Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HW03
Uploaded by
陳信儒Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HW03
Uploaded by
陳信儒Copyright:
Available Formats
Classical Mechanics Problem Set #3 Date:03/22 /2016
1. (Goldstein 2-14) A uniform hoop of mass m and radius r rolls without slipping on a
fixed cylinder of a larger radius R (R > r). The only external force is that of gravity. If
the small cylinder starts rolling from rest on top of the bigger cylinder, use the method
of Lagrange multipliers to find the point at which the hoop falls off the cylinder.
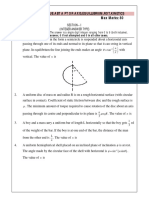
2. (Goldstein 2-18) A point mass is constrained to move on a massless hoop of radius a
fixed in a vertical plane that rotates about its vertical symmetry axis with constant
angular speed . Obtain the Lagrange equations of motion assuming the only external
forces arise from gravity. What are the constants of motion? Show that if is greater
than a critical value 0 , there can be a solution in which the particle remains stationay
on the hoop at a point other than at the bottom, but that if < 0 , the only stationary
point for the particle is at the bottom of the hoop. What is the value of 0 ?
3. (Goldstein 2-19) A particle moves without friction in a conservative field of force produced by various mass distributions. In each instance, the force generated by a volume
element of the distribution is derived from a potential that is proportional to the mass
of the volume element and is a function only of the scalar distance from the volume
element. For the following fixed, homogeneous mass distributions, state the conserved
quantities in the motion of the particle:
(a) The mass is uniformly distributed in the plane z = 0.
(b) The mass is uniformly distributed in the half-plane z = 0, y > 0.
(c) The mass is uniformly distributed in a circular cylinder of infinite length, with axis
along the z axis.
(d) The mass is uniformly distributed in a circular cylinder of finite length, with axis
along the z axis.
(e) The mass is uniformly distributed in a right cylinder of elliptical cross section and
infinite length, with axis along the z axis.
(f) The mass is uniformly distributed in a dumbbell whose axis is oriented along the z
axis.
(g) The mass is in the form of a uniform wire wound in the geometry of an infinite
helical solenoid, with axis along the z axis.
You might also like
- Mechanics Problem Set - 8Document1 pageMechanics Problem Set - 8Perry EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2chunmunpathakNo ratings yet
- Collection of Problems in Classical Mechanics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandCollection of Problems in Classical Mechanics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Problem Set 6Document4 pagesProblem Set 6James ConnaughtonNo ratings yet
- Classical 093Document33 pagesClassical 093Julian David Henao EscobarNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Rigid Body DynamicsDocument9 pagesAssignment On Rigid Body DynamicsKaveesh KulkarniNo ratings yet
- General Relativity 3: Astrophysics with Tensor CalculusFrom EverandGeneral Relativity 3: Astrophysics with Tensor CalculusRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Problem Set VI Lagrangian DynamicsDocument4 pagesProblem Set VI Lagrangian DynamicsDiego ForeroNo ratings yet
- A Course of Mathematics for Engineers and Scientists: Volume 3: Theoretical MechanicsFrom EverandA Course of Mathematics for Engineers and Scientists: Volume 3: Theoretical MechanicsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Problem Sheet 8Document7 pagesProblem Sheet 8AliOucharNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 Recitation 7 RotationDocument10 pagesPhysics 1 Recitation 7 RotationAlexNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Mechanics Exam: Classical Mechanics Problems and SolutionsDocument139 pagesPreliminary Mechanics Exam: Classical Mechanics Problems and SolutionsLawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- Lagrangian Dynamics ProblemsDocument5 pagesLagrangian Dynamics Problemsvivekrajbhilai5850No ratings yet
- Prob Set 5Document2 pagesProb Set 5Debolina DasNo ratings yet
- Momento Linear e Centro de Massa: Resolução de Problemas de MecânicaDocument4 pagesMomento Linear e Centro de Massa: Resolução de Problemas de MecânicaThales FreireNo ratings yet
- Energi Momentum Dan Dinamika Rotasi Pelatihan Osn 2012Document7 pagesEnergi Momentum Dan Dinamika Rotasi Pelatihan Osn 2012Ivandito HerdayandityaNo ratings yet
- Prob01s - H C VermaDocument6 pagesProb01s - H C VermaManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Practice-Problems For Kleppner Mechanics 2nd EditionDocument2 pagesPractice-Problems For Kleppner Mechanics 2nd Editiongayatri rainaNo ratings yet
- Rotational Mechanics 2Document25 pagesRotational Mechanics 2Ujib DamianNo ratings yet
- PHYS 314 Final Exam Questions: R= 2 v sin (β - α) cos β g cos αDocument3 pagesPHYS 314 Final Exam Questions: R= 2 v sin (β - α) cos β g cos αs_nimalanNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion and WPEDocument5 pagesCircular Motion and WPEMy Moto G2No ratings yet
- IIT Kanpur Physics Problem Set on Newton's LawsDocument3 pagesIIT Kanpur Physics Problem Set on Newton's LawsRajesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics ProblemDocument9 pagesMechanics ProblemSon CaoNo ratings yet
- Problems and oscillationsDocument2 pagesProblems and oscillationssdenkaspNo ratings yet
- Nsejs 2015 SOLUtION PDFDocument7 pagesNsejs 2015 SOLUtION PDFamit kumarNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemDocument10 pagesProblem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics: Challenge Problems Problem 1: Double Star SystemVongNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Practice Problems Target IIT ADVANCE-2019Document4 pagesMechanics Practice Problems Target IIT ADVANCE-2019Shivam JaggiNo ratings yet
- Chapters 10-11 Conceptual QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapters 10-11 Conceptual QuestionsShasha Jain100% (1)
- Advanced HandoutDocument8 pagesAdvanced Handoutparthkalra1981No ratings yet
- Draw A Picture!: You May Treat The Child As A Point ParticleDocument24 pagesDraw A Picture!: You May Treat The Child As A Point Particlebat.laughNo ratings yet
- Mit Ocw Mechanics Problems For Jee AdvancedDocument77 pagesMit Ocw Mechanics Problems For Jee Advancedpranav.padhle6No ratings yet
- Er. Shravan Katiyar: Physics For Iit-Jee (Main & Advanced)Document4 pagesEr. Shravan Katiyar: Physics For Iit-Jee (Main & Advanced)ShreyanshNo ratings yet
- Assign7 PDFDocument1 pageAssign7 PDFRishab PandaNo ratings yet
- Wa0010.Document3 pagesWa0010.BxkxnzixbNo ratings yet
- STR 1 Unit 2Document8 pagesSTR 1 Unit 2Milan SuranaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 11 Dec 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 11 Dec 2023Deyasini PaulNo ratings yet
- Energy and Momentum - Level 3Document8 pagesEnergy and Momentum - Level 3Kusharg rahejaNo ratings yet
- Physics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsDocument9 pagesPhysics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsNathaly SosaNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document6 pagesHomework 2Ale Gomez100% (3)
- Classical MechanicsDocument15 pagesClassical MechanicsPengintaiNo ratings yet
- CBP I Problems PDFDocument56 pagesCBP I Problems PDFsgw67No ratings yet
- EP 222: Classical Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 2Document2 pagesEP 222: Classical Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 2Ashok GargNo ratings yet
- mf2 PDFDocument4 pagesmf2 PDFShweta SridharNo ratings yet
- Tarea3 Covid2020Document1 pageTarea3 Covid2020sannintkdNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Rigid BodyDocument32 pagesKinetics of Rigid BodyMuhammad FirdawsNo ratings yet
- Lagrangian Dynamics: PHYS20401 Terry Wyatt Example Sheet 8: Revision ProblemsDocument7 pagesLagrangian Dynamics: PHYS20401 Terry Wyatt Example Sheet 8: Revision ProblemsAgtc TandayNo ratings yet
- Torque Abt A PT or Axis, Equillibrium, Rot - Kinetics QDocument8 pagesTorque Abt A PT or Axis, Equillibrium, Rot - Kinetics Qmanonymous5519No ratings yet
- Rotational Motion by Kota Practice Test Iit JeeDocument6 pagesRotational Motion by Kota Practice Test Iit JeeTEACHING TECHNICAL TIPSNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Motion of System of Particles and Rigid BodyDocument8 pagesUnit 5 Motion of System of Particles and Rigid BodySabia IdrisiNo ratings yet
- Assignment UNIT 1Document4 pagesAssignment UNIT 1Abhi WaliaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesMechanics Exam Questionsnikhil pandyaNo ratings yet
