Existence of God Part 1Document2 pagesDesign Arguments For The Existence of God Part 1Finney WilsonNo ratings yet
- INDIAN Steel TableDocument8 pagesINDIAN Steel Tablezaveeq80% (5)
- Effective Study: WelcomeDocument113 pagesEffective Study: WelcomeFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Vbs 2017 SongsDocument12 pagesVbs 2017 SongsFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Design Arguments For The Existence of God Part 3Document2 pagesDesign Arguments For The Existence of God Part 3Finney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Seismic design forces for a four-storey RC buildingDocument26 pagesSeismic design forces for a four-storey RC buildingjonnyprem100% (1)
- CE2402 Estimation and Quantity Surveying PDFDocument107 pagesCE2402 Estimation and Quantity Surveying PDFMuthu Praveen SarwanNo ratings yet
- Vbs 2017 SongsDocument12 pagesVbs 2017 SongsFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Know Your FruitsDocument18 pagesKnow Your FruitsFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- ST7201finiteelementanalysis Mayjune2015Document4 pagesST7201finiteelementanalysis Mayjune2015Finney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Bar Bending Schedule & Quantity Estimation of Reinforcement SteelDocument19 pagesBar Bending Schedule & Quantity Estimation of Reinforcement SteelnaeemNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Anti Termite TreatmentDocument4 pagesChecklist For Anti Termite TreatmentFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Steel AllDocument30 pagesSteel AllKhin Maung SoeNo ratings yet
- SSLC Maths Notes Prepared Students by HandDocument57 pagesSSLC Maths Notes Prepared Students by HandSundarapandiyan SundaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- Maths concepts for 10th standardDocument10 pagesMaths concepts for 10th standardrashidNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Advanced Concrete Technology NotesDocument15 pagesUnit IV Advanced Concrete Technology NotesFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Who Is An EngineerDocument64 pagesWho Is An EngineerFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)