Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Landing Gear Layout Design For Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
Landing Gear Layout Design For Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
Uploaded by
anon_838503350Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Landing Gear Layout Design For Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
Landing Gear Layout Design For Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
Uploaded by
anon_838503350Copyright:
Available Formats
14th National Conference on Machines and Mechanisms (NaCoMM09),
NIT, Durgapur, India, December 17-18, 2009
NaCoMM-2009-TKAj2
Landing Gear Layout Design for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
Akhilesh Jha
SDET Division, ADE/DRDO, Bangalore, India
Corresponding author (email: akhilsdet@yahoo.com)
landing gear system required for those UAVs, which has
conventional take-off and landing.
Abstract
1.2 Landing Gear
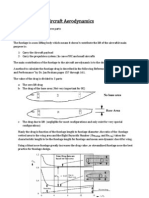
Aircraft landing gear mechanism serves several design
purpose such as supporting the weight of aircraft, providing rolling chassis/taxiing and shock absorption function especially during takeoff and landing etc. The present study carried out to layout design of landing gear
system for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) at conceptual design stage. The nose wheel tricycle landing gear
has been the preferred configuration for UAV. The most
attractive feature of this type of undercarriages is the
improved stability during braking and ground maneuvers. The results of present study indicated that landing
gear stability could be improved by longer wheel axle,
stiffer damping mechanism and smaller wheel mass and
lower aircraft sinking velocity. The present approach has
been following the recommendations of the previous
design of landing gear layout of other aircraft and international standard federal aviation regulations (FAR).
More work to be done to prove the viability of this conceptual layout design. Detailed results needed further
simulation study for validations.
Landing gear system is a major component of every
aircraft. The landing gear serves a triple purpose in providing a stable support for aircraft at rest on the ground,
forming a suitable shock-absorbing device and acting as
a rolling chassis for taxiing during manhandling. It is the
mechanical system that absorbs landing and taxi loads as
well as transmits part of these loads to the airframe so
that a majority of impact energy is dissipated. The main
functions of the landing gear are as follows:
1. Energy absorption 2. Braking 3. Taxi control
The important types [1] of landing gear are as follows:
1. Tri-cycle type (nose gear in fuselage and
main gear on wing)
2. Bicycle type (with or without outriggers)
3. Tail-gear type
In above-mentioned types of landing gear arrangement,
the tricycle type with nose gear in fuselage and main
gear on wing also called nose wheel landing gear has a
series of unquestioned advantages over other layout of
landing gear. In a general sense, the analytical solution
of UAVs landing gear layout has received very little
attention. One reason for this neglect is that its very
wider classification and applications. The traditional
landing gear design process for transport aircraft has
described in textbooks [1-4]. Therefore, in this paper
nose wheel landing gear layout design for unmanned
aerial vehicle has been described on basis of theoretical
kinematics and international standard FAR.
Keywords: UAV, Landing gear stability, Shock absorber, Tip back angle, Landing gear load factor.
Introduction
This section contains the basic definition, classification
and function of unmanned aerial vehicle and landing
gear systems.
1.1 Unmanned aerial vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) commonly referred
to is a remotely piloted aircraft. UAVs come in two
class: some are controlled from a remote location and
others fly autonomously based on pre-programmed
flight. There is a wide variety of UAV shapes, sizes,
configurations, and characteristics.
UAVs perform a wide variety of functions. The
majority of these functions are some form of remote
sensing this is central to the reconnaissance role most
UAVs fulfill, others functions include transport, research and development, to search for and rescue people
in perilous locations etc. Nishant, Predator and Global
hawk are importantly placed in the list of UAVs. The
2 Landing Gear Layout Design Parameters
This section represents a typical step by step approach
that would be taken by the landing gear layout designer
during conceptual design phase.
2.1 Main landing gear location
In the landing gear layout, the aircraft centre of gravity
(c.g) location is needed to position the main landing gear
such that ground stability, maneuverability and clearance requirements are met. The aerial vehicle has two
471
14th National Conference on Machines and Mechanisms (NaCoMM09),
NIT, Durgapur, India, December 17-18, 2009
c.g positions, forward c.g. corresponding to full fuel
mass at the time of take-off and the aft c.g. when fuel
has been used or at the time of landing.
