Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Gerund Phrase Functions As The Subject of The Sentence.: Finding A Needle in A Haystack
Uploaded by
Ernesto Barajas Santana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesA noun phrase refers to a phrase built around a noun that functions as the head of the phrase, such as "the young man" or "pretty girls". A gerund phrase begins with a gerund and can include modifiers, objects, and prepositional phrases, functioning as the subject or direct object of a sentence. An infinitive phrase consists of an infinitive that can be modified, functioning as the direct object or complement of a verb.
Original Description:
Original Title
Noun Phrase
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA noun phrase refers to a phrase built around a noun that functions as the head of the phrase, such as "the young man" or "pretty girls". A gerund phrase begins with a gerund and can include modifiers, objects, and prepositional phrases, functioning as the subject or direct object of a sentence. An infinitive phrase consists of an infinitive that can be modified, functioning as the direct object or complement of a verb.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesThe Gerund Phrase Functions As The Subject of The Sentence.: Finding A Needle in A Haystack
Uploaded by
Ernesto Barajas SantanaA noun phrase refers to a phrase built around a noun that functions as the head of the phrase, such as "the young man" or "pretty girls". A gerund phrase begins with a gerund and can include modifiers, objects, and prepositional phrases, functioning as the subject or direct object of a sentence. An infinitive phrase consists of an infinitive that can be modified, functioning as the direct object or complement of a verb.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
A.
NOUN PHRASE
A noun phrase refers to a phrase that built upon a noun which functions as the
headword of the phrase.
Example:
1. The young man threw the old dog a bone.
(NP)
(NP)
(NP)
2. Pretty girls whispered softly.
(NP)
________________________________________________
I have a very old house (Identificar)
________________________________________________
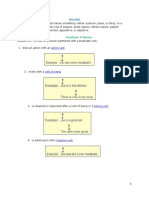
A Gerund Phrase is a group of words beginning with a gerund and followed
most often by modifiers, direct objects, and/or prepositional phrases.
The gerund phrase functions as the subject of the sentence.
Finding a needle in a haystack would be easier than what were trying to do.
Finding (gerund)
a needle (direct object of action)
in a haystack (prepositional phrase)
The gerund phrase functions as the direct object of the sentence.
My teacher likes questioning us on our math skills.
questioning (gerund)
us (direct object of action)
on our math skills (prepositional phrase)
________________________________________________________
An Infinitive Phrase is a group of words consisting of an infinitive and
followed most often by modifiers, direct objects, and/or prepositional
phrases.
We intended to leave early.
The infinitive phrase functions as the direct object of the verb
intended.
to leave (infinitive)
early (adverb)
I have a paper to write before class.
The infinitive phrase functions as an adjective modifying paper.
to write (infinitive)
before class (prepositional phrase)
Phil agreed to give me a ride.
The infinitive phrase functions as the direct object of the verb agreed.
to give (infinitive)
me (indirect object of the infinitive)
a ride (direct object of the infinitive)
______________________________________________________
Type of Modifier
Single word adjective
Single word adverb
Relative pronoun clause
Verb ed modifier
Verb ing modifier
Prepositional modifier
Noun + noun modifier
What does it Modify?
Modifies the closest noun
Modifies the verb
Modifies the noun
Which, that - modify things
Who modifies people
Whose modifies people or things
Modifies the noun
If separated by comma, modifies preceding clause and
associates with the subject
If separated by comma, modifies the following clause or
modifies only the subject
If not separated by comma, modifies the noun
Modifies verb or noun depends on the context
Modifies any aspect of the preceding clause
You might also like
- GerundsDocument13 pagesGerundsscpsdiNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument18 pagesEnglish Grammarembi76No ratings yet
- + Grammar For Students and Teachers - 8-8-11Document319 pages+ Grammar For Students and Teachers - 8-8-11Tiffany JamesNo ratings yet
- Gerunds, Participles and InfinitivesDocument18 pagesGerunds, Participles and InfinitivesCristea AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Verbs: Types and Tenses: Examples: I RanDocument4 pagesVerbs: Types and Tenses: Examples: I RanDelgado Maria AngelaNo ratings yet
- Noun Self Study NotesDocument69 pagesNoun Self Study Notesdeepak9352398562100% (1)
- Grammar ReviewDocument15 pagesGrammar Reviewapi-263349579No ratings yet
- Relative Pronouns: Relative Pronoun Use ExampleDocument3 pagesRelative Pronouns: Relative Pronoun Use ExampleAnonymous yyzxrD3No ratings yet
- Structure of EnglishLETDocument25 pagesStructure of EnglishLETLeonora Erika Rivera50% (2)
- GROUP 1-Nouns and PronounDocument29 pagesGROUP 1-Nouns and PronounAMA MUTTAHIZI AHADAN AUHANNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument13 pagesParts of SpeechAlex SallyNo ratings yet
- CPHTH - c7 - w4 - SlidesDocument49 pagesCPHTH - c7 - w4 - SlidesHuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Purdue OWL Verbal PhrasesDocument13 pagesPurdue OWL Verbal PhrasesJenny MachadoNo ratings yet
- VerbalsDocument14 pagesVerbalsissay irisNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 KEYDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 KEYSzilagyi Barna BelaNo ratings yet
- Syntax: The Sentence Patterns of Language: Lintang Gumelar Utami (19706251007) Rizki Eka Safitri (19706251014)Document39 pagesSyntax: The Sentence Patterns of Language: Lintang Gumelar Utami (19706251007) Rizki Eka Safitri (19706251014)Tia Rahman IslamiNo ratings yet
- 3.3. Adjective Clauses and Noun Clause (2020)Document23 pages3.3. Adjective Clauses and Noun Clause (2020)Hakam FikriNo ratings yet
- Eng1 TopicsDocument5 pagesEng1 TopicsKatrina SantosNo ratings yet
- Grammar Terms and What They MeanDocument4 pagesGrammar Terms and What They Meanmuslimuser610No ratings yet
- Verbal Phrases: ASC Learning Packet College of The RedwoodsDocument11 pagesVerbal Phrases: ASC Learning Packet College of The RedwoodsRsdasd PetsNo ratings yet
- Randi Ramadhan - 2001032054 - 2C D3 TLDocument8 pagesRandi Ramadhan - 2001032054 - 2C D3 TLRandii RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 3rdQEnglish 10 Week 7Document62 pages3rdQEnglish 10 Week 7arshpogi123No ratings yet
- Verbals Week 8 Flinguis 3Document18 pagesVerbals Week 8 Flinguis 3Shane Mendoza BSED ENGLISHNo ratings yet
- GAT 9 สามัญ ENGDocument66 pagesGAT 9 สามัญ ENGAdissaya BEAM S.No ratings yet
- Sentence Analysis. Levels of Analysis.Document5 pagesSentence Analysis. Levels of Analysis.Blue MoonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 LS 01 Content Words PDFDocument7 pagesUnit 2 LS 01 Content Words PDFAnfal ZaneNo ratings yet
- Grammar 5Document46 pagesGrammar 5drakness722No ratings yet
- A Syntactic Functions of Nouns and NounDocument11 pagesA Syntactic Functions of Nouns and NounHà Trần Thị ThuNo ratings yet
- VerbalsDocument36 pagesVerbalsimomapNo ratings yet
- SUMMER Remediation Lingva LATINA VII Grammar I, Ii, Iii: Lessons 1 - 2 - 3Document23 pagesSUMMER Remediation Lingva LATINA VII Grammar I, Ii, Iii: Lessons 1 - 2 - 3Gabriela MccawleyNo ratings yet
- REASERCHDocument21 pagesREASERCHRichelle MoralesNo ratings yet
- Writing Explanation - 1681147573630Document72 pagesWriting Explanation - 1681147573630Hossam SabryNo ratings yet
- Prepositional Phrase: by Windawati M.PDDocument10 pagesPrepositional Phrase: by Windawati M.PDalan subagioNo ratings yet
- A Simple Sentence Can Also Be Referred To As AnDocument8 pagesA Simple Sentence Can Also Be Referred To As AnShreya KamraNo ratings yet
- Ministry of The Education of Azerbaijan: Nakhchivan State UniversityDocument14 pagesMinistry of The Education of Azerbaijan: Nakhchivan State UniversityIsmayil RzayevNo ratings yet
- Summary of SyntaxDocument9 pagesSummary of Syntaxria mrdhkpNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - English - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument17 pagesUnit 1 - English - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inabc asassNo ratings yet
- Written Report Eng103Document10 pagesWritten Report Eng103Jstn RjsNo ratings yet
- Part I: Content Update: Roses Are SweetDocument35 pagesPart I: Content Update: Roses Are SweetRommel BansaleNo ratings yet
- Syntax 7-8Document42 pagesSyntax 7-8NuriNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns: Three Grammatical PersonsDocument7 pagesPersonal Pronouns: Three Grammatical PersonsJohn Alvin de LaraNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument21 pagesEnglish Grammarcontact.asif.directNo ratings yet
- English Syntax RangkumanDocument10 pagesEnglish Syntax RangkumanDewa Bagas Edhita PrajaNo ratings yet
- VerbalsDocument2 pagesVerbalsCalvin MallariNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument4 pagesPronounsMecislavs GrigorcuksNo ratings yet
- Advanced English Grammar On Verbals (Infinitive-Participle-Gerund)Document10 pagesAdvanced English Grammar On Verbals (Infinitive-Participle-Gerund)English Teacher ESL 영어교사, 英語教師, 英语教师, 英語の先生, Преподаватель английского языка, مدرس اللغة الإنجليزيةقوتابخانه ي زماني ئينكليزيNo ratings yet
- CRDI312 TECHNICAL ENGLISH PrelimsDocument7 pagesCRDI312 TECHNICAL ENGLISH PrelimsCATHLEENE MAYNE BELIRANNo ratings yet
- DokumenmmmmDocument2 pagesDokumenmmmmagustinaraveniNo ratings yet
- PhraseDocument13 pagesPhrasenandiniNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesParts of SpeechTurningPoint JindNo ratings yet
- PhrasesDocument3 pagesPhrasescoupranghae143No ratings yet
- ELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Document38 pagesELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Becira LiNo ratings yet
- TESOL2Document8 pagesTESOL2Kerri GastonNo ratings yet
- Lee Esto Primero... !Document13 pagesLee Esto Primero... !Orlando Chandía OchoaNo ratings yet
- Paper English Lesson RmytaDocument7 pagesPaper English Lesson RmytaVan Der ZeusNo ratings yet
- Pronouns Are Used To Replace Nouns. Pronouns Are Usually Shorter and Quicker Ways of Referring To A Noun To Help Make Sentences Less RepetitiveDocument5 pagesPronouns Are Used To Replace Nouns. Pronouns Are Usually Shorter and Quicker Ways of Referring To A Noun To Help Make Sentences Less RepetitiveAnaNo ratings yet
- Curs 1 Syntax IntroDocument9 pagesCurs 1 Syntax IntroRoxanneNo ratings yet
- Nouns: Action VerbDocument15 pagesNouns: Action VerbJerica PalomariaNo ratings yet