Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BPMN 2.0 Poster
BPMN 2.0 Poster
Uploaded by
vedran188Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BPMN 2.0 Poster
BPMN 2.0 Poster
Uploaded by
vedran188Copyright:
Available Formats
BPMN 2.
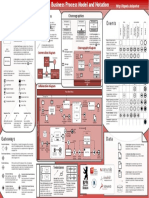
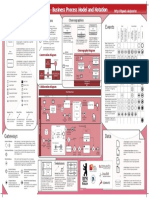
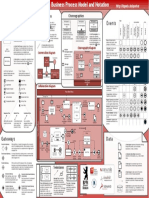
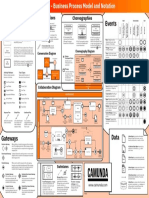
0 - Business Process Model and Notation
An Event Sub-Process is placed into a Process or
Sub-Process. It is activated when its start event
gets triggered and can interrupt the higher level
process context or run in parallel (noninterrupting) depending on the start event.
Event
Sub-Process
Choreography Diagram
Conversation Diagram
Communication
Choreography
Task
Participant B
Participant B
Participant A
Pool
(collapsed)
Choreography
Task
Participant A
Types specify the nature of
the action to be performed:
Sub-Process Marker
Send Task
Loop Marker
Receive Task
Parallel MI Marker
User Task
Sequential MI Marker
Manual Task
Ad Hoc Marker
Business Rule Task
Compensation Marker
Service Task
Pool
(collapsed)
Participant B
Participant C
Message Flow
has a condition
assigned that defines
whether or not the
flow is used.
Receive Task
Timer
Intermediate
Event
Event Sub-Process
Conditional
Start Event
Parallel
Link
Intermediate Multiple
Intermediate
Event
Event
Inclusive Gateway
When splitting, one or more
branches are activated. All
active incoming branches must
complete before merging.
Exclusive Event-based Gateway
(instantiate)
Each occurrence of a subsequent
event starts a new process
instance.
Complex Gateway
Complex merging and
branching behavior that is not
captured by other gateways.
Parallel Event-based Gateway
(instantiate)
The occurrence of all subsequent
events starts a new process
instance.
Task
Task
Attached
Intermediate
Error Event
Error End
Event
Manual Task
Task
Multiple: Catching one out of
a set of events. Throwing all
events defined
Parallel Multiple: Catching
all out of a set of parallel
events.
Signal
End
Event
Link
Intermediate
Event
Throwing
Group
Swimlanes
Data
Multi Instance
Task (Parallel)
Call Activity
End
Event
Terminate: Triggering the
immediate termination of a
process.
Collection
Text Annotation
condition
Looped
Sub-Process
Start
Event
Is always followed by catching events or receive tasks.
Sequence flow is routed to the subsequent event/task
which happens first.
When used to split the sequence flow, all outgoing
branches are activated simultaneously. When merging
parallel branches it waits for all incoming branches to
complete before triggering the outgoing flow.
Escalation
End Event
Sub-Process
Data
Store
Signal: Signalling across different processes. A signal thrown
can be caught multiple times.
End
Event
Data Object
Lane
Parallel Gateway
Task
Message
Start Event
Lane
Event-based Gateway
When splitting, it routes the sequence flow to exactly
one of the outgoing branches. When merging, it awaits
one incoming branch to complete before triggering the
outgoing flow.
Event-based
Gateway
Attached
Intermediate
Timer Event
Input
Send Task
Exclusive
Gateway
Parallel
Gateway
Task
Output
Message
End Event
Pools (Participants) and Lanes
represent responsibilities for
activities in a process. A pool
or a lane can be an
organization, a role, or a
system. Lanes subdivide pools
or other lanes hierarchically.
Message Flow
symbolizes information
flow across organizational
boundaries. Message flow
can be attached to pools,
activities, or message
events.
The order of message
exchanges can be
specified by combining
message flow and
sequence flow.
A Data Input is an external input for the
entire process. It can be read by an activity.
A Data Output is a variable available as result
of the entire process.
A Data Object represents information flowing
through the process, such as business
documents, e-mails, or letters.
A Collection Data Object represents a
collection of information, e.g., a list of order
items.
Pool
Exclusive Gateway
Collapsed
Sub-Process
Lane
Gateways
Compensation: Handling or
triggering compensation.
Ad-hoc Sub-Process
Conditional Flow
is the default branch
to be chosen if all
other conditions
evaluate to false.
Cancel: Reacting to cancelled
transactions or triggering
cancellation.
Pool (Collapsed)
Pool (Expanded)
defines the execution
order of activities.
Error: Catching or throwing
named errors.
Collaboration Diagram
Lane
Default Flow
Link: Off-page connectors.
Two corresponding link events
equal a sequence flow.
Sub-Conversation
Script Task
Sequence Flow
Choreography
Task
Participant C
Response
Message
Multi Instance Pool
(collapsed)
Conditional: Reacting to
changed business conditions
or integrating business rules.
Pool
Markers indicate execution
behavior of activities:
Escalation: Escalating to
an higher level of
responsibility.
Pool
Task Types
None: Untyped events,
indicate start point, state
changes or final states.
Timer: Cyclic timer events,
points in time, time spans or
timeouts.
Participant A
Initiating
Message
End
Message: Receiving and
sending messages.
Participant A
Participant B
Activity Markers
A Choreography SubProcess contains a refined
choreography with several
Interactions.
Boundary NonInterrupting
denotes a set of
Participants of the
same kind.
Boundary
Interrupting
Multiple Participants Marker
Intermediate
Catching
A Choreography Task
represents an Interaction
(Message Exchange)
between two Participants.
A Forked Conversation Link connects
Communications and multiple
Participants.
A Call Activity is a wrapper for a globally defined
Sub-Process or Task that is reused in the current
process.
Call Activity
Participant B
Participant C
Participant B
A Conversation Link connects
Communications and Participants.
A Transaction is a set of activities that logically
belong together; it might follow a specified
transaction protocol.
Transaction
Choreography
Task
Start
Event Sub-Process
Non-Interrupting
Task
Events
Choreography
Sub-Process
Participant A
A Communication defines a set of
logically related message exchanges.
When marked with a
symbol it
indicates a Sub-Conversation, a
compound conversation element.
A Task is a unit of work, the job to be
performed. When marked with a
symbol
it indicates a Sub-Process, an activity that can
be refined.
Participant A
Event Sub-Process
Interrupting
Activities
Choreographies
Top-Level
Conversations
http://bpmb.de/poster
Data Store
A Data Store is a place where the process can
read or write data, e.g., a database or a filing
cabinet. It persists beyond the lifetime of the
process instance.
A Message is used to depict the contents of a
communication between two Participants.
You might also like
- Accenture Professional Services IndustryDocument32 pagesAccenture Professional Services IndustryEsayas DeguNo ratings yet
- Google Letters To Shareholders (ALL)Document108 pagesGoogle Letters To Shareholders (ALL)José Díaz OropezaNo ratings yet
- Manage Multiple ProjectDocument5 pagesManage Multiple ProjectaskyeungNo ratings yet
- Discovering Customer Journey Maps Using A Mixture of Markov ModelsDocument25 pagesDiscovering Customer Journey Maps Using A Mixture of Markov ModelsYou Be ManompoZanaharyNo ratings yet
- Drift Conversational Marketing BlueprintDocument31 pagesDrift Conversational Marketing BlueprintunomynameNo ratings yet
- Pragmatic Marketer: Volume 6, Issue 4Document32 pagesPragmatic Marketer: Volume 6, Issue 4Pragmatic MarketingNo ratings yet
- LandingAI Playbook AI-Transformation Playbook 2Document5 pagesLandingAI Playbook AI-Transformation Playbook 2tantaliz3rNo ratings yet
- This I Know: Marketing Lessons from Under the InfluenceFrom EverandThis I Know: Marketing Lessons from Under the InfluenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Bpmn2 0 Poster enDocument1 pageBpmn2 0 Poster enTubora100% (1)
- CB Insights What Is 5GDocument38 pagesCB Insights What Is 5GShailaja UdtewarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Implementation Work EbookDocument10 pagesAdobe Implementation Work Ebookapi-581667744No ratings yet
- WEF National AI StrategyDocument20 pagesWEF National AI Strategyirahta randoNo ratings yet
- 12 Books in One HourDocument33 pages12 Books in One Hourshahmed999No ratings yet
- Job Readiness: by Vedant DahibawkarDocument7 pagesJob Readiness: by Vedant Dahibawkarvedant100% (1)
- How To Implement Intelligent AutomationDocument26 pagesHow To Implement Intelligent AutomationJiaJien LeongNo ratings yet
- Product Launch PlaybookDocument1 pageProduct Launch PlaybookStella NguyenNo ratings yet
- Making Technology Investments Profitable: ROI Road Map from Business Case to Value RealizationFrom EverandMaking Technology Investments Profitable: ROI Road Map from Business Case to Value RealizationRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Applying Goldratt S Theory of ConstraintDocument12 pagesApplying Goldratt S Theory of ConstraintvictorNo ratings yet
- One-to-One Personalization in the Age of Machine Learning: Harnessing Data to Power Great Customer ExperiencesFrom EverandOne-to-One Personalization in the Age of Machine Learning: Harnessing Data to Power Great Customer ExperiencesNo ratings yet
- Mind+Machine: A Decision Model for Optimizing and Implementing AnalyticsFrom EverandMind+Machine: A Decision Model for Optimizing and Implementing AnalyticsNo ratings yet
- BPMN 2.0 - Business Process Model and Notation Innovator For Business AnalystsDocument1 pageBPMN 2.0 - Business Process Model and Notation Innovator For Business Analystssauloarvelos58167% (3)
- The Automated EnterpriseDocument20 pagesThe Automated EnterpriseLarry Eduardo Figueroa BarrazaNo ratings yet
- Developing A Product Team Checklist by ProductPlanDocument5 pagesDeveloping A Product Team Checklist by ProductPlanMohammad AmirNo ratings yet
- Product Portfolio ManagementDocument4 pagesProduct Portfolio ManagementAna Maria Spasovska100% (1)
- Conversations Choreographies: BPMN 2.0 - Business Process Model and NotationDocument1 pageConversations Choreographies: BPMN 2.0 - Business Process Model and NotationOswaldo MendietaNo ratings yet
- Bain New Rules For M&a in Consumer ProductsDocument12 pagesBain New Rules For M&a in Consumer Productsm_vullingsNo ratings yet
- Business IT Alignment From Business Model To Enterprise ArchitectureDocument12 pagesBusiness IT Alignment From Business Model To Enterprise ArchitectureJuan Carlos Mejia100% (1)
- The Executive Guide To Artificial Intelligence Burgess en 34606Document5 pagesThe Executive Guide To Artificial Intelligence Burgess en 34606Leslie Dhanaraj100% (1)
- Next-best-action marketing A Complete GuideFrom EverandNext-best-action marketing A Complete GuideRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Reflection On Innovation and ChangeDocument2 pagesReflection On Innovation and Changeapi-329102110No ratings yet
- Course Outline-English For Business Studies-Anh228de01Document8 pagesCourse Outline-English For Business Studies-Anh228de01Vũ Nguyễn Xuân NhiNo ratings yet
- Collections Credit Cards Workflow PDFDocument1 pageCollections Credit Cards Workflow PDFBea LadaoNo ratings yet
- Ewsd v16Document11 pagesEwsd v16Eugen BleulerNo ratings yet
- Scaling Laws For Neural Language ModelsDocument30 pagesScaling Laws For Neural Language ModelsMarcos CostaNo ratings yet
- Data Teams: A Unified Management Model for Successful Data-Focused TeamsFrom EverandData Teams: A Unified Management Model for Successful Data-Focused TeamsNo ratings yet
- The ROI of Optimizing Product ManagementDocument6 pagesThe ROI of Optimizing Product Managementicrapper100% (1)
- Design Principles for Process-driven Architectures Using Oracle BPM and SOA Suite 12cFrom EverandDesign Principles for Process-driven Architectures Using Oracle BPM and SOA Suite 12cNo ratings yet
- Visual Auditory Kinaesthetic PDFDocument10 pagesVisual Auditory Kinaesthetic PDFSelvi TamaraNo ratings yet
- Business Case Example - 2Document4 pagesBusiness Case Example - 2Rupert UlepNo ratings yet
- Analytics Reference AdobeDocument333 pagesAnalytics Reference Adobenandan100% (3)
- The Pragmatic FrameworkDocument1 pageThe Pragmatic FrameworkZNo ratings yet
- Director Program Project Management IT in Denver CO Resume John MalyDocument3 pagesDirector Program Project Management IT in Denver CO Resume John MalyJohnMalyNo ratings yet
- The Forrester Wave™ - Robotic Process Automation, Q4 2019Document22 pagesThe Forrester Wave™ - Robotic Process Automation, Q4 2019AJAY KUMAR THAKURNo ratings yet
- What Are Typical Commissions For A Value Added Reseller For A SaaS Product - QuoraDocument3 pagesWhat Are Typical Commissions For A Value Added Reseller For A SaaS Product - QuoraEbookintheplaceNo ratings yet
- Process Level of PerformanceDocument16 pagesProcess Level of PerformanceRenato GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chordiant Next-Best-Action Marketing White PaperDocument20 pagesChordiant Next-Best-Action Marketing White PaperDeepinder Singh DhingraNo ratings yet
- Article - Forget Strategy Focus On Operating Models PDFDocument4 pagesArticle - Forget Strategy Focus On Operating Models PDFParas DhamaNo ratings yet
- BMP TutorialDocument15 pagesBMP TutorialFarhan AhmadNo ratings yet
- What Is Event StormingDocument5 pagesWhat Is Event Stormingjuanmarl73No ratings yet
- Board Training ManualDocument221 pagesBoard Training ManualreidrenNo ratings yet
- BPMN 2.0 Poster ENDocument1 pageBPMN 2.0 Poster ENJony SilvaNo ratings yet
- Activities Events: Conversations ChoreographiesDocument1 pageActivities Events: Conversations ChoreographiesMoataz BelkhairNo ratings yet
- BPMN2 0 Poster EN 2021Document1 pageBPMN2 0 Poster EN 2021markokuszNo ratings yet
- BPMN2 0 Poster NL PDFDocument1 pageBPMN2 0 Poster NL PDFBasNo ratings yet
- RPH M5Document13 pagesRPH M5skmempaga090No ratings yet
- Event Planning ProposalDocument2 pagesEvent Planning ProposalJake BatacNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Mgt162 ObeDocument4 pagesSyllabus Mgt162 Obennisa_8No ratings yet
- Accommodations For Dyslexic Young LearnerDocument7 pagesAccommodations For Dyslexic Young LearnerArief NugrahaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Approaches and Methods in Language TeachingDocument2 pagesThe Nature of Approaches and Methods in Language TeachingAlicia Cáceres0% (1)
- 25 PS 007 Polomolok Creek IS Lapid Kathy BDocument40 pages25 PS 007 Polomolok Creek IS Lapid Kathy BRobert Kier Tanquerido TomaroNo ratings yet
- Individual Teacher User Guide ENDocument37 pagesIndividual Teacher User Guide ENMariel Estela Silia CornelioNo ratings yet
- Development Plan 21 22Document2 pagesDevelopment Plan 21 22Duhannie Marie Duranza100% (1)
- The Benefits of Learning A Foreign LanguageDocument2 pagesThe Benefits of Learning A Foreign LanguageUnkown WetlordNo ratings yet
- Types of Media and Media EffectsDocument19 pagesTypes of Media and Media EffectsJumar Divinagracia DimpasNo ratings yet
- School of Saint Anthony: A Comparative Study On The Effectiveness of Classroom Instruction in Selected Grade 7 SectionsDocument32 pagesSchool of Saint Anthony: A Comparative Study On The Effectiveness of Classroom Instruction in Selected Grade 7 SectionsAloisia Rem RoxasNo ratings yet
- Advertisment Evaluation MethodsDocument4 pagesAdvertisment Evaluation MethodsMathew JcNo ratings yet
- Lesson A: Review of Simple Present Be: Unit 1 PeopleDocument1 pageLesson A: Review of Simple Present Be: Unit 1 PeopleVinicius DennysNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 AssignmentDocument10 pagesUnit 5 AssignmentSolver TutorNo ratings yet
- Air Col Purcomm Session 01Document34 pagesAir Col Purcomm Session 01Khim CofuentesNo ratings yet
- Hathway InternetDocument3 pagesHathway InternetSaurab RaoNo ratings yet
- Audio Lingual MethodDocument13 pagesAudio Lingual MethodAinun FahiraNo ratings yet
- FYPC - 2012: WelcomesDocument25 pagesFYPC - 2012: WelcomesWaqasNo ratings yet
- DM Assignment - 211202046Document21 pagesDM Assignment - 211202046Muktha NayakNo ratings yet
- Ariane CotDocument5 pagesAriane CotAriane Grace LopezNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Account and Report WritingDocument2 pagesDifference Between Account and Report WritingSabina Saba100% (3)
- Public Relations and Social MediaDocument11 pagesPublic Relations and Social MediaPetar MilosavljevićNo ratings yet
- Scope of Ict in Future EducationDocument5 pagesScope of Ict in Future EducationMundiarti MundiartiNo ratings yet
- Company Feedback From AlumniDocument32 pagesCompany Feedback From AlumnisravanbrahmaNo ratings yet