NaCoMM-2009-TKAj2
gear so that the appropriate level friction forces needed
for steering can be generated.
Nose gear loads in the static condition generally
vary about 6-20%, but these should be considered as
extremes. A preferable range would be 8% with the c.g
aft, increasing to 15% with the c.g. forward has been
considering in present design calculations.
Max static main gear load (per strut)
F-M
= W
(0.42-0.46)W
2F
Max static nose gear load
Fig. 1: Aerial vehicle with two c.g. positions.
F-L
= W
(0.08-0.15)W
F
The position of aircraft c.g. can be obtained by knowing
the component weight and their positions. Mean aerodynamic chord calculation (MAC) calculation based in
Fig. (2) and Eqs. (1-2).
Fig. 2: Half 2-D plan view of UAV for calculation of
MAC.
2
MAC length (M) =
3
CR CT
CR + CT
C R +CT
(3)
(4)
Fig.3: Diagram for Nose landing gear load calculation.
Min static nose gear load
(1)
F-N
= W
(0.08)W
F
Max breaking nose gear load
S (CR - M)
H=
(2)
C R - CT
The following steps are needed to position the main
landing gear.
1a: Determination of mean aerodynamic chord of aircraft by using above Eqs. (1-2).
1b: Locate the forward and aft c.g. limit on the mean
aerodynamic chord .
1c: Lines are drawn vertically from these forward and
aft c.g. limits to locate the vertical position of the c.g.
along these lines.
1d: Involves a recheck of the ensuing location of the
main landing gear. It should be between about 50-55%
of the MAC [2].
(5)
W
= Max static load+ 10J
(6)
32.2F
Where W is the Take-off weight of aerial vehicle and
other quantities are defined in Fig. (3). The equation (6)
determines nose gear dynamic load, this is important for
tire selection of landing gear [4].
2.3 Shock absorber stroke length calculation
The landing gears in most unmanned aircraft today are
those making use of the solid steel spring or rubber and
those making use of a fluid acting as spring with gas or
oil, commonly known as the oleo-pneumatic landing
gears. This technical paper has focused for conceptual
layout design of oleo-pneumatic type shock absorber
for both the main landing gears and the nose landing
gear. The oleo-pneumatic shock absorber has been selected because it has the highest energy-dissipating efficiency among the various types of shock absorbers currently in use in the UAVs industry. It has efficiencies
ranging as high as 0.7- 0.9.
Based upon the required sink speeds and load factors,
the vertical wheel travel must be determined. Normal
2.2 Load calculation on nose wheel and
main wheel
The calculation of nose wheel and main wheel load are
based on the diagram shown in Fig.(3) and the following as given relations and their constraints in Eqs. (3-5).
The nose gear should be placed as far forward as to
minimize its load, maximize flotation and maximize
stability. Conversely, to allow for adequate nose wheel
steering, a minimum normal force must act on the nose
472
14th National Conference on Machines and Mechanisms (NaCoMM09),
NIT, Durgapur, India, December 17-18, 2009
design in which the wheel and strut travel the same distance.
The first step is to determine the maximum
loads accept able in the shock strut. This load comprises
the static load plus the dynamic reaction load. When that
load divided by the static load, the reaction factor N obtained. This is some time called to landing gear load
factor or merely landing load factor. Its valued ranges
from 2.03.0 for small utility aircraft or UAVs. Its permissible magnitude is determined by the airframe to
accommodate those factors during landing impact.
Initially, the aircraft is assumed a rigid body
with no relative acceleration between the c.g. and gear
attachment point. Thus, the load factor at the c.g. is the
same as the attachment. To understand fully the relationship between the load factor at the center of gravity Nc.g
and the landing gear load factor N, consider a free body
being acted upon by shock strut forces and lift, as
Shown in Fig. (4), Where Fs is the shock strut force and
L, the lift. Thus
Sum of all external forces Fs +L
Nc.g =
=
(7)
Mass
M
NaCoMM-2009-TKAj2
Thus, for a given aircraft load factor, N will be higher
for FAR Part23 aircraft than for FAR Part 25 aircraft.
