Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHEMISTRY 1B (CHEM1102) - June 2012
CHEMISTRY 1B (CHEM1102) - June 2012
Uploaded by
divaaaaaaaaaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEMISTRY 1B (CHEM1102) - June 2012
CHEMISTRY 1B (CHEM1102) - June 2012
Uploaded by
divaaaaaaaaaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEMISTRY 1B (CHEM1102) - June 2012
2012-J-2
In Group 17 oxyacids, electron density is drawn away from the O atom as the
electronegativity of the halogen increases. This in turn draws electron density away
from the OH bond and weakens it. The weaker the OH bond, the stronger the acid.
Cl is more electronegative than Br so HOClO3 is stronger acid than HOBrO3.
In binary acids such as HBr and HCl, the HBr bond is longer than the HCl bond as Br
is larger than Cl. The HBr bond is therefore weaker than the HCl bond and HBr is
thus a stronger acid than HCl.
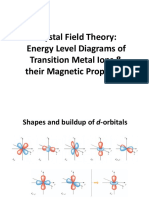
Cu2+ is d 9
Ti3+, d 1
is paramagnetic
is paramagnetic
Ti4+, d 0
is diamagnetic
bromidochlorido(ethylenediamine)nickel(II) or
bromidochlorido(ethane-1,2-diamine)nickel(II)
No. Both structures are superimposable on (i.e. identical to) their mirror images.
2012-J-3
+III
+III
+V
5
+
Na (aq), [FeCl4] (aq)
2012-J-4
3.77
10.77
0.42 mol
0
2+
[CrCN(NH3)5] (aq), Br (aq)
K (aq), [VO2(ox)2]3(aq)
2012-J-5
1 105 M
1 109 M
No. The lethal [Ba2+(aq)] is 40 times greater than the [Ba2+(aq)] in normal aqueous
solution.
2012-J-6
4
2012-J-7
sublimes
liquid
N. The increase in pressure can never cause the solid to liquid phase change due to the
slope of the solid/liquid equilibrium line.
2012-J-8
Energy from light causes the water to split. The energy input is constant and this
determines the maximum rate of reaction. (Essentially, light is the limiting reagent.)
Increasing the amount of catalyst increases the amount of light captured (0 - 200
catalyst loading), but cant increase it above the amount being provided (plateau
region).
2012-J-9
sp3
sp2
2012-J-10
2012-J-11
(Z)-2-butene
1-butene
2012-J-12
Around C*1, the priority of the groups are a > b > c > d. Looking down the C-H bond
the groups a b c go anticlockwise. Therefore configuration is (S)-.
Around C*2, the priority of the groups are a' > b' > c' > d'. Looking down the C-H bond
(i.e. from behind the plane of the paper) the groups a' b' c' go anticlockwise.
Therefore configuration is (S)-.
2012-J-13
2012-J-14
C11H12O4
2012-J-15
Racemic mixture. The carbon where the Br is attached has 4 different groups around it,
so is stereogenic. The carbocation from which it forms is planar and so attack by the
Br is equally likely from either the top or bottom side. This results in equal amounts of
both enantiomers being formed.
This product is derived from the primary carbocation intermediate. Secondary
carbocations are more stable than primary carbocations, so little of this product forms.
