Professional Documents
Culture Documents
R09a10191 - Engineering Drawing - Unlocked
R09a10191 - Engineering Drawing - Unlocked
Uploaded by
Naani ChowdaryOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
R09a10191 - Engineering Drawing - Unlocked
R09a10191 - Engineering Drawing - Unlocked
Uploaded by
Naani ChowdaryCopyright:
Available Formats
Code.
No: R09A10191
R09
SET-1
JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY HYDERABAD
I B.TECH REGULAR EXAMINATIONS JUNE - 2010
ENGINEERING DRAWING
(COMMON TO ME, CHEM, MMT, ICE)
Time: 3hours
Max.Marks:75
Answer any FIVE questions
All questions carry equal marks
--1.a)
b)
Construct a forward reading Vernier scale to read distance correct to a decameter
on a map in which the actual distances are reduced in the ratio of 1 : 40000. The
scale should be long enough to measure upto 6 km. Mark on the scale lengths of
3.34 km and 0.59 km.
The ordinate of a point P on the curve is 40 mm and is at a distance of 20 mm
from the vertex. Draw the parabola.
[8+7]
2.
The HT and the VT of a straight line coincides with each other and 20 mm away
from one of the ends as measured parallel to XY. The distance between the end
projectors of the line measured parallel to XY is 50 mm. Draw the projections.
Find the TL and the true inclinations of the line. The end nearer to the HT and the
VT is 15 mm from the VP and 25 mm from the HP.
[15]
3.
A square lamina is placed such that one of the corners is touching the VP and the
diagonal through this is perpendicular to the VP and measures 60mm. The other
diagonal appear to be 40 mm in the view from above. Draw the projections and
find the inclination of the plane to the ground.
[15]
4.
A pentagonal prism of base edge 30 mm and height 70 mm is placed with one of
its rectangular faces on the ground and the axis parallel to the VP. It is cut by a
section plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 300 to the ground. It passes
through the mid point of the axis. Develop the remaining surface of the object.
[15]
5.
Two cylinders of base diameter 60mm penetrate each other. One cylinder is
placed vertically and another horizontally. The axes of the two objects are 30mm
apart. Draw the curves of intersection.
[15]
6.
An equilateral triangular prism of base edge 40mm and height 70mm is resting on
one of the corners on the ground. The rectangular face opposite to the corner on
the ground is perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 300 to the ground. Draw the
isometric projection of the object.
[15]
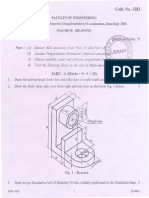
7.
Draw top, front and side views of the isometric projection given in figure. All
dimensions are in mm.
[15]
8.
A pentagonal prism of side of base 30mm, axis 60mm long rests on one of its
rectangular faces on the ground with a pentagonal face touching the PP. The point
of sight is 60mm to the right of the axis of the prism, 70mm from the PP and 80
mm above the ground. Draw the perspective view of the prism.
[15]
---oOo---
Code.No: R09A10191
R09
SET-2
JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY HYDERABAD
I B.TECH REGULAR EXAMINATIONS JUNE - 2010
ENGINEERING DRAWING
(COMMON TO ME, CHEM, MMT, ICE)
Time: 3hours
Max.Marks:75
Answer any FIVE questions
All questions carry equal marks
--1.a)
b)
A small length of 1 mm is to be enlarged to 20 times and a diagonal scale is to be
constructed to represent this such that the LC is 0.01 mm. Construct this scale and
mark on it a distance of 0.73 mm and 0.29 mm. What is the RF of this scale?
A circle of 50 mm diameter rolls on a horizontal line for half a revolution. For the
remaining half revolution it rolls on a line perpendicular to the first. Draw the
curve traced by a point on the circumference of the circle.
[8+7]
2.
The HT and the VT of a straight line AB is below and above XY respectively.
The distance between the HT and the VT as measured parallel to XY is 200mm.
The end B of the line is nearer to the VP than the end A. The view from above of
the line makes 300 to XY. The end B is 10 mm from the VP and 20 mm from the
HP. The distance between the end projectors of the line measures 50mm parallel
to XY. Draw the projections of the line.