- Set 4Document3 pagesSet 4shanker GNo ratings yet
- Advanced Physics SHMDocument23 pagesAdvanced Physics SHMUnknownNo ratings yet
- IIT Physics Sample Paper 1 Rotational Kinematics & DynamicsDocument2 pagesIIT Physics Sample Paper 1 Rotational Kinematics & DynamicsVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- CM Qualifier2013fallDocument5 pagesCM Qualifier2013fallpusa123No ratings yet
- Summary & ConclusionDocument2 pagesSummary & ConclusionAngela Dimaano SaladaNo ratings yet
- EMT Electromagnetic Theory MODULE IIDocument161 pagesEMT Electromagnetic Theory MODULE IIARAVIND100% (2)
- KCC - DATASHEET - Komarine Anti-Rust Oil RV490 - EngDocument2 pagesKCC - DATASHEET - Komarine Anti-Rust Oil RV490 - EngNguyen1987 TrungNo ratings yet
- A Simple HPLC Method For The Simultaneous Analysis of Phosphatidylcholine and Its Partial Hydrolysis Products 1-And 2-Acyl LysophosphatidylcholineDocument5 pagesA Simple HPLC Method For The Simultaneous Analysis of Phosphatidylcholine and Its Partial Hydrolysis Products 1-And 2-Acyl LysophosphatidylcholineChang Woo JongNo ratings yet
- EFB As Fuel For Biomass Boilers PDFDocument7 pagesEFB As Fuel For Biomass Boilers PDFAnonymous T7zEN6iLHNo ratings yet
- SCM25 steel alloy properties and applicationsDocument1 pageSCM25 steel alloy properties and applicationsPeterWayNo ratings yet
- Clariant Chemical Taiwan Roadshow Highlights Key Issues in Leather DyeingDocument74 pagesClariant Chemical Taiwan Roadshow Highlights Key Issues in Leather Dyeing高文恩No ratings yet
- Estabilización Con CalDocument20 pagesEstabilización Con CalJosé SantiNo ratings yet
- Cancer Treatment Healthcare Center by SlidesgoDocument50 pagesCancer Treatment Healthcare Center by SlidesgotaridaNo ratings yet
- Ramalan Paper 3 SPM 2012 EditDocument10 pagesRamalan Paper 3 SPM 2012 EditA. SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Distillation LabDocument18 pagesDistillation LabWong XimeiNo ratings yet
- 230 Sp18 PREP5 Blank PDFDocument24 pages230 Sp18 PREP5 Blank PDFKhang HuynhNo ratings yet
- Niog Plates2Document12 pagesNiog Plates2YVAN GUEEN M. NIOGNo ratings yet
- % of Calcium Nitate & Acetic Acid in Coagulant TankDocument3 pages% of Calcium Nitate & Acetic Acid in Coagulant TankO S SELVAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Resistance+List+Tank+Linings,+Protective (1) JotunDocument28 pagesResistance+List+Tank+Linings,+Protective (1) JotunIbrahim KhalilNo ratings yet
- MSDS Sodium Hypochlorite SolutionDocument4 pagesMSDS Sodium Hypochlorite SolutionPan SoapNo ratings yet
- What Is LightDocument2 pagesWhat Is LightZac GarciaNo ratings yet
- GT DURACOIL 130 DATASHEET US 3-22 v2Document3 pagesGT DURACOIL 130 DATASHEET US 3-22 v2Ahmed BenayadNo ratings yet
- English Task 4Document2 pagesEnglish Task 4wahyu ghofurNo ratings yet
- FLT93 Complete Manual Surface Mount (06EN003401f)Document100 pagesFLT93 Complete Manual Surface Mount (06EN003401f)May Rodyn Cuba de la CruzNo ratings yet
- SE2NAAFAVA33S0091Document4 pagesSE2NAAFAVA33S0091Ariana GrandeNo ratings yet
- HTCR Vs HTERDocument7 pagesHTCR Vs HTERlaquetengoNo ratings yet
- How Atoms and Molecules Support LifeDocument6 pagesHow Atoms and Molecules Support Lifemelan pNo ratings yet
- Melbourne Soil Shrink-Swell Index Database EstablishedDocument16 pagesMelbourne Soil Shrink-Swell Index Database EstablishedTharun DelpachitraNo ratings yet
- Sohn, Hoon Et Al - 2007 - Damage Detection in Composite Plates by Using An Enhanced Time Reversal MethodDocument11 pagesSohn, Hoon Et Al - 2007 - Damage Detection in Composite Plates by Using An Enhanced Time Reversal Methodxiaohui sunNo ratings yet
- FDTT (KD)Document11 pagesFDTT (KD)blip2604No ratings yet
- Food (Fish) Processing NCII: Not For SaleDocument18 pagesFood (Fish) Processing NCII: Not For SaleBhe Both Arizo-bodo100% (1)
- Chemistry 231 Tutorial Session #5 QuestionsDocument8 pagesChemistry 231 Tutorial Session #5 QuestionsFiqkyAkbarNo ratings yet
- Acs Energyfuels 7b03733Document12 pagesAcs Energyfuels 7b03733Dinesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- 22 Lecture OutlineDocument26 pages22 Lecture OutlineElangFatahillahNo ratings yet
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (76)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityFrom EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (380)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)