Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Teaching 10
Teaching 10
Uploaded by
jlhiezel210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views11 pagesppt
Original Title
teaching+10
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views11 pagesTeaching 10
Teaching 10
Uploaded by
jlhiezel21ppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
One dimensional monatomic linear lattice
al Space and reciprocal space.
dispersion relation is actually periodic in k
k+2pi/a.
Will give us back exactly the same
wave
This set of points is known as the reciprocal lattice. The
original periodic set of points x = na is known as the
direct lattice or real-space lattice
Normal modes in the first brillouin zone:
This means that the k-axis is actually a discrete set of
many individual points; the spacing between two of these
consecutive points being 2Pi/L.
Long wavelength limit:
In the long wavelength limit k 0
V=
velocity = d omega /dk
Phase velocity = omega Group
/k
vp = v g = v
Brillouin zone boundaries k = pi/a vg = 0.
In the long wavelength
limit k 0
The one-dimensional diatomic solid
The acoustic branch:
e acoustic mode start at k = 0 so omega should be 0 at the limit k
roup velocity and Phase velocity
Optical Branch.
You might also like
- Optical Fiber Communication by Gerd Keiser, 3rd EdDocument622 pagesOptical Fiber Communication by Gerd Keiser, 3rd EdNgoc Phuc Le100% (3)
- Derivation of Plancks Formula Radiation Chapter10Document14 pagesDerivation of Plancks Formula Radiation Chapter10TewodrosNo ratings yet
- Compton EffectDocument17 pagesCompton EffectShouvik Roy100% (1)
- 2.57 Nano-To-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ikn A IkxDocument7 pages2.57 Nano-To-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ikn A IkxcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Bloch FunctionsDocument5 pagesBloch Functionsalvaro562003No ratings yet
- 10 28 10 Exam 2 AllDocument28 pages10 28 10 Exam 2 AllcontactsitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document11 pagesChapter 6Dr-Dharmendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Lattice Dynamics - 1: Book References: Solid State Physics by A. J. Dekker Solid State Physics by D. S. BlakemoreDocument12 pagesLattice Dynamics - 1: Book References: Solid State Physics by A. J. Dekker Solid State Physics by D. S. BlakemorePragyaNo ratings yet
- EM-2C-Quantum Theory PhononDocument23 pagesEM-2C-Quantum Theory PhononS S AcharyaNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: E HN MDocument10 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: E HN McaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Motion of The Atoms: Lattice VibrationsDocument11 pagesMotion of The Atoms: Lattice VibrationsBadri DadiNo ratings yet
- Phy PresentationDocument29 pagesPhy Presentationnocap7884No ratings yet
- The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Final 2014Document58 pagesThe Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Final 2014Asad ChoudaryNo ratings yet
- E R Williams - New Experimental Test of Coulomb-S LawDocument40 pagesE R Williams - New Experimental Test of Coulomb-S LawNestor GasparNo ratings yet
- Modern and Nonlinear OpticsDocument181 pagesModern and Nonlinear Opticssoma_venuNo ratings yet
- CH2209 - Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy, Quantum ChemistryDocument18 pagesCH2209 - Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy, Quantum ChemistryJohnNo ratings yet
- Lecture16 Roger 136604Document9 pagesLecture16 Roger 136604Sanhita DasNo ratings yet
- Physical Lec 10-14Document13 pagesPhysical Lec 10-14rupayandaripaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 3Document17 pagesQuantum 3Hemang ChopraNo ratings yet
- Kittel Chap4 Revised 10-25-2013newDocument24 pagesKittel Chap4 Revised 10-25-2013newIntan Karisma Smashblast BismaniacNo ratings yet
- CHEM F111: General Chemistry: PilaniDocument21 pagesCHEM F111: General Chemistry: PilaniPurveshNo ratings yet
- Photonics 02 Light PropertiesDocument39 pagesPhotonics 02 Light PropertiesVandana SharmaNo ratings yet
- PHYS4 SpecialRelativityDocument19 pagesPHYS4 SpecialRelativitySeaton HarnsNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Band GapsDocument4 pagesDirect and Indirect Band GapsSai Swetha KVNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Periodic PotentialDocument8 pagesElectrons in Periodic PotentialsouvenirsouvenirNo ratings yet
- Lect 6Document3 pagesLect 6digi1988No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 1 - N 2016Document29 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Set 1 - N 2016monish gowda gNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 - 26-10-22Document30 pagesLecture-3 - 26-10-22Alkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rubidium Hyperfine StructureDocument4 pagesRubidium Hyperfine StructureKapila Wijayaratne100% (2)