[15]
3.
A cone of base 60 mm diameter and height 80mm has the mid point of the axis 60
mm away from both the planes. The axis is inclined at 300 to the VP and 600 to
the ground. Draw the projections of the cone.
[15]
4.
Two faces of a prism are equilateral triangles of sides 40mm long. The remaining
three faces of the prism are squares of 40 mm sides. The object is cut by two
section planes such that the view from the front gives an impression of a square
pyramid. Draw the development of the surface of the object after it is being cut.
[15]
5.
A horizontal cone of base diameter 80mm and height 90mm penetrates a vertical
cylinder of base diameter 60mm. The axes intersect each other and the axis of the
cone is 600 to the VP. The apex of the cone is towards the VP. Draw the views
with the curves of interpenetration.
[15]
6.
An equilateral triangular pyramid of base edge 40mm and height 60mm is resting
on its base on the ground with one of the base edges being perpendicular to the
VP. It is cut by a section plane parallel to 15mm from triangular face containing
the base edge which is perpendicular to the VP. Draw the isometric projection of
the object.
[15]
7.
Draw top, front and side views of the isometric projection given in figure. All
dimensions are in mm.
[15]
8.
A square prism of base edge 50mm by 70mm long is resting on one of its longer
edges on the ground, this edge being perpendicular to the PP. The rectangular
faces containing this edge make equal inclinations with the ground. The base of
the prism touches the PP. The station point is 70mm to the right of the axis, 60mm
from the PP and 60mm above the ground. Draw the perspective projection of the
object.
[15]
---oOo---
Code.No: R09A10191
R09
SET-3
JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY HYDERABAD
I B.TECH REGULAR EXAMINATIONS JUNE - 2010
ENGINEERING DRAWING
(COMMON TO ME, CHEM, MMT, ICE)
Time: 3hours
Max.Marks:75
Answer any FIVE questions
All questions carry equal marks
--1.a)
b)
A line of length 100 mm is divided into 10 equal parts and each part represents a
main scale division. With the help of a diagonal scale obtain a LC of 0.2 mm and
mark on it a length of:
a)
41.6 mm
b)
53.8 mm and
c)
67.4 mm
Draw the locus of a point on the circumference of a circle of radius 20 mm which
rolls on a straight line for one and half revolutions of the circle. Take the initial
position of the point to be diametrically opposite to the straight line.
[8+7]
2.
A room has the dimensions 6m 4m 3m. Two nails are driven on two adjacent
walls at heights of 2.5m and 1.5m from the ground respectively. One nail is 3m
away and another is 2m away from the common edge of the walls. Find
graphically the minimum length of the thread required to connect the nails. What
is the inclination of the thread to the ground and to the wall?
[15]
3.
A tetrahedron of edge 50 mm long is standing on one of its corners on the ground
with one of the edges connected with this corner making 600 with the ground and
one of the triangular faces connected with this corner making an angle of 300 with
the VP. Draw the projection of the object.
[15]
4.
A hexagonal prism of base edge 20 mm and 60 mm long is standing on its longer
edge on the HP and the edge on the HP is parallel to the VP. It is cut by a section
plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 600 to the HP. The section plane
passes through the axis at a point 20 mm from its base. Draw the development of
the surface of the sectioned object.
[15]
5.
A cone of base diameter 60mm and height 80mm stands on its base on the
ground. A horizontal square prism of base edge 30mm with two of its adjacent
base edges being equally inclined to the ground penetrates the cone. The two axes
bisect each other, at right angles to each other and both parallel to the VP. Draw
the projections of the objects showing the curves of interpenetration.
[15]
6.
A sphere of 60mm diameter is intersected by a cylinder of 30mm diameter. The
axis of the cylinder passes through the centre of the sphere. The tip of the axis of
the cylinder is 70mm from the centre of the sphere. Draw the isometric projection
of the objects when the axis of the cylinder is parallel to both the VP and the HP.
[15]
7.
Draw top, front and side views of the isometric projection given in figure. All
dimensions are in mm.
[15]
8.
A square pyramid of base edges 50mm long and altitude 70mm is resting on its
base on the ground with one of the corners of the base touching the PP. Two
adjacent base edges having this corner makes equal inclination with the VP. The
station point lies on the central line of the object 60mm in front of the PP and
90mm above the ground. Draw the perspective projection of the object. [15]
---oOo---
Code.No: R09A10191
R09
SET-4
JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY HYDERABAD
I B.TECH REGULAR EXAMINATIONS JUNE - 2010
ENGINEERING DRAWING
(COMMON TO ME, CHEM, MMT, ICE)
Time: 3hours
Max.Marks:75
Answer any FIVE questions
All questions carry equal marks
--1.a)
b)
An isosceles triangle ABC is lying on the edge BC on the ground and the plane
of the triangle is perpendicular to the ground. AC=BC=90mm, AB = 68 mm. If
the length CB represents 900 on a scale of chords, construct the full scale
representing all angles from 0 to 900 at an interval of 100. Using this, set off an
angle of 1300.
Construct a cycloid whose length is equal to 200 mm. Draw a tangent and normal
to the curve at any suitable point on it.
[8+7]
2.
A room is 8m 5m 4m. A peg is driven at the centre of the roof. Another peg is
driven on a common edge between the two mutually perpendicular walls. The
minimum length of the thread connecting these two pegs is 5.5 m. Find the height
of the peg on the common edge above the ground.
[15]
3.
A frustrum of a cone has a base dia of 60 mm and top dia of 40mm. The height of
the object is 40mm. A through square hole is centrally made (25 mm side) along
the axis. Any two edges of the hole starting from the same corner make equal
inclination to the HP. The axis is 300 to the VP and parallel to the HP. Draw the
projections of the solid.
[15]
4.
The development of a lateral surface of a cylinder is a rectangle 220 mm by
60mm. The height of the cylinder is greater than the base. Draw the development
of the lateral surface of this cylinder when it is cut by a section plane bisecting the
[15]
axis and at an angle of 300 to the base of the cylinder.
5.
A cone of base diameter 60mm and height 80mm stands on its base on the
ground. Hexagonal prism (base edge 15mm) with two opposite faces
perpendicular to the ground penetrates the cone. The axes of the objects are 10mm
away from each other and the axis of the cone is nearer to the VP. Both the axes
are parallel to the VP. The axis of the prism is parallel to the HP. Draw the view
from above and the view from the front and show the curves of interpenetrations.
[15]
6.
A square prism of base edge 50mm and height 60mm is resting on its base on the
ground with one of the base edges parallel to the VP. A square hole 30mm
30mm is made through the prism. The axis of the hole and that of the prism bisect
each other at right angles to each other. Two adjacent short edges of the hole are
equally inclined to the ground. Draw the isometric projection of the object. [15]
7.
Draw top, front and side views of the isometric projection given in figure. All
dimensions are in mm.
[15]
8.
A rectangular prism of base edges 60mm 40mm and height 80mm is resting on
its broader rectangular face on the ground with the base parallel to the PP. The PP
bisects the axis of the object. The station point is on the central line of the object
80mm in front of the PP and 70mm above the ground. Draw the perspective
projection of the object.
[15]
---oOo---
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 978-0!00!818953-2 A Level Physics Support Materials Year 2, Sections 6, 7 and 8Document25 pages978-0!00!818953-2 A Level Physics Support Materials Year 2, Sections 6, 7 and 8Γιαννης Μπαζιωτης100% (2)
- Chap 07Document48 pagesChap 07api-261894355No ratings yet
- Exam 2010Document6 pagesExam 2010hennyykNo ratings yet
- New k-12 Grading SystemDocument31 pagesNew k-12 Grading Systemprecious mherr100% (3)
- Design and Drawing of Irrigation StructuresDocument2 pagesDesign and Drawing of Irrigation StructuresnvemanNo ratings yet
- Machine DrawingDocument2 pagesMachine DrawingnvemanNo ratings yet
- Part-A: FA B.E. Iv/Iv (MJP) I Se AutomDocument1 pagePart-A: FA B.E. Iv/Iv (MJP) I Se AutomnvemanNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemsDocument2 pagesManagement Information SystemsnvemanNo ratings yet
- 157 - Metallurgy and Material Science (Sem - I) (Supply)Document2 pages157 - Metallurgy and Material Science (Sem - I) (Supply)nvemanNo ratings yet
- Math 501 Problem Set Topic: Fraction: Submitted To: Ms. Rosyl S. Matin-Ao, MAT-Math Submitted By: Buscagan, Valleree TDocument7 pagesMath 501 Problem Set Topic: Fraction: Submitted To: Ms. Rosyl S. Matin-Ao, MAT-Math Submitted By: Buscagan, Valleree TVeeNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Question Paper 2017 With Solutions - Free PDFDocument22 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Question Paper 2017 With Solutions - Free PDFKalaiNo ratings yet
- Edm 518-Management of Alternative Learning SystemDocument38 pagesEdm 518-Management of Alternative Learning SystemTeacher BhingNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 (Angle, Arcs, Segment & Sector of Circles)Document14 pagesTopic 12 (Angle, Arcs, Segment & Sector of Circles)saikoderNo ratings yet
- Pyramid FormulaDocument4 pagesPyramid FormulajavedNo ratings yet
- Math 10Document11 pagesMath 10ronald bantuganNo ratings yet
- Sasmo 2020Document25 pagesSasmo 2020vanessa.livaniaNo ratings yet
- Model Paper P1S1 MATHSDocument6 pagesModel Paper P1S1 MATHSJanapareddy JanapareddyNo ratings yet
- Solved ECAT 2006 (Mathematics Portion) by MTMDocument9 pagesSolved ECAT 2006 (Mathematics Portion) by MTMSaira Ali100% (2)
- F. E. (Semester - I) Examination - 2010: Total No. of Questions: 12) (Total No. of Printed Pages: 7Document7 pagesF. E. (Semester - I) Examination - 2010: Total No. of Questions: 12) (Total No. of Printed Pages: 7Pratik WalimbeNo ratings yet
- REVIEW Final 1 TestDocument6 pagesREVIEW Final 1 TestThảo ThanhNo ratings yet
- 03-04 S5 Mock (Paper II) (E)Document10 pages03-04 S5 Mock (Paper II) (E)Anson Ka Kin ChanNo ratings yet
- Maths Soalan SetaraDocument8 pagesMaths Soalan SetarasiaoruiNo ratings yet
- Complex Number 1Document25 pagesComplex Number 1pabitra mondalNo ratings yet
- 40 1Document24 pages40 1jbeydajournoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W2Document10 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W2Lei DollosaNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Additional Maths Note2022Document10 pagesForm 5 Additional Maths Note2022indahinsyirahNo ratings yet
- Gawsyszawski Resume 2017Document3 pagesGawsyszawski Resume 2017api-311208054No ratings yet
- Circle - Formula Sheet - MathonGoDocument7 pagesCircle - Formula Sheet - MathonGoTimmy LNo ratings yet
- Aops Community 1985 Aime ProblemsDocument3 pagesAops Community 1985 Aime ProblemsAmanNo ratings yet
- English-Q3-Wk5 Day 2Document36 pagesEnglish-Q3-Wk5 Day 2Sheryl MahinayNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Exercises and Problems (Fractions) - Inicial Con ErroresDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Exercises and Problems (Fractions) - Inicial Con ErroresbemdasNo ratings yet
- Teaching Resume For Online 06 14 - Ashley JonesDocument2 pagesTeaching Resume For Online 06 14 - Ashley Jonesapi-257672273No ratings yet
- Triangles in Geometry (Definition, Shape, Types, Properties & Examples)Document13 pagesTriangles in Geometry (Definition, Shape, Types, Properties & Examples)Thanuja RaniNo ratings yet
- Classroom NewsletterDocument3 pagesClassroom Newsletterapi-287198566No ratings yet
- PVTmathscope 1376530257Document56 pagesPVTmathscope 1376530257Minh TuấnNo ratings yet