Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rates of Reaction Questions
Uploaded by
KelumOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rates of Reaction Questions
Uploaded by
KelumCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTION
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 1
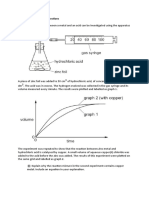
Calcium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce the gas carbon dioxide.
The table below gives the results from a reaction when 40 cm3 dilute hydrochloric acid was added
to one marble chip (calcium carbonate) at room temperature of 20oC. The calcium carbonate was
in excess.
One of the results in the table is unreliable.
Mass of flask
and contents (g)
71.00
70.74
70.54
70.40
70.30
70.24
70.26
70.20
70.20
70.20
time (min)
(i)
On the grid below plot a graph of the results shown in the table above.
Draw a smooth curve through the reliable points and label it A.
[3]
Mass of
flask and
contents
(g)
70.00
0
Time (min)
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTIONS
QUESTIONSHEET 1 CONTINUED
(ii) Sketch carefully on the grid the graph that would be obtained if:
I.
the same reaction was carried out at a temperature of 50oC. Label this graph B.
II. when an identical piece of calcium carbonate was reacted with only 20 cm3 of
the dilute acid. Label this graph C.
[2]
[2]
(iii) Explain your answer to part (ii) I, in terms of particle collision.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
TOTAL / 10
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTION
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 2
Some chemical reactions may take place twice as quickly if their temperature is raised by 10oC.
(a)
If a particular reaction takes 32 minutes at 20oC, how long will it take if the temperature is raised
to 50oC?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
Plot a graph of temperature against time taken to complete the reaction.
[3]
Temperature/ oC
(b)
Time / min
(c)
Explain why the line on your graph does not meet either axis.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 7
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTIONS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 3
Carbonates react with acids to produce a salt, carbon dioxide and water.
(a)
The equation describes the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid.
CaCO3
(i)
2HCl
CaCl2
CO2
H2O
Add state symbols to complete the equation.
[1]
(ii) Name the salt produced in this reaction.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Use the relative atomic masses C =12, Ca = 40 and O=16 to calculate the relative formula mass of
calcium carbonate. Show your working.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iv)
How much carbon dioxide can be produced from:
A 100 g calcium carbonate?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
B 1 g calcium carbonate?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
A student wished to measure the production of carbon dioxide in the above reaction. She considered the
two methods outlined in the diagram.
Method A
add
25 cm3
hydrochloric
acid
Method B
boiling
tube
with
25 cm3
hydrochloric
acid
1g
calcium
carbonate
weigh immediately
leave for 2 minutes
weigh
pour acid into beaker,
replace boiling tube
in beaker
reweigh
leave for 2 minutes
reweigh
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTION
QUESTIONSHEET 3 CONTINUED
(i)
Before carrying out the experiment, she performed the calculation in part (a) (iv) B of this question.
Suggest how this information could be of use to her.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(ii) Explain why, of the two methods shown, method B would provide a more reliable estimate of the
amount of carbon dioxide produced during the reaction.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 10
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTIONS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 4
Rajs chemistry teacher puts a beaker of sodium thiosulphate on the windowsill.
Raj can clearly see a tree on the school field through the beaker. The teacher adds hydrochloric acid to the
beaker. After 120 seconds Raj cannot see the tree although he is looking carefully.
(a)
Explain why.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
The teacher repeats the experiment with three other classes. The tree disappears from view at different times.
Class
9X
9Y
9Z
Time for tree to disappear
in seconds
120
200
150
The three experiments were identical except for the day on which they were done.
(b)
(i)
Which class did the experiment: on a warm spring day?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) during a summer heat wave?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) on a January day when the school heating was not working well?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
The following year the local group of schools agree to do the same experiment on the same day under
exactly the same conditions using the same chemicals. They look at objects that are the same distance away.
The results are: School
St Peters
St Pauls
St Marys
Time for tree to
disappear in seconds
110
100
150
The teachers tested the chemicals used. They found that the sodium thiosulphate was of different
concentration in each school.
(c)(i)
Which school had the strongest solution?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTION
QUESTIONSHEET 4 CONTINUED
(ii) Give reasons for your answer.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
Hanif decides to use an ultraviolet lamp and an electric motor powered by a photoelectric cell.
(d)
How could he use this equipment to measure the cloudiness of the liquid in a more objective way?
Draw a diagram of how the equipment might be set up.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
[4]
TOTAL / 12
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTIONS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 5
Cotton is starched to make it easier to weave into denim cloth. Before the cloth is made up into clothing the
starch is removed so that it can be more easily sewn.
Denim from a newly woven roll is tested to find out the best conditions for the removal of starch using the
biological catalyst amylase. A solution of amylase is made up and five equal pieces are cut from the roll of
denim. Equal quantities of amylase are added to four of the five pieces in separate beakers. The beakers are kept
at temperatures of 20oC, 40oC, 60oC and 80oC respectively for 15 minutes. Afterwards all five pieces are tested
for starch.
(a) (i)
What is a catalyst?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(ii) What is the name given to biological catalysts?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b) (i)
Which of the cotton samples would you expect to contain the most starch?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Explain your answer.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
(iii) Which sample would you expect to contain the least starch?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iv) Explain your answer.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(v) What chemical is most often used to detect starch?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 11
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTION
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 6
The following equation shows what happens when magnesium ribbon reacts with hydrochloric acid.
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
(a)
What would you see happening to the magnesium ?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
40 cm3 of gas is collected in 10 seconds. What is the rate of reaction?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
How would the rate compare if you used very dilute hydrochloric acid?
Explain why.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(d)
State two ways in which the reaction could be speeded up besides changing the concentration of
hydrochloric acid.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(e)
Calculate how many moles of hydrogen gas are collected.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
[24 dm3 is the volume of 1 mole of gas at room temperature]
TOTAL / 8
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTIONS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 7
When 0.15 M sodium thiosulphate solution (Na2S2O3(aq)) is added to hydrochloric acid, sulphur is formed.
(a)
What would you observe during the reaction?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
What other products are formed?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(c)
Apart from heating it, how else could you speed up the reaction?
How would this work?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
The following results table was obtained by mixing various amounts of sodium thiosulphate solution, water and
1 M hydrochloric acid.
Na2S2O3(aq)
Volume H2O(l)
(cm3)
HCl(aq)
Reaction Time (s)
(d) (i)
Plot a graph of the results
50
0
5
5
40
10
5
13
30
20
5
27
20
30
5
56
10
40
5
3 min
[3]
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTION
QUESTIONSHEET 7 CONTINUED
(ii) Which variable are you testing?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Why is the volume of acid kept the same?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iv) What would you observe during the reaction?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 11
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTIONS
High Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 8
Yoghurt is made from milk. Yoghurt contains lactic acid formed from lactose, the sugar present in milk.
Recently a new type of yoghurt has appeared in the shops in which bacteria from Russian cosmonauts has
been used in the process.
(a)
Describe a test to show that an acid is formed when milk is turned into yoghurt.
State the result of the test.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(b)
For all practical purposes, a solution of lactose does not change into lactic acid. Adding bacteria increases
the rate of reaction. What is meant by the phrase rate of reaction?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(c)
Why does the addition of bacteria have this effect?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(d)
Describe or draw diagrams to show what is happening to individual molecules of lactose in the reaction
to form lactic acid molecules in yoghurt.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
[3]
(e)
After a while the rate of formation of lactic acid decreases. Why is this?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(f)
The yoghurt milk mixture is heated to about 70oC.What effect does this have on the rate of the
production of lactic acid? Explain your answer.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 11
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTION
QUESTIONSHEET 9
Medium Demand Questions
The apparatus shown can be used to collect gas formed by reacting magnesium and sulphuric acid. The
following table of data was collected.
Time (s)
Volume (cm3)
(a)
0
0
2
10
Plot a graph of the results.
4
16
6
20
8
-
10
22
[3]
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTIONS
QUESTIONSHEET 9 CONTINUED
(b)
One experimental result was missed.
(i)
What value could it have?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Why is it easy to miss results like this during experiments?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c) (i)
Which gas is formed in the reaction ?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) How could you test for this gas?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 8
GCSE CHEMISTRY
Medium Demand Questions
RATES OF REACTION
QUESTIONSHEET 10
Some cars are fitted with catalytic converters to remove harmful substances from exhaust gases.
The platinum catalyst is coated onto a honeycombed ceramic support.
It works best when the engine has warmed up.
(a)(i)
Explain why a honeycombed support is better than a solid one.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Explain why the catalyst works better when the engine is warm.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(b)
Heavy metals may stick to the catalyst and prevent it from working.
The catalyst is said to be poisoned.
(i)
Explain how catalysts work and how poisoning with heavy metals prevents this.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
(ii) Why should the owners of cars with catalytic converters always use unleaded petrol?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 8
GCSE CHEMISTRY
Medium Demand Questions
RATES OF REACTIONS
QUESTIONSHEET 11
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) breaks down slowly to form water and oxygen.
(a)
Write a balanced symbol equation for the reaction.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(b)
The reaction can be greatly speeded up by a catalyst.
(i)
Name a possible catalyst.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) How does the catalyst work?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(iii) How could you show that the catalyst was unchanged at the end of the reaction?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 7
GCSE CHEMISTRY
Medium Demand Questions
RATES OF REACTION
QUESTIONSHEET 12
The diagram shows a flask of zinc metal reacting with hydrochloric acid on a chemical balance.
150 g
(a)
How could this apparatus be used to measure the speed of the reaction?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(b)
(i)
What is the gas being produced?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii)
How would you test the gas to identify it?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(iii)
Write an equation for the reaction which is taking place.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(c)
How would you expect the results to change if:
(i)
the temperature was increased?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) the zinc was ground into a fine powder?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) the concentration of the hydrochloric acid was increased?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 10
GCSE CHEMISTRY
Medium Demand Questions
RATES OF REACTIONS
QUESTIONSHEET 13
Chemical reactions are caused when molecules of different chemicals collide.
(a)
Describe the effect of increasing the pressure of two gases on the rate of reaction using this
collision theory.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(b)
Cornflour is used on the production line in some sweet factories. It is carried in the air.
Special precautions have to be taken to remove the cornflour from the air as a fire hazard.
Why is this fine powder a fire hazard?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(c)
10 g of magnesium ribbon burns up in 1 minute.
How fast would you expect 10 g of magnesium powder to burn?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(d)
Why is heat often provided as a means of speeding up chemical reactions?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(e)
Why does food not keep for ever in a freezer?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
Medium Demand Questions
RATES OF REACTION
QUESTIONSHEET 14
A research laboratory is investigating the effectiveness of various catalysts for the reduction of pollution in
petrol powered car exhausts.
They obtain the following results using their own pollution units, P.
[10 P = 10 pollution units.]
Catalyst
None
A
B
C
Petrol
P
100
30
50
10
Carbon monoxide
P
700
150
250
75
Oxides of nitrogen
P
500
150
300
90
In his lab notebook the scientist uses the abbreviations CO, NOx and CH.
(a)
What do these abbreviations stand for?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
(b) (i)
Which catalyst is most effective at reducing total pollution?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Which is the largest pollutant in the exhaust before a catalyst is used?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Which is the largest pollutant in the exhaust from the most effective catalyst?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 6
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTIONS
QUESTIONSHEET 15
Medium Demand Questions
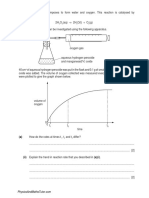
Hydrogen peroxide and a catalyst are mixed in the apparatus below.
The hydrogen peroxide decomposes into water and oxygen.
chemicals A or B
added here
heat
energy
The results obtained are represented on the graph below
no catalyst
volume
of gas
30
(a) (i)
(b)
60
90
time in seconds
On the same axes, draw a line to represent the volume of oxygen produced when the reaction is
repeated with 5 g of a granulated catalyst in the flask. Label this (i).
[1]
(ii) On the same axes, draw a line to represent the volume of oxygen produced when the reaction is
repeated with 5 g of a powdered catalyst in the flask. Label this (ii).
[1]
John measures the volume of gas produced when 5 g of two chemicals X and Y are added to
hydrogen peroxide under identical conditions. His results for this experiment look like this.
Y
volume
of gas
30
60
90
time in seconds
He claims that they show that Y is a better catalyst than X.
Johns partner Steven does not agree.
(Continued...)
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTION
QUESTIONSHEET 15 CONTINUED
What does Steven find wrong with the results?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(c)
After the experiment Steven recovers 5 g of X and 1 g of Y from the two experiments. He claims that
this shows that John is wrong.
Why might he think this?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 8
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTIONS
QUESTIONSHEET 16
Medium Demand Questions
200 cm3 of hydrogen peroxide solution are warmed in a flask. The volume of gas produced is measured using a
syringe. After 30 seconds 5 g of a chemical A is added to the hydrogen peroxide and the volume of gas
continues to be measured. The experiment is then repeated but this time another chemical, B, replaces A.
A third experiment has chemical B replaced by chemical C.
chemicals A, B or C
added here
heat
energy
The graph below shows the volume of gas produced over time when the chemicals A, B and C are added.
volume
of gas
time in seconds
30
(a)
60
What is the formula of hydrogen peroxide?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
What is the gas produced?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c) (i)
What is a catalyst?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(ii) Which of the three chemicals A, B and C is not a catalyst? (Give a reason for your choice)
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(iii) Which of the three chemicals is the best catalyst? (Give a reason for your answer)
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(d)
How much of the compounds B and C should be recovered from the flasks after the experiment?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 9
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTION
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 17
(a)
List three ways of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
(b)
Explain why it is not possible to light a dead tree with a match.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(c)
Why is it difficult to light coal, but coal dust in mines can cause explosions?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
TOTAL / 7
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTIONS
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 18
The graph below shows the volume of gas produced in an experiment over a period of time.
70
E
60
Volume of gas/ cm3
50
C
40
30
20
10
A
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
Time/s
(a)
(i)
Write down the letter which represents:
the point at which the reaction has first stopped.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) the point at which the reaction is going at its fastest.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b)
(i)
Use the graph to estimate:
the volume of gas produced after 60 seconds.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) the time taken for 30 cm3 of gas to be collected.
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(c)
If the experiment was repeated with a catalyst present, how much gas would you expect to collect
in total?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(d)
(i)
If the experiment in (c) was repeated with twice as much catalyst, how much gas would you expect
to collect in total?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii)
Would the speed of collection of the gas be faster, slower or the same as in experiment (c)?
......................................................................................................................................................................... [1]
TOTAL / 7
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTION
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 19
Rates of reactions can be measured in a number of ways.
(a)
Name two pieces of apparatus which could be used to measure volumes of gases.
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(b)(i) If you were timing how long magnesium took to dissolve in different concentrations of acid,
what controls would you use to make sure the experiment was fair?
..............................................................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................... [3]
(ii) Which of the following would be best for timing the reactions? (Underline the correct answer)
Stop clock
(c)
kitchen clock
alarm clock
egg timer
[1]
Which of the following pieces of apparatus would be most suitable for weighing a marble chip?
(Underline the correct answer)
spring balance
balance reading to 4 decimal places
balance reading to 2 decimal places
balance reading in whole grams
[1]
TOTAL / 7
GCSE CHEMISTRY
RATES OF REACTIONS
Low Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 20
Complete the following sentences.
(i)
Heat energy is measured in _______.
(ii)
One thousand of these is called a _______.
(iii)
A reaction which gives out heat is described as _______.
(iv)
A reaction which takes in heat is described as _______.
(v)
A _________ will speed up a chemical reaction without being permanently used up.
(vi)
Reactions involving gases can be speeded up using _________ pressure.
(vii) Powders have a greater ______ _______ than lumps of a solid.
(viii) Curtains fading and _______ are examples of reactions which
(ix)
are triggered by _______.
TOTAL / 9
You might also like
- C2 Foundation Revision Questions - Sets 3,4&5Document45 pagesC2 Foundation Revision Questions - Sets 3,4&5madhujayanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Mid Exam 2019Document12 pagesClass 10 Mid Exam 2019Khalid HassanNo ratings yet
- Rate of Chemical ReactionsDocument20 pagesRate of Chemical ReactionsJavariaAjmalNo ratings yet
- 2 Hours: Candidate's Name: ... SignatureDocument16 pages2 Hours: Candidate's Name: ... SignatureOTTO OLIMANo ratings yet
- GCE Chemistry A2C2Document6 pagesGCE Chemistry A2C2cafffy100% (1)
- Water and HydrogenDocument7 pagesWater and HydrogenOkumu KevinsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsDocument13 pagesChapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsAmanda AnushaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics PDFDocument10 pagesChemical Kinetics PDFbilly ogadaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Concentration on Reaction RateDocument2 pagesEffect of Concentration on Reaction RateMark FerdinandNo ratings yet
- Problems On Kinetics IDocument10 pagesProblems On Kinetics IsirholmezzNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/22Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/22Spider Gamer22No ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 19Document16 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 19Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction PPsDocument23 pagesRate of Reaction PPstcs202231No ratings yet
- Balanced Equations & Associated Calc's 05 QPDocument8 pagesBalanced Equations & Associated Calc's 05 QPlmao lmaoNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Past Papers Questions With Mark SchemeDocument60 pagesTopic 9 Past Papers Questions With Mark SchemeQasim PerachaNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 2 QP (Tomek)Document9 pagesRate of Reaction 2 QP (Tomek)Tomasz OstrowskiNo ratings yet
- Alternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1Document15 pagesAlternative To Practical Questions IGCSEset 1danielphilip68100% (1)
- 1 Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposes To Form Water and Oxygen. This Reaction Is Catalysed byDocument9 pages1 Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposes To Form Water and Oxygen. This Reaction Is Catalysed byKelvin DenhereNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction vs Temperature GraphDocument15 pagesRate of Reaction vs Temperature Graphdanielphilip680% (1)
- As-Level Paper 1 pp9Document15 pagesAs-Level Paper 1 pp9ConorNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry: Topic 2 - Amount of Substance TestDocument10 pagesAs Level Chemistry: Topic 2 - Amount of Substance Testkarima akterNo ratings yet
- WCH06 01 Que 20140514Document12 pagesWCH06 01 Que 20140514Paras AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Plants Questions ks3Document4 pagesPlants Questions ks3Eshal AmirNo ratings yet
- 0625 w14 QP 33Document20 pages0625 w14 QP 33Haider Ali100% (2)
- Read These Instructions First: 7 Printed PagesDocument7 pagesRead These Instructions First: 7 Printed PagesZainab ShigriNo ratings yet
- A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY PAPER 3 PRACTICE PAPER 8Document19 pagesA-LEVEL CHEMISTRY PAPER 3 PRACTICE PAPER 822S48 SUNDARAM RAMASUBBU RAKSHANo ratings yet
- Mock 1Document15 pagesMock 1G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Y12 Chemistry Unit 1 Test SolutionsDocument8 pagesY12 Chemistry Unit 1 Test Solutionsviyas07No ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionsDocument54 pagesRates of ReactionsjohnyeapNo ratings yet
- All G485 Questions - Part 2Document90 pagesAll G485 Questions - Part 2sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 525 1 Eot 3 2022Document17 pages525 1 Eot 3 2022OTTO OLIMANo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry: Paper 3 Practice Paper 3Document20 pagesA-Level Chemistry: Paper 3 Practice Paper 3Jesus ChristNo ratings yet
- Using Conc. of Solutions in Mol (DM) - 3 QPDocument15 pagesUsing Conc. of Solutions in Mol (DM) - 3 QPw276No ratings yet
- Acids, Alkalis and Titrations 1 QPDocument14 pagesAcids, Alkalis and Titrations 1 QPkhalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- AQA AS CHEMISTRY ORGANIC ANALYSISDocument19 pagesAQA AS CHEMISTRY ORGANIC ANALYSISHamza AbulailaNo ratings yet
- Module 20A Paper 3Document11 pagesModule 20A Paper 3Mohd HafiezNo ratings yet
- Ii Term QP 9Document20 pagesIi Term QP 9G M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Test 1 As Chemistry Unit 2 - KineticsDocument10 pagesTest 1 As Chemistry Unit 2 - KineticsKajana Sivarasa Shenthan100% (1)
- Chemistry Jan2012 Unit-3b QPDocument16 pagesChemistry Jan2012 Unit-3b QPAkila RahmanNo ratings yet
- 9701 s17 QP 42 RemovedDocument18 pages9701 s17 QP 42 RemovedSherise EeNo ratings yet
- 2021 Sda F5 June Test 1Document11 pages2021 Sda F5 June Test 1blueegofxNo ratings yet
- Buffer Action 1 QPDocument8 pagesBuffer Action 1 QPvictoriaNo ratings yet
- EquilibriaDocument10 pagesEquilibriaNkemzi NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Revision 3Document4 pagesRevision 3Nur HidayahNo ratings yet
- 8i QPDocument9 pages8i QPRemoo ChanNo ratings yet
- Physics/Science: Edexcel GCSEDocument28 pagesPhysics/Science: Edexcel GCSEfractoremNo ratings yet
- Respiration - Questions PDFDocument25 pagesRespiration - Questions PDFHolly Robinson0% (1)
- WS 2 - 19.08.22Document2 pagesWS 2 - 19.08.22Micheelle JeannethNo ratings yet
- Buffer Action 2 QPDocument10 pagesBuffer Action 2 QPvictoriaNo ratings yet
- 0620 w10 QP 63Document12 pages0620 w10 QP 63Haider AliNo ratings yet
- Kinetics IIDocument46 pagesKinetics IIHannah IqbalNo ratings yet
- Gcse Chemistry: Questionsheet 1Document26 pagesGcse Chemistry: Questionsheet 1Shashibhushan AshokNo ratings yet
- Chlorine and Its Compounds Chemistry Form 3 Topical Questions and AnswersDocument18 pagesChlorine and Its Compounds Chemistry Form 3 Topical Questions and Answersideal writersNo ratings yet
- Optical Isomerism 1 QPDocument8 pagesOptical Isomerism 1 QPfajrk8567No ratings yet
- 2 HoursDocument17 pages2 HoursOTTO OLIMANo ratings yet
- Quantitative Gas Chromatography for Laboratory Analyses and On-Line Process ControlFrom EverandQuantitative Gas Chromatography for Laboratory Analyses and On-Line Process ControlNo ratings yet
- Advanced Synthesis of Gold and Zirconia Nanoparticles and their CharacterizationFrom EverandAdvanced Synthesis of Gold and Zirconia Nanoparticles and their CharacterizationNo ratings yet
- Princeton Problems in Physics with SolutionsFrom EverandPrinceton Problems in Physics with SolutionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Energetics QuestionsDocument20 pagesEnergetics QuestionsKelum100% (1)
- Industrial QuestionsDocument35 pagesIndustrial QuestionsMaha NazirNo ratings yet
- GCSE Metals & Reactivity Series Practice QuestionsDocument28 pagesGCSE Metals & Reactivity Series Practice QuestionsKelumNo ratings yet
- Reactions QuestionsDocument22 pagesReactions QuestionsG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Non-Metals High Demand QuestionsDocument26 pagesGCSE Chemistry Non-Metals High Demand QuestionsG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Periodic QuestionsDocument22 pagesPeriodic QuestionsDrRemyaranjith MenonNo ratings yet
- Atomic QuestionsDocument22 pagesAtomic QuestionsKelumNo ratings yet
- GCSE CHEMISTRY ACIDS, BASES & SALTS HIGH DEMAND QUESTIONSDocument21 pagesGCSE CHEMISTRY ACIDS, BASES & SALTS HIGH DEMAND QUESTIONSeeenusNo ratings yet
- Oil QuestionsDocument24 pagesOil QuestionsKelumNo ratings yet
- Periodic AnswersDocument11 pagesPeriodic AnswersKelumNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Atomic Structure & Bonding QuestionsDocument10 pagesGCSE Chemistry Atomic Structure & Bonding QuestionsKelumNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry: Metals & the Reactivity SeriesDocument11 pagesGCSE Chemistry: Metals & the Reactivity SeriesKelumNo ratings yet
- Industrial AnswersDocument15 pagesIndustrial Answerslianchen251110No ratings yet
- Gcse Chemistry Answers and Mark Schemes Questionsheet 1: Reactions & FormulaeDocument9 pagesGcse Chemistry Answers and Mark Schemes Questionsheet 1: Reactions & FormulaeShyweyNo ratings yet
- Rates AnswersDocument10 pagesRates AnswersKelumNo ratings yet
- Oil AnswersDocument11 pagesOil AnswersKelumNo ratings yet
- Acids AnswersDocument9 pagesAcids AnswersKelumNo ratings yet
- Energetics AnswersDocument8 pagesEnergetics Answerslianchen251110No ratings yet