You might also like
- DPP-Chemical Bonding - CombinedDocument67 pagesDPP-Chemical Bonding - CombinedKeerthana Reddy DomaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Bonding CFTDocument39 pagesChapter 6 Bonding CFTAmirahKamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Crystal Field TheoryDocument25 pagesCrystal Field TheoryArnab Chatterjee100% (1)
- D Block Elemnets Theory EDocument31 pagesD Block Elemnets Theory EKenny FernandoNo ratings yet
- Review - Before Final 2023 AnswersDocument37 pagesReview - Before Final 2023 AnswersLinn ThànhNo ratings yet
- 02-Chapter 02-PostDocument60 pages02-Chapter 02-PostfzoidguinNo ratings yet
- J1 Promos 2015 AnswersDocument14 pagesJ1 Promos 2015 AnswersaliciaNo ratings yet
- CH 18 SummaryDocument5 pagesCH 18 Summaryalstjq1003No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding SPECIAL ASSIGNMENTDocument25 pagesChemical Bonding SPECIAL ASSIGNMENTprexa indiaNo ratings yet
- Elimination Reactions: C C H X KOH Alcohol C C KX O HDocument14 pagesElimination Reactions: C C H X KOH Alcohol C C KX O HSreehari ES100% (1)
- 5 6194909700736155970Document6 pages5 6194909700736155970Ayur GreenNo ratings yet
- Organohalogen NotesDocument76 pagesOrganohalogen NotesBella HannaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document11 pagesLecture 1Fang GaoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1 - INE SolutionsDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding 1 - INE SolutionsJee AspirantNo ratings yet
- Chemistry All Notes UnacademyDocument480 pagesChemistry All Notes UnacademyAdityaNo ratings yet
- Section B AnsDocument7 pagesSection B AnsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- 1457156375-Inorganic Chemistry Revision Book JEE Main-2016.PmdDocument49 pages1457156375-Inorganic Chemistry Revision Book JEE Main-2016.PmdSummer GreenNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument25 pagesChemical BondingNityanand NanduNo ratings yet
- CH - CH - BR 1° Halide 2° Halide 3° Halide: H H C CH CL CHDocument8 pagesCH - CH - BR 1° Halide 2° Halide 3° Halide: H H C CH CL CHShahbaz NazirNo ratings yet
- 2022 SAJC H2 Chem SolutionsDocument36 pages2022 SAJC H2 Chem SolutionsBooNo ratings yet
- 2016 11 Sample Paper Chemistry 05 Ans As867L1Document8 pages2016 11 Sample Paper Chemistry 05 Ans As867L1AshutoshNo ratings yet
- Chem 26Document5 pagesChem 26vathsalaraonNo ratings yet
- SUSAN MARAJ - Energetics, Q4,5,7,8,9Document7 pagesSUSAN MARAJ - Energetics, Q4,5,7,8,9Mariah BissoonNo ratings yet
- Organic Effect - 15.3.2020Document26 pagesOrganic Effect - 15.3.2020Roban SinghNo ratings yet
- (Done Edu - Joshuatly.com) N9 STPM Trial 2010 Chemistry (W Ans) (8DB31AAC)Document0 pages(Done Edu - Joshuatly.com) N9 STPM Trial 2010 Chemistry (W Ans) (8DB31AAC)BlaireNo ratings yet
- 38 Daily Tutorial SheetDocument7 pages38 Daily Tutorial SheetMeera SarangapaniNo ratings yet
- Nature of Chemical Bond S IVDocument13 pagesNature of Chemical Bond S IV4 bagwe OmNo ratings yet
- Substitution ReactionsDocument39 pagesSubstitution ReactionsAnil Kumar KadianNo ratings yet
- Instructor Supplement 01Document295 pagesInstructor Supplement 01vanigedalaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Revision (ANSWERS)Document31 pagesChemical Bonding Revision (ANSWERS)Daniel ChuNo ratings yet
- 2009 RI Prelims Chem H2 P1 QPDocument16 pages2009 RI Prelims Chem H2 P1 QPniveumaNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution ReactionDocument17 pagesNucleophilic Substitution ReactionRojo JohnNo ratings yet
- Osb - Chemical Bonding MCQ With SolutionsDocument18 pagesOsb - Chemical Bonding MCQ With SolutionsFathima SurayaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document23 pagesChemical Bonding 1Gowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- IC Lecture2Document27 pagesIC Lecture2DusuNo ratings yet
- AB Chemistry CAB SampleDocument63 pagesAB Chemistry CAB SampleMichael BesplugNo ratings yet
- 2022 Chem Bond Tut Qns and SolnsDocument16 pages2022 Chem Bond Tut Qns and SolnsBooNo ratings yet
- Xi Chem SP Set 1 MsDocument5 pagesXi Chem SP Set 1 MsAnanya AryaNo ratings yet
- CHM 1321 Assignment 4 AnswersDocument12 pagesCHM 1321 Assignment 4 AnswersSara YuenNo ratings yet
- All Exceptions of IOCDocument90 pagesAll Exceptions of IOCHarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- فاينال كيم 2017Document19 pagesفاينال كيم 2017Mona Against DampersNo ratings yet
- Task 1 P BlockDocument11 pagesTask 1 P Blocksanka.naren2005No ratings yet
