Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCPBA Analysis
MCPBA Analysis
Uploaded by
kasliwalrajesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesAnalysis of MCPBA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnalysis of MCPBA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesMCPBA Analysis
MCPBA Analysis
Uploaded by
kasliwalrajeshAnalysis of MCPBA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
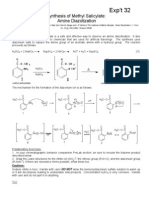
MCPBA analysis
Iodometric titration of the moist extracts indicates approximately
51 g. of m-chloroperbenzoic acid present. A 4.0-ml. aliquot of the
solution requires approximately 20 ml. of a 0.1000 N solution of
sodium thiosulfate. To prepare the sample, 10 ml. of 10% sodium
iodide and 5 ml. of acetic acid are added to the 5-ml. aliquot, and
the mixture is diluted to 50 ml. The dark red solution is titrated to
a pale yellow. At this point 1 ml. of starch solution is added and
the titration continued to the end point, i.e., a change from dark
blue to clear.
5. The dichloromethane solvent should be removed as rapidly as
possible because contact with glass and heat cause
decomposition of the peracid. A convenient method for the
removal of the solvent involves a short-path vacuum distillation
using a 2-l. distillation flask and trapping the solvent at dry ice or
liquid nitrogen temperatures. The pressure should be reduced
slowly at first and at least three traps used to minimize the
amount of solvent introduced into the vacuum pump. Adjustment
of a stopcock located between the first and second traps will help
to control this problem. The distillation flask is placed in a water
bath maintained between 25 and 35 so that the rate of solvent
evaporation is quite rapid. Removal of the solvent over prolonged
periods and drying of the solid peracid by excessive heating
results in drastic losses of active oxygen. m-Chloroperbenzoic,
once isolated, is stable over long periods of time when stored in
polyethylene containers and refrigerated.
6. Iodometric titration of the solid product involves the use of 0.2g. samples of the peracid and the procedure in (Note 4).
You might also like
- AOCS CD 8 53 Peroxido Con CL PDFDocument2 pagesAOCS CD 8 53 Peroxido Con CL PDFIvone Sulistya93% (14)
- LAB QO 4 - Nitration of ChlorobenzeneDocument9 pagesLAB QO 4 - Nitration of Chlorobenzenemario100% (1)
- Synthesis of An Alkyl HalideDocument4 pagesSynthesis of An Alkyl HalideJoseph CatiisNo ratings yet
- Preparation of IodoformDocument3 pagesPreparation of Iodoformjerry green100% (2)
- Synthesis of Tryptamine From TryptophanDocument5 pagesSynthesis of Tryptamine From TryptophanAnaiza EchelonNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - P-NitroacetanilideDocument5 pagesLab 4 - P-Nitroacetanilidechamanyusuff100% (2)
- (Ebook - PDF) How To Make LSDDocument4 pages(Ebook - PDF) How To Make LSDDemetrio Trio100% (1)
- Lab2 ReductionofPinacolonewithSodiumBorohydrideDocument9 pagesLab2 ReductionofPinacolonewithSodiumBorohydrideGopal RavindhranNo ratings yet
- The Preparation of Methylamine Hydrochloride From Acetamide by Means of Calcium HypochloriteDocument3 pagesThe Preparation of Methylamine Hydrochloride From Acetamide by Means of Calcium Hypochloritegeovani2100% (1)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- LSD-25 Synthesis From " "Document7 pagesLSD-25 Synthesis From " "LNo ratings yet
- Experiment 12 Preparation of Adipic Acid From CyclohexeneDocument6 pagesExperiment 12 Preparation of Adipic Acid From Cyclohexenesaransh1994No ratings yet
- EXP6Document4 pagesEXP6conker4No ratings yet
- Postlab-Grignard Reagent-Synthesis of TriphenylmethanolDocument8 pagesPostlab-Grignard Reagent-Synthesis of TriphenylmethanolMarleny ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Proced I Mien ToDocument6 pagesProced I Mien ToMariaNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 Grignard Report UpDocument5 pagesExp 3 Grignard Report UpUyen V. NguyenNo ratings yet
- 21 - Appendix II PDFDocument11 pages21 - Appendix II PDFSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Mercury, Atomic Absorption Spectrometric, Flameless: 1. ApplicationDocument4 pagesMercury, Atomic Absorption Spectrometric, Flameless: 1. ApplicationCristian Javier Guzman DiazNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Potassium TrioxaloferrateDocument10 pagesPreparation of Potassium Trioxaloferratemukund_seethamrajuNo ratings yet
- Arclightshroom's 4 Aco DMT WorkDocument6 pagesArclightshroom's 4 Aco DMT Workj.pedrogomes84No ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis Test (ASTM C114)Document8 pagesChemical Analysis Test (ASTM C114)Ayaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- The Nitration of Aniline: + H O 1. H So 2. Naoh +Document4 pagesThe Nitration of Aniline: + H O 1. H So 2. Naoh +vijpraNo ratings yet
- Method 410.3: Chemical Oxygen Demand (Titrimetric, High Level For Saline Waters) by TitrationDocument4 pagesMethod 410.3: Chemical Oxygen Demand (Titrimetric, High Level For Saline Waters) by TitrationMulti Idola TriciaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of An Unknown Vinegar SampleDocument8 pagesAnalysis of An Unknown Vinegar Samplearfanadib13No ratings yet
- Extraction of Alkene From AlcoholDocument4 pagesExtraction of Alkene From AlcoholMsShu93No ratings yet
- H2 O2 Assaywith KMNO4Document4 pagesH2 O2 Assaywith KMNO4U6 Rayon RamoutarsinghNo ratings yet
- LSDDocument19 pagesLSDapi-3699610No ratings yet
- 2007 07 10 Methods Method 410 3Document3 pages2007 07 10 Methods Method 410 3Syahrul AminNo ratings yet
- FL SopDocument45 pagesFL SopSara JohnsonNo ratings yet
- How To Make AcidDocument6 pagesHow To Make Acidasdsa asdsdNo ratings yet
- Santa Monica College Chem 22 Lab ManualDocument59 pagesSanta Monica College Chem 22 Lab ManualMide Ogundipe100% (1)
- 41.1.28 AOAC Official Method 969.33 Fatty Acids in Oils and FatsDocument1 page41.1.28 AOAC Official Method 969.33 Fatty Acids in Oils and FatsNguyễn Khang LuânNo ratings yet
- AOAC 960.05-MolybdenumDocument1 pageAOAC 960.05-MolybdenumYến PhiNo ratings yet
- GA6 Iron Ore Titr Rev4 94Document3 pagesGA6 Iron Ore Titr Rev4 94pathisharmaNo ratings yet
- 2C-B Synthesis Without LAH PDFDocument4 pages2C-B Synthesis Without LAH PDFatomosco100% (3)
- KsynDocument3 pagesKsynFlorianLiestNo ratings yet
- Ochem 2 Grignard LabDocument17 pagesOchem 2 Grignard Labchevaunnes100% (1)
- Determination of CalciumDocument2 pagesDetermination of Calciumcocomelon8454No ratings yet
- NaOCl Ox of 9-Fluorenol NewDocument3 pagesNaOCl Ox of 9-Fluorenol NewJared HinkleNo ratings yet
- AstmDocument3 pagesAstmphamkieuNo ratings yet
- Corn StarchDocument2 pagesCorn StarchVanNo ratings yet
- Analytical Methods Hyprox EvonikDocument3 pagesAnalytical Methods Hyprox EvonikSham SajaNo ratings yet
- Lieberman NDocument3 pagesLieberman NTitis Adisti HapsariNo ratings yet
- Objectives: 1. To Compute The Percent by Weight of Acetic Acid in A Vinegar Sample. 2. To Compute The Dissolved Oxygen Content of A Water SampleDocument5 pagesObjectives: 1. To Compute The Percent by Weight of Acetic Acid in A Vinegar Sample. 2. To Compute The Dissolved Oxygen Content of A Water SamplePaul JavenNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Alkyl HalideDocument3 pagesSynthesis of Alkyl HalideKelvin LabarezNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Digestible Crude Protein Pepsin ActivityDocument3 pages5.2 Digestible Crude Protein Pepsin Activitypavan patelNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument4 pagesPDFلوغيتفيكافوزيةNo ratings yet
- FR 1 (E6)Document5 pagesFR 1 (E6)JR CastorNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydrogen SulfideDocument3 pagesSpectrophotometric Determination of Hydrogen SulfideVictor HugoNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastFrom EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastNo ratings yet
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidFrom EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidNo ratings yet
- Glass Transition and Phase Transitions in Food and Biological MaterialsFrom EverandGlass Transition and Phase Transitions in Food and Biological MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Of Of: The 'Fhe FromDocument2 pagesOf Of: The 'Fhe FromkasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- 6116 W. R. Vol. 76: Pregnane-17a, 20p-Diol-3,1l-Dione (X)Document4 pages6116 W. R. Vol. 76: Pregnane-17a, 20p-Diol-3,1l-Dione (X)kasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- Mumbai Drugs Market - IndiaDocument2 pagesMumbai Drugs Market - IndiakasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- Russian Journal of Organic Chemistry: Contact Us Useful LinksDocument1 pageRussian Journal of Organic Chemistry: Contact Us Useful LinkskasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- H30+) " BR O: 2 - (2-Amino - 5 - B Rom Obenzoyl) Py Ri DineDocument4 pagesH30+) " BR O: 2 - (2-Amino - 5 - B Rom Obenzoyl) Py Ri DinekasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- Be Lost Ots Kaya 2005Document4 pagesBe Lost Ots Kaya 2005kasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- Us 3064000Document4 pagesUs 3064000kasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- Product SpecificationDocument1 pageProduct SpecificationkasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- M INOXIDocument1 pageM INOXIkasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 1Document59 pages07 Chapter 1chem_dream00No ratings yet
- Defining The Purpose of An Occupational Health and Safety AgreementDocument24 pagesDefining The Purpose of An Occupational Health and Safety AgreementkasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- Working With Hazardous Chemicals: A Publication of Reliable Methods For The Preparation of Organic CompoundsDocument5 pagesWorking With Hazardous Chemicals: A Publication of Reliable Methods For The Preparation of Organic CompoundskasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- ATN-A New Infrared SpectraDocument1 pageATN-A New Infrared SpectrakasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- Proforma of Application For Recognition of In-House R&D Units Part-ADocument9 pagesProforma of Application For Recognition of In-House R&D Units Part-AkasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- Nardbeäs/M : Edited by Toke Lindegaard KnudsenDocument4 pagesNardbeäs/M : Edited by Toke Lindegaard KnudsenkasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet
- SolventDocument1 pageSolventkasliwalrajeshNo ratings yet