- RadiationDocument3 pagesRadiationPudipeddi L N MurtyNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics and Quantum Mechanics Mod-2 PDFDocument28 pagesModern Physics and Quantum Mechanics Mod-2 PDFShreyas SeshadriNo ratings yet
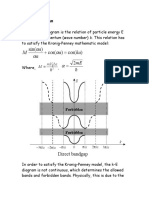
- ka a a a M:) cos cos sin (= + αDocument5 pageska a a a M:) cos cos sin (= + αFaizan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Photonic Crystals: Bloch's Theorem, Band Diagrams, and Gaps (But No Defects)Document16 pagesIntroduction To Photonic Crystals: Bloch's Theorem, Band Diagrams, and Gaps (But No Defects)Silvio SavoiaNo ratings yet
- Phy PresentationDocument29 pagesPhy Presentationnocap7884No ratings yet
- Simulado - 2 IPhODocument12 pagesSimulado - 2 IPhOleonardo sathlerNo ratings yet
- KP Theory of SemiconductorsDocument13 pagesKP Theory of SemiconductorstransfinitumNo ratings yet
- 1 Gravitational Plane WavesDocument27 pages1 Gravitational Plane WavesketiNo ratings yet
- PhononsDocument29 pagesPhononsFikriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: The Fermi Liquid: L.D. Landau December 22, 2000Document55 pagesChapter 6: The Fermi Liquid: L.D. Landau December 22, 2000padma princessNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Photonic Crystals: Bloch's Theorem, Band Diagrams, and Gaps (But No Defects)Document16 pagesIntroduction To Photonic Crystals: Bloch's Theorem, Band Diagrams, and Gaps (But No Defects)ms853732No ratings yet
- Semiconductors: Physics 355Document34 pagesSemiconductors: Physics 355Houssem Eddine SassiNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For Special Relativity A Heuristic Approach Sadri Hassani Download 2024 Full ChapterDocument47 pagesSolutions Manual For Special Relativity A Heuristic Approach Sadri Hassani Download 2024 Full Chaptermary.hunter239100% (10)
- Short Question Bank Physics IIDocument12 pagesShort Question Bank Physics IIAshish Vimal0% (1)
- Physics Assignment PDFDocument15 pagesPhysics Assignment PDFHarsh MittalNo ratings yet
- Engg. Physics - II Unit-I: (Wave Mechanics and X-Rays)Document15 pagesEngg. Physics - II Unit-I: (Wave Mechanics and X-Rays)muhammadfaisal32717No ratings yet
- UNIT - I Wave Mechanics - Nmamit 2019-20Document50 pagesUNIT - I Wave Mechanics - Nmamit 2019-20Mr.Manjunath K.B NMAMIT PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Properties of SemiconductorsDocument34 pagesProperties of SemiconductorsMohammad Gulam AhamadNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorDocument20 pagesSemiconductormdtayyab212121No ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Davisson and Germer ExperimentDocument15 pagesQuantum Mechanics Davisson and Germer Experimentvivek patel100% (2)
- Modern Physics 7Document40 pagesModern Physics 7Brenda Michelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Limesi FormuleDocument54 pagesLimesi Formulecasejc.justinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Quantum Mechanics Dual Nature of Radiation:: De-Broglie WavelengthDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Quantum Mechanics Dual Nature of Radiation:: De-Broglie Wavelengtheswar kousikNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: I T KXDocument8 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: I T KXcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- The Radio and Electronic Engineer: The Journal of The British Institution of Radio EngineersDocument2 pagesThe Radio and Electronic Engineer: The Journal of The British Institution of Radio EngineersshirtquittersNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics in A Nutshell: 2.1 PhotonsDocument26 pagesQuantum Mechanics in A Nutshell: 2.1 PhotonsMaitraNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Full Mock 2Document3 pagesClass Xii Full Mock 2physicshari.bwnNo ratings yet
- 8 Nuclear Instability (Transmutation)Document14 pages8 Nuclear Instability (Transmutation)Fatin IziantiNo ratings yet
- Has AlgorithmDocument5 pagesHas Algorithm140557No ratings yet
- MP Pset1Document7 pagesMP Pset1tackyjcNo ratings yet
- Score Board Ultimate Spy ChallengeDocument4 pagesScore Board Ultimate Spy Challengejlhiezel21No ratings yet
- Check List For GuestsDocument2 pagesCheck List For Guestsjlhiezel21No ratings yet
- Y10 School Network AssignmentDocument1 pageY10 School Network Assignmentjlhiezel21No ratings yet
- Safety & Environmental PlanDocument2 pagesSafety & Environmental Planjlhiezel21No ratings yet
- Bulk To Nano Transition: Surface Area EnhancementDocument13 pagesBulk To Nano Transition: Surface Area Enhancementjlhiezel21No ratings yet
- Art 16 25.R.A 9184Document46 pagesArt 16 25.R.A 9184jlhiezel21No ratings yet