- Sheet-Chemical BondingDocument50 pagesSheet-Chemical BondingAffan FarukiNo ratings yet
- 2015 Year 5 H1 Chemistry Common Test Suggested SolutionsDocument4 pages2015 Year 5 H1 Chemistry Common Test Suggested SolutionsMelissaNo ratings yet
- Userdata Paziras Chem101 Review 09ANSDocument4 pagesUserdata Paziras Chem101 Review 09ANSMark CarpesoNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemistryRanjan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 04 20 2023 LQWDocument30 pagesLecture 20 04 20 2023 LQWAle Hernández MoyersNo ratings yet
- GOC-I TH E 1wWC0LiDocument15 pagesGOC-I TH E 1wWC0LiAnurag SinghNo ratings yet
- Substitution Elemination Reactions 1Document32 pagesSubstitution Elemination Reactions 1oureducation.inNo ratings yet
- Trial P1 2008Document14 pagesTrial P1 2008sherry_christyNo ratings yet
- The D and F Block Elements - WatermarkDocument43 pagesThe D and F Block Elements - WatermarkIT'S SHAMEELNo ratings yet
- 2015 A Level P1Document12 pages2015 A Level P1Faith SeahNo ratings yet
- D & F-Block Elements - Short Notes - VIJETA SERIES CLASS-12THDocument2 pagesD & F-Block Elements - Short Notes - VIJETA SERIES CLASS-12THanshurao112233No ratings yet
- Physical Properties & POC II Theory - EDocument13 pagesPhysical Properties & POC II Theory - EthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity2 180412185954Document37 pagesElectronegativity2 180412185954amrutha tkNo ratings yet
- Physics: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pagesPhysics: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceWing Hong Antony LukNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument13 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesDharmvir TantyNo ratings yet
- XXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973From EverandXXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973No ratings yet
- Plasma Chemistry: International Symposium on Plasma ChemistryFrom EverandPlasma Chemistry: International Symposium on Plasma ChemistryD. E. JensenNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryFrom EverandOrganometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryF. G. A. StoneNo ratings yet
- Marks: D-Block Elements Have From 1 To 10 Electrons in The D-Orbitals. When FormingDocument15 pagesMarks: D-Block Elements Have From 1 To 10 Electrons in The D-Orbitals. When FormingdivaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- AMME 4990/5990 Essay Marking Sheet: Student Name/ID: / AMME 4990 / 5990Document1 pageAMME 4990/5990 Essay Marking Sheet: Student Name/ID: / AMME 4990 / 5990divaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Problem Due Friday 27 March, in Friday Tutorial 1) Problem 5 From Tutorial Sheet 2Document1 pageAssignment 3 Problem Due Friday 27 March, in Friday Tutorial 1) Problem 5 From Tutorial Sheet 2divaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- 084400Document2 pages084400divaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Chem1102exam Nov2012Document19 pagesChem1102exam Nov2012divaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Engineering IT 2014 UGDocument445 pagesEngineering IT 2014 UGdivaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- MECH3660 9660 Tutorial Sheet Metal and Welding 2015Document2 pagesMECH3660 9660 Tutorial Sheet Metal and Welding 2015divaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- I. So Cos: Week 4 Tutorial Solutions 1Document5 pagesI. So Cos: Week 4 Tutorial Solutions 1divaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- AMME2200 2014 Semester 2 StudentDocument3 pagesAMME2200 2014 Semester 2 StudentdivaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- AMME 2500 Assig 4 2014Document4 pagesAMME 2500 Assig 4 2014divaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Eq NsDocument2 pagesFinal Exam Eq NsdivaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Practice Session 11 (Week 11) : 2013 The University of SydneyDocument1 pagePractice Session 11 (Week 11) : 2013 The University of SydneydivaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Practice Session 9 (Week 9) : 2013 The University of SydneyDocument1 pagePractice Session 9 (Week 9) : 2013 The University of SydneydivaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Practice Session 7 (Week 7) : 2013 The University of SydneyDocument5 pagesSolutions To Practice Session 7 (Week 7) : 2013 The University of SydneydivaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet