Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Time Chart: Data Action Response
Uploaded by
Aziil Liiza100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
6K views2 pages1) The patient presented with ineffective airway clearance related to tuberculosis as evidenced by an abnormal respiratory rate of 30 breaths per minute.
2) Nursing interventions included assessing vital signs and respiratory characteristics every 2 hours, administering supplemental oxygen and prescribed medications, maintaining humidified oxygen, and positioning the patient.
3) After 2 hours, the patient was able to maintain airway patency and improve clearance as evidenced by a normal respiratory rate.
Original Description:
Original Title
fdar charting 1 oct12
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The patient presented with ineffective airway clearance related to tuberculosis as evidenced by an abnormal respiratory rate of 30 breaths per minute.
2) Nursing interventions included assessing vital signs and respiratory characteristics every 2 hours, administering supplemental oxygen and prescribed medications, maintaining humidified oxygen, and positioning the patient.
3) After 2 hours, the patient was able to maintain airway patency and improve clearance as evidenced by a normal respiratory rate.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
6K views2 pagesTime Chart: Data Action Response
Uploaded by
Aziil Liiza1) The patient presented with ineffective airway clearance related to tuberculosis as evidenced by an abnormal respiratory rate of 30 breaths per minute.
2) Nursing interventions included assessing vital signs and respiratory characteristics every 2 hours, administering supplemental oxygen and prescribed medications, maintaining humidified oxygen, and positioning the patient.
3) After 2 hours, the patient was able to maintain airway patency and improve clearance as evidenced by a normal respiratory rate.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Time Chart
7:00-3:00 am F> Ineffective airway clearance related to the disease process of Tuberculosis
as evidenced by abnormal respiratory rate of 30 count per minute
D> Received with an intact IVF of PNSS @ 1L x KVO with a side drip of D5W 1L
x 16 @ 500 cc level; with productive cough; “nahihirapan akong huminga”
A> Assessed VS and characteristic of respirations at least every 2 hours.
Noted chest movement; use of accessory muscles during respiration. Noted
ability to expectorate mucus and cough effectively. Administered
supplemental oxygen as prescribed. Administered prescribed TB
medications, bronchodilators, steroids, mucolytics, and antiprexial
medications. Maintained humidified oxygen as prescribed. Elevated the head
of the bed and assumed semi-fowler’s position. Instructed of the proper
ways of coughing and breathing exercises. Educated to do optimal
positioning; use of pillow or hand splints when coughing; use of abdominal
muscles for more forceful cough
R> After 2 hours of nursing intervention, the patient was able to maintain
airway patency and improve airway clearance as evidenced by normal
respiration.
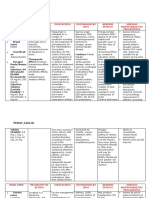
DATA GOALS/ ACTION/ NURSING RATIONALE RESPONSE &
Expected outcomes INTERVENTIONS EVALUATION
Subjective findings: STG: within Dxtc: After __8____hr/s of
-“nahihirapan akong ___2___hour/s of NI Assessed the To assist in creating NI, the patient was
huminga” as verbalized the patient will be able patient’s VS and an accurate able to
by the patient to characteristic of diagnosis and Maintain airway
maintain airway respirations at least monitor patency and improved
Objective findings: patency and improve every 2 hours effectiveness of airway clearance as
-vital signs as follows: T- airway clearance as medical treatment manifested by normal
38.2C, PR- 116 bpm, manifested/evidenced Noted chest Use of accessory respiratory rate
RR-30 cpm, BP- 130/80 by: respiratory rate movement; use of muscles of between 12-20 counts
mmHg, SPO2- 90% between normal range accessory muscles respiration may per minute
-productive cough of 12-20 cpm during respiration occur in response to STG: fully/partially/un
LTG: after _3__days of ineffective ventilation MET
Focus/ Nursing Dx: NI the patient will be Expectoration may
(PE/S) able to: expectorate Noted ability to be difficult when
-Ineffective airway secretions without expectorate mucus secretions are very After ___8___hr/s of
clearance related to the assistance and identify and cough thick as a result of NI, the patient was
disease process of potential complications effectively infection which may able to expectorate
Tuberculosis as and initiate appropriate require further secretions without
evidenced by abnormal actions as manifested intervention assistance and
respiratory rate of 30 by: normal respiration identified potential
count per minute and oxygen saturation Txc: To help clear thick complications and
through applying proper Performed phlegm that the initiated appropriate
way of coughing and suctioning of patient is unable to actions
breathing exercises secretions as expectorate as manifested by
necessary To increase the normal respiration and
Administered oxygen level and oxygen saturation
supplemental achieve an SPO2 through applying
oxygen as value at least 94% proper way of
prescribed A variety of coughing and
Administered medications are breathing exercises
prescribed TB prepared to manage STG: fully/partially/un
medications, specific problems. MET
bronchodilators, Most promote
steroids, mucolytics, clearance of airway
and antiprexial secretions and may
medications reduce airway
resistance
Increasing humidity
Maintained of inspired air will
humidified oxygen reduce thickness of
as prescribed secretions and aid
their removal
Head elevation and
proper positioning
Elevated the head of help improve the
the bed and assisted expansion of the
the patient to lungs, enabling the
assume semi- patient to breathe
fowler’s position more effectively
Edx: To help remove
Instructed the patient secretions and to
of the proper ways of promote oxygenation
coughing and before controlled
breathing exercises coughing
Educated the patient The proper sitting
in optimal position and splinting
positioning; use of of the abdomen
pillow or hand splints promote effective
when coughing; use coughing by
of abdominal increasing
muscles for more abdominal pressure
forceful cough and upward
diaphragmatic
movement.
Controlled coughing
methods help
mobilize secretions
from smaller airways
to larger airways
because the
coughing is done at
varying time
You might also like
- FDARDocument2 pagesFDARCharlayne Anne40% (5)
- Character, Onset, Location, Duration, Severity, Pattern and Associated - FactorsDocument1 pageCharacter, Onset, Location, Duration, Severity, Pattern and Associated - FactorsJohn CuencoNo ratings yet
- FdarDocument1 pageFdarEloisa Claire DayananNo ratings yet
- Nursing Documentation Template for Abdominal Pain and FeverDocument1 pageNursing Documentation Template for Abdominal Pain and FeverKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- D Received Patient Sitting On Bed With Bottle # 1DDocument24 pagesD Received Patient Sitting On Bed With Bottle # 1DMai Love100% (4)
- Hyperthermia: Date/Hour Focus Progress NotesDocument11 pagesHyperthermia: Date/Hour Focus Progress NotesCai Sumayod Delloro100% (3)
- D-Patient Verbalized "Sakit Gyod Akong Tiyan", Pain: Sample 1Document29 pagesD-Patient Verbalized "Sakit Gyod Akong Tiyan", Pain: Sample 1jaypee100% (3)
- Patient history and assessments for care planningDocument5 pagesPatient history and assessments for care planningmikrobyo_ng_wmsu100% (3)
- FDAR (Sample)Document3 pagesFDAR (Sample)Zarah Joy Tabuyan88% (17)
- Difficulty Breathing, Cough, Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesDifficulty Breathing, Cough, Discharge PlanSoleil Maxwell100% (1)
- Patient Discharge SummaryDocument4 pagesPatient Discharge SummaryJulliza Joy PandiNo ratings yet
- Lester Fdar MarchDocument4 pagesLester Fdar MarchLeanne Joie LozanoNo ratings yet
- D F-Elevated Blood Pressure DDocument2 pagesD F-Elevated Blood Pressure DMenly SusadaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Focus Charting for Mary Jane TulabotDocument2 pagesNursing Focus Charting for Mary Jane TulabotJane Umali Tulabot83% (6)
- Nurses Progress Notes for Kaoru T. PasyenteDocument3 pagesNurses Progress Notes for Kaoru T. PasyenteAndrea Marie Sevilla100% (1)
- FDARDocument5 pagesFDARKris TejereroNo ratings yet
- FDAR Ineffective Breathing Pattern ManaoisDocument2 pagesFDAR Ineffective Breathing Pattern ManaoisDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- D Received Patient Sitting On Bed With Bottle #Document17 pagesD Received Patient Sitting On Bed With Bottle #jaypee100% (2)
- Fdar Charting and Discharge PlanningDocument2 pagesFdar Charting and Discharge PlanningFaine Angela Caones100% (1)
- Risk for Infection r/t Knowledge DeficitDocument3 pagesRisk for Infection r/t Knowledge DeficitcattleyaNo ratings yet
- Post-Op Monitoring and Comfort MeasuresDocument2 pagesPost-Op Monitoring and Comfort MeasuresRoxanne Ganayo ClaverNo ratings yet
- Fdar (March 4-5)Document4 pagesFdar (March 4-5)Darlyn AmplayoNo ratings yet
- FDARDocument1 pageFDARjesabel_caraigNo ratings yet
- FDAR ChartingDocument3 pagesFDAR ChartingCarol Neng Calupitan100% (1)
- SAMPLE FDAR CHARTING PainDocument1 pageSAMPLE FDAR CHARTING PainjpmNo ratings yet
- Date/Time Focus Progress Notes: Charisse Dl. LimosDocument6 pagesDate/Time Focus Progress Notes: Charisse Dl. LimosCharisse Limos100% (6)
- Focus charting SEODocument15 pagesFocus charting SEOHarley Justiniani Dela Cruz25% (4)
- Fdar 2Document4 pagesFdar 2Raidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- FdarDocument33 pagesFdarTatiana's Couture100% (2)
- FDARDocument1 pageFDARCzar BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Time Chart: Data Action ResponseDocument2 pagesTime Chart: Data Action ResponseAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Improving Nutrition Through Nursing InterventionsDocument2 pagesImproving Nutrition Through Nursing InterventionsAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Date Focus Data, Action, Response: 9/07/20 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument2 pagesDate Focus Data, Action, Response: 9/07/20 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasePrince Rupee GonzalesNo ratings yet
- FDAR Chart - CamahalanDocument1 pageFDAR Chart - CamahalanCamahalan, Johnry G.100% (1)
- Fdar Samples PresentationDocument29 pagesFdar Samples PresentationAnnette Aquino Guevarra100% (2)
- FDAR Charting - Docx3Document1 pageFDAR Charting - Docx3jennylyn guadalupeNo ratings yet
- Grand Case Pres FDARDocument11 pagesGrand Case Pres FDARMika SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Fdarcharting 120314214902 Phpapp02Document5 pagesFdarcharting 120314214902 Phpapp02John Louie SolitarioNo ratings yet
- FDAR CHARTING POSTPARTUM, Nurse's Progress NotesDocument2 pagesFDAR CHARTING POSTPARTUM, Nurse's Progress NotesFrederene Javelona100% (2)
- Male Patient Treatment for DehydrationDocument2 pagesMale Patient Treatment for DehydrationJamie Lee100% (2)
- FDARDocument1 pageFDARDan Tijam50% (2)
- Focus ChartingDocument46 pagesFocus ChartingIsmail Alnemr100% (5)
- FDAR Charting - Readiness For Enhanced ComfortDocument1 pageFDAR Charting - Readiness For Enhanced ComfortWyen Cabatbat100% (1)
- FOCUS CHARTING MasterlistDocument29 pagesFOCUS CHARTING Masterlistramoli1988100% (6)
- FDARDocument4 pagesFDARViolBernados0% (1)
- FDARDocument1 pageFDARRona-Gloria Selma-Lopez100% (1)
- Fdar Charting: Date, Time, and Shift Focus Progress NotesDocument1 pageFdar Charting: Date, Time, and Shift Focus Progress NotesYuvi Luardo100% (1)
- Nurses Notes: Student Nurse: Casas, Jannen A. Patient's Name: - N.T.M - Doctor: Bed No.Document2 pagesNurses Notes: Student Nurse: Casas, Jannen A. Patient's Name: - N.T.M - Doctor: Bed No.Jannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Fdar Samples PresentationDocument29 pagesFdar Samples PresentationKewkew Azilear92% (37)
- FDARDocument2 pagesFDARRajenne Blanche C. KHONo ratings yet
- IMPIT - HA FdarDocument4 pagesIMPIT - HA FdarJohn Colem ImpitNo ratings yet
- NCP For CAP TB.Document5 pagesNCP For CAP TB.Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Promoting Effective Breathing and Airway ClearanceDocument7 pagesPromoting Effective Breathing and Airway ClearanceJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisYael EzraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument10 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Ncps FinalDocument13 pagesCase Pres Ncps FinalMariejoy YadaoNo ratings yet
- Group5 NCPDocument24 pagesGroup5 NCPAkira AtomarNo ratings yet
- University of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument3 pagesUniversity of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn MhoreNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic StudiesDocument9 pagesDiagnostic StudiesAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- NCP Fdar Activity1Document3 pagesNCP Fdar Activity1Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- NCP Esrd 2Document4 pagesNCP Esrd 2Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map on Risk Factors and Nursing Care for End Stage Renal DiseaseDocument4 pagesConcept Map on Risk Factors and Nursing Care for End Stage Renal DiseaseAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Breathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionDocument3 pagesBreathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- ETHICO EsrdDocument1 pageETHICO EsrdAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Identify & Evaluate Patients With Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesIdentify & Evaluate Patients With Chronic Kidney DiseaseAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument2 pagesPhysical AssessmentAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- NCP EsrdDocument2 pagesNCP EsrdAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map on Risk Factors and Nursing Care for End Stage Renal DiseaseDocument4 pagesConcept Map on Risk Factors and Nursing Care for End Stage Renal DiseaseAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- ISBAR Handoff CommunicationDocument2 pagesISBAR Handoff CommunicationAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- NCP Esrd 2Document4 pagesNCP Esrd 2Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- NCP Fdar Activity1Document3 pagesNCP Fdar Activity1Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- NCP EsrdDocument2 pagesNCP EsrdAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- NCP Esrd 2Document4 pagesNCP Esrd 2Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Time Chart for Risk of Self-Directed and Other-Directed ViolenceDocument1 pageTime Chart for Risk of Self-Directed and Other-Directed ViolenceAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- ISBAR Handoff CommunicationDocument2 pagesISBAR Handoff CommunicationAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Eval ExamDocument1 pageEval ExamAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument2 pagesPhysical AssessmentAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- ETHICO EsrdDocument1 pageETHICO EsrdAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Identify & Evaluate Patients With Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesIdentify & Evaluate Patients With Chronic Kidney DiseaseAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic StudiesDocument9 pagesDiagnostic StudiesAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Frdar Psyche 4Document1 pageFrdar Psyche 4Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Breathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionDocument3 pagesBreathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Examination 3Document5 pagesMental Status Examination 3Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Frdar Psyche 4Document1 pageFrdar Psyche 4Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Psyche Prefinal CrisisDocument5 pagesPsyche Prefinal CrisisAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Fdar Psyche 3Document1 pageFdar Psyche 3Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Dug Study PsycheDocument33 pagesDug Study PsycheAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Care for Patients with Cardiovascular and Renal IssuesDocument6 pagesPostoperative Care for Patients with Cardiovascular and Renal IssuesAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- By Pass System in The Dry ProcessDocument34 pagesBy Pass System in The Dry Processfaheemqc100% (1)
- Worthington LN 71576423-E PDFDocument32 pagesWorthington LN 71576423-E PDFPaul BrimhallNo ratings yet
- MA Only Notice Explains Coverage ChangeDocument2 pagesMA Only Notice Explains Coverage ChangeAnonymous Zp7kAtNo ratings yet
- English Form 2 Mod23042022001Document10 pagesEnglish Form 2 Mod23042022001Qiash JontezNo ratings yet
- Proposed Plan For Increasing The Entrepreneurial Skills of Students in Food PreservationDocument13 pagesProposed Plan For Increasing The Entrepreneurial Skills of Students in Food PreservationAnonymous B0hmWBTNo ratings yet
- OSHA Group Assigtment 1Document4 pagesOSHA Group Assigtment 1Muhammad SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Future Reference Craftsman Scroll Saw Serial and Model NumbersDocument22 pagesFuture Reference Craftsman Scroll Saw Serial and Model NumbersJL AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Devsecops Course Content: Module-1 Devops BasicsDocument3 pagesDevsecops Course Content: Module-1 Devops Basicshelo nameNo ratings yet
- Lifting Plan ProcedureDocument4 pagesLifting Plan ProcedureNath YauNo ratings yet
- Global Leader: in Glass IonomerDocument2 pagesGlobal Leader: in Glass IonomerAnggini ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Thermal Destruction of Microorganisms in 38 CharactersDocument6 pagesThermal Destruction of Microorganisms in 38 CharactersRobin TanNo ratings yet
- Criminalsocio2022ratio Malindan RcrimDocument42 pagesCriminalsocio2022ratio Malindan RcrimWenilyn SmanNo ratings yet
- MONO POWER AMPLIFIER SERVICE MANUALDocument34 pagesMONO POWER AMPLIFIER SERVICE MANUALAlexey OnishenkoNo ratings yet
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak YojanaDocument19 pagesPradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojanapriyajaiswal428No ratings yet
- Action On Agricultural. Calculating Agricultural EmissionsDocument27 pagesAction On Agricultural. Calculating Agricultural EmissionsXoel UrriagaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Population Growth and Losses Cause by Beetle Trogoderama Granarium (Everts) To Selected Past and Present Wheat GenotypesDocument12 pagesComparative Population Growth and Losses Cause by Beetle Trogoderama Granarium (Everts) To Selected Past and Present Wheat GenotypesInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Nigelaycardo 1Document8 pagesNigelaycardo 1ANGELICA AYCARDO FLORESNo ratings yet
- Factors, Impact, Symptoms of NPADocument7 pagesFactors, Impact, Symptoms of NPAMahesh ChandankarNo ratings yet
- Case Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNDocument5 pagesCase Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNRogelio Saupan Jr100% (1)
- MP Maxat Pernebayev Tanvi Singh Karthick SundararajanDocument117 pagesMP Maxat Pernebayev Tanvi Singh Karthick SundararajansadiaNo ratings yet
- Hedging FuturesDocument39 pagesHedging Futuresapi-3833893100% (1)
- District Potential Analysis of PilibhitDocument57 pagesDistrict Potential Analysis of PilibhitJasraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Viom Networks Becomes The First Indian Telecom Infrastructure Company To Receive ISO 14001 & OHSAS 18001 CertificationDocument2 pagesViom Networks Becomes The First Indian Telecom Infrastructure Company To Receive ISO 14001 & OHSAS 18001 CertificationViom NetworksNo ratings yet
- Convey 1996Document8 pagesConvey 1996Moises Tinte100% (1)
- Bone Tumours and MalignanciesDocument55 pagesBone Tumours and MalignanciesFreeburn SimunchembuNo ratings yet
- Product RD Session 16 - Phase Eqm Part 3Document38 pagesProduct RD Session 16 - Phase Eqm Part 3Rishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Sheath CurrentsDocument5 pagesSheath Currentsscribdkkk100% (1)
- Contracts Summary: 601 Totaling $4.76 BillionDocument186 pagesContracts Summary: 601 Totaling $4.76 BillionJAGUAR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in Rheumatology: Applications and ChallengesDocument39 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Rheumatology: Applications and ChallengesMaryame BoutkhilNo ratings yet
- A Review of Empathy Education in NursingDocument11 pagesA Review of Empathy Education in Nursinglora ardyaNo ratings yet