Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern Tala
NCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern Tala
Uploaded by
christineleesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern Tala
NCP Ineffective Breathing Pattern Tala
Uploaded by
christineleesCopyright:
Available Formats
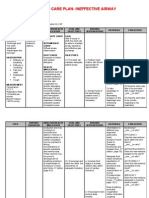
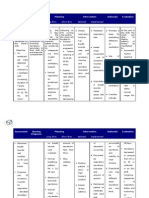
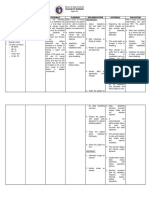
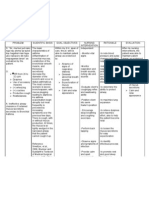
NURSING CARE PLAN
Nursing Problem
Cues
Analysis
Goal/Objectives
Nursing
Interventions
Rationale
Evaluatio
n
Nursing Diagnosis:
Ineffective
Breathing Pattern is
defined as
inspiration and/or
expiration that do
not provide
adequate
ventilation.
Goal:
After 8 hours of
nursing
intervention, the
client will be able to:
a) Monitor vital
signs
a) These signs,
which should be
looked at in
total, are
checked to
monitor
functions of the
body. The signs
reflect changes
in function that
otherwise might
not be
observed.
The client
was able
reestablish
Ineffective Breathing
Pattern secondary to
community acquired
pneumonia as
manifested by
alterations in depth
of breathing.
Subjective:
Nahihirapan
huminga yung baby
ko, may halak daw
kasi siya. Verbalized
by the clients
mother.
Objective:
-
Use of
accessory
muscles
Labored
breathing
A dyspneic person
often appears
anxious and may
experience
shortness of
breath, a feeling of
being unable to get
enough air.
Dyspnea have
many causes, most
of which stem from
cardiac and
respiratory
disorders. It is a
Reestablish
and maintain
effective
respiratory
pattern via
oxygen
administration
thru nasal
cannula
without the use
of accessory
muscles and
other signs of
hypoxia
Objectives:
After 2 hours of
nursing
intervention, the
b) Assess
respiratory rate,
rhythm and
depth
c) Assess for
pain/discomfort
d) Administer O2
regulated at 2
lpm via nasal
cannula as
ordered and
administer
b) Respiratory
rate and rhythm
changes are
early warning
signs of
impending
respiratory
difficulties
c) That may
restrict
and
maintain
effective
respiratory
pattern via
oxygen
administrati
on thru
nasal
cannula
without the
use the use
of
accessory
muscles
and other
signs of
hypoxia
Restlessness
Measurement:
T: 36C
RR: 68 cpm
PR: 125 bpm
subjective feeling
as it cannot be
directly observed
but is reported by
the client. (Kozier,
Vol. 2, 7th Ed., p.
1346)
client will be able to:
Maintain
normal vital
signs
prescribed
respiratory
medications
respiratory
effort
d) For
management of
underlying
pulmonary
condition and
respiratory
distress
You might also like
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternruguNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageNCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeRryje Salleva100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternReichelle Perlas62% (13)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument7 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternKrisJane Ratilla Abiva100% (2)
- Ncp-Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNcp-Ineffective Breathing PatternRoxanne Ganayo Claver100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Patternimneverwrong249280% (5)
- NCP-Ineffective AirwayDocument5 pagesNCP-Ineffective Airwayjava_biscocho1229No ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaKullin Rain100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJoy Arizala CarasiNo ratings yet
- Prioritization of Nursing ProblemsDocument1 pagePrioritization of Nursing ProblemsAbigail Lonogan100% (2)
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaAngel Cabatingan100% (4)
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeKen Simon100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAdelaine LorestoNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDDocument7 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDMa. Elaine Carla Tating67% (3)
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisFatima Zainab Matlih IdjiraniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway Clearancearlee marquez96% (118)
- NCP For AsthmaDocument1 pageNCP For AsthmaMelvin Martinez100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern - NCPDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern - NCPHsintan HsuNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearancejomerdalonaNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeGabriel Tolentino70% (10)
- SAMPLE NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 pagesSAMPLE NCP For Pneumoniakana_mercado100% (6)
- Pneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesPneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceNursesLabs.com86% (7)
- POC Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pagePOC Ineffective Breathing Patterncuicuita100% (1)
- NCP-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument13 pagesNCP-Ineffective Airway ClearancePaulo Manlangit86% (22)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearanceniomi0884% (31)
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (3)
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP - Impaired Gas Exchangejanelee2824No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionTrixie Anne GamotinNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeNader AbdurasadNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternEds Sy50% (4)
- NCP - Difficulty of BreathingDocument2 pagesNCP - Difficulty of BreathingTarquin Tomada33% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezNo ratings yet
- NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNCP For PneumoniaKahMallari100% (10)
- College of Nursing: Independent: That Would Cause Breathing Respiratory Ailments in GeneralDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Independent: That Would Cause Breathing Respiratory Ailments in GeneralChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument3 pagesNursing DiagnosisPuspita DiahNo ratings yet
- Competencymr McdougalcopdDocument17 pagesCompetencymr Mcdougalcopdmac_rymrt7569No ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPBeverLyNo ratings yet
- NCP Kochs2Document2 pagesNCP Kochs2Ava VierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKoleen KirstenNo ratings yet
- Myrna CruzDocument3 pagesMyrna CruzChris Opal NamocatcatNo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAbegail Abaygar100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanmariasomorayNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Ncps FinalDocument13 pagesCase Pres Ncps FinalMariejoy YadaoNo ratings yet
- 7 NCPDocument7 pages7 NCPVina EmpialesNo ratings yet
- Time Chart: Data Action ResponseDocument2 pagesTime Chart: Data Action ResponseAziil Liiza100% (2)
- Chapter 29: Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases Test BankDocument15 pagesChapter 29: Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases Test BankBriseidaSolisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Careplan #1Document15 pagesNursing Careplan #1aninNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternChristianmel JavierNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nanda DiagnosesDocument4 pagesAsthma Nanda DiagnosesZinya RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Incentive SpirometryDocument6 pagesIncentive SpirometryRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- 2 NCPDocument2 pages2 NCPJohn CenasNo ratings yet
- Revised NCP (Baiae)Document9 pagesRevised NCP (Baiae)Jennifer BactatNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Times Delhi 21 - 6Document44 pagesHindustan Times Delhi 21 - 6Hmbe hmbeNo ratings yet
- MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesMetronidazolehauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- POLIOMYELITISDocument26 pagesPOLIOMYELITISIzhra Margate100% (1)
- Test 5 - Oral Surgery, Oral Diagnosis & RoentgenologyDocument6 pagesTest 5 - Oral Surgery, Oral Diagnosis & Roentgenologydr.jah9No ratings yet
- Of Burning Fat: While You SleepDocument16 pagesOf Burning Fat: While You SleepMcel PadiernosNo ratings yet
- Health Anxiety Inventory HAI 18 PDFDocument3 pagesHealth Anxiety Inventory HAI 18 PDFIonelia PașaNo ratings yet
- Direct OphthalmosDocument22 pagesDirect OphthalmosTiti Multi SaariNo ratings yet
- Micropara CompilationDocument101 pagesMicropara Compilation2140916No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing (Group 1) - 92 QuestionDocument36 pagesFundamentals of Nursing (Group 1) - 92 QuestionTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (13)
- Student Assessment Booklet-I: CHCCC S025 Support Relationships With Carers and FamiliesDocument24 pagesStudent Assessment Booklet-I: CHCCC S025 Support Relationships With Carers and FamiliesIkhsan Misbahuddin80% (5)
- TOB Ad NationalDocument8 pagesTOB Ad Nationalmuhdm7771No ratings yet
- Standard: For Producing Hygienically Clean Reusable Textiles For Use in The Food and Beverage Industry (Apparel)Document20 pagesStandard: For Producing Hygienically Clean Reusable Textiles For Use in The Food and Beverage Industry (Apparel)Linda Setya WatiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Endocrine NeoplasiaDocument10 pagesMultiple Endocrine NeoplasiacarmenNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome - UpToDateDocument13 pagesJuvenile Polyposis Syndrome - UpToDateHartemes RosarioNo ratings yet
- Aphasia and Aphasic Syndromes, Neurourology Rehabilitation PDFDocument19 pagesAphasia and Aphasic Syndromes, Neurourology Rehabilitation PDFTahysse Andrea Varela SilvaNo ratings yet
- List of Culture Media Used in Microbiology With Their UsesDocument7 pagesList of Culture Media Used in Microbiology With Their UsesImmu JiNo ratings yet
- Heliyon: Joseph Kiambi Mworia, Cromwell Mwiti Kibiti, Mathew Piero Ngugi, Joseph Ngari NgeranwaDocument8 pagesHeliyon: Joseph Kiambi Mworia, Cromwell Mwiti Kibiti, Mathew Piero Ngugi, Joseph Ngari NgeranwaSiti Arum WidiyantiNo ratings yet
- National TB Control ManualDocument223 pagesNational TB Control ManualTrishenth FonsekaNo ratings yet
- Hartz Ell 2005Document3 pagesHartz Ell 2005Mohie Eddine BoudiaNo ratings yet
- Book Reviews SampleDocument14 pagesBook Reviews SampleJohn Rey JumauayNo ratings yet
- Jan 2022 NewsletterDocument10 pagesJan 2022 Newsletterapi-310272078No ratings yet
- (Hedwig Weiß MPhil., Florian Prinz (Auth.) ) OccupDocument197 pages(Hedwig Weiß MPhil., Florian Prinz (Auth.) ) OccupjoseNo ratings yet
- Summary of Workplace Injury, Illness and Fatality StatisticsDocument52 pagesSummary of Workplace Injury, Illness and Fatality Statisticspankaj DevrariNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Swallow Infantile and AdultDocument2 pagesAbnormal Swallow Infantile and Adultfinix33No ratings yet
- PE 12, (HOPE3) Q2, Module 2, Lesson 5 FinalDocument25 pagesPE 12, (HOPE3) Q2, Module 2, Lesson 5 FinalRex Chambers LadaoNo ratings yet
- Distonía Del Guitarrista: Tratamiento Con Reeducación SensorialDocument4 pagesDistonía Del Guitarrista: Tratamiento Con Reeducación SensorialSara M.No ratings yet
- Mimay MimaropaDocument1 pageMimay MimaropaErrol LlanesNo ratings yet
- FHO - One Pager - Version 1.1 - MayDocument2 pagesFHO - One Pager - Version 1.1 - MaySakshi Jain50% (2)
- Padzi 1: Vacci Ne # Dose 1 Dose Rou Te SiteDocument8 pagesPadzi 1: Vacci Ne # Dose 1 Dose Rou Te SiteMarga AlvarezNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument28 pagesSchizophreniaSathish Rajamani100% (1)