When the aircraft comes to rest on the ground, the lift is
zero and the shock strut force is equal to the aircraft
weight i.e. Fs =W Therefore
Nc.g =1+N for FAR part 23 Aircraft
The shock absorbers and tire act together to decelerate
the UAVs from landing vertical velocity to zero vertical
velocity. Therefore shock absorber and tire must also
absorb the sum of the kinetic energy and potential energy of the aircraft; thus,
Tire
Strut
Kinetic Potential
Energy
Energy
Energy
Energy
St n t NW + St n s NW =
W V2
+
2g
( W-L ) (S+St )
(9)
Where St = Tire deflection under N times static load, ft
S = Vertical wheel travel, ft
nt = Tire efficiency
ns = Shock strut efficiency
N = Reaction
W = Aircraft weight
L = Lift
V = Sink speed
2.4 Lateral location of main gear
The tread and wheel base should to be determined. The
relationship between the tread and wheel base is dictated
by the turnover angle, which is determined as follows(Ref.Fig.5 ).
(1) Draw a top view showing the desired nose most forward C.G location
(2) Draw a side view showing the landing gear with
shock absorbers and tire statically deflected and the C.G
position.
Fig. 4 Shock strut dynamics
When lift = weight W ( as specified in FAR part25 for
transport- type aircraft*)
Fs L
F
+
= s +g
W
M
M
g
If, for convenience, the landing gear load factor N is
defined as being equal to Fs/Mass, the gear load factor
determine how much load ,the gear passes to the airframe, which affects the airframe structural weight as
well as strength.
Then
Nc.g =1+N for FAR part 25 Aircraft
On utility and aerobatic aircraft, the rules of FAR part
23* apply and lift = 0.67w; i.e, W=l/0.67, as
F 0.67 g
Nc.g = s + L
(8)
M
L
Fig. 5 Wheel track calculation based on turn over angle
473
14th National Conference on Machines and Mechanisms (NaCoMM09),
NIT, Durgapur, India, December 17-18, 2009
(3) Establish line A-B Extend the line to a point C.
(4)Through point, C draws a perpendicular to line A-B.
(5) Through the c.g. (in the plane view draw a line parallel to A-B and obtain point D.
(6)From point D measure height of the c.g. (H) obtained from the side view and obtain point E.
= 63deg for aircraft that are restricted to operate on
smooth, hard surfaced runways. This values is based on
a side friction coefficient of = 0.55 and the assumption
that the aircraft will slide sideways instead of tipping
over.
NaCoMM-2009-TKAj2
11
12
MAC
Fwd C.G position
13
Load factor
0.74 m (7 cm max)
4.90 m
(Approx)from nose
2.5
3.1 Load calculation
Nose gear loads calculation based on 8% with the c.g.
aft, increasing to 15% with the c.g. forward.
Max nose gear load = 2000x15/100 = 300kg
Min nose gear load = 2000x8 /100 = 160 kg
2.5 Tire selection
Main gear load (per strut) = 850kg and 920 kg
The tires are sized to be carried out the weight of the
aircraft .Typically the main tires are carry about 90% of
the total weight of the aircraft weight .Nose tires carry
only about 10 % of the static load but experience
higher dynamic loads during landing. In conceptual
design stage we can find a tire size by using a statistical
approach [3]. Given below equations developed from
data for rapidly estimating main tire size (assuming that
main tire carry about 90% of aircraft weight). These
calculated values for diameter and width should increase
about 30% if the aircraft is to operate from rough unpaved runways. Nose tires can be assumed to be about
60- 100% the size of main tire.
Calculation of wheel diameter and width for main
wheel Main wheels diameter or width (inch) =A WBW
WW = weight on wheel. For general aviation aircraft,
A=1.51, B = 0.349 for calculation of diameter
A=0.715, B = 0.312 for calculation of width
3.2 Shock absorber stoke length calculation
For instance, let N =3, St =0.9 ft and V=15ft/s and assume 1 g wing lift such that L/W=1(at the time of landing ) Then stroke length calculation as given in eq.(9)
3(0.9 x 0.47 + S x 0.8) = 152 / 2 x 32.2 + (1-1)
Stroke (S) = 11.10 inch
(S+0.9)
Table -2: Shock absorber stoke length
1.
2.
3.
3 Numerical Case Study
Sink velocity
(ft/s)
Load factor
(g load)
15
12
10
3
2.5
2.0
Stroke
length
(Inch)
11.10
7
5.3
For an initial layout, assume that a quarter to a third of
the total stroke is used in moving from static to compressed thus for a 11.10inch stroke,3.7 inch is the distance from static to compressed and 7.4 inch that from
static to extended.
In this section we will discuss a case study of landing
gear layout for following given dimensions
Table -1: Landing gear layout case study parameters
3.3 Nose landing gear position
1
Analysis Parameters
Aircraft Take off
weight
Value
2000 kg
2.
Length of UAV
10 m (approx)
3.
Wing location
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
The length of landing gear must be set so that the tail
does not hit the ground on landing. This is measured
from the wheel in the static position assuming an aircraft angle of attack (0 0.9) for landing which gives 90%
of the maximum lift this range from about 3-8 deg for
most types of aircraft.
3.5 m (L.E) from
nose of UAV
Wing span
21 m
Root chord
0.975m
Calculated Data
MAC position
4.34 m
C.G (vertical)
1.5m ( From ground)
C.G shift
0. 10 times of MAC
length
Tip chord
0.5 m
Aft C.G location
5.0 m from nose
Another hand the tip back angle is the maximum aircraft nose up attitude with the tail touching the
ground and strut fully extended. To prevent the aircraft
from tipping on its tail, the angle off () the vertical
from the main wheel position to the c.g. should be
greater than the tip back angle or 15 deg whichever is
larger. There is a rule-ofthumb which are correlate between alpha (0 0.9) and theta () as That is
0 = 0 0.9 + 30
474
14th National Conference on Machines and Mechanisms (NaCoMM09),
NIT, Durgapur, India, December 17-18, 2009
NaCoMM-2009-TKAj2
For a given parameters C.G height H = 1.5 approx and
value of D = 2.7 m and wheel base = 3 m
At conceptual design stage we have taken a
range ( 30-80 ) of value alpha (0 0.9 )which are feasible
for this solution than corresponding value of thita ( )
in that range is (60 110) With known value of vertical
c.g. height (H) from the level ground so corresponding
(M) distance between Aft c.g. to main wheel position
horizontally
as
shown
previous
Fig.6.
From given geometry in Fig. 5, we can calculate wheel
track as given
Tan = H / K,
Where CD =K ,Then
Tan50 = 1.5/K => K = 1.3
There fore sin = K / D
=> = 28 deg
( where D = 2.7 m)
Now Tan = Z / F
=> Z
= tan 28 X F
=> Z = 0.53 x3 => Z =1.53 m
(F =4.115 m)
wheel track = 2 Z =2x1.53 = 3.2m
For a given wheel base F= 3m, M =2.37m, for different
turnover angle wheel track as below
Fig. 6 Tricycle landing gear geometry
Suppose as ideal value 0 0.9 is 6 deg than corresponding value of is 9 deg an nose wheel carry 10% of
MTOW than wheelbase can be calculated as
Table- 3: Wheel track corresponding given wheelbase
So value of M = H tan () => 1.5 tan 90 = 0.237 m
(where value of H = 1.5m approx) Load on nose wheel
is 200 and corresponding load main wheel 900kg
Take moment about nose wheel
We have calculated the wheel track for the turnover angle range from 45 deg to 55 deg
Max static main gear load (per strut) = W (F-M)/2F,
where F is wheel base in meter
3.5 Tire sizing
=> 900= 2000 (F-M) /2F
Calculation of wheel diameter and width for main wheel.
For general aviation aircraft and UAVs,
F = 10X.0.237 = 2.4m
A=1.51, B = 0.349 for calculation of diameter [4].
D =AWBw for diameter calculation,
wheel of main landing gear = 1000 kg
Table- 2: Wheelbase corresponding given turnover
Angle
max load per
Use log both sides logD = log A+ B log Ww
logD = log1.51 + 0.349 log 920
D = 16.40 in
Tire dia range from (14-16.40 in )
Similar way for width (T) calculation of main wheel
T = AWBw, By using log both sides, log T = log A +B
log Ww
Log T = log0.7150 +0.312 log 1000 kg
Tire width (5.0-6.1in)
3.4 Lateral location of main landing gear
Calculation of tire diameter for nose wheel where nose
wheel total (static +dynamic) Max load 650 kg (including 7% margin of safety) Nose wheel tire can be assumed to be about 60- 100% the size of the main wheel
tires. Nose wheel tire detail tire size 13-16 in and tire
width is around 4-6 in.
Calculation of lateral location of main landing gear,
which is, depends upon turnover angle and C.G height.
For a given C.G height, we can calculate the lateral location of main landing gear in a given feasible range of
turnover angle. The turn over angle must not be more
63 deg for typical UAV to operate on smooth, hard surfaced runways. We can calculate the lateral separation
of landing gear
475
14th National Conference on Machines and Mechanisms (NaCoMM09),
NIT, Durgapur, India, December 17-18, 2009
quirement. While the shock absorber stroke is not a
function of the aircraft weight, nevertheless it is vital to
increase the size of the stroke to lower the landing load
factors and thereby minimizing the structure weight due
to landing loads. To accommodate this requirement,
larger-section tires can be utilized. However, the penalty
for this solution is the increase in aircraft weight and
therefore reduced payload that would be too costly for
UAVs.
4.0 Results and Discussion
The results of the study also indicated that landing gear
stability could be improved by longer wheel axle,
smaller wheel mass and lower aircraft velocity. The nose
wheel tricycle gear has been the preferred configuration
for UAV. It leads to a nearly level fuselage when the
aircraft is on the ground, important for payload safety.
The most attractive feature of this type of undercarriages
is the improved stability during braking and ground maneuvers. Under normal landing attitude, the relative location of the main assembly to the aircraft cg produces a
nose-down pitching moment upon touchdown. This
moment helps to reduce the angle of attack of the aircraft and thus the lift generated by the wing.
4.5
Wheel Base
5 Concluding Remark
Based on present study of landing gear layout design of
UAVs the following concluding remark are drawn.
Nose gear loads in the static position preferable or
optimum range would be 8-12%.
The wheel track of landing gear is approximately
25-30 % of wing span in UAVs cases.
The stroke length of oleo pneumatic shock absorber is approximately equal to touchdown sink speed.
The strut length is about 2.5 to 3.0 times the
stroke length.
Nose wheel diameter is 60-100 % of main wheel
dim in nose wheel landing gear.
Many more options could be decided to functionally
and operationally improve the present conceptual design by using various computer simulation programs.
These results needed experimental data to validate it.
8% MT Ow on Nose wheel
9% MT OW on Nose wheel
10% MT OW on Nose Wheel
11% MT OW on Nose wheel
12% MT OW on Nose wheel
5
4
3.5
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
2.5
3.5
4.5
5.5
6.5
7.5
CL Max Angle
8.5
Fig. 7: Nose wheel Vs wheel base at constant angle
References
30
L.G.F =2.5g
L.G.F =3g
[1] Roskam(1986), Airplane design part IV: Layout
design of landing gear systems, Roskam aviation and
engineering corporations
L.G.F=2g
25
Stroke Length
NaCoMM-2009-TKAj2
20
15
[2]Currey (1988). Aircraft Landing Gear Design: Principles and Practices 1st Edition, American Institute of
Aeronautics and Astronautics.
10
5
0
7.5
10
12.5
Sinking Velocity
15
[3]H.G Conway, Landing gear design, The Royal
Aeronautical Society Chapman and Hall Ltd, 1958.
17.5
Fig. 8: Sink speed Vs vertical wheel travel
[4]Daniel P. Raymer (1992). Aircraft Design: A Conceptual Approach 1st Edition, American Institute of
Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc, p229-256.
Sinking velocity=10fps
19
17
15
13
11
9
7
5
3
Stroke Length
Sinking Velocity =11 fps
[5] Joseph E. Shigley (1977). Mechanical Engineering
Design 3rd Edition, McGraw Hill, Inc., p26, 34, 37-40,
43-45, 60, 94-120, 295-313.
Sinking velocity = 9fps
1.5
2
2.5
Landing Gear Load Factor
[6]Department of Transportation, Federal Aviation
Administration (1976). Airframe and Power plant Mechanics Airframe Handbook Revised 1st Edition, Aviation Maintenance Publishers, Inc., p341-405.
3.5
Fig. 9: Vertical wheel travel Vs load factor
[7].Young ,D,E., Aircraft landing gears-The past, present and future, proceedings of the institute of mechanical engineers,vol 200,noD2,1986,pp. 75-92.
In addition, the braking forces, which act behind the
aircraft c,g., have a stabilizing effect and thus enable the
external pilot to make full use of the brakes. These factors all contribute to a shorter landing field length re-
[8]S.F.N Jenkins, Landing Gear Design and Development, Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs. Vol. 203, pp. 67-73.
476
You might also like
- An Introduction to the Longitudinal Static Stability of Low-Speed AircraftFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Longitudinal Static Stability of Low-Speed AircraftRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sumitomo SH200-3Document2 pagesSumitomo SH200-3Daman Huri75% (4)
- Manual Skygo 250Document21 pagesManual Skygo 250alejandro100% (1)
- Small Unmanned Aircraft: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandSmall Unmanned Aircraft: Theory and PracticeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Matlab Based Software For Aircraft Structural Analysis and DesignDocument11 pagesMatlab Based Software For Aircraft Structural Analysis and DesignsaadNo ratings yet
- Thesis Tail DesignDocument115 pagesThesis Tail Designtiantaufik100% (1)
- 4.torque Diagram of The WingDocument3 pages4.torque Diagram of The WingBalaji AeroNo ratings yet
- Wing Rib Stress Analysis and Design OptimizationDocument90 pagesWing Rib Stress Analysis and Design Optimizationsrikanthlaxminrayan586967% (3)
- Aircraft Dynamic Stability and Response: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesFrom EverandAircraft Dynamic Stability and Response: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Unconventional Aircraft ConceptsDocument172 pagesUnconventional Aircraft ConceptsJack Azad100% (4)
- Motion in 2 DDocument12 pagesMotion in 2 DVenesia Ayu Dewanti0% (1)
- Adp 2 FinalDocument70 pagesAdp 2 Finalrahul_vh0% (2)
- Conceptual Design of A Business Jet Airc PDFDocument6 pagesConceptual Design of A Business Jet Airc PDFHamza TurhanNo ratings yet
- Small Unmanned Fixed-wing Aircraft Design: A Practical ApproachFrom EverandSmall Unmanned Fixed-wing Aircraft Design: A Practical ApproachNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics Design AssignmentDocument11 pagesAerodynamics Design AssignmentRanggi Sahmura100% (1)
- Proadvice 3 - Aileron SizingDocument12 pagesProadvice 3 - Aileron SizingSnorri Gudmundsson100% (1)
- Simulation of Aircraft Landing Gear Dynamics Using Flexible MultibodyDocument10 pagesSimulation of Aircraft Landing Gear Dynamics Using Flexible MultibodyElvindinata100% (1)
- Hinge Moment Theoretical CalculationDocument13 pagesHinge Moment Theoretical CalculationArmghan ShabirNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Fuselage DragDocument7 pagesMinimizing Fuselage DragYvess100% (1)
- Light Aircraft DesignDocument29 pagesLight Aircraft DesignjustincosgroveNo ratings yet
- Wing Layout DesignDocument12 pagesWing Layout DesignVanCarotNo ratings yet
- Endurance GliderDocument16 pagesEndurance Gliderumunera2997100% (1)
- Schrenks MethodDocument50 pagesSchrenks MethodMukesh KarunanethyNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Stress Analysis and Structural Design Full VersionDocument20 pagesAircraft Stress Analysis and Structural Design Full VersionErhanNo ratings yet
- Section3 Flight TestDocument30 pagesSection3 Flight TestOmri AmayaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing and Struct. Analysis of A UAVDocument129 pagesManufacturing and Struct. Analysis of A UAVsaifchi555No ratings yet
- Analysis of Composite WingDocument260 pagesAnalysis of Composite WingIr AyenNo ratings yet
- Wing Rib Analysis Shear Center For 3 Stringer Closed CellDocument33 pagesWing Rib Analysis Shear Center For 3 Stringer Closed Cellpramodssg100% (1)
- Pitch StabilityDocument6 pagesPitch StabilityAirPlaneTrainMobileNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Design Approach of The Wing BoxDocument3 pagesPreliminary Design Approach of The Wing BoxWhyDirgantara IDNo ratings yet
- Wing Box - Role and LayoutDocument24 pagesWing Box - Role and LayoutNguyen Van Trong100% (2)
- NASA - Composite StructuresDocument50 pagesNASA - Composite StructuresDragomirescu Alina100% (1)
- Performance Analysis of An Aircraft Propeller1Document9 pagesPerformance Analysis of An Aircraft Propeller1Puloma DwibediNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design ReportDocument95 pagesAircraft Design ReportMayank Agrawal100% (1)
- Aircraft Design With Maneuver and Gust Load AlleviationDocument15 pagesAircraft Design With Maneuver and Gust Load AlleviationNeoNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design Project 2Document120 pagesAircraft Design Project 2Sandeep NrynNo ratings yet
- Analytic Wing and FuselageDocument55 pagesAnalytic Wing and FuselageJack100% (2)
- Aircraft Wing Rib DesigningDocument97 pagesAircraft Wing Rib DesigningNagaraj Ramachandrappa100% (1)
- Wing FencesDocument5 pagesWing FencesErnesto SousaNo ratings yet
- ME3608 Aeroelasticity #1Document31 pagesME3608 Aeroelasticity #1djtj89No ratings yet
- Background On Aircraft AerodynamicsDocument8 pagesBackground On Aircraft AerodynamicsAbdelrahman NassifNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design Project 2Document117 pagesAircraft Design Project 2Mahesh J Rao85% (13)
- A02 External LoadsDocument17 pagesA02 External LoadsNarendra PalandeNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Wing LoadsDocument55 pagesCalculation of Wing LoadsJony Oliver Lazo RamosNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Engine Attachment and Vibration ControlDocument8 pagesAircraft Engine Attachment and Vibration ControlSivaramanNo ratings yet
- C. T. Sun Mechanics of Aircraft StructuresDocument192 pagesC. T. Sun Mechanics of Aircraft StructuresYogendraKumarNo ratings yet
- ADA160718 - AGARD-R-723 - Aircraft Drag Prediction and ReductionDocument270 pagesADA160718 - AGARD-R-723 - Aircraft Drag Prediction and ReductionopedroestebanNo ratings yet
- Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams Due To Loads Along Chordwise DirectionDocument11 pagesShear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams Due To Loads Along Chordwise DirectionERÃŋkîtÇhàñdràkàr100% (1)
- Components Weight EstimatingDocument19 pagesComponents Weight Estimatingmurad_ashourNo ratings yet
- Aero 2017 CatalogDocument68 pagesAero 2017 CatalogFatih AkgülNo ratings yet
- Aermacchi Landing GearDocument10 pagesAermacchi Landing GearRahman Ehvan100% (1)
- Wing Flutter Analysis2Document23 pagesWing Flutter Analysis2Muthu VelNo ratings yet
- Wing Finite Element Analysis1Document16 pagesWing Finite Element Analysis1usakalambaNo ratings yet
- Flutter - Reducing The RiskDocument9 pagesFlutter - Reducing The RiskffontanaNo ratings yet
- Unmanned Aircraft SystemsFrom EverandUnmanned Aircraft SystemsElla AtkinsNo ratings yet
- Morphing Aerospace Vehicles and StructuresFrom EverandMorphing Aerospace Vehicles and StructuresJohn ValasekNo ratings yet
- Sense and Avoid in UAS: Research and ApplicationsFrom EverandSense and Avoid in UAS: Research and ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Design and Computational Analysis PDFDocument143 pagesDesign and Computational Analysis PDFJack AzadNo ratings yet
- Taxilian Wings Final Design Report PDFDocument33 pagesTaxilian Wings Final Design Report PDFAisha ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Modeling of A Membrane WingDocument236 pagesAerodynamic Modeling of A Membrane Wingmatthew_6No ratings yet
- 0408 PDFDocument258 pages0408 PDFRisgam PutraNo ratings yet
- RC Hovercraft Customized Remote ControlDocument16 pagesRC Hovercraft Customized Remote ControlJack AzadNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of A Ducted FN UAVDocument10 pagesConceptual Design of A Ducted FN UAVJack AzadNo ratings yet
- 06 ATA29 Hydraulics 2012Document17 pages06 ATA29 Hydraulics 2012Jack AzadNo ratings yet
- 03 ATA24 Electrics 2012Document25 pages03 ATA24 Electrics 2012Jack Azad100% (1)
- Ultra and Very Light Ducted Fan PropulsionDocument10 pagesUltra and Very Light Ducted Fan PropulsionJack Azad100% (1)
- Calculation Design Duct Ed FanDocument15 pagesCalculation Design Duct Ed FanJennyparisNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Worm and Wheel DriveDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of Worm and Wheel DriveSadeesh ManujaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Lab QuizDocument4 pagesDynamics Lab QuizSudhananda MallickNo ratings yet
- United States PatentDocument10 pagesUnited States PatentendhylakausuNo ratings yet
- RT 08 NRBC PDFDocument17 pagesRT 08 NRBC PDFAdrian García MoyanoNo ratings yet
- Rigidity and Mass Center 1480317129Document9 pagesRigidity and Mass Center 1480317129Alban Hysomemaj100% (1)
- Text Demo: Gyroscope, Tennis Racket, Old CD: Lecture 26 - Torque-Free Rotation - Body-Fixed AxesDocument5 pagesText Demo: Gyroscope, Tennis Racket, Old CD: Lecture 26 - Torque-Free Rotation - Body-Fixed Axesabhi101010No ratings yet
- Elco CatalogDocument48 pagesElco CatalogEduardo Antonio Duran SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Girbau Express Dryer KT030 SpecificationDocument1 pageGirbau Express Dryer KT030 Specificationmairimsp2003No ratings yet
- TMG E1630Document82 pagesTMG E1630hardikNo ratings yet
- Performance On Mechanics of Materials - MAE 243 (Section 002)Document18 pagesPerformance On Mechanics of Materials - MAE 243 (Section 002)Reivax50No ratings yet
- Tribology The Science of Combatting WearDocument33 pagesTribology The Science of Combatting Wearahmed titoNo ratings yet
- 2015 Logik 9 GBDocument2 pages2015 Logik 9 GBsebastianNo ratings yet
- CoverteredDocument4 pagesCoverteredSuyog GawandeNo ratings yet
- Oil Mist Manual PDFDocument34 pagesOil Mist Manual PDFWong DaNo ratings yet
- Identifying Compressor Failure Modes: Indicators, Symptoms, and CorrectionsDocument2 pagesIdentifying Compressor Failure Modes: Indicators, Symptoms, and CorrectionsElvis DiazNo ratings yet
- Kartu Riwayat AlatDocument26 pagesKartu Riwayat AlatAwaluddin HanafieNo ratings yet
- Actuators: Electromagnetic RelayDocument19 pagesActuators: Electromagnetic Relaymanjunath100% (1)
- PPTDocument25 pagesPPTPranaya NahakNo ratings yet
- A2 MECH Momentum QuestionsDocument8 pagesA2 MECH Momentum Questionsfootball_frenzy_2004No ratings yet
- Bs 8006 PDFDocument26 pagesBs 8006 PDFNaresh Sharma100% (5)
- EPC4A HUC Estimating Methodology Rev 0Document21 pagesEPC4A HUC Estimating Methodology Rev 0Amine DabbabiNo ratings yet
- 001-03 - Hydraulic Charge Pressure Switch Shorted To High SourceDocument6 pages001-03 - Hydraulic Charge Pressure Switch Shorted To High Sourceكؤمپيوته رى ديارىNo ratings yet
- ASTM A193-A193M-04cDocument12 pagesASTM A193-A193M-04cNadhiraNo ratings yet
- Panasonic Conduits PDFDocument1 pagePanasonic Conduits PDFAirvin John PalacioNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineer-Syed Zain AliDocument3 pagesMechanical Engineer-Syed Zain AliSyed Zain AliNo ratings yet
- Research GateDocument34 pagesResearch GateMustafa ÇakırNo ratings yet
- 19 - Dowel BarsDocument22 pages19 - Dowel BarsboyzesNo